Why is pelvic presentation of the fetus considered dangerous, what causes it and how does the birth proceed?
About 6% of pregnant women at the time of the next ultrasound they hear an alarming conclusion - “pelvic presentation”. It is obvious to all that nature has provided for the crumbs in the womb of the mother a more natural position of the body - head down. Heading forward is easier to move through the birth canal, to be born into this world, it is the head previa does not threaten complications.
And what to do to those who have kids decided to settle down differently? Is pelvic presentation always an indication for a cesarean section? How is it dangerous and is it possible to force the child to change the position of the body? We will try to answer all these questions as fully as possible in this material.
What it is?
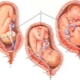
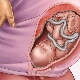
Pelvic presentation is called an abnormal location of the fetus in the uterine cavity, in which not the head of the fetus, but the butt or lower limbs are facing the exit to the pelvic area. The head is located at the bottom of the uterus. Baby actually sitting.
Pelvic presentation refers to the pathological conditions of pregnancy, the birth of it is also considered pathological. There is nothing natural in this arrangement of the fruit. However, about 4-6% of all pregnancies occur against the background of pelvic presentation of the fetus.
For obstetricians, every such case is a real test of professionalism. Conducting pregnancy in the pelvic location of the baby, as well as childbirth at this location, crumbs require a lot of experience and knowledge from the medical staff.
In modern obstetrics, it is more and more often suggested that a woman whose baby is located downside down has a cesarean section. But you should know that there is an alternative to surgery - natural childbirth. With pelvic presentation, the risks of complications during childbirth are higher, but an experienced and well-trained doctor may well conduct the birth process successfully. The baby will naturally be born with its feet forward.
Kinds
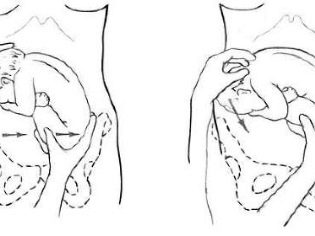
The concept of "pelvic presentation" is wider than future mothers think. An experienced doctor is not enough to know where the head of the baby is, he needs to clarify which part of the lower half of the body is located in relation to the small pelvis. Therefore, all pelvic presentation is quite clear and understandable classification.
Buttock
To the exit of the pelvis in this position, the baby adjacent buttocks. The gluteal presentation may be incomplete, with only the buttocks adjacent to the exit of the uterus, and the legs are bent at the hip joints and stretched along the body so that the heels are at the very face of the child. Also, the buttock presentation can be mixed (combined) or full, in which the priest fits with the legs, the baby as if squatting.
Incomplete (exclusively buttock presentation) occurs in 75% of cases of all pelvic presentations. Every fifth case refers to a full or combined (mixed) buttock presentation.
Foot
This concept refers to the location of the legs of the fetus from the uterus. Foot previa is much less common buttock. With a full foot position, both legs, slightly bent at the knees, are attached to the exit to the pelvis. But such a picture - rather a rarity. Incomplete pedal presentation is usually observed, in which one leg presses against the exit of the uterus, while the other leg is bent at the knee and hip joint and in level is significantly higher than the first.
There are also such inventive kids, which are located to the exit to the small pelvis with their knees. This is also a variant of the foot presentation - the knee. With it, the baby does not bend the legs in the hip joint, but bends them at the knee joints, it looks as if the baby is kneeling in the womb and both knees are pressed to the exit to the pelvis.
Options for foot presentation are considered the most dangerous from the point of view of the development of complications during childbirth.
Hazards and Risks
Pelvic presentation in labor is dangerous by the development of severe complications. Water may be poured out prematurely, together with them the loss of the umbilical cord, its parts and even parts of the body of the fetus. Often, women develop weakness of labor forces when contractions do not lead to the opening of the cervix. Often the birth of a child with a pelvis and legs forward leads to acute hypoxia, the death of the baby, irreversible changes in its central nervous system.
In the process of childbirth the baby can throw back the handles, chin. The latter is the most dangerous development of disabling birth trauma associated with fractures, displacement of the cervical vertebrae, brain and spinal cord. For mothers such childbirth is dangerous by ruptures of the cervix, vagina, the occurrence of severe bleeding.
For a child, the consequences of pelvic presentation can be quite unpleasant - it is congenital dislocation of the hip, pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys and urinary system, trauma, and development of cerebral palsy.
