Ultrasound in the second trimester of pregnancy: the timing and standards
Mid-pregnancy is the most beautiful time. The future mother is still not tired of her “interesting position”, but has already managed to enjoy the baby’s waiting period. It is during this period that the second planned survey, which is called second-trimester screening, falls. It includes ultrasound diagnostics and blood biochemical analysis. The fact that the baby can show on ultrasound at this time and how to decipher the examination protocol will be described in this material.
Why do you need it?
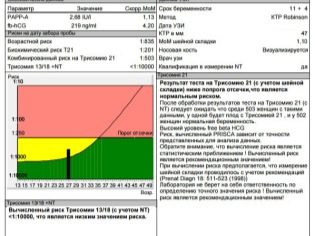
Ultrasound examination in the second trimester is part of the screening, the task of which is to identify the increased risks of having a baby with genetic and other pathologies and anomalies. By order of the Ministry of Health of Russia, studies that are conducted in the first and second trimester, are considered mandatory. Women pass them for free in consultations at the place of residence
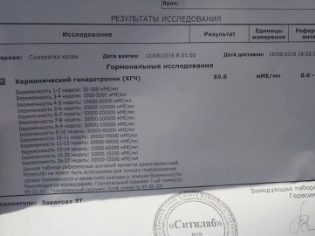
The indicators that the doctor receives ultrasound diagnosis, using a special computer program are processed together with the results of the blood test, which determines the hormones and proteins, the level of which can talk about possible pathologies in the child and problems of gestation.
In the first trimester, the content of hCG and PAPP-A is established in the blood, in the second, the so-called triple test is carried out - hCG, estriol, alpha-fetoprotein.
The program “brings together” the data obtained from two sources, analyzes individual risks - the age of the woman, the presence of bad habits and chronic diseases, the facts of the presence of genetic pathologies in the families of the future mother and father and gives a result that indicates how likely this woman is Down's syndrome, Edwards, Patau and other incurable and even fatal pathologies
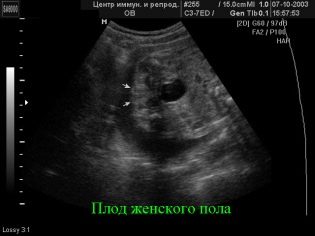
Screening the first trimester, which runs from week 10 to week 13, considered the most informative. The second study provides much less information on genetic pathology markers, but it allows the expectant mother to see her fairly grown up baby on the ultrasound scanner monitor, find out how the baby develops, and also specify the sex of the baby. It is in the second trimester that sex on an ultrasound is the easiest to determine.
The child is not yet so big as to contract into a lump and thereby close the view of intimate places, but not so small as to not see the genitals that have formed.
Special features
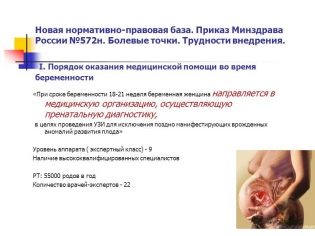
The timing of the second planned ultrasound is not as tight as in the case of the first screening study. The Ministry of Health recommended to conduct an examination in the period from 18 to 21 weeks. In practice, these terms can be shifted both up and down.Often, a pregnant woman is screened for a period of 16–17 weeks, and periods of 10–24 weeks are also quite common and popular with obstetricians and gynecologists.
Not so long ago, the second planned ultrasound scan could not have been sent if the first screening showed results that did not cause concern to the attending physician. The second ultrasound scan was mandatory for women at risk - pregnant after the age of 35, women who already had children with genetic pathologies, and some other categories of expectant mothers. Now the second survey is carried out to all, without exception, therefore you should not worry if the doctor gives the direction to the second screening examination.
Ultrasound in the second trimester is carried out in order to identify:
the number of children (it happens that during the first examination the second fetus is not visible and opens to the doctor’s view only on the second examination);
the position of the crumbs in the uterus, its supposed weight, height;
the size of the limbs, head, abdomen of the baby separately (the development of each part of the body is of great importance for determining the proportions and characteristics of the development of the baby);
heart rate of the child and the structure of his heart;
structural features of the facial bones, chest, spine;
structural features of all important internal organs - kidneys, liver, lungs, brain);
the amount of amniotic fluid (waters surrounding the child);
degree of maturity, thickness and location of the placenta;
condition of the cervical canal, cervix, the presence or absence of uterine wall tone.
