Breast growth and soreness in her early pregnancy
Many women reasonably believe that chest pains are peculiar to pregnant women even at the earliest periods, when the “interesting position” is still impossible to determine with tests. But the mammary glands do not always hurt and not at all, although for most people this statement can be considered true. In this material, we will consider in detail why the mammary glands grow in early pregnancy, as well as why pain is observed and how to reduce it.
Breast growth and pain - causes
Pain in the chest in the language of doctors is called mastalgia. This is not an independent disease, but only a description of the symptom. With it, the breast increases in size, swells, the touch to it becomes painful, the nipples become hypersensitive and can cause discomfort to the woman. By itself, mastalgia can accompany various pathologies, as well as be natural. In women with physiological mastalgia, the chest usually begins to hurt before menstruation.
Before the delay of menstruation, about 60% of women report growth and painful changes in the state of the mammary glands, and 95% of pregnant women notice the appearance of such a symptom during the first trimester.
The glandular tissue of the female mammary glands is very sensitive to changes in hormonal levels. Before menstruation, there is a decrease in the production of progesterone and an increase in the production of estrogen, because of this, the increased sensitivity of the glands, characteristic of the second phase of the menstrual cycle, is replaced by a softening of the breast. Many people notice that the breast becomes soft the day before menstruation or the first day after the start of menstruation.
If conception took place, the level of progesterone does not decrease at the end of the second phase of the cycle, on the contrary, it begins to be produced more. This is facilitated by the attachment of the embryo in the uterus, because immediately after implantation, the chorionic gonadotropic hormone begins to be produced, its task is to stimulate the formation of progesterone in the maternal organism. Against the background of insufficient levels of progesterone, gestation is interrupted, fetal vital activity is impossible.
The structural unit of the mammary glands, not having received the hormonal command "hang up", under the influence of progesterone begins to grow. It produces new alveoli. Outside of pregnancy, the ducts remain closed, but at the earliest terms of the “interesting position” the number of the so-called “milk tubes” tends to increase, the network of ducts expands, and the breast looks filled. So nature prepares the future mother for the breastfeeding coming after the birth.
The pain also occurs by chance. The growth of any organ is accompanied by excessive irritation of the nerve endings. How intense the pain will be depends on the individual sensitivity threshold.
A well-coordinated “team” is responsible for preparing the mammary glands for lactation - the pituitary gland, already 2 weeks after the onset of pregnancy (that is, from the moment of fertilization under the condition of implantation) begins to increase the amount of prolactin produced. Already a week after the start of the delay, its concentration in the blood plasma of a pregnant woman exceeds the standard values by 4 times.
Progesterone stimulates the growth of glandular tissue, an increase in the lobules of the mammary gland, and also triggers the development of a prototype of breast milk - colostrum. For women who become pregnant for the first time, colostrum can appear only before or after childbirth, and for multiparous women, whose ducts are already dilated, colostrum can begin to be allocated as early as 10-12 days after conception.
The hormone estrogen helps progesterone, because of his chest "poured", the formation of new alveoli - also his "merit".
Breast changes as a sign of pregnancy
Many women consider breast enlargement and tenderness to be the first sign of pregnancy even before the delay, but this is not always true. We already know that the natural menstrual cycle every month is accompanied by changes in the female breast, and therefore sensitivity and pain can be a sign of premenstrual syndrome. Paradoxically, but a fact - many pregnant women noted that the sensations in the breast during the “pregnant” cycle are unusual.
If a woman has always experienced nipple tension, increased sensitivity and some increase in glands in size before menstruation, then after conception the breast remained soft and painless until around the middle of the first trimester. If the woman usually did not complain of mastalgia before her menstruation, it was in the “happy” cycle before the start of the delay that her breasts began to ache and increased markedly.
Changes in the breast alone cannot be considered a reliable sign of pregnancy. More accurate clinical data are needed: elevated levels of hCG in the blood, in the urine, delayed menstruation, and, finally, determination of the ovum in the uterus by ultrasound.
However, many women, especially those who had previously given birth, and therefore more experienced ones, start to guess about pregnancy in terms of sensations in the breast even before tests and tests show pregnancy.
Darkening and Venous Mesh
In the first trimester of pregnancy, areoles (areola circles) may increase in diameter by 30-50%, the venous mesh may appear on the chest. This is due to the peculiarities of blood circulation during the preparation for lactation. The first periods are considered the time of the most intensive growth of the mammary glands. The next such period comes after 34 weeks of pregnancy, when the preparation for breastfeeding goes to the "finish line".
Growing breasts require more intensive blood supply, and therefore the number of blood vessels in it increases. The bloodstream becomes stronger, because of this, a bluish venous reticulum may appear on the body of the mammary glands. The areoles darken and expand under the action of pregnancy hormones and as a result of increased blood circulation. Because of the same factors, the breasts become hot, which is why pregnant women are advised to measure body temperature, after separating the breasts from the thermometer with a towel or thick diaper, otherwise the thermometer readings will be too high.
Itching and stretching
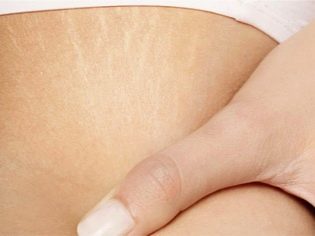
Many women note that the breast in the early stages is itchy and sore. We have already dealt with the cause of the pain, it is time to talk about itching. Itching is associated with stretching the layers of the skin, because only glandular tissue grows, and the skin remains the same. Nature has provided a certain stretching mechanism and elasticity reserve for the skin of the mammary glands. But this process is accompanied by unpleasant sensations.
