What is the edge presentation of the chorion and what does it affect?
With such a diagnosis as the regional presentation of the chorion, according to statistics, up to 45% of pregnant women in the early stages of carrying a baby. Should we be wary of such a medical verdict, and what to do, this article will discuss.
What it is?
Chorion - a temporary body that performs the functions of a pharmacist. It is formed from the moment of the implantation of the ovum from the fallopian tube, where the meeting of the egg and spermatozoon, into the uterine cavity took place. As soon as the blastocyst (the fertilized egg turns into it by the 8-9 day after ovulation) reaches the uterus, it tends to gain a foothold in it. It is this process that is called implantation.
At the site of attachment of the shell, the blastocysts secrete special enzymes that make the mucous membranes of the uterus more pliable and allow the ovum to "grow". Chorion forms at the site of attachment. It is necessary for the nutrition of the ovum with useful substances from the mother’s blood. In its place a placenta appears a little later. But up to 12-13 weeks we are talking about the chorion, since the placenta is still being formed and does not function.
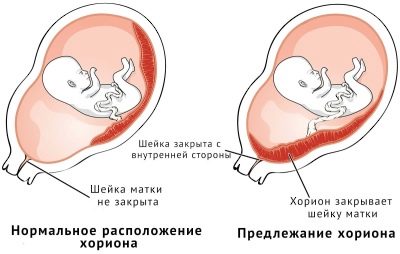
If the implantation is successful, the ovum is fastened in the area of the bottom of the uterus (this is its upper part). If for some pathological reasons it was not possible to implant in the upper or middle part of the uterus by the blastocyst, it may descend into the lower uterine segment. And then the chorion will be formed low.
Preposition of the chorion is its location relative to the cervical canal - a thin passage inside the cervix connecting the uterine cavity and the vagina. About the presentation of speech is not only if the chorion was formed in the area of the uterus or in its middle part (in the body of the uterus).
If the chorion is low, there are several types of presentation.
Classification
Depending on the degree of overlap of the cervical canal, through which the fetus will later pass in labor distinguish and types of pathology.
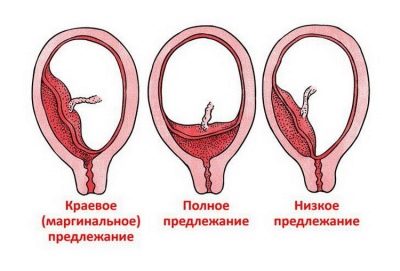
- Regional presentation of chorion - the chorion is located low, its edge slightly affects the region of the cervical canal with one edge. Such presentation is considered the most favorable, in terms of projections, for further pregnancy and childbirth.
- Incomplete previa - The chorion is located low and covers about two thirds of the entrance to the cervical canal. The predictions are less optimistic, since this position of the chorion in the uterus increases the likelihood of miscarriage or bleeding due to chorionic detachment.
- Full previa - the chorion is formed low and completely closes the entrance to the cervical canal. This is a rather dangerous pathology, the forecasts for which are very unfavorable.
Any presentation of the chorion, but especially complete and incomplete, pose a threat of miscarriage, chorion detachment. In its place, a placenta will form, a network of blood vessels will develop, and it is dangerous if the vessels grow into the lower part of the uterus, which, according to the laws of nature, should open up and release the baby out when the time of birth comes.
Often, the presentation of the chorion can turn into another pathological condition - placenta previa, and then independent labor naturally will most likely be contraindicated. A woman will undergo a caesarean section. It will also be difficult to bring the child to the due time, since the low-lying and adjacent to the exit of the uterus placenta will create the risk of spontaneous bleeding at any time.
A child with a breech will receive less oxygen and nutrients, and this is fraught with hypotrophy and hypoxia.
Causes and symptoms
The main reason for the regional presentation is the internal prerequisites that prevented the ovum from implanting normally and into a more suitable bottom of the uterus. These prerequisites include endometrial disorders of the uterus. It is usually observed in women who undergo several abortions or undergo diagnostic curettage.
Miscarriages, missed abortion in history and also increase the likelihood of improper location of the ovum. An obstacle to full implantation may be a scar or several scars on the uterus from previous operations or cesarean section.
Women who have given birth to many, can not boast of strong and elastic muscle tissues of the reproductive organ, they also increase the likelihood that subsequent pregnancy may occur against the background of low placentation.