If the sex of the crumbs is not yet known, or the parents have doubts about the results of the first ultrasound, now is the time to ask the doctor the interesting question of who “lives in a tum” - a boy or a girl. But you should be aware that the standard examination protocol does not include the child’s gender, therefore the doctor has the right to refuse this request or you will have to pay for this service. Many consultations officially included the determination of the gender of the baby in the list of paid services.
The procedure of ultrasound examination is carried out by transabdominal method - through the abdominal wall. However, in some cases, the doctor uses the transvaginal method. The vaginal sensor makes it easier to get a clearer picture of the child, if the mother has excess weight, a dense fatty layer on the stomach, which makes it difficult to visualize through the peritoneum. Sometimes both methods of research are used at once.
Diagnosis lasts about 10 minutes, it is painless and completely safe for both women and her baby.
Preparation for the study
If before the first ultrasound the woman was recommended to prepare - to empty the intestines before visiting the doctor's office, including from the accumulated gases, then before the second planned ultrasound, no specific preparation is required. If even in the intestine there are accumulations of gases, then the results of the ultrasound examination will not have any impact at all. Grown in size, the uterus draws intestinal loops into the background.
Filling the bladder is also not necessary.
You can eat everything before the examination, but just before you go into the ultrasound room, a woman can eat a small chocolate bar. The tiny person inside her will quickly respond to the sweet and begin to move more actively, which will allow the doctor to evaluate also the motor functions of the baby and better consider it in different projections.
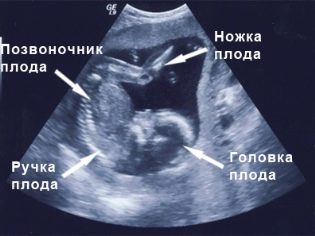
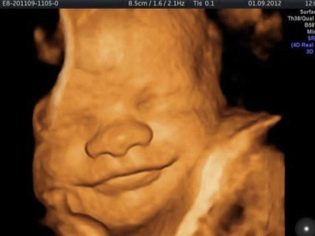
In agreement with the diagnostician for the second ultrasound, you can take with you and the father of the unborn child. On the monitor of the scanner it is waiting for something rather interesting, because now the fruit is clearly visible, you can admire its profile, see the arms and legs, fingers, nose, mouth, eye sockets, genitals. If the ultrasound is done in 3D-format, then future parents will even be able to see who the toddler looks like.
After the procedure, the woman is given a test protocol in which she finds a lot of abbreviations and numerical values.Not every doctor in the consultation has the opportunity in the process of diagnosis to tell each expectant mother, which means a particular indicator, what he says. Therefore, to understand the pile of numbers and letters will have on their own. We will help with this.
Decoding results
By the second trimester, the woman had already learned very well that there is a period she calculates herself (from the moment of conception), and there is a generally accepted obstetric term - it is customary to calculate it from the first day of the last menstruation. Doctors of ultrasound diagnostics, as well as obstetricians and gynecologists use obstetric terms, therefore all data on the compliance of parameters with certain terms are indicated in the calculation (conception day + approximately 2 weeks).
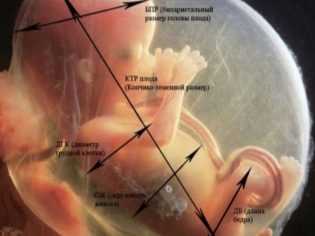
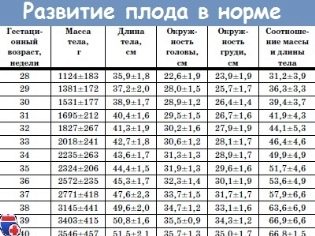
Fetometric indicators of the fetus, which look at the ultrasound and describe in the protocol include the following.
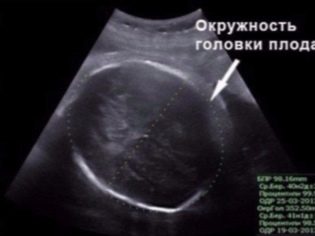
BPR (biparient size)
This is the distance between the two parietal bones. This indicator is considered the most informative in determining the exact duration of pregnancy in the second trimester. If it does not meet the deadline, it may be a symptom of the delayed development of the crumbs.
