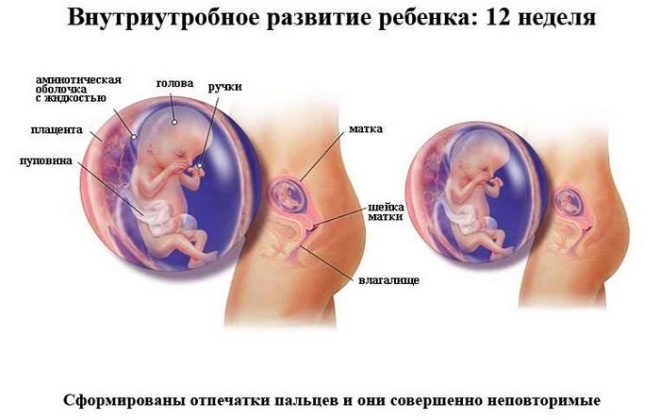
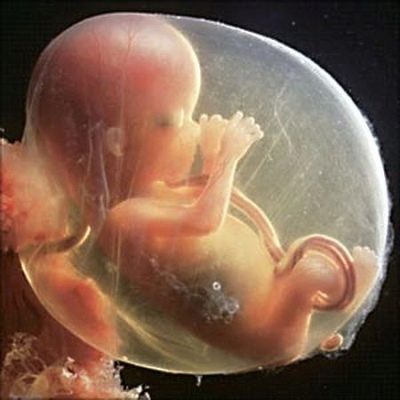
Fetal development in the 12th week of pregnancy
The development of the child in my mother's tummy in the first 12 weeks of its development undergoes a number of important specific changes.
What does it look like?
By the end of the 12th week, the tail already disappears from the child, and the body acquires a somewhat elongated shape. Skeleton baby continues to form. Babies of this age have rudiments of teeth and small nails.
Changing the shape of the face. It acquires a more "human" appearance. It is important to note that the baby’s final features will form a little later.
The upper layers of the skin, on which the eyelashes and eyebrows will appear in the future, will change somewhat. While in their place the child has a special fluff. Soft downy hairs are also present in the lower half of the face - in the chin area, as well as over the upper lip.
The ability to open and close the mouth contributes to the fact that the baby can swallow the amniotic fluid in which it is located. To panic about this is not worth it. This reaction is absolutely physiological and necessary for the full development of the urinary system in a child. Baby, swallowing a little amniotic fluid, it can even urinate.
At this period of his prenatal life, the child begins to actively explore his world. He touches his face. Experts say that the twins can "study" each other and even play with the umbilical cord of a little brother or sister. The child often bends and straightens the arms and legs. On his face may appear unconscious grimaces or a smile.
Digestive organs
So he already begins to gradually function the liver. This is manifested by the fact that bile begins to appear. It is necessary for the digestion of various nutrients that will enter the baby’s gastrointestinal tract.
There are also specific changes in the intestines. He begins to make his first cuts. Doctors call this contractile activity of the intestines peristalsis. At the 12th obstetric week of pregnancy, the child appears only the first attempts to reduce the intestinal wall. Subsequently, intestinal motility will develop and improve, but this will take several more weeks of intrauterine life of the baby.
Nervous system
Interesting changes occur in the nervous system. So, the baby begins to actively develop the brain. In its anatomical structure, it already resembles an adult brain, but only in a miniature size. The number of interneuronal connections is still insignificant. Neurons (nerve cells) of the child continue to actively develop.
Musculoskeletal system
The body of the baby on this period of its intrauterine development grows disproportionately. At the same time, his limbs grow and develop somewhat faster than his head. In the future, the proportions of the body will change.
The active growth of the limbs leads to the fact that by the 12th week of his intrauterine life the elbow joints, as well as small fingers and toes, are already formed in the child. Formed and ears. The thumbs of the hands are slightly different in size.
The active development of the musculoskeletal system contributes to the fact that the first motor movements appear in the child. The kid begins to move little by little hands and legs. His mother, as a rule, does not feel such movements at this stage of pregnancy at all, and there are no particular sensations in her stomach. This is because the size of the baby is still relatively small.
At the 12th week of his prenatal development, the baby can already open or close the mouth. He does it while still completely unconsciously. Such a physical activity in a child is only a kind of “rehearsal” of future chewing movements.
Circulatory and immune systems
The child has red blood cells - red blood cells. They deliver all the nutrients necessary for growth, as well as oxygen into the cells of a small growing organism. By the end of 12 weeks of intrauterine life, the first leukocytic cells appear in the baby. They are necessary to protect the child's body from various dangerous infections.
By this time of pregnancy, the baby’s heart has already been formed. It already has 4 chambers: the right and left ventricle, as well as the right and left atria. The heart of the baby is already really beating. The rate of heart rate (HR) in a child during this period of his intrauterine life is presented in the table below.
Clinical indicator of the heart | Norm |
Heart rate (beats per minute) | 150-160 |
Frequent work of the heart leads to the development of tachycardia. In this condition, the doctor must determine the cause that contributed to its development.
During the ultrasound, you can assess the condition of all the chambers of the heart in a child. At the same time, not only the anatomical structure of the heart valves is evaluated, but also various clinical conditions are identified. One of them is tricuspid regurgitation (reverse blood flow).
Endocrine system
In the baby, the endocrine glands are already beginning to function. Runs the pituitary gland. "Awakens" to work and the thyroid gland. She begins to secrete specific hormones into the blood. For their education, sufficient intake of iodine into the children's organism is necessary.
His mom should keep an eye on this, not forgetting to use the multivitamin preparations recommended by her doctor.
