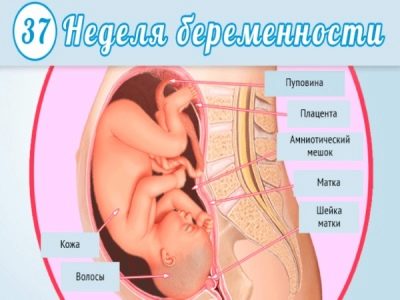
Fetal development at 37 weeks gestation
Few weeks remained before the meeting of future parents with their baby. The baby will be born in less than a month. This article will tell about the features of fetal development at week 37.
What does it look like?
In appearance, a child at 37 weeks is completely similar to a normal newborn baby. The fetus already, like a little man, has formed all the basic features of the face. And the face of the fetus has a number of unique features inherent only to him. On the face of the baby, you can quite clearly define the nose and forehead. These anatomical structures look quite voluminous, not flat, as before. On the sides of the face are ears. The shape and size of the ears of each child is individual. The child has quite plump cheeks. This feature is due to the fact that under the skin of the cheek areas on the face is adipose tissue. Its amount and causes individual cheek plumpness.
By the 37th week on the head of a child has a lot of hair. Also continue to grow eyebrows and eyelashes. But on the body of the baby every day the hairline decreases. At the same time, gentle fluff hairs easily fall away on their own. This contributes to the fact that the skin gradually becomes more and more smooth. Smooth skin still can not be called. It has quite a lot of wrinkles. They appear on the skin of the fetus because it is always in the amniotic fluid.
These wrinkles of the baby will completely disappear after he is born. The skin of the fetus is still quite thin and tender.
The color of the skin is pink. The original grease that covers the outside of the body of the baby gives a special gray tint to the skin.
The proportions of the body in the fetus at week 37 are significantly different from the proportions of the body in the first half of pregnancy. The head of the child is already quite large, but does not seem gigantic in relation to other parts of the body. The hands and feet of the baby have grown quite well.
An interesting feature of this period is the structure of the bones of the skull. They are still quite soft. This feature is necessary for the fetus. It is precisely because of the special "softness" of the bones of the skull that a child can be born. If the skull of the fetus were too hard, then the movement of the head through the birth canal would be impossible or accompanied by massive lesions. But nature has provided a more physiologically favorable option. The density of the bones of the skull of the fetus will change. So, after the appearance of the crumbs on the light, they will become more dense.
Movements
By week 36-37, pipsqueak has already grown quite a bit. A kid who weighs more than two and a half kilograms is quite hard to make any frequent and active movements. With each subsequent week of pregnancy, the child will change its position and move towards the pelvis of his mother. The closer the onset of labor, the lower will be the head of the baby to the birth canal.
The larger the fetus, the harder it is for him to move in the already close maternal womb. However, it can also move the arms and legs. These movements are usually quite intensely felt by his mother. At such moments, the woman usually feels that her baby is pushing hard.
The fruit is usually very active during the daytime. At night, he calms down and even sleeps. Often at night, the expectant mother simply feels that her baby is "quiet" and practically does not move. However, it is not uncommon for the baby to simply “confuse” day and night. In this situation, he can wake up his mother, who will feel the stirring of the baby suddenly increased in her stomach.
If a child is calm and no factors cause him concern, then at week 37 he is, as a rule, not as active as before.
If the baby is in constant “movement” and in every possible way tries to roll over, then this is a reason for consulting with a doctor. Such active movements can be dangerous for a rather large child by the development of certain pathologies.
Anatomical features
Up to 36-37 weeks of pregnancy, the baby quickly grew in length and gained weight. Now he does it much slower. This stage of pregnancy is not a strategically important period for increasing the size of a baby’s body. More importantly, the body crumbs prepared for the imminent emergence of the world and the change of habitat.
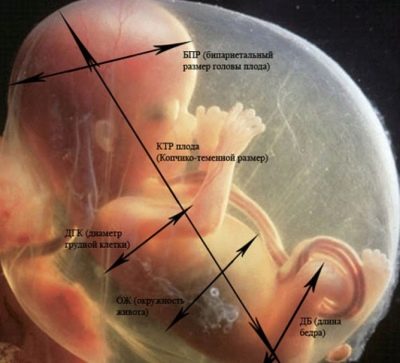
Measuring fetal size at 37 weeks is also possible. This is easy to do, since the baby has already quite large body sizes. Conducting accurate measurements of the main anatomical structures of the fetus is carried out through the use of ultrasound techniques. Each week of pregnancy is characterized by certain normal values of the determined indicators. The table below shows the norms for such determinable parameters.
Study criteria | Norm in the 37th week of pregnancy |
Growth | 47-48 cm |
Weight | 2600-2700 grams |
Biparietal size (BPR) | 86-98 mm |
Forearm Bone Length | 51-60 mm |
Bone length of shin | 58-68 mm |
Thigh length | 65-76 mm |
Shoulder length | 58-69 mm |
Abdominal circumference | 29.9-36 cm |
Head circumference | 30.6-35.3 cm |
Frontal-nuchal size | 106-127 mm |
How is it developing?