LZR (frontal-occipital size)
This distance is a segment between the two bones of the skull - the frontal and occipital. This indicator in itself is never evaluated and says nothing. It is considered only in conjunction with the BPR described above. Together, these dimensions indicate gestational age.
Table of BPR and LZR in the second trimester:
Obstetric term | BPR is the norm mm | BPR- permissible fluctuations mm | LZR norm, mm | LZR - allowable vibrations, mm |
16 weeks | 34 | 31-37 | 45 | 41-49 |
17 weeks | 38 | 34-42 | 50 | 46-54 |
18 weeks | 42 | 37-47 | 54 | 49-59 |
19 weeks | 45 | 41-69 | 58 | 53-63 |
20 weeks | 48 | 43-53 | 62 | 56-68 |
21 weeks | 51 | 46-56 | 66 | 60-72 |
22 weeks | 54 | 48-60 | 70 | 64-76 |
23 weeks | 58 | 52-64 | 74 | 67-81 |
24 weeks | 61 | 55-67 | 78 | 71-85 |
25 weeks | 64 | 58-70 | 81 | 73-89 |
26 weeks | 67 | 61-73 | 85 | 77-93 |
27 weeks | 70 | 64-76 | 88 | 80-96 |
28 weeks | 73 | 67-79 | 91 | 83-99 |
If the size of the head differs slightly from the norm of the indicators slightly, then this may be due to the constitutional features of the fetus - mom and dad may be owners of small skulls. However, if BPR or LZR is significantly lagging behind (more than 2 weeks from the actual period), the doctor may have questions about the development of the child - whether there is a developmental delay, whether the baby has enough nutrients and vitamins.
The decrease in these indicators is often in pregnant women who, during the carrying of the baby, could not say goodbye to bad habits (alcohol, smoking), as well as during pregnancy with twins or triplets. The ratio of BDP to the rest of the fetus is important. If the head is reduced proportionally and other dimensions also do not reach the lowest threshold of the norm, then we can talk about both the constitutional peculiarity (thin child) and the symmetrical retardation of development.
If the other parameters are normal and only the head is reduced, additional examinations will be scheduled, including ultrasound ultrasound in dynamics, in order to exclude brain pathologies, microcephaly and other abnormalities.
Exceeding the upper threshold of the normative values, if it is symmetrical to the rest of the baby’s size, may indicate an error in the calculation of the period, for example, due to late ovulation, a tendency towards a large fetus. Asymmetric increase in the head of the baby needs a separate examination, because it can talk about brain edema, about other disorders of the central nervous system, which caused swelling of the brain.
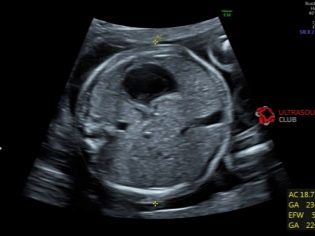
OG (head circumference) and coolant (abdominal circumference)
The size denoting head circumference is important for assessing a child’s development. The term of gestation on this parameter is not separately calculated, the OG is considered in relation to the BPR and LZR (mainly for understanding the head proportions). The head of the baby grows most actively in the second trimester, and therefore this size is changing rapidly.
Exhaust gas table - second trimester (average norms and tolerances):
Obstetric term (week) | Exhaust gas - normal, mm | Lower limit of normal, mm | Upper limit of normal, mm |
16 | 124 | 112 | 136 |
17 | 135 | 121 | 149 |
18 | 146 | 131 | 161 |
19 | 158 | 142 | 174 |
20 | 170 | 154 | 186 |
21 | 183 | 166 | 200 |
22 | 195 | 178 | 212 |
23 | 207 | 190 | 224 |
24 | 219 | 201 | 237 |
25 | 232 | 214 | 250 |
26 | 243 | 224 | 262 |
27 | 254 | 235 | 273 |
28 | 265 | 245 | 285 |
Exceeding the norm of exhaust gas for 2 weeks or more will require additional examination, as it may indicate hydrocephalus. A slight excess may be due to an error in the calculation of the obstetric period. Reducing the exhaust gas below the permissible rate of more than 2 weeks indicates intrauterine growth retardation, if other parameters of the child’s body are reduced.
If only the head is less than the norm, the child will be examined for pathologies of the development of the brain and the central nervous system.
