How many vessels should the umbilical cord normally have and what does the presence of a single artery mean?
The umbilical cord has a special diagnostic value during pregnancy. This strong cord reliably binds the fetus and the placenta, providing a continuous connection with the source of food, oxygen. How the umbilical cord is arranged, how many vessels it should have, and what deviations from the norm can mean, we will tell in this article.
Structure and functions
The umbilical cord is a long and very durable organ that is connected at one end to the umbilical opening of the fetus, and the other to the placenta. The length of the umbilical cord - from 50 to 70 centimeters and even more, it is she who allows the baby to move normally in the uterus, to make coups. A shorter umbilical cord complicates the course of pregnancy and is dangerous in the birth process, since its tension at the moment of birth of the baby can cause tearing and detachment of a large part of the placenta before time.
The thickness of the umbilical cord is about 2 centimeters, it is durable and can withstand substantial loads, in its structure resembling durable rubber.
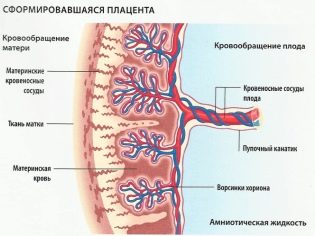
Normally, the umbilical cord has 3 vessels. They are located inside the cord. Umbilical arteries - two. They come from the internal iliac vessels. Two umbilical arteries perform a transport function - the baby’s blood is saturated with carbon dioxide and metabolic products to the placenta. The placenta helps to remove the substances that have become unnecessary into the mother’s blood so that later they leave her body in the traditional way - with urine, then.
Umbilical vein in the structure of the umbilical cord one. Initially, in the early stages of fetal development, they are also two, but one is obliterated later. The task of the umbilical vein is to carry to the baby blood enriched with oxygen, vitamins, and minerals.
Normally, the blood flow through the umbilical cord vessels is balanced — the amount of blood enriched through the vein is equal to the amount of blood flowing through the arteries, which removes metabolic products and carbon dioxide. At the 20th week of pregnancy, the rate of blood flow through them is almost 35 milliliters per minute. As the duration of pregnancy increases, the bloodstream becomes more intense, and by the estimated day of birth, its rate is already 230-240 ml per minute.
Research methods
The study of the structure of the umbilical cord in the early stages of pregnancy is usually not done, because there is no possibility to study its detailed structure before the second trimester. From the 7th week of pregnancy, it is theoretically possible to see the umbilical cord itself, more precisely, to establish the fact of its presence, to determine the place of its attachment, to see signs of pulsation in it (usually this rhythm fully corresponds to the rhythm of the baby’s heartbeat).
Later on the ultrasound, you can install other important details - the length of the umbilical cord, the form of attachment to the placenta, the possible entanglement in the neck. In order to obtain data on the number of vessels and blood flow velocity over them, a so-called Doppler ultrasound (Doppler ultrasound) is done. Even if the umbilical cord entanglement on a conventional ultrasound could not be established, doplerometry will definitely detect it for certain blood flow disorders.
The exact number of vessels in the umbilical cord, vascular resistance index and other important mathematical parameters will be set on the USDG.If there are deviations in the umbilical structure: it is short - less than 30 centimeters, long - more than a meter, not attached to the central part of the placenta, there are fewer vessels in it, the woman will be recommended to undergo an additional examination.
Causes of deviations
The most common abnormality is the only artery in the umbilical cord. This does not mean that the vessel is one. Just one of the two arteries is present. Thus, the diagnosis “the only artery in the umbilical cord” implies that there are two vessels - a vein and one artery. The blood enriched with nutrients moves to the baby through the vein, while the blood contaminated with metabolic products leaves the baby’s body through the artery. In principle, one artery copes with the task, but it experiences significant overloads.
The reason for the abnormal structure of the umbilical cord is often diabetes of the mother, as well as the presence of chronic diseases of the kidneys, heart, liver. Other adverse factors, such as bad habits, infectious diseases, venereal diseases, influenza or ARVI in early pregnancy, as well as the causes of unclear etymology, which cannot be determined, can affect the structure of the umbilical cord.