About fetal membranes and placenta
Placenta is very important for the full development of the child. In the first weeks of pregnancy, its function "takes over" the yellow body. By the 11th-12th week, the placenta appears along with the fetal membranes. Doctors call this specific complex of organs.
In appearance, the placenta resembles a flattened flat cake. Inside it are numerous blood vessels. They are of two types: maternal and fetal. The first belong to the mother, and the others - to the baby.
There is a specific membrane between these blood vessels. It performs a very important function, since it serves as a specific barrier against the entry of dangerous microbes into the children's organism. This uteroplacental barrier protects the baby from infection with pathogenic viruses and bacteria, and also reduces the likelihood of various toxic substances entering the children's bloodstream.
It is thanks to this abundant circulatory network that the baby receives all the nutritional components necessary for its development. Also through them, the child receives the oxygen necessary for the gas exchange process in the child’s body.
Also, due to the placenta, important metabolic processes occur in the baby.Waste and unwanted substances from the body of the child through the blood vessels of the mother enter her kidneys, from where they are subsequently removed along with urine.
In addition to the protective function, the placenta also has endocrine. The cells that form it release certain hormones. They are necessary for the normal course of pregnancy and optimal fetal development of the baby.
External genitalia
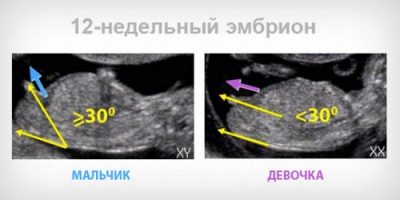
There are also changes in the reproductive system of the baby. Active prior development of the genital organs leads to the emergence of the first gender differences. So, the boys appear the first specific signs of male external genital organs, and in girls - female.
Sex determination
Often, mothers are in a hurry to determine the sex of their baby. It is important to remember that in the early stages to find out if a boy or a girl will be born, it is possible, but with a high degree of probability of inaccuracy or even an error. It all depends on the experience of the ultrasound doctor who is conducting this study.
Determine the sex of the unborn child should be by ultrasound, and not by heartbeat or some other less informative methods.
Main dimensions
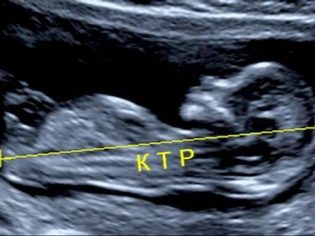
To assess the parameters of the baby at this time of its intrauterine development, specialists use special clinical indicators. One of them is the coccyx parietal size or CTE. In fact, this parameter estimates the length of the body of the child. Measure it from the tailbone to the crown of the baby.
No less important clinical parameter is weight. During each study, doctors determine the body weight of the baby. This simple clinical parameter indicates how well a baby develops in the womb. Weight standards and KTR are shown in the table below.
Estimated parameter | Norm |
Copical parietal size | 6-9 cm |
Weight | 14-15 grams |
To assess the intensity of intrauterine development, some experts recommend that the intracranial space be evaluated in the posterior cranial fossa. In their opinion, this study provides information on whether the fetus has any neural tube formation defects.
It is better to conduct this study after 11-13 weeks of pregnancy.
Possible pathologies
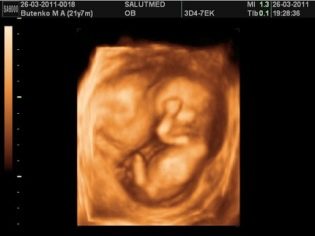
It is possible to identify abnormalities in the prenatal development of the baby using ultrasound. At 12 weeks of pregnancy, as a rule, the first such study is conducted. During the meeting, the doctor determines the basic parameters of the child, assesses the state of the internal genital organs of the mother, and can also tell about the estimated date of the upcoming birth. Also, performing an ultrasound, the doctor assesses where the baby is and is located in the uterus. Squeezing the growing uterus adjacent organs leads to the fact that the venous blood flow in them is broken. This condition is dangerous development of a number of pathologies.
To assess the parameters of intrauterine development, the specialist uses special medical tables. He compares the clinical values obtained during the study with the norms for this age. If they significantly deviate from normal values, then he will definitely make a mark about this in the medical report.
Special tests, which are also included in the first screening during pregnancy, help to suspect dangerous genetic and chromosomal pathologies at this time. These tests include hCG (its beta fraction) and PAPP-A. Reviews of many women indicate that such a comprehensive study they passed at 11-13 week of pregnancy.
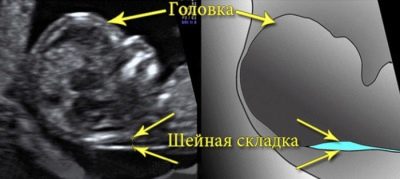
One of the main markers of various pathologies is the neck area. Liquid is accumulated in this space. This zone is located on the neck - between the skin and soft tissues. In babies at 12 weeks is estimated the thickness of this space.
When conducting a study it is very important that an experienced doctor conduct it. After all, the wrong result can lead to its incorrect interpretation.
With the help of ultrasound in some cases, a specialist identifies:
- omphalocele - a clinical variant of the congenital defect of the anterior abdominal wall;
- megacystis - an increase in the size of the bladder;
- nasal hypoplasia - nasal bone underdevelopment;
- duodenal atresia is an underdevelopment of one of the intestinal sections;
- cervical hygroma-cystic formation in the neck.
The detection of these pathologies is the most important reason for consulting with your doctor. It is important to remember that only one conclusion of ultrasound is not a diagnosis. To determine the genetic or chromosomal pathology, a number of additional tests and tests are required.
On the need for advanced screening at the 12th week of pregnancy and its decoding, see the following video.