Abdominal circumference - an important parameter that helps the doctor to clarify the condition of the child in case of suspected developmental delay. Most often in the second trimester there is such a form of delay, in which the proportions of the baby are not symmetrical. In other words, not all measurements speak of decreasing. In this case, lagging standards are compared with the abdominal circumference in order to understand whether there is a pathological lag, or thinness and small height - a hereditary sign of a particular child.
Second trimester coolant table:
Obstetric term (weeks) | Coolant, mm |
16 | 102 |
17 | 112 |
18 | 124 |
19 | 134 |
20 | 144 |
21 | 157 |
22 | 169 |
23 | 181 |
24 | 193 |
25 | 206 |
26 | 217 |
27 | 229 |
28 | 241 |
Slight lag behind the mean not considered pathological, close attention of doctors deserves a situation where the girth of the tummy crumbs behind the norm by more than 2 weeks. In this case, the parameter is compared with BPR, OG, LZR, as well as with the length of the baby’s limbs, and the umbilical cord and placenta are examined to exclude oxygen starvation and insufficient nutrition of the child.
The deviation of this parameter alone, if all the others correspond to the gestational period, does not mean anything alarming, just babies grow spasmodically and unevenly in the second trimester.
It is possible that after a couple of weeks on an extraordinary ultrasound (and he will be appointed to double-check the data), the “normal” will be indicated in the column OJ.
Bone length
In the ultrasound protocol, these dimensions indicate the following: DBK (femur length), DKG (tibia bone length), DKP (forearm bone length), WPC (humerus length), DTC (nasal bone length). All of these bones are paired, so the protocol will indicate double numeric values, for example, DBK - 17 left, 17 right
The length of the limbs in the second trimester is a marker of genetic disorders. For example, many incurable syndromes (Patau, Cornelia de Lange and others) have shortened limbs. Although to judge the norms and deviations so uniquely no one, of course, will not. Suspicions must be supported by the negative results of the first screening, as well as biochemical blood tests.
Often, deviations in the length of paired bones are observed in girls, because they develop at a different pace, and in most cases have more miniature parameters than boys, and the tables used by doctors to verify ultrasound data are compiled without gender.
DBK (thigh length) in the second trimester:
Obstetric term, weeks | DBK - average rate, mm | Lower limit of normal, mm | Upper limit of normal, mm |
16 | 20 | 17 | 23 |
17 | 24 | 20 | 28 |
18 | 27 | 23 | 31 |
19 | 30 | 26 | 34 |
20 | 33 | 29 | 37 |
21 | 36 | 32 | 40 |
22 | 39 | 35 | 43 |
23 | 41 | 37 | 45 |
24 | 44 | 40 | 48 |
25 | 46 | 42 | 50 |
26 | 49 | 45 | 53 |
27 | 51 | 47 | 55 |
28 | 53 | 49 | 57 |
DKG (length of the bones of the leg) in the second trimester:
Obstetric term, weeks | DKG - normal, mm | Lower threshold of normal, mm | Upper threshold of normal, mm |
16 | 18 | 15 | 21 |
17 | 21 | 17 | 25 |
18 | 24 | 20 | 28 |
19 | 27 | 23 | 31 |
20 | 30 | 26 | 34 |
21 | 33 | 29 | 37 |
22 | 35 | 31 | 39 |
23 | 38 | 34 | 42 |
24 | 40 | 36 | 44 |
25 | 42 | 38 | 46 |
26 | 45 | 41 | 49 |
27 | 47 | 43 | 51 |
28 | 49 | 45 | 53 |
The duodenum (humerus length) and DKP (forearm bone length) in the second trimester:
Obstetric term, weeks | Humerus - normal, mm | Allowable vibrations, mm | Forearm bone - normal, mm | Allowable vibrations, mm |
16 | 18 | 15-21 | 15 | 12-18 |
17 | 21 | 17-25 | 18 | 15-21 |
18 | 24 | 20-28 | 20 | 17-23 |
19 | 27 | 23-31 | 23 | 20-26 |
20 | 30 | 26-34 | 26 | 22-29 |
21 | 33 | 29-37 | 28 | 24-32 |
22 | 35 | 31-39 | 30 | 26-34 |
23 | 38 | 34-42 | 33 | 29-37 |
24 | 40 | 36-44 | 35 | 31-39 |
25 | 43 | 39-47 | 37 | 33-41 |
26 | 45 | 41-49 | 39 | 35-43 |
27 | 47 | 43-51 | 41 | 37-45 |
28 | 49 | 45-53 | 43 | 39-47 |
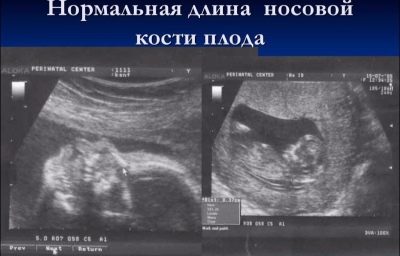
The length of the nasal bone in the second trimester is not as important as during the passage of the first screening. It can no longer be considered a marker indicating a possible Down syndrome in a child. By mid-pregnancy, the baby’s nose has the size and proportions that are inherent in it by nature, and this size is individual. In some consultations, doctors on the second ultrasound they don't even measure the nasal bones, but simply indicate in the protocol that these bones are visualized or write that the bones of the nose are normal.