However, the dangers lurk not only in childbirth, but also during pregnancy. In the first half of the gestation period, pelvic presentation of the fetus increases the likelihood of miscarriage, hypoxia, and the risks of developing early preeclampsia are also considered elevated. In the second half of the pregnancy, the woman whose baby is head-up is threatened with premature labor, preeclampsia, including severe, premature placental abruption.
Women with pelvic presentation of the fetus by 60% increased the risk of developing placental insufficiency and subsequent malnutrition of the fetus. In a state of lack of nutrients, vitamins and oxygen, the baby is not well enough and quickly develops the nervous and digestive systems, there are problems with the endocrine system and the work of the heart and blood vessels.
From 34-35 weeks of pregnancy, if the child does not turn over to the head position, the pace of development of the structures of the medulla oblongata slows down, which leads to disruption of the pituitary gland, the adrenal cortex. Negative changes in a child who occupies a wrong position in space also occur in the genital area - edemas and hemorrhages occur, and later the girl’s ovarian syndrome may appear, and the boy oligozoospermia or azoospermia. Among children with congenital heart defects there are quite a few who have spent the first nine months head up and booty down.
Among the congenital cases of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, about 40% are due to such a cause as pelvic presentation of the fetus during pregnancy.
The reasons
Physicians and scientists are completely incomprehensible mechanisms for the development of pathology, it is difficult enough to explain why the kid, who is supposed to be the head down by nature, occupies a different position, which is not convenient either for him or for his mother. Therefore, it is not customary to speak of reasons as such; rather, these are prerequisites for pelvic presentation. And they can be very diverse.
Pathology of the uterus and pelvis
This premise is considered the most common. Tumors, uterine fibroids, narrow pelvis, and the presence of postoperative scars on the uterus can interfere with the correct head position of the baby. Quite often, the prerequisites are the anatomical features of a particular woman - the two-horned or saddle-shaped uterus. Increased tonus of the uterine muscles also creates the risk that the baby will assume an abnormal body position.
Often women who have given birth to pelvic prevalence often have given birth - the uterine musculature is weakened, “stretched”, it cannot ensure reliable fixation of the fetus. Often women face the pelvic presentation of the baby, who have had many abortions before, often undergoing curettage of the uterus. The child instinctively tries to occupy a position in which his head will be in that part of the uterus where spasms occur less frequently. For women who have had several abortions, this section is the bottom of the uterus. Its lower segment is tense.
Fetal pathology
Quite often in the pelvic presentation are children who have gross chromosomal abnormalities and malformations. So, according to statistics, up to 90% of babies with microcephaly (reduced brain volume), anencephaly (absence of the brain) and hydrocephalus (dropsy of the brain) in the mother's womb are located head up.
Pelvic presentation is often characteristic of one of twins, if the pregnancy is multiple, and in this case the position of the child in the uterus may not be in any way connected with any of its pathologies.
Sometimes the wrong position of the body relative to the exit to the small pelvis is an indirect sign of problems with the vestibular apparatus in a child.
Amount of amniotic fluid
With the polyhydramnios, the fetus has more room for coups, somersault and somersaults. And this sometimes affects the fact that the baby takes the wrong position of the body inside the space of the uterus. With the lack of water, the movement of the child, on the contrary, is difficult, and it is difficult to roll over into the correct position.
Umbilical cord and placenta
A short umbilical cord restricts the movement of the baby, and too long is often combined not only with pelvic presentation of the fetus, but also with entanglement around the neck or limbs. Pathological location of the placenta is also a prerequisite for pelvic presentation - it is a question of placenta previa or its low location.
Heredity
Obstetricians have long noticed that most often the pelvic presentation of the baby develops in pregnant women who themselves were born in pelvic presentation or the entire pregnancy of the mother was in this position.
In fairness it should be noted that the above reasons do not always explain this fact. Sometimes pelvic presentation is fixed in the crumbs, which does not have any of these prerequisites. Not all cases of pelvic or oblique pelvic presentation can be explained, as it is not always possible to understand why the baby, which was head up, just a few hours before the birth suddenly does the impossible and turns over to the head previa. This is rare, but there are enough such examples in obstetrics and gynecology.
