Retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy
Every third pregnant woman encounters a retrochorial hematoma on her own experience. This is one of the most common early pathologies of pregnancy. Whether this condition is dangerous, why it develops, whether it is necessary to treat the hematoma, will be discussed in this article.
What it is?
Retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy is an insidious and dangerous pathology, which can have very sad consequences for mother and child. A hematoma is a hemorrhage, a bruise. To understand where and how this bruise is formed during pregnancy, you need to understand how a fertilized egg is attached to the uterus.
8-10 days after ovulation, the fertilized egg after a long journey through the fallopian tube enters the uterine cavity. Her task is to implant, to consolidate. Special enzymes that produce fetal membranes help literally dissolve the epithelial layer of the uterus, infiltrate and grow tightly into it.
The place of attachment of the chorion is a tight vascular connection between the fetal egg and the embryo growing in it and the wall of the uterus, which becomes looser before implantation under the action of the hormone progesterone. The vascular grid provides the germ with nutrition, access of oxygen with maternal blood.
The chorion subsequently changes and becomes a young placenta. But this happens only by the 12-14 week of pregnancy. Until the end of the first trimester, the placenta does not exist as such, there is only the chorion - its predecessor.
Any, even slight detachment of the ovum from the wall of the uterus causes ruptures of blood vessels from the vascular network. From the damaged blood vessels flows and accumulates between the fetal egg and the uterine wall. This is a hematoma.
Since we are talking about the chorion, the hematoma is called retrochorial. In this way, pathology occurs only in early pregnancy. If detachment occurs later, when the placenta is formed, the hematoma is called retroplacental.
The danger of such detachment is that the hematoma itself will not pass. If there is no way out for accumulated blood, the hematoma will increase, all new chorionic areas will be involved in the detachment until the fertilized egg loses its connection with the uterine wall over a large area or does not move away from it at all. For an embryo, discharge means death, because it will no longer receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen. In the pregnant woman's body, the chorion, damaged and deprived of blood supply, will no longer produce the hormone necessary for carrying the baby, hCG, and this will lead to a spontaneous miscarriage in the early period.
The mechanisms of hematoma are not completely clear to modern medicine, but statistics exist, and it is far from comforting: about 35-40% of pregnant women are diagnosed with retrochorial hematoma.
This does not mean that all pregnancies end in miscarriage, since the presence of such a hematoma does not necessarily lead to the cessation of fetal life.
Causes
The causes can be very different, and it is far from always possible to find the true cause of a woman, because doctors tend to believe that several negative factors are usually “guilty” of hematoma formation. The most likely of them are several reasons.
- Hormonal disruptions. If the pregnancy occurred against the background of insufficient progesterone levels, if the woman has other hormonal pathologies, thyroid gland dysfunction, then it is very likely that in the very early stages of pregnancy the endometrium of the uterus will not be ideally ready for implantation. The risk of developing partial or complete detachment increases. Hormonal causes - one of the most common, they accompany miscarriages in the early stages in about 15% of pregnant women.
- Stress. Violation of the close relationship between the chorion and the endometrium of the uterus can occur due to severe stress, feelings, emotional distress, since the stress hormones produced by this block the production of female sex hormones. In addition, stress causes fluctuations in blood pressure levels, and detachment may occur due to them.
- Early toxicosis. If the toxicosis appeared early, and it is very strong, the woman's functioning of all organs and systems, including the cardiovascular, nervous, endocrine, is disturbed. Due to complex disorders associated with changes in the composition of the blood, its viscosity, detachment may occur.
- Bad habits. Smoking and alcoholic beverages, if a woman continues to use them during pregnancy, adversely affect the condition of the blood vessels and pressure. Chorion detachment at an early period in this case is associated precisely with the fragility and vulnerability of the blood vessels, which is characteristic of all women who smoke and drink.
- Gynecological diseases and burdened history. Quite often, the detachment of the chorion from the uterine wall occurs in women who, even before pregnancy, had problems with reproductive health - uterine myoma, endometriosis, often had abortions or postoperative scars on the uterus.
- Autoimmune processes. It is relatively rare, but it happens that a woman’s immunity cannot be reconstructed for pregnancy in any way and produces specific antibodies to her own cells and germ cells. Then rejection occurs by the action of immune processes. This is the most difficult reason, which is difficult to correct.
- Fetal pathology. For a short time, a woman may still not be aware of chromosomal or structural anomalies existing in a child, but nature already knows this, the fetal egg is sometimes rejected due to the impossibility of further development of the fetus. It is usually not possible to stop such detachment.
- External negative impacts. Work on harmful production, with paints, varnishes, toxic substances, can affect a woman’s body. Dangerous and household chemicals, and radioactive radiation. And also increased risks are created by vibration, shaking, strong physical exertion, and jumping.
In addition, medication may be used to affect the integrity of the contact between the chorion and the uterine wall without the doctor's permission, chronic heart disease, kidney, liver and urinary system. Sometimes the cause of detachment is not obvious, and it is almost impossible to establish it.
Symptoms
Most often the retrochorial hematoma is manifested by aching pains in the lower abdomen and lower back (as in menstruation), unusual secretions from the genital tract. The secretions have blood impurities and can be bloody, pink, succinic, orange and others. The abundance of the discharge depends on the degree of detachment and the size of the hematoma, as well as the presence of a flow of blood from the damaged vessels into the vagina.
If the hematoma is closed, there is no way out, the pathology proceeds without secretions, but with aching and drawing pains. The presence of red blood on the daily pads suggests that the detachment has just begun, the blood has not dried yet, it is fresh. Brown discharge suggests that the detachment occurred earlier, and now began the process of release of dried blood and resorption of hematoma.
Brown discharge is considered the most favorable sign.The more abundant they are, the better the predictions - the hematoma resolves, the detachment stops.
