What is the presentation of the fetus and what does it affect?
A pregnant woman in nine months of carrying a baby often has to hear about the presentation of the fetus. Obstetricians and gynecologists talk about him on examination, ultrasound diagnostics specialists. About how it happens and what affects, we will tell in this material.
What it is?
During pregnancy, the baby repeatedly changes its position in the womb. In the first and second trimester, the child has a lot of free space in the uterus to roll over, tumble and take a variety of positions. Presentation of the fetus on these dates is voiced only as a fact and no more than that, this information has no diagnostic value. But in the third trimester, everything changes.
The baby has little room for maneuver, By the 35th week of pregnancy, a permanent location in the uterus is established and a coup becomes very unlikely.. In the final third of the gestation period it is very important which position the baby is in - right or wrong. On this depends on the choice of tactics of delivery and the likely risk of complications for both the mother and her baby.
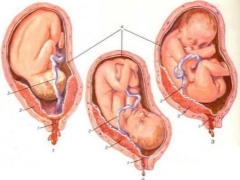
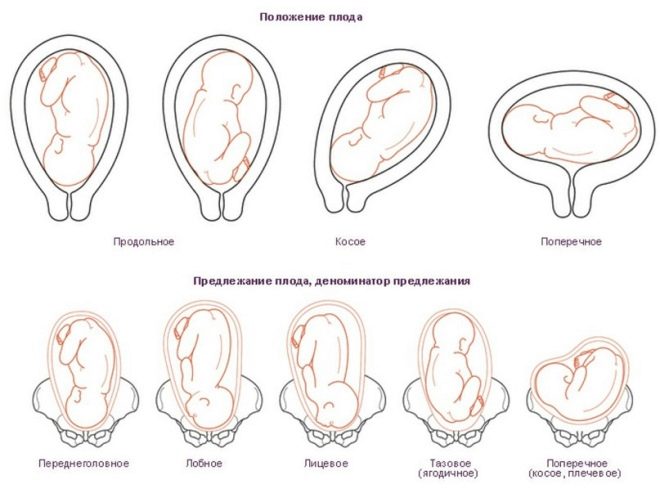
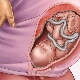
Speaking of presentation, it is important to understand what exactly it is about. Let's try to go broke in terminology. The presentation of the fetus is the ratio of a large part of the fetus to the exit from the uterus cavity to the pelvic area. The baby can be turned to the exit either by the head, or by the buttocks, or be in an oblique position, across the uterus.
The position of the fetus is the ratio of the location of the longitudinal axis of the baby’s body to that of the uterine cavity. The crumb can be located longitudinally, transversely or obliquely. The norm is considered a longitudinal position. The position of the fetus is the ratio of its back to one of the walls of the uterus - left or right. The type of position is the ratio of the back to the back or front wall of the uterus. Chidrenozhennostyu called the ratio of arms, legs, baby head in relation to his own body.
All these parameters determine the position of the baby, and it is necessarily taken into account when deciding how to give birth to a woman - naturally, naturally with stimulation or by caesarean section. This decision can be influenced by a deviation from the norms in any of the listed parameters, but the previa is usually the decisive one.
Kinds
Depending on which part of the body is closest (adjacent) to the exit from the uterus into the small pelvis (and this is the beginning of the baby’s path at birth), there are several types of presentation:
Pelvic
In about 4-6% of pregnant women, the baby is positioned towards the booty or legs. A complete pelvic presentation is a position in the uterus in which the baby is aimed toward the exit of the buttocks. It is also called the buttock. An ankle is considered to be a presentation in which the child's legs “look” towards the exit — one or both. Mixed (combined or incomplete) pelvic presentation is considered to be such a position in which the buttocks and legs are adjacent to the exit.
There is also a knee breech, in which the baby's legs bent at the knee joints are attached to the exit.
Pelvic previa is considered a pathology. It can be very dangerous for both mother and child. The most common is gluteal presentation, with his predictions are more favorable than with the foot, especially with the knee.
The reasons for which the baby takes breech presentation may be different, and not all of them are obvious and understandable to physicians and scientists. It is believed that the head up and booty down most often are children whose mothers suffer from pathologies and abnormalities of the structure of the uterus, appendages, ovaries. Women who have experienced many abortions and surgical curettage of the uterus, women with scarring on the uterus, who often give birth to a lot, are also at risk.
The cause of pelvic presentation may be a chromosomal disorder in the child himself, as well as abnormalities in the structure of his central nervous system - lack of brain, microcephaly or hydrocephalus, violation of the structure and functions of the vestibular apparatus, congenital malformations of the musculoskeletal system. Of the twins, one baby can also take a sitting position, and it is dangerous if this baby is lying first to the exit.
