Fetal development at 36 weeks gestation
Until the birth of the baby left quite a bit. Soon his parents will be able to meet the baby. This article will tell about the features of fetal development at week 36.
What does it look like?
The appearance of the fetus by the 36th week of pregnancy is completely the same as that of the newborn. By this time all the main features of the little man are already formed. So, the child has a clearly visible nose, the forehead is easily distinguished. These formations on the face already look very voluminous, and not flat, as before. The fetal cheeks are rather plump - this is caused by accumulations of fatty tissue under the skin. Lips on the face. Their plumpness is an individual feature inherent in every child.
On the head of the baby grow hair. By this time of pregnancy, they have grown quite long. There is practically no hair on the body, and every day the baby's fetal gun cover decreases. The baby’s skin seems rather wrinkled. This is mainly because the baby is constantly in the aquatic environment. After he is born, his skin will smooth out, and the number of wrinkles will decrease significantly.
By week 36, the proportions of the baby’s body also changed. Thus, the child’s head no longer seems excessively large in relation to the arms and legs, but the limbs are physiological in length. Every day the baby mobility of joints increases.
The bones of the skull of a child are quite soft. It is provided by nature so that the baby can be born. Such a special density of bones allows the head of the fetus to move freely through the birth canal without any impairments, and therefore without damage. After the birth of the child's bones, the child’s skull will become harder.
The baby's skin color becomes pink with a slight gray tint due to the original lubricant, which outside covers the body of the fetus. The largest accumulations of lubricant are in places of natural folds on the body of the child.
Movements
A baby that weighs more than 2.5 kg already, in the womb becomes every day more and more closely. Of course, the child can move while in the womb, but does not do it as actively as before. The relatively large size of the baby and the gradual lowering of it into the small pelvis of the mother contribute to the fact that the child is trying to take a functionally more favorable position for him. To do this, he somewhat brings his chin to the neck, crosses his arms and legs.
The fruit is usually very active during the day. The ability to recognize the day and night appeared in a child a few weeks ago, it is due to a fairly good development of the brain. Doctors call this feature circadian rhythm. In the daytime, the baby is usually pushed, and at night he sleeps or rests.
During the daytime, a pregnant woman, as a rule, feels quite strong pushes in her stomach. Thus, the baby shows its vitality. He can push the walls of the uterus with his legs without using his hands. Since the child is already quite large in size, the amplitude of his movements continues to grow every day. If the baby kicks heavily, it can cause pain in his mom's stomach.
Also, a pregnant woman may feel mild tremors in the abdomen if the baby often has hiccups. Hiccup is a common occurrence. It is part of the complex process of intrauterine development and is necessary for the improvement of the respiratory and digestive systems.
Anatomical features
By week 36, the baby has grown up. If before 36 weeks the fetus grew rapidly in length and gained weight, then after this period it will already grow much more slowly. This feature is due to the fact that the children's body is fully formed and ready to be born.
Measuring the size of the fetus at this time can be very simple, since the fetus is already quite well grown. Conducted accurate measurements of the main anatomical structures in the baby using ultrasound examinations.
The normal values of the different studied parameters for each week are different. Below is a table of parameters of the basic values that are determined during the survey.
Study criteria | Norm at 36 weeks gestation |
Growth | 46-47 cm |
Weight | 2500-2600 grams |
Biparietal size (BPR) | 84-97 mm |
Forearm Bone Length | 50-58 mm |
Bone length of shin | 57-67 mm |
Thigh length | 63-74 mm |
Shoulder length | 56-67 mm |
Abdominal circumference | 29.1-35.3 cm |
Head circumference | 30.4-35 cm |
Frontal-nuchal size | 105-124 mm |
How is it developing?
The main task of the weeks ending the third trimester is the preparation of the child's body for the forthcoming life outside the mother's womb. Most of the bodies of the crumbs are already formed and even started to work.
An important feature of this period is the accumulation of subcutaneous fat. The child has both brown and white fat in the body. Experts believe that the amount of adipose tissue in a child by week 36 reaches 7% of body weight.
Fat for a child's body is necessary. It is the fatty tissue, “burning down”, that releases a huge amount of heat. At the stage of intrauterine development, such energy is not needed by the child, since he is constantly in the womb, where a certain comfortable temperature is constantly maintained. After birth, the temperature regime changes, and without enough fat, the baby can quickly freeze.
The accumulation of adipose tissue on the body contributes to the fact that the baby has cute plump dimples. Also, fat accumulates in the abdomen, on the buttocks, on the legs, in the upper shoulder girdle.
In order for a baby born on week 36 to be viable, all vital organs must work for him. It is very important that the child has a functioning heart.
The cardiovascular system in the fetus to this stage is already well formed, but so far the fetus receives all the nutrients necessary for its growth and development through a common blood supply system with the mother. Independently in full mode, the heart and blood vessels will begin to function in the fetus only after its birth.