Diagnostics
Until the third scheduled screening ultrasound, or rather, up to 32-34 weeks of gestation, the position of the fetus does not play a large diagnostic role, because the baby still has free space inside the uterus to change the position of the body spontaneously. Therefore, the diagnosis of pelvic presentation at an earlier date is not considered, it is only a statement of fact. The doctor describes the position of the fetus, in which he was "caught" during the ultrasound.
After 34 weeks, the odds of a coup diminish to negligible values. It is at 32-34 weeks that pelvic presentation sounds like a diagnosis. Tactics of observation of the pregnant woman is changing, the issue of the mode of delivery is resolved in advance.
The pelvic position of the baby is first determined by the obstetrician. For this, he uses the so-called Leopold method.The height of the uterus floor exceeds the norm, probing the medic’s hands through the anterior abdominal wall of the expectant mother is determined by a rounded element, quite mobile, slightly shifted to the right or left of the median line passing through the navel. This is the head baby. To eliminate the mistake, the obstetrician uses auxiliary methods: the lower part of the abdomen is palpated, if it is the priest, it is not capable of mobility. Also listens to the baby's heartbeat. A tiny heart with a pelvic location usually knocks above the mother's navel, slightly to the right or slightly to the left of it.
By the location of the heartbeat, a woman can determine the presentation of her baby and independently, using a phonendoscope. The points and kicks of the baby, which is head up, more painful and palpable felt in the lower abdomen, almost above the pubis.
At vaginal examination, the presumptive diagnosis is clarified. Through the anterior vaginal fornix, the doctor determines a softer presentation part. The head, if the fetal position of the head, more solid and dense to the touch.
After examining the gynecologist, the woman will be offered to undergo an ultrasound examination, which should put everything in its place. Ultrasound will determine not only the position of the baby, but also the nuances important for delivery - whether its head is unbent, cord entanglement, what is the estimated body weight of the baby, is there developmental pathologies, where exactly is the placenta, what is the degree of its maturity.
The angle of extension of the head with the greatest value. If it is unbent and the child seems to be looking up, then there can be no talk about independent childbirth, because the risks are too great that, when passing through the genital tract, the baby will receive serious spinal injuries.
When the fact that the baby is lying incorrectly is placed on the ultrasound, it is necessary to carry out an ultrasound with a doppler, as well as CTG, in order to have all the data on possible violations in the state of the child caused by hypoxia.
Only after the end of the examination can the doctor be able to give an exhaustive answer about the prospects for further pregnancy management and the desired mode of delivery.
Natural revolution of the fetus
Till 28-30 weeks nothing is required from a woman. Doctors take an observant position and strongly recommend the expectant mother to sleep more, rest, eat normally, take vitamins and means to reduce the tone of the uterus, to prevent fetal hypotrophy and reduce the risks of placental insufficiency. From 30 weeks the doctor may recommend a woman to do corrective gymnastics.
Exercises on Dikan, Shuleshov, Grischenko are aimed at maximally relaxing the muscles of the uterus and pelvis, to enable the child to take the correct position while it is still possible. The effectiveness of gymnastic exercises in combination with respiratory gymnastics is estimated at about 75%. In most cases, if the gymnastics helped, the child turns upside down naturally, without coercion, during the first week after the start of classes.
Gymnastics for a fetal coup is contraindicated in women with diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver and kidneys. Undesirable classes are for women with scars on the uterus from surgical operations or cesarean section in history, for future mothers with signs of preeclampsia, the threat of premature birth. When urethral discharge from the vagina (watery, blood) is unusual for gestational age, gymnastics is contraindicated.
In a natural way, children can take a head position in 70% of multiparous women and in about a third of pregnant women with firstborn babies. To achieve the result, they use not only gymnastics, but also swimming in the pool, as well as psychological influence. According to most obstetricians, the child may well "heed" the persuasion of his mother and roll over. If up to 35-36 weeks he does not do this, then with a 99% probability the baby will remain in pelvic presentation before birth.
Hope for 1% of his coup already during the bouts or shortly before them is not worth it.
Exercises to reverse the fetus, see below.
Obstetric turn over
If gymnastics, swimming, proper breathing and adherence to clinical recommendations of up to 35 weeks did not have any effect on the baby, a forced obstetric coup could be made. He is also called the coup according to the Archangel method. Outdoor coup is carried out exclusively in the hospital. Previously, doctors tried to practice it for 32-34 weeks, now it is considered the most reasonable to turn the child manually for a period of 35-36 or 36-37 weeks.