Low water and high water, short umbilical cord, entanglement, preventing crumble, low placenta previa are all additional risk factors.
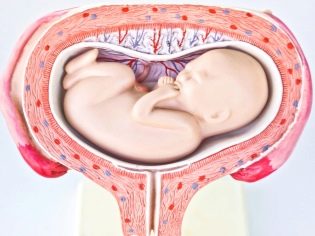
Headache
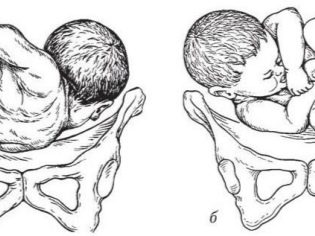
Headache presentation is considered to be correct, provided as nature itself is ideal for the child. When it to the exit in the small pelvis of a woman adjacent baby head. Depending on the position and type of position of the child, there are several types of head presentation. If the crumb is turned to the exit by the nape, then this is an occipital headache presentation. The first to appear is the back of the head. If the baby is located at the exit to the profile, this is a front-heel or temporal presentation.
In this position, childbirth usually proceeds a little more difficult, because this size is wider and it is a little more difficult for the head to move in such a position in a woman’s genital tract.
Frontal previa - the most dangerous. With him, the baby "punches" his way forehead. If the baby is turned to exit with faces, this means that the presentation is called facial, it is the facial structures of the crumbs that will be born first. The occipital variant of head presentation is considered safe for mother and fetus during labor. The remaining species are extensor variants of cephalic presentation, and it is rather difficult to consider them normal. When passing through the birth canal, for example, when the facial presentation, there is a possibility of injury to the cervical vertebrae.
Also headache presentation may be low. They talk about him at the "finish line", when the stomach is "lowered", the baby presses his head against the exit to the small pelvis or partially goes into it too early. Normally, this process takes place in the last month before birth. If the omission of the head occurs earlier, pregnancy and presentation are also considered pathological.
In headache previa, up to 95–33 weeks of gestation, up to 95% of all babies are located.
Transverse
Both the oblique and transverse position of the baby’s body in the uterus, characterized by the absence of the presenting part as such, are considered pathological. Such presentation is rare, only 0.5-0.8% of all pregnancies occur with this complication. The reasons for which the baby can be located across the uterus or at an acute angle to the exit into the pelvis, it is also quite difficult to systematize. They are not always amenable to a reasonable and logical explanation.
Most often, the lateral position of the fetus is characteristic of women whose pregnancy proceeds against the backdrop of polyhydramnios or low water. In the first case, the baby has too much space for movement, in the second its motor capabilities are significantly limited.Often, women who have given birth suffer from overstretching of the ligaments and muscles of the uterus, which do not have sufficient elasticity to fix the position of the fetus even during long periods of pregnancy, the child continues to change the position of the body.
Often transversely located fruit in women with uterine myoma, because the nodes prevent the child from settling down normally. In women with a clinically narrow pelvis, the baby often cannot fix in the correct position.
Diagnostics
Up to 30-32 weeks, the diagnosis of fetal presentation does not make sense. But at this time, an obstetrician-gynecologist can make conclusions about which part of the body the baby adjoins to the exit from the uterus on a routine external examination. Usually, if the baby is in the wrong position in the mother's womb, the height of the uterus floor exceeds the norm (with the pelvic) or lags behind the norm (with transverse presentation).
With the transverse arrangement of the baby, the belly looks asymmetrical, like a rugby ball. Such a position can easily be determined independently, just standing up in full growth in front of a mirror.
A child's heartbeat, in the wrong position, is tapped around the navel of the mother. Palpation in the lower part of the uterus is not determined by a dense rounded head. With pelvic presentation, it is palpable in the area of the uterus, with the transverse - in the right or left side.
The doctor also uses a vaginal examination to clarify the information. An indisputable confirmation of the diagnosis is an ultrasound scan (ultrasound). When it determines not only the exact position, position, presentation, posture, but also the weight of the fetus, height and other parameters necessary for a more careful selection of the mode of delivery.
Possible complications
From complications in childbirth and during the carrying of the child no one is insured, even if the baby is located at first glance correctly. However, the most dangerous are pelvic and transverse presentation.
The main danger of pelvic presentation of the fetus lies in the likelihood of premature birth. This happens in about 30% of pregnancies in which the baby is head-up in the mother’s stomach. Very often such women have a premature rupture of the amniotic fluid, it is of a swift nature, along with the waters often fall out body parts of the baby - leg, handle, umbilical cord loops. All of these complications can lead to serious injury that can make a baby an invalid from birth.