Striae (stretch marks) are formed during micro-breaks, which are then filled with connective tissue. Women with small breast sizes are most susceptible to stretching if, after conception, the mammary glands have increased by 2-3 sizes.
Stretch marks rarely appear in the first trimester, but sometimes it happens.Striae most often begin to appear after 34 weeks of pregnancy, when the second stage of rapid growth and swelling of the breast “starts”.
Unusual changes
There are no uniform standards by which the breasts should change after the onset of pregnancy, much depends on the individual characteristics, physique, hormonal levels, the number of previous pregnancies and childbirth. But women are actively discussing situations that are difficult to understand right away - sometimes the mammary glands behave strangely.
Such oddities include a dramatic change in the state of the breast of a pregnant woman. If yesterday she grew up, hurt and scratched, and today she stopped hurting, was “blown away”, became soft and painless, you should visit your gynecologist and be examined for missed abortion. If for some reason the fetus ceases to develop in the womb, the hormonal background changes rapidly: progesterone is declining, the estrogens are increasing, the amount of prolactin begins to decrease. All this hinders the process of growth and expansion of the ducts and lobules, which leads to the disappearance of the previously present symptoms.
The sudden appearance of unpleasant symptoms, if they were not there or they were moderate, is also a reason for a visit to the doctor, because hormonal “jumps” are not excluded, which may pose a threat to carrying the child.
Breast of a nursing mother during a new pregnancy
The onset of pregnancy shortly after birth is quite common. Usually this pregnancy is not planned. A woman will unwittingly face the question of whether the second child can be breastfed during the second pregnancy.
A woman can feed the firstborn, it does not affect the state of the developing new pregnancy. It is clear that an increase in ducts and lobes of the mammary gland in the early period in this situation proceeds almost imperceptibly, because the ducts of the nursing mother have already been expanded.
The firstborn, however, may refuse the “treat”, because the taste of mother’s milk changes under the influence of progesterone. If this does not happen, the woman needs to be morally prepared for the fact that feeding can be more painful, because the sensitivity of the nipples will also be increased.
It is recommended to stop breastfeeding only if a woman has previously had a miscarriage, if during a pregnancy the doctor finds a threat of spontaneous abortion, and also if the expectant mother is obese. Breastfeeding increases the level of oxytocin, and this hormone has a reducing effect on the uterine muscles.
If the pregnancy occurred during the breastfeeding period, you should definitely consult with the obstetrician-gynecologist, who will answer whether a particular woman can continue to feed the first child during the childbearing period or whether it should now be transferred to infant formula for the safe development of the second baby.
How to reduce pain?
It is possible to reduce the pain caused by physiological changes in the breast. To tolerate unpleasant manifestations of breast growth is not necessary. To alleviate the condition, a pregnant woman should do special gymnastics, wear a comfortable bra that will tightly embrace the glands and support them from the bottom, and also apply some means for local application.
In case of severe pain, early release of colostrum, a woman should wash her breasts several times a day with cool water, the temperature of which does not exceed 35 degrees. Daily hygiene with the use of children's hypoallergenic soap will not only reduce pain, but also prevent infection through nipples with bacterial and fungal infections.
Special gymnastics, which helps to slightly reduce the swelling of the breasts in early pregnancy, is based on exercises that promote lymph flow and strengthen the lateral muscles.You can find out how to do this kind of gymnastics with the attending gynecologist. He will definitely show these exercises or ban them if the woman has contraindications.
At the beginning of pregnancy you should take care of the right bra: it should be made of natural materials, have wide and comfortable straps and supporting cups. If colostrum is released and there is a risk of staining the blouse or tank top, you need to use the busts for nursing mothers - they are sold in any clothing store for pregnant and nursing. These bras have special pockets for absorbent hygienic chest pads.
If there is an increased sensitivity of the nipples, which causes pain, doctors advise not to remove the bra, even at night, in order to prevent the chest from touching the bed. This will allow you to sleep more calmly and get enough sleep.
With strong itching, you can use a cream for stretch marks, "Bepatenten" or baby cream, which should be applied with light massaging movements. They will not get rid of stretch marks, but they will reduce some discomfort.
It is not recommended to take painkillers for mastalgia.
Are changes reversible?
A woman who has just embarked on the path of carrying a fetus can be rejoiced: the pain and hypersensitivity of the mammary glands in most women become significantly weaker already by the 7-8 week of pregnancy. After 12 weeks, they, as a rule, disappear and can return to one degree or another only at the very end of pregnancy, before childbirth.
Stretch marks (stretch marks) are considered lifelong, over time they turn pale and become less noticeable.
Increasing the size of the areola should not be frightening: the ear circles are reduced after giving birth, gradually becoming the same size and appearance. Unfortunately, many women’s breasts do not remain after giving birth the size it was when carrying a child. And after the end of breastfeeding, it returns to almost the same size.
Enlarged ducts inside the breast can remain for many years after the end of breastfeeding. Outwardly, this will not manifest in any way and will become noticeable only with the onset of another pregnancy, when colostrum will appear earlier and less intense pain associated with dilatation will be observed.
The following video is waiting for you advice of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia on the preparation of the mammary glands for pregnancy.