The woman should have a sufficient amount of amniotic fluid, the coup takes place under the constant supervision of an ultrasound. Doctors control the heart activity of the baby through CTG both before turning and for some time afterwards. The essence of the method is to gently gently move the head and buttocks of the fetus at the same time clockwise or counterclockwise (depending on the position of the back). It is not always possible to turn the baby, no one will give guarantees that the Arkhangelsky method will give the expected result.
Obstetric coup is contraindicated in women who have a threat of premature birth, if her pelvis is very narrow, if her age at the time of first birth is more than 30 years. Doctors will not turn over the baby forcibly if there is not sufficient mobility, if a woman has preeclampsia.
The Arkhangelsky method is not used in cases of multiple pregnancies, in the presence of uterine scars, as well as with a lack of amniotic fluid (low water) or an excess of them (polyhydramnios).
If the pelvic presentation of the baby is due to the anatomical malformations of the uterus, the manual revolution is also not carried out. Recently, more and more obstetricians refuse to hand coup in principle. It is believed that it increases the likelihood of placental abruption, fetal entanglement and asphyxia, violation of the integrity of the fetal membranes. Medicine knows cases where an obstetric coup ended in preterm labor, uterine rupture and trauma to the fetus.
Given that there may be no effect, and there may be side effects, many obstetricians continue observational tactics until 37-38 weeks of pregnancy, after which they routinely hospitalize the expectant mother to the maternity hospital and choose the method of delivery.
Caesarean section or vaginal delivery?
This is the main question that torments a pregnant woman and does not give rest to her doctor. It is up to him to decide even before 38 weeks of pregnancy. Opinion that giving birth with a pelvic presentation will have exclusively through the operation of cesarean section, erroneously. A baby that sits in the uterus head up can be born in many ways:
- natural childbirth, which began spontaneously;
- natural childbirth, stimulated in the DA, a little earlier or a little later than this date;
- planned caesarean section.
To select the appropriate delivery tactics, doctors use a special scale of childbirth. If the total amount of points exceeds 16, it is considered that a woman can give birth on her own with pelvic presentation. Points are awarded as follows:
- gestational age - 37-38 weeks - 0 points;
- gestational age over 41 weeks - 0 points;
- gestational age 40-41 week - 1 point;
- gestational age 38-39 weeks - 2 points;
- large fruit (from 4 kilograms) - 0 points;
- fruit weight 3500 -3900 grams - 1 point;
- baby weight from 2500 to 3400 grams - 2 points;
- foot previa - 0 points;
- combined (mixed) presentation - 1 point;
- buttock - 2 points;
- highly unfolded fetal head - 0 points;
- moderately extended head - 1 point;
- bent head - 2 points;
- immature cervix - 0 points;
- insufficiently mature neck - 1 point;
- Mature cervix - 2 points.
Also, from 0 to 12 points is given for the size of the pelvis - the wider it is, the more points a woman will receive. And only the sum of points shows whether it is possible to take a risk and give birth to oneself or it is better to trust the experience and qualifications of the surgical team and give birth by caesarean section.
It should be noted that the assertions of many pregnant women that they will not give consent to the operation, which are often heard in women's forums devoted to issues of pregnancy and childbirth, do not have a special meaning. A cesarean section, if the score is less than 16, is medically indicated and only when there is a high risk of injury to the child during childbirth in a natural way.
The decision on a planned caesarean section with pelvic presentation should always be weighted.
If it seems to a woman that she was sent for an operation simply because of the doctor’s unwillingness to “tinker” with problem pathologies, you need to contact the head of the antenatal clinic and ask to appoint a medical expert commission, which again calculates the risk points and gives its opinion.
DFor a woman in respect of whom a decision is made about a possible natural birth, it is important to timely go to the maternity hospital. You can’t wait for the contractions to start at home. Even the most initial, first period of the labor process must take place under the vigilant supervision of a qualified doctor.
With the advent of contractions, strict bed rest is recommended for the woman. She can not get up, walk along the corridor or antenatal ward. She should lie, repeating the position of her baby (on which side to lie down, the doctor will tell).
At this stage, it is important not to allow premature rupture of the fetal bladder, the outpouring of water, their particular rapid outflow, because umbilical loops and even parts of the baby's body can fall out together with the waters.