The doctor who monitors the course of pregnancy, necessarily evaluates the fetal heartbeat. He conducts such research several times during the entire life of the fetus in the womb. The fact is that with the help of listening to the fetal heartbeat, you can not only get information about how the heart works, but also assess the overall well-being of the baby. Too fast heart rate (tachycardia) indicates, as a rule, that the baby is experiencing some discomfort.
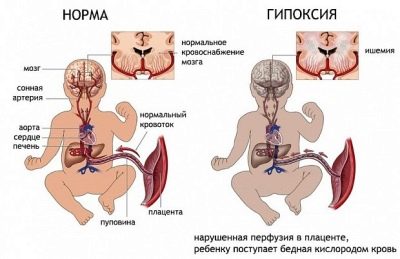
The reasons for the development of this state may be different. Often hypoxia leads to an increase in heartbeat - a decrease in oxygen supply.
Upon the occurrence of hypoxia, the doctor must make a plan of recommendations, which the expectant mother should strictly adhere to in order for the baby to feel normal.
For independent living, the child also needs breathing. In this period, the lungs and bronchial trunk are quite well developed in the fetus.Interestingly, a special substance, a surfactant, is formed and accumulates in the lung tissue. It is necessary so that the pulmonary vesicles (alveoli) do not “stick” to each other during breathing. Without sufficient surfactant, spontaneous breathing is impossible.
In full force, the lungs can earn only after the child takes his first breath in his life. The first portion of the atmospheric air that has entered the children's organism will force the lungs to start working.
Interesting changes to the 36 week occur in the brain. The cerebral cortex at this time is already quite well formed. The furrows and gyrus, which give the brain a distinctive look, are also well visualized. A large number of pre-existing nerve synapses contribute to the fact that a child forms a variety of different reflexes. They are necessary for the baby in order for it to exist outside the maternal abdomen and respond to stimuli coming from the external environment.
One of the important reflexes that has formed by this time is sucking. Baby almost all the time sucking on it. This, by the way, is often observed by ultrasound specialists who conduct examinations of pregnant women.
The sucking reflex is very important and necessary so that after birth the infant instinctively sucks mother's breast.
Also, the baby has already formed a swallowing reflex, which is quite vividly manifested when the fetal waters are swallowed. Such an organized structure of the cerebral cortex and nerve analyzers contributes to the fact that the child has his own feelings. So, the baby can determine the taste of amniotic fluid, is able to respond to light and painful effects, hears various sounds.
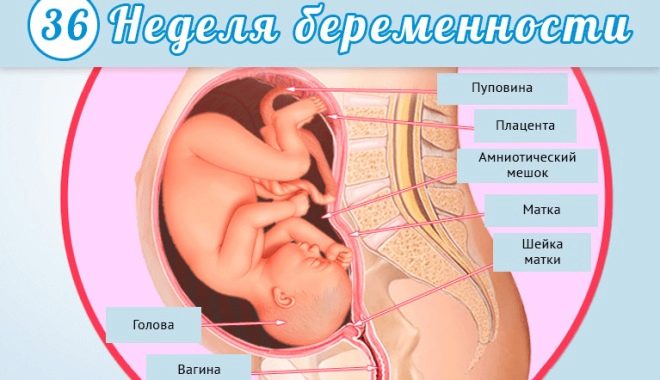
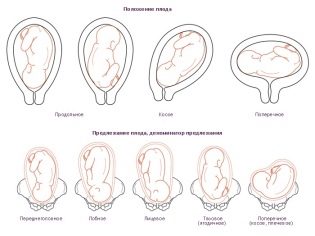
How is it located in the womb?
Obstetricians and gynecologists who work with pregnant women in their patients must evaluate the most important criterion - the presentation of the fetus. To do this, they determine how the main large parts of the baby's body are located in the uterus. From where the head, pelvis and extremities of the child are located, and its presentation.
It is considered that head presentation is most physiologically favorable. In this case, the child’s head is down, first towards the birth canal. The legs and pelvis of the baby are above the upper humeral girdle. With this option, the position of the fetus in the uterus during the upcoming birth is quite favorable. The risk of birth injury and damage in this case is minimal.
A less favorable location is pelvic presentation. In this case, the baby is the opposite. With this option, the pelvic end of the child is directed first towards the birth canal, and the head of the child is above.
Such presentation is dangerous because in the process of childbirth, there may be dangerous complications and even injuries.
Also quite unfavorable is the lateral position. It occurs if the child for some reason has not turned its head down. With the transverse arrangement of the fetus, all large parts of the baby’s body are perpendicular to the longitudinal line of the birth canal. In this case, the birth of a child is fraught with the development of many pathologies.
By week 36, the baby is already in a fixed position in the uterus. With each subsequent week, he will gradually sink lower and lower into the pelvis of his mother. The closer to childbirth, the stronger such a movement of the child will occur.
The final stage of pregnancy is very important. At this time, the future mother should carefully monitor their state of health. If a pregnant woman has noticed the leakage of amniotic fluid or the appearance of a strong pain syndrome in the abdomen, she should immediately seek medical help. The risk of childbirth ahead of schedule now certainly exists.
For information on how the fetus develops at 36 weeks gestation, see the following video.