Fetal development at 6 weeks gestation
Every day, the baby in the womb grows and develops. In the early stages of his embryonic life, very interesting anatomical changes begin to occur.
What is the term?
By the 6th obstetric week of pregnancy, a small embryo has been developing for a month. This time corresponds to 4 weeks from the date of conception.
The difference in these terms is due to the choice of a different counting system. Gynecologists and doctors of other specialties use the terms Obstetric Month and Obstetric Week.
The calendar count from the moment of conception is somewhat different: it will be less than the obstetric period. In order not to be confused, during pregnancy, expectant mothers need to use the same terminology that doctors use.
What happens to the baby?
By this period of prenatal life, the baby is still very small. However, it is actively growing: at this time many important processes of formation and insertion of internal organs, called organogenesis, occur.
This biological process proceeds gradually. The first trimester is the main period of organogenesis. The initial laying of the internal organs occurs during this period. For their final development, it will take several more weeks, and for some even months.
The developing baby contributes to the fact that the future mother has various sensations and symptoms in the body. The physiology of the female body during pregnancy varies significantly. During the first and subsequent pregnancies, the symptoms may be different.
Fetal development
In the sixth week, a small embryo actively grows and develops. Outside the embryo covers a thin layer of skin.
One of the most important anatomical structures of pregnancy is the corpus luteum. It is present in the female body throughout the entire period of elevated chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Doctors note that in some cases it may persist until the prenatal period.
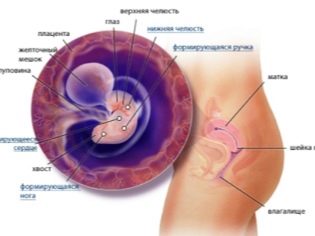
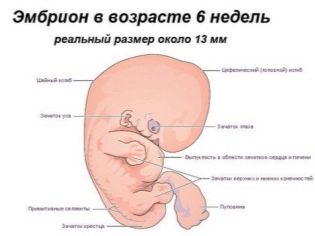
On the sixth week, the child continues to actively form the main internal anatomical structures. So, in the embryo the most important elements of the nervous system begin to form. By the sixth week of pregnancy, the structural elements of the brain and spinal column begin to form. The final development of these anatomical structures will occur somewhat later.
In the embryo, cartilage tissue begins to form. Gradually, the foundation is laid for the formation of cartilage, bones and tendons. In the future, the spine will continue to form and will take the correct functional position.
By this period of pregnancy, nerve analyzers, eyes, and ears begin to form. They will fully function, of course, much later. Also, to this period of pregnancy, the main organs of the digestive and respiratory systems begin to form: the beginnings of the liver, lungs, stomach, and pancreas begin to form.
In the sixth week of pregnancy, the embryo begins to form and the germs of the genitals. The sex of the baby can be found out a bit later, when the sexual signs are finally formed.
By this date, also begin to form the first structural elements of the arms and legs. They are located on the sides of the thoracic region of the body of a small embryo and look like small tubercles. In embryos of this embryonic age tails and gill slits disappear. Gradually, the baby begins to take a real "human" look.
An important feature of this gestational age is the beginning of the laying of organs of the immune system. At this time, the thymus gland begins to form, which will later be an important participant in children's immunity.
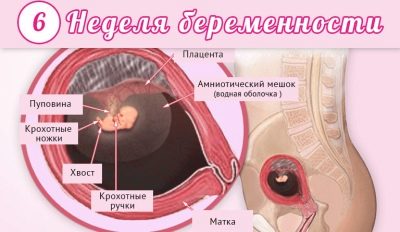
In order for a small embryo to grow and fully develop, it needs nutritional components. He gets them with the help of an important organ of pregnancy, which is called the umbilical cord.
Blood vessels pass through the umbilical cord. Between mother and baby throughout the entire pregnancy, the general blood flow system is functioning. It is because of this that the baby receives all the necessary nutrients and oxygen that are important for his vital activity.
In a baby of this embryonic age, the umbilical cord, fastened in the area of the tail, begins to move to the tummy. This is necessary to ensure that the process of intrauterine development proceeds optimally, and that the baby’s nutrition is not disturbed.