This anomaly has no symptoms, does not affect the course of pregnancy, and in 95% of cases it allows a woman to quite normally bring her baby to the proper time and give birth to a child. In the singular, the artery may be laid initially, or it may remain the only one as a result of aplasia of the second artery already during the carrying of the baby.
A single artery may be due to a genetic predisposition (the baby’s mom or dad developed during pregnancy with this pathology), and in some cases the presence of a single artery may indicate chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus or congenital malformations of its respiratory system, intestines, heart, or kidneys. .
That is why when a single artery is found instead of two that are normal, doctors examine the baby more closely for possible defects and abnormalities in development and formation - an expert ultrasound is performed and an invasive diagnosis or a non-invasive prenatal DNA test that is capable of fetal blood cells in the bloodstream is recommended mothers determine baby's DNA and possible chromosomal pathologies.
Women with diagnosed polyhydramnios and multiple pregnancies, with severe early toxicosis, pathologies of the placenta, and obesity are at risk for the development of the syndrome of a single umbilical cord artery. If you confirm the presence of a single artery in the umbilical cord, the woman will in no case be advised to terminate the pregnancy, there is no medical indication for this.
If additional studies show that the baby is healthy, the pregnant woman will be monitored normally, although they will have to do an ultrasound scan with a Doppler more often to assess blood flow, and in later periods also CTG to assess the condition of the fetus.
If violations in the single artery are detected (zero diastolic blood flow, retrograde blood flow), an emergency caesarean section will be decided to save the baby from death due to lack of oxygen and nutrients.
What to do?
First of all, pregnant women who, at 20 weeks, heard the verdict “the only umbilical cord artery” at the ultrasound, are recommended to calm down and not exacerbate the situation. Signs of congenital malformations of the fetus or chromosomal abnormalities (Down syndrome, Patau, and others) are only one artery in 1-1.5% of cases of the detection of such a structural umbilical anomaly. In all other cases, the baby is completely healthy. However, it is not worth refusing from additional diagnostics, it needs to be passed in order to know what to do next.
If it is confirmed that the child has defects and chromosomal abnormalities, it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy, but only the woman and her relatives should decide this question. If she wants to leave the baby, the pregnancy will be observed and saved further.
Women with a single umbilical artery and a healthy fetus are advised to visit the doctor more often, and also to take certain safety measures that will prevent the occurrence of an unbearable load on a single vessel. The consequences of the load can be quite significant - it is a delay in fetal development, hypotrophy, low weight, the threat of premature birth due to the developed placental insufficiency, fetal hypoxia.
In the first place, it is dangerous for the future mother and her baby to increase blood pressure. A woman needs to keep a close eye on him, measure it daily, and in case of hypertension, undergo appropriate treatment with drugs approved and recommended by a doctor. In order to avoid sudden pressure surges, it is recommended to limit any stresses, conflicts, experiences, emotional outbursts.
To maintain normal blood flow, the expectant mother is advised to abandon any hard work, especially related to weight lifting and long standing or sitting in one position. Sex and walking should be moderate, gentle, not exhausting.
A woman with a single artery in the structure of the umbilical cord should not smoke, take even small doses of alcohol, and also stay in a stuffy room for a long time - the access of oxygen is extremely necessary for the mother and her baby.
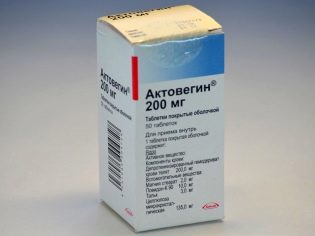
It is recommended to take an additional oxygen cocktails and drugs that improve uteroplacental blood flow ("Curantil" or "Actovegin") In the dosages prescribed by the doctor.
A woman's diet must be rich in vitamins; in addition, it may be necessary to take vitamin complexes so that the baby does not need the nutrients it needs. Otherwise, pregnancy against the background of the umbilical cord’s single artery syndrome is no different from pregnancy with a normal umbilical cord. Reviews of doctors and patients can safely say that there is nothing wrong with this anomaly.
For more information on what the diagnosis of the “Single umbilical cord artery” means, see the following video.