All about fetal heartbeat
Fetal heartbeat is an important marker of its vitality and vital activity. Practically from the very beginning of pregnancy and up to the very moment of childbirth, as well as during the birth process, the rhythm and the beat frequency of the baby's heart can tell a lot to the doctors. In this material we have collected all the fun about the heartbeat of the fetus.
How is the heart formed?
The heart and vessels of the embryo are among the very first. It is on them that a great responsibility lies - to provide the growing body with blood. The very process of forming a heart in a child is very thin, precise and complex. It is surprising that all these processes proceed very quickly, literally within a few weeks. Any negative impact from the outside can interfere with the normal formation, and then later defects are identified.
In order to protect your baby, even when two cherished stripes are found on the test, it is important to do everything possible to eliminate negative factors - smoking, alcohol, taking medications without early permission from the doctor during pregnancy can lead to disruption of the formation of the heart and blood vessels. After 2 weeks after conception, the tiny heart begins to emerge.
But at the very beginning there are only two so-called heart tubes - one of them is to form an unpaired organ that will be responsible for blood circulation. At 3 weeks of gestation, 2 tubules become one, blood begins to flow into it, but is not yet divided into separate streams.
This week, women usually learn about their "interesting position" and are still getting used to the idea that they will soon become mothers. And the child in the womb has already begun the process of complicating the now single heart tube. By the end of 3 weeks of gestation, the heart becomes sigmoid. Its form is still far from familiar to us and so far more resembles a worm or the Latin letter S. But then it already has a first ventricle and primary atrium.
A week later, single chamber heart starts beatingbut these first muscle contractions cannot yet be heard, their sizes are too small. On the 5th week of pregnancy, the heart departments grow, a partition appears, which makes a two-chamber organ from a single-chamber organ. At the 6th week of pregnancy, the heart of the baby acquires three cameras, and by the end of the week it becomes what it should be - four-chamber.
It is believed that the entire process of the formation of the heart of the fetus ends by week 7. From now on, nothing changes in its structure, it only grows and grows, it works and supplies the rest of the organs with the right amount of blood. Doctors closely monitor the state of the baby’s heart throughout pregnancy - the tone, frequency, and rhythm can tell you how your baby is feeling, whether he has signs of hypoxia or malnutrition. This is one of the main diagnostic features.
Listening - timing and ways
At the 5th obstetric week of pregnancy, the baby's heartbeat is determined on an ultrasound scanner.True, provided that the scanner is of good quality, the doctor is highly qualified, and the ultrasound is performed in a transvaginal way. If external ultrasound is done through the abdomen (transabdominal), then the baby's heartbeat can be heard no earlier than 7 weeks of pregnancy.
Despite the fact that the small heart is already listening, it is not yet felt by a woman. Some, even in later periods, cannot feel the heartbeats on their own, if the child is uncomfortable - they turn their chest cells away from the anterior abdominal wall of the mother.
You can hear a baby's heart through a stethoscope at the end of the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. It is this device, which is a wooden tube with an extended end, will be used by the doctor at each scheduled admission in the antenatal clinic.
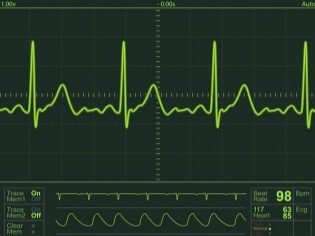
After 29-30 weeks of pregnancy, the CTG method is used additionally. When it records the readings of two sensors at once - one captures the heartbeat, and the second locomotor activity. The same sensors can be used in labor for monitoring the cardiac activity of the born fetus. In the third trimester, a woman can listen to the child's heart with a stethoscope at home alone, but at least something can be heard provided that the mother is not obese, that the baby is located with her chest close to the abdominal wall of the mother.
More informative may be a special device - home fetal monitor. Now such devices are available, any future mother can buy them. They determine the heart rate (heart rate) of the fetus. The listening device is equipped with headphones and a convenient ultrasonic sensor. At any time, according to indications, the doctor may prescribe a duplex scan - Doppler ultrasound (Doppler), which assesses not only the development of the organ, but also the speed and characteristics of blood flow in the heart and blood vessels.
Norms
At different stages of the formation of the baby’s heart, the baby will have different heart rate indicators recorded. And it will be completely normal. Therefore, after an ultrasound scan, the doctor always compares the data with tables that indicate the normal range of heart rate for the current period of gestation. In the earliest terms, the heart of the baby is weak - the heart rate does not exceed 90-115 beats per minute. Most often, at week 5, the baby's heart knocks at a frequency of about 100 beats per minute. We remember that during this period the heart of the baby has not yet acquired four cameras, and reductions are more rare. At week 7, when the body becomes a four-chamber, the heart rate normally ranges from 105 to 130 beats per minute.
On ultrasound examination, which will take place in the period of 8-9 weeks, the child's heart will beat even more often - 130-155 beats per minute, and by 10 weeks - up to 160 cuts per minute. The fastest and most active heart becomes by the 14th week of pregnancy - the heart rate can reach 185 beats. During the rest of the baby’s life, the heart rate from 120 to 175 beats is considered normal, and before giving birth in a week or two, the heart usually knocks with a frequency of 120-160 beats.