An equally important organ of pregnancy is the placenta. As the embryo grows, the size of the “baby seat” also increases. By this period of pregnancy, the placenta gradually begins to attach to the walls of the uterus. In the cardiovascular system of the embryo, important changes begin to occur at this stage of pregnancy. Thus, cardiac activity begins to manifest itself. The heart of the embryo at the sixth week of pregnancy is still very small: its size is about 0.5 cm.
Such features of the baby’s cardiovascular system also determine that first signs of palpitations appear. You can determine them during the ultrasound.
In order to assess how well a child’s heart functions, doctors use a special clinical indicator. It is called heart rate or heart rate. To determine it, the number of beats of a baby's heart is determined within one minute. All values obtained are necessarily recorded in the conclusion of the ultrasound examination, and later in the medical documentation.
Fetal heart rate is a non-permanent clinical indicator during pregnancy. In each period of pregnancy there are certain norms of the values of this criterion of vital activity of the fetus.
It is very important that the number of strokes of the child’s heart be within the normal range. This indicates that the body of the baby does not feel discomfort. Doctors will determine the heart rate of the baby until the end of pregnancy.
If the number of heart beats exceeds the age norm, then this clinical condition is called tachycardia. If the heart rate decreases, doctors talk about the presence of bradycardia.
Experts point out that Normal values of heart rate for a period of 6-7 weeks are 110-130 contractions in 60 seconds. For example, if the embryo at this period has a heart rate of 156-160 beats per minute, then in such a situation, tachycardia will be established in the sixth week of pregnancy.
If during an ultrasound examination, an ultrasound specialist revealed any irregularities in the heart rhythm, he will make a note of this in his conclusion. In such a situation, the expectant mother should consult with her obstetrician-gynecologist.
The doctor will be able to assess the reason why the embryo has such abnormalities in the heart activity. Also, the doctor will make a set of recommendations for the pregnant woman for the daily regimen and, possibly, prescribe a drug therapy to normalize the condition.
What does a baby look like?
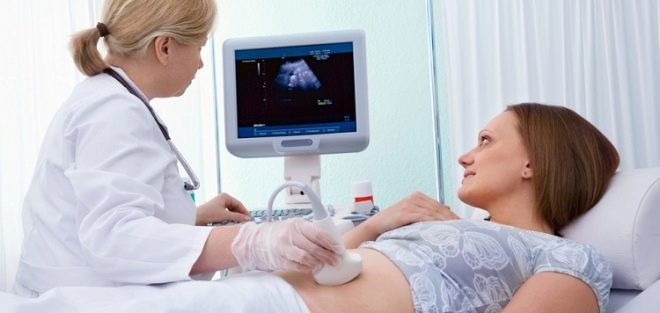
In order to determine the appearance of the embryo, various diagnostic methods are used. You can “see” a child at this stage of pregnancy using the ultrasound method. This examination is widespread in medical practice. Every day, hundreds of thousands of expectant mothers are tested.
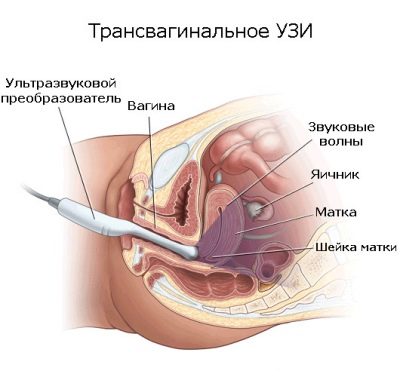
Ultrasound can be performed in several ways. In the early stages of pregnancy, as a rule, doctors prefer the transvaginal method. In this case, the doctor conducting the study may better examine the embryo and all fetal components.
There are a number of contraindications for the transvaginal method. When they are detected, the doctor will recommend choosing a transabdominal method when the examination is performed through the anterior abdominal wall.
Many pregnant women are interested in the question of whether they need some kind of special training before conducting an ultrasound examination in order to better visualize the baby. No, this training is not required.
Early pregnancy is a very important period for an ultrasound. It is very important that at this stage of intrauterine development of the baby, the study was conducted by an experienced and qualified specialist. In this case, the result of the ultrasound examination will be more reliable. The doctor should be able to conduct research in both single and multiple pregnancies.