At the onset of labor, women with pelvic prevalence often develop weakness of labor forces, contractions do not bring the desired result - the neck does not open or opens very slowly. In childbirth, there is a risk of the child's head dropping or handles, injuries of the cervical spine, brain and spinal cord, placental abruption, the onset of acute hypoxia, which can lead to the death of the child or total disruption of the nervous system.
For a woman in labor, the pelvic position of the fetus is dangerously severe ruptures of the perineum, uterus, the occurrence of massive bleeding, pelvic injuries.
Quite often, pelvic presentation is combined with entanglement with umbilical cord, fetal hypoxia, pathology of the placenta. Children in pelvic presentation often have less body weight, they are hypotrophic, have metabolic disorders, suffer from congenital heart defects, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys. By the 34th week of pregnancy, if the baby does not accept the correct position, the development rates of some structures of the child’s brain slow down and are disrupted.
If the baby is located longitudinally in the back of the head to the nape of the head, no complications should arise either during pregnancy or during childbirth.Other options for headache presentation can cause difficulties in childbirth, because the head will be more difficult to move along the birth canal, its extension will not happen in the direction of the mother's sacrum, which can lead to hypoxia, weakness of labor forces. In this case, if there are concerns about the life of the child, doctors apply the application of forceps. In itself, it raises many questions, because the number of birth injuries received by children after applying obstetric forceps is very high.
The most unfavorable predictions in frontal presentation. It increases the likelihood of rupture of the uterus, its cervix, the appearance of fistulas, the death of the baby. Almost all types of cephalic presentation can be allowed to natural childbirth, except the frontal. Low headache presentation is fraught with childbirth ahead of time, and this is where its main danger lies.
These genera will not necessarily be complicated or heavy, but the baby’s nervous system may not be able to mature itself to independent life outside the maternal abdomen, as sometimes his lungs do not have time to ripen.
The danger of lateral presentation is that vaginal delivery can hardly be done without severe deviations. If the oblique position of the baby can somehow be tried to be corrected already in the process of childbirth, if it is nevertheless closer to the head one, then the full lateral correction is practically not subject to.
The consequences of such childbirth can be severe trauma to the musculoskeletal system of the baby, his limbs, hip area, spine, as well as the brain and spinal cord. These injuries are rarely in the nature of a dislocation or fracture, usually these are more serious lesions that essentially make the child disabled.
Often, children in cross presentation show chronic hypoxia during pregnancy, prolonged oxygen deprivation leads to irreversible changes in the nervous system and the development of the sense organs - sight, hearing.
How to give birth?
This question is usually solved at 35-36 weeks of pregnancy. By this time, by the standards of physicians, any unstable position of the fetus in the womb becomes stable and permanent. Of course, there are isolated cases when a large fetus literally just a few hours before giving birth changes an abnormal body position to the correct one, but it is at least naive to expect such an outcome. Although the best is recommended to believe and most pregnant, and her doctors.
The choice of tactics of delivery is influenced by many factors. The doctor takes into account the size of the pelvis of the future mother - if, according to ultrasound, the fetus's head is larger than the size of the pelvis, then the woman will most likely be offered a planned caesarean section for any presentation of the fetus. If the fetus is large, then this is the reason for the appointment of a planned cesarean section with pelvic and transverse presentation, and sometimes with the head, it all depends on how much weight the ultrasound diagnostics experts predict.
An immature cervix may also be a reason for prescribing a cesarean section, regardless of presentation. In addition, doctors are trying not to risk and make the operation to women who become pregnant as a result of IVF - their childbirth can give a lot of unpleasant surprises.
With pelvic presentation, vaginal delivery is possible, if the fetus is not large, the birth canal is wide enough, the size of the pelvis allows the pope of the child, and then his head can pass through without hindrance. Natural childbirth is permitted to women with a full buttock presentation, and also sometimes with a mixed presentation. If the child is lightweight, there are signs of hypoxia, entanglement, will not be allowed to give birth.
When the foot previa or knee his variant of the optimal method of delivery is considered to be a cesarean section. It will avoid birth injuries in the child and bleeding from the mother.
In case of a frontal headache presentation, doctors also try to prescribe a cesarean section in order not to risk the life and health of the baby.If one of two babies is in the wrong position during a multiple pregnancy, a cesarean section is also recommended, especially if the baby is sitting or lying across the uterus, which will be born first. With transverse and oblique presentations, they most often try to prescribe a planned cesarean section. Natural childbirth is very dangerous.
Caesarean section in a routine mode is usually carried out at 38-39 weeks of pregnancy, without waiting for the start of spontaneous labor. The central importance in the choice of the method lies with the individual characteristics of the female body, the anatomical features of her baby. There is no universal risk assessment system. There can be so many nuances that only an experienced doctor can take them into account.
About what is the presentation of the fetus, see the following video.