HR deviations
Since the speed and intensity of contractions of the heart muscle of a baby is considered an important diagnostic sign, one should know what these or other deviations in values may indicate. If the real heart rate of the fetus exceeds the norm, it is considered a less dangerous condition than slowing the heart rate. Heart palpitations can be regarded as a sign of threatening hypoxia, oxygen starvation at its very initial stage. The heart of the baby begins to beat more often when fasting has already arisen, but has not yet brought serious destructive consequences. When hypoxia is prolonged, uncompensated, a slow heartbeat is fixed.
The heart rate increases with violations of the structure and function of the placenta. So, the baby can respond to placental insufficiency, reduced maternal hemoglobin.In addition, the increased heart rate of children in the womb can respond to a violation of the health of the mother.
Colds, viral infections, insomnia, and severe stress can all cause an increase in the heart rate of the fetus. Elimination of the factor affecting the heart rate usually returns the baby’s heart rate to normal.
If the heart rate is slow, the doctor is more scared, because it can be a sign of a child’s distress at the stage of decompensation, when his small body cannot compensate for the lack of something (oxygen, nutrition). Some severe congenital malformations are accompanied by delayed heart rate, it can also be a sign of hemostasis disorders in a woman or her child. When abnormalities are detected, it is important to understand how permanent they are.
If the deceleration is temporary and quickly recovers to normal, then the reaction of the crumbs to the fact that the mother was in the supine position for a long time (the uterus of the uterus, in particular, the vena cava), could appear. Such a deviation is not dangerous. In any case, when establishing regular deviations of the heart rate from the norms, an additional examination will be shown to the woman to determine the causes that could lead to the deterioration of the fetus.
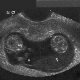
What else can be found in the heart for an ultrasound?
In all that concerns the heart and its health, future mothers are very tremulous and vulnerable. And without special medical knowledge, it is completely obvious that without a healthy heart, the full existence of a child is impossible. That is why pregnant women and their relatives very often painfully perceive complex medical terms that may sound during the next ultrasound examination.
7% of expectant mothers, according to existing statistics, hear from the doctor the wording "hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle. " Nothing terrible is said. This is called the area of the heart muscle, which gives increased "echo", that is, it looks most clearly on the monitor of the ultrasonic apparatus. It is believed that this is due to the deposition of calcium salts in the heart muscle, or due to the presence of an extra chord in the heart. Neither one nor the other state is considered pathological, does not need any treatment and does not affect the health of the child in general and his heart in particular.
Only occasionally hyperfocus is a sign of anomaly. We are talking about chromosomal pathologies, such as Down's syndrome, Turner, Patau, etc. But in this case hyperfocus will not be the only sign of illness in the baby - other characteristic markers that are established on prenatal screenings will also be positive. If the screening does not reveal a high risk of chromosomal abnormalities, if (except for hyperfocus) there is nothing suspicious, they say about an isolated GEF, which is considered a variant of the norm. There is no reason to worry.
Often, expectant mothers care about how heart defects are determined. The current level of development of medicine makes it possible to establish in the baby most types of congenital defects even during pregnancy. Hypoplasia of the left or right ventricle, aortic stenosis, anomalies of the connection of the pulmonary veins, septum are not difficult to diagnose. Forecasts are individual and largely depend on the type of vice, its severity.
Early detection helps doctors plan the treatment of the crumbs from the first minutes of his independent life - many heart operations today can be done almost immediately after birth.
HR and child sex
Many believe that the nature and heart rate of the baby can determine its floor. Scientists could not find differences in the heart rate of boys and girls, gynecologists repeatedly told that there is no connection between the sex of the child and his heartbeat. However, women continue to be interested in how to establish the sex of the heart rate, as evidenced by women's forums on the Internet.
For example, the folk method ascribes more frequent heartbeats to girls than boys.In practice, everything is not so clear. At the time of heart rate measurement, the mother could worry, and therefore the heart of the baby could beat more often, the woman could get sick, feel bad, suffer from toxicosis. The baby himself could sleep or be awake, which would also affect the speed of his heartbeat.
Those who sincerely believe that the hearts of little girls are beating deafly, confusedly, are mistaken. So the hearts of children with malformations, severe uncompensated hypoxia are beating, in healthy boys and girls the heart should beat rhythmically and clearly, and the floor has nothing to do with it. Those who are interested in how accurate is the method of determining sex from the heartbeat of the fetus should know that the accuracy does not exceed 50%. In other words, Regardless of the specific values of the heart rate, there is either a boy or a girl in the womb. Chances are equal.
To find out the sex of the child, it is better to use other, more reliable ways. After 12-13 weeks on the ultrasound, the baby's sex is set with an accuracy of 75%, after 18 weeks the accuracy rises to 90-93%. After 9 weeks of gestation, a non-invasive DNA test can be done, which, up to 97%, will answer the question of what gender should be expected, and whether or not he has a chromosomal abnormality. On sale today you can find the so-called gender tests for home use. They offer to establish the sex of the child by rapid analysis of urine. Such tests are quite expensive, and you may be disappointed, because their accuracy is low.
About what the ultrasound specialist sees when looking at the fetal heartbeat, see below.