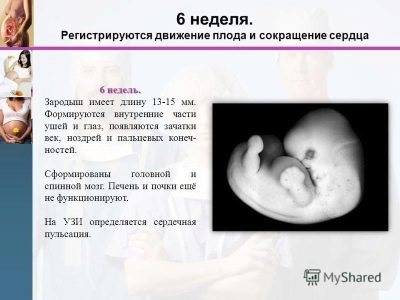
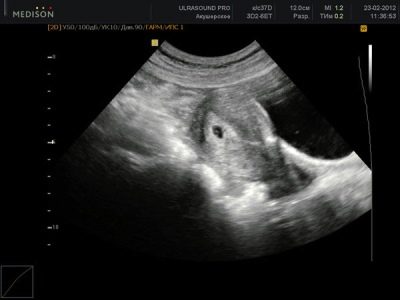
At the beginning of the sixth week of pregnancy, the embryo living in the maternal tummy resembles the letter "C". A general view of the child at this time during ultrasound examination resembles a bean.
During the study, the doctor must evaluate a number of clinical parameters. They are necessary for understanding how well the baby is developing.
One of these clinical parameters is the coccyx parietal size (CTE). At this time, the norm of this indicator is about 4 mm.. The size of the ovum is about 2.2 cm.
An equally important clinical indicator is the volume of amniotic fluid. For the development of the baby throughout its prenatal development is very important aquatic environment. It is amniotic fluid.
At this stage of pregnancy, its amount is still insignificant - a couple of milliliters. In the future, the amount of amniotic fluid will only grow. This is necessary for the child to fully grow and develop in the maternal tummy.
To study the embryo at this stage of pregnancy it is impossible to apply many methods of research. One of such prohibited tests is x-ray.
X-ray studies are not conducted for pregnant women. High radiation exposure to the body of a child and a woman during an examination can cause harm. So, X-ray has a negative effect on actively dividing cells. This significantly increases the risk of possible mutations, especially during organogenesis.
For the same reason, computer tomography during pregnancy is also not performed. Such studies are permitted only for the strictest medical reasons. If the expectant mother for some reason is going to undergo an x-ray, then she should definitely warn a specialist that she is pregnant.
Another method of research that doctors have been using for many centuries is a routine clinical medical examination. However, at this stage of pregnancy, the doctor can only assess the state of the female reproductive organs and the signs of pregnancy.
What pathologies can be on this period?
The first weeks of the embryonic life of the baby are a very important period. At this time, the probability of miscarriage is quite high.
It is especially important to monitor their well-being during this period for women who are at high risk. These include future mothers with a burdened gynecological history.
If a woman or one of her close relatives has had miscarriages in the early stages or spontaneous abortion, the risk of such pathologies is very high. This is called a burdened gynecological history.
Also, you should especially carefully monitor your health of expectant mothers who have any diseases of the reproductive organs. Women after IVF should also carefully treat any sensations in their body.
It is extremely unfavorable clinical condition, when suddenly a woman disappears all the signs of pregnancy. In such a situation it is very important to assess the condition of the fetus.
At this time, the most important clinical indicator is heartbeat. If it is not audible, the doctor needs to assess whether the further course of the pregnancy is possible, whether the embryo is alive in the female womb.
In the absence of a baby’s heartbeat, consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist is extremely important. Also, the doctor will be able to evaluate and single heartbeats that are detected during the ultrasound.
One of the most dangerous pathologies is hemorrhage in the placenta or wall of the uterus. It can lead to malnutrition of a small embryo. In this case, the expectant mother is very important to seek medical help in a timely manner.
The development of hemorrhage in the uterine wall can lead to the appearance of adverse symptoms in a woman. Thus, a woman may feel a pulling pain in the lower abdomen. The intensity of the pain syndrome in this case, as a rule, increases. Taking analgesics does not bring a woman much relief and does not significantly improve her well-being.
Another sign that should worry the future mother is the appearance of characteristic bloody discharge from the vagina. EIf a woman starts bleeding from the genital tract, she should immediately seek medical attention. This condition can lead to spontaneous abortion.
About what to expect on the 6th week of pregnancy, see the following video.