The presence of fibroids, fibromas and other formations in the upper part of the uterus also creates obstacles for the attachment of the blastocyst, and it is forced to descend in search of a “shelter” in the lower uterine segment. The reason may be a congenital anomaly of the structure of the uterus - two-horned or saddle-shaped uterus. Some sequence of such pathologies has been noticed - if during a previous pregnancy the woman had low placentation, with a high degree of probability the attachment of the fetus and the development of the chorion during the subsequent pregnancy will also be low.
Symptoms of the edge presentation of the chorion in the early stages may not be, and may appear a small short spotting. Usually they are always evaluated by a woman correctly - as a threat to the preservation of the child.
If the chorion, and subsequently the placenta, do not migrate, such bleeding associated with rupture of small blood vessels due to stretching of the walls of the uterus, can often recur, in some - until the birth. Because of them, a woman begins to suffer from anemia, she is chronically short of iron, and there is a small amount of hemoglobin in her blood. Be that as it may, when a bloody discharge from the genital tract of a pregnant woman appears, you should immediately call an ambulance.
With timely hospitalization with the help of conservative treatment, up to 90% of all babies growing up in the womb against the background of the regional presentation of the chorion, the placenta and even the umbilical cord can be saved.
What to do?
As already mentioned, the regional presentation of the chorion is diagnosed in about 4-5 women in ten pregnant women up to 12 weeks. However, not all of them immediately fall into the risk group and patient lists for elective cesarean section. Projections are favorable, and in 90% of cases the chorion, and then the placenta, which forms in its place, migrates higher simultaneously with the growth of the uterus.
Baby in the womb is growing rapidly. To meet its needs for comfort, the uterus and ligaments are forced to stretch. Together with them, "crawl" up and the placenta, which at the beginning of the pregnancy was located in the regional presentation. On the front or back of the uterus will migrate the placenta - does not matter. It is important that in most cases it really rises, and all the threats and risks associated with low placentation remain in the past.
Influence the process of migration, accelerate it or stimulate medicine can not.A woman with a diagnosis of “regional presentation of the chorion” needs to follow all the recommendations of her doctor, to eliminate physical exertion, weight lifting, jumping, sudden movements, squats. She will often have to visit her doctor, do an ultrasound to monitor the migration process of the chorion (placenta). Sex in marginal presentation is prohibited, because the orgasm associated with the contraction of the uterus muscles may contribute to rapid traumatic chorion detachment and the occurrence of severe bleeding, in which the child may die in utero, and the woman may lose a lot of blood and die from it.
The process of migration of the placenta is usually completed by 18-20 weeks of pregnancy. By this date or a little later (by week 35-28), the true state of affairs becomes clear - if the placenta has risen, the restrictions will be lifted, if not - the pregnant woman will be classified as at risk for preterm birth and will continue with increased attention and trembling.
Treatment
It is impossible to accelerate the migration, but most likely, a woman will be prescribed treatment for a woman with a marginal presentation of chorion. Only it will be directed not at the chorion itself, but at relaxing the muscles of the uterus in order to prevent its tone and not to provoke new detachment and bleeding. Depending on the degree of presentation, treatment may be carried out in the hospital, and may be allowed to take the necessary drugs at home. This question the doctor leaves at its discretion.
A woman is shown bed rest or semi-bed rest, complete sexual and psychological rest. Of the medications effective are considered antispasmodics "Papaverin" and "No-shpa", Hemostatics -" Ditsinon ", vitamins of group B," Magne B 6 ", vitamin E in large dosages.
In the hospital, women are given magnesia with novocaine, and hormonal medications, for example, Duphaston, are often recommended at home, but only if it is proved that the woman has a deficiency in certain pregnancy hormones.
For better nutrition of the baby, drugs that improve the uteroplacental blood flow are recommended - “Curantil”, “Actovegin". Medicines should be taken regularly, without missing and not forgetting.
The courses of treatment are usually quite long - up to the moment when it will be possible to establish on the ultrasound that the placenta has risen and there is no more danger, or even to the birth, if the placenta does not rise higher.
Childbirth
In the overwhelming majority of cases, in the absence of migration of the placenta until 35-36 weeks of gestation, the decision is made to conduct a cesarean section. Even regional presentation can be dangerous, in terms of the development of abundant, massive bleeding during childbirth, which is dangerous both for the mother and for the fetus. Rapid placental abruption before the birth of the child also leads to acute hypoxia and can be fatal for it.
If the placenta rises higher, doctors may well allow the expectant mother to give birth naturally, unless she has other contraindications.
In the video below, see the history of pregnancy with chorion detachment. Is this diagnosis so terrible?