As soon as the contractions become regular, and the cervix opens up to 3-4 centimeters, spasmolytic drugs and painkillers are administered to the woman in order to prevent too rapid labor activity. At this stage, the CTG apparatus is connected, the entire delivery process will be accompanied by constant monitoring of the fetal heart activity. For the prevention of hypoxia, curantil, cocarboxylase, sietin and halosquine are injected into solutions for injection.
As soon as the water leaves, the doctor will carefully assess the condition of the baby using CTG, as well as conduct an intravaginal study for the loss of the umbilical loops or parts of the baby’s body. If the loops fall out, they will try to refill them, but in case of failure at this stage, the woman will be urgently sent to the operating room for a caesarean section.
By the way, about 30% of natural childbirth with pelvic presentation ends in a cesarean section. And to him morally should be prepared, and the woman herself, and her relatives.
Predict the course of childbirth, if the baby goes with legs or booty forward, no one can.
In the second stage of labor, if everything goes well, a woman begins to receive oxytocin, stimulating a reduction and faster opening of the neck. As soon as it unfolds enough to let the child’s buttocks pass, the medical team performs an episiotomy - a surgical dissection of the perineum and the posterior wall of the vagina. This will help protect women from spontaneous breaks and facilitate the passage of the baby.
It is considered a favorable sign if the birth of the head occurs no later than 5 minutes after the birth of the body of the baby. In the process of the appearance of the baby on the light, the obstetrician may use different techniques. With one, the buttocks are supported manually without trying to pull them out or somehow speed up the process, while the other baby is gently removed by one or both legs, by the inguinal fold. There are many options in the third period of birth, it all depends on how the birth proceeds, how the baby will be born.
A delay or inattentive attitude of the staff towards such a woman in labor can lead to acute hypoxia, fetal death, and serious injuries that they will make a disabled child forever.
That is why a woman who is going to give birth in a pelvic presentation, should with great responsibility come to the choice of obstetric institution, a doctor, once again weigh all the risks.
Postpartum period
The postpartum period after such births is not much different from the same period for non-pathological births. A woman should not be afraid that she will spend more time in bed or will not be able to take care of the newborn. If there are no complications, no bleeding has opened, then from the birth of the newly-minted mother is transferred to the ward, where she can rest, and the child is sent to the children's ward, where there will be a special relationship to him.
All babies who were born with legs or booty forward, even if there were no visible complications in labor, neurologists observe more closely, because some of the consequences of pathological labor can be quite remote. It is possible that feeding such a baby will be brought later than other children, often babies after birth with lower body in front require resuscitation support.
These newborns need regular follow-up by a neurologist before they reach the age of three.
If the pathology manifests itself, then the dispensary registration for the child can become life-long.
Memo for moms
Pregnancy on the background of pelvic presentation has its own characteristics, and a woman needs to remember that:
She is strictly forbidden sudden movements in the third trimester of pregnancy, sleeping on her back, bending forward;
Prenatal bandage, if the child is head up, can only be worn until 30 weeks of pregnancy. If then the baby has an incorrect body position in space, you cannot wear a bandage.
Before childbirth or shortly before them, the abdomen is lowered in pregnant women - the head of the fetus with head previa pressed against the exit to the pelvis. With pelvic presentation, abdominal prolapse does not occur until the birth.
Reviews
According to reviews of those who gave birth naturally, it is better to go to childbirth in specialized perinatal centers, there is a different technical equipment and more opportunities to prevent complications. Most women who left reviews had a caesarean section, but a fairly large percentage of pregnant women went through vaginal delivery.
After birth, the baby, according to moms, requires a more careful attitude, because many babies born to booty in advance have disturbed sleep and appetite, they are more often worried.
Many mothers from the first days began to do the baby foot massage, under the supervision of a pediatrician practiced hardening, because children who spent nine months headfirst, often do not have sufficiently strong immunity.
More distant effects of pelvic presentation, according to moms, are often manifested in preschool age. Boys and girls, who were born in an unusual way, have a disturbed attention and reduced ability to learn, and such phenomena can be observed even in those children who have been removed by caesarean section.
On forums for mothers of “special” children, children with cerebral palsy, birth in pelvic presentation is given a special place, because many of these children have acquired severe systemic disease as a result of such births. Moms of these babies advise pregnant women to think carefully before insisting on natural childbirth and resisting planned cesarean section.
You will learn more about the pelvic position of the fetus in the following video.