For the independent life of the baby in the external environment, it is very important that all its internal organs are formed and function. A baby born at 37 weeks is viable if he has adequate breathing and blood circulation. The child’s heart and blood vessels are already formed, but the blood supply of the internal organs of the fetus is still achieved through the common uteroplacental blood flow system with his mother. Truly, the baby’s heart and blood vessels will begin to function only after his birth.
An important clinical criterion that allows you to evaluate the work of the heart activity in the fetus is the heart rate. This simple diagnostic test allows you to evaluate not only the work of the cardiovascular system in the fetus, but also indirectly understand what is happening with the baby.
If a child experiences any discomfort while in the womb, it will cause his heart rate to change (HR).
Doctors identify several options for violations of the heartbeat:
tachycardia (this condition is characterized by rapid heart rate);
bradycardia (in this state, the heart rate is below normal).
Normacardia is a clinical option when the heart of a baby beats within the age norm. This condition indicates that the child feels well in the womb and does not experience any discomfort. The heart rate of a child at this time is presented in the table below.
Heart rate | Normal values at week 37 |
Heart rate | 130-150 beats per minute |
Independent breathing is impossible without the full work of the lungs. To prevent pulmonary alveoli from “sticking together” when breathing, a special substance is needed - surfactant. It begins to appear in the lung tissue at the final stage of pregnancy. A sufficient amount of surfactant is necessary so that after his birth, the child can take his own first breath.
Every day the number of reflexes increases. This is largely due to the good development of the brain cortex. The ability to respond to external stimuli is the most important criterion for the adaptation of the baby to new living conditions. The swallowing reflex is very important. It was formed at the crumbs a few weeks ago, but continues to improve every day. Thus, the baby already swallows amniotic fluid quite easily. After that, he usually hiccups often. Hiccup is quite a physiological phenomenon and even part of a stepwise complex process of intrauterine development.
Another important reflex that has recently formed in the fetus is sucking. It is manifested by the fact that the child, while still in the womb, begins to suck his thumb almost all the time. The sucking reflex is necessary so that in the future the baby could, at the level of instincts, suck breast milk on its own.
The development of the senses in the baby contributes to the fact that the fetus appears quite a lot of sensations. He can already react to bright light and sound, distinguishes certain tastes, gradually the baby has tactile and pain sensitivity. The final period of pregnancy is very important. At this time, the expectant mother should definitely monitor any symptoms in her body.
It is important to remember that the onset of labor for a variety of reasons may be much earlier than the deadline. So, a strong leakage of amniotic fluid or intense pain in the abdomen should be the reason for consulting a doctor. It is better to be safe in such a situation than not to receive medical assistance in time.
During each pregnancy has its own characteristics. So, in some cases, the process of fetal development of the fetus is somewhat disturbed. In this case, the child is registered developmental delay. The doctor can determine this pathology, who monitored the course of pregnancy and knows its features.
How is it located in the womb?
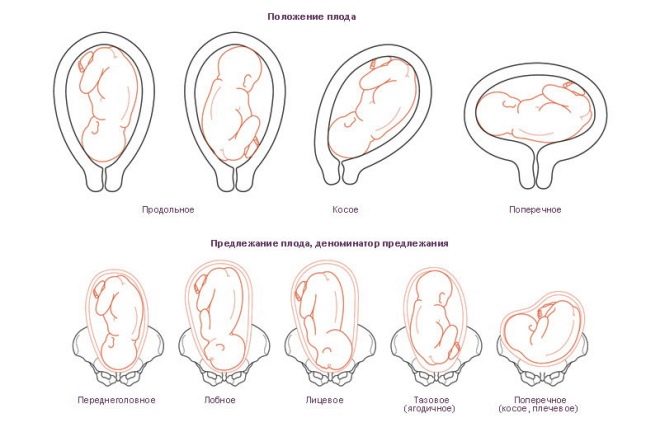
The doctor must evaluate the presentation of the fetus. This clinical criterion is very important. It provides specialists with information on how large parts of the baby are located in the uterus. The choice of tactics for further obstetric care depends on the location of the head, arms and legs, as well as the child’s buttocks.
The most favorable presentation from the physiological point of view is the headache. Passage of the baby through the birth canal in this case is quite normal. At the same time, the head first enters the birth canal. It is she who first comes into the world, and behind it all the other parts of the body. When headache previa is usually the risk of birth trauma and damage is minimal.
A less favorable presentation is pelvic. In this situation, closer to the birth canal is not the head of the fetus, but its pelvis. Such a "reverse" position of the baby can contribute to the appearance of various dangerous complications during natural childbirth.
With breech presentation, the baby’s buttocks are closer to the birth canal. In everyday life they say that the child "sits on the pope." With breech presentation, the development of birth injuries and injuries is also quite high. Independent natural childbirth in this case can be dangerous by the development of a number of complications for both the mother and her baby.
The choice of obstetric aid tactics is individual. For this, a doctor who monitors the course of a particular pregnancy evaluates a combination of various factors.
If the potential risk of birth injuries and injuries is quite high, then a surgical method of obstetric aid - cesarean section - will be used as a choice of obstetric benefits.
About what happens in the 37th week of pregnancy, see the next video.