If the scarlet secretions continue, and the pain becomes stronger, it is likely that the detachment of the ovum from the uterus wall continues. At the same time, pain intensifies, they become cramping, permanent. Due to changes in the hormonal background, a woman begins to experience great anxiety, anxiety and even fear. Palpitations become more frequent, and blood pressure decreases. A woman begins to feel strong weakness, malaise.
If the chorion is located in the bottom of the uterus (in the highest and widest part of it), then the symptoms may be absent. And the future mother can find out about the probable detachment only during the passage of the next ultrasound scan or when it is too late to do something - if the fertilized egg is completely exfoliated, and a miscarriage begins.
Retrochorial hematoma is considered one of the main causes of the risk of miscarriage in the initial stages of pregnancy. This is bad news. But there is a good - up to 95% of all cases of such detachment of the chorion ends quite safely - pregnancy can be saved, the child grows and develops further, this incident does not affect his condition later.
Diagnostics
There is no great difficulty in determining the retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy. If there are symptoms, a preliminary diagnosis is established on the basis of clinical signs, if there are no symptoms, the hematoma can only be detected by ultrasound scanning. The doctor will send an ultrasound scan in any case, if he has even the slightest suspicion of chorionic detachment.
Risk group - women who previously suffered from chorionic or placental detachment, bearing twins or triplets, mothers of many children, whose uterine walls have already lost their natural elasticity, women with a history of complications, and who became pregnant after a long period of infertility alone or through IVF.
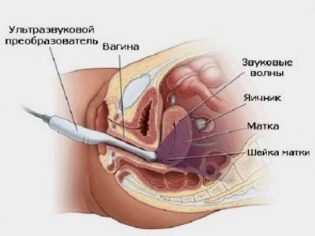
Ultrasound is performed intravaginally, this allows not only to assess the presence or absence of a hematoma, to determine its exact location and size, but also to examine the cervix, to assess the condition of the internal os. If the detachment is large, and the pharynx opens slightly, they say about the miscarriage that has begun, but if the fragments of the ovum have already begun to leave the uterine cavity, they say that the miscarriage has taken place.
In case of retrochorial hematoma, the cavity filled with blood is defined as a darkened echogenic area, the fetal egg itself may have an irregular shape, be deformed.
To clarify the condition of the woman is recommended to pass a general and biochemical blood tests, blood for progesterone, urinalysis. The size of the detachment will be a decisive factor in the choice of treatment tactics.
How to treat?
If the doctor offers hospitalization, you should not refuse her - the detachment is a serious matter, and you are offered to go to the hospital only in case of a rather serious detachment. A small hematoma may well be treated at home.
A pregnant woman will be sent to the hospital if she has a severe pain syndrome, bright red blood is secreted from the genital tract, blood pressure is reduced, and there is a general worsening of the condition. And also women are sent to the hospital, in which the hematoma is quite large, and the blood has no way out (no discharge).
The accumulation of blood between the chorion and the uterus in an amount of more than 20 milliliters is considered dangerous. For small pink or brown discharge, a woman may well be allowed to be treated at home.
The main task of treatment is the resorption of hematoma. In order for the smooth muscles of the uterus not to come in tone and thus not increase the detachment, they are prescribed antispasmodic drugs: “No-shpa, Papaverine. To improve blood circulation, common systemic drugs are used. "Actovegin"," Curantil ", and to stop bleeding in the event of its increase - hemostatic agents, for example," Ditsinon "," Vikasol. "
If detachment occurs on the background of hormonal deficiency, progesterone drugs are prescribed - “Utrogestan”, “Duphaston” and others in an individual dosage, which the doctor selects on the basis of a blood test for hormonal profile. Particular attention is paid to vitamins, they are shown to all pregnant women with the threat of miscarriage. To eliminate the symptoms of stress and uterine tone, “Magne B 6” is recommended.
Iron products are recommended for women to eliminate the symptoms of anemia, if any, as well as to prevent anemia, which can increase and exacerbate the detachment. A woman, even with a small retrochorial hematoma, is recommended bed rest or semi-bed rest, in the supine position it is best to place a cushion under the waist.
Not recommended products that thin the blood. The ban, in particular, applies to cabbage, peas and other legumes.
A woman is not recommended to have sex, masturbate, lift weights, bend down, abruptly change body position, drive in a car on uneven roads.
But you should also avoid visiting baths and saunas, do not swim in the hot tub. Hygiene procedures should be limited to a warm shower, any overheating of the body threatens to result in the development of uterine bleeding and loss of pregnancy.
It is important to avoid constipation, because excessive attempts at defecation can lead to undesirable consequences. If the constipation did happen, you should find out from your doctor what kind of mild laxative you can use in early pregnancy.
If you do not follow the recommendations, it is possible that a miscarriage does happen. It is also possible that, even with a preserved pregnancy, placental abruption may occur later in life, and this is the most dangerous.
Reviews
According to numerous reviews that future mothers have left on the pages of thematic forums on the Internet, the most often signs of retrochorial hematoma appear as obvious symptoms in the period of 6-7 and 9-11 weeks. Hidden retrochorial hematoma is most often detected during the period of the first mandatory screening - at 12-13 weeks of pregnancy.
According to women, it takes from two weeks to one and a half months for treatment. Usually, at the end of the course, re-ultrasound shows either a decrease in retrochorial hematoma, or its complete disappearance. In some cases, the visual signs of hematoma residues persist for quite a long time, they should not frighten the future mother.
Women emphasize that in almost all cases of pregnancy loss due to extensive detachment of the ovum, the visit to the doctor was late.
The experience of a girl who has faced such a serious problem during pregnancy will be very useful for all the fair sex who are planning to become a mother.