Nevertheless, future mothers who have numbers in the ultrasound protocols in the “Nasal bones” column will be interested to know how “nosy” their child will be.
The average size of the nasal bones of the fetus in the second trimester:
Obstetric period, weeks (periods) | Nose bone length - mean values | Lower limit of normal, mm | Upper limit of normal, mm |
16-17 weeks | 5,4 | 3,6 | 7,2 |
18-19 weeks | 6,6 | 5,2 | 8,0 |
20-21 weeks | 7,0 | 5,7 | 8,3 |
22-23 weeks | 7,6 | 6,0 | 9,2 |
24-25 weeks | 8,5 | 6,9 | 10,1 |
26-27 weeks | 9,4 | 7,5 | 11,3 |
28-29 weeks | 10,9 | 8,4 | 13,4 |
Internal organs, face and brain
If there are no gross malformations in the baby, the diagnosticians do not go too far into the description of the internal organs of the crumbs. In the received protocol, the future mother will be able to see a simple list: the kidneys are the norm, the heart has 4 cameras and so on.
If pathologies are noticed, the type of anomaly detected will be indicated in the corresponding column, for example, a cyst or underdevelopment formation.
Assessing the state of the brain, diagnosticians note the size of the lobes, their outlines, the structure of the ventricles, the size of the cerebellum. Facial bones on 5 months pregnant well-formed, and the doctor can easily examine the orbits, measure them, make sure that the baby has normally developed upper and lower jaws, as well as note, if any, crevices - the so-called “wolf's mouth” and the cleft lip.
When examining the spine, the doctor will assess his general condition, examine him for possible clefts. In the diagnosis of the lungs, the doctor will note the degree of their maturity, in the second trimester, it is normally the third
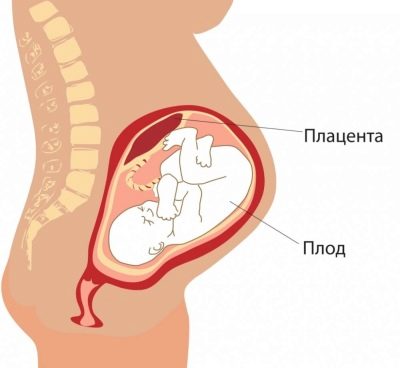
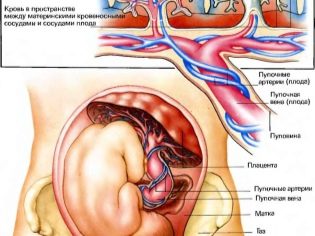
Placenta
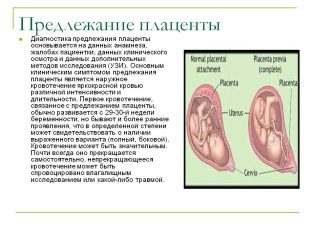
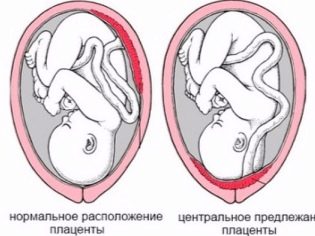
Of particular importance is the location of the "children's place". The most common location is on the back wall, although the front deployment is not considered an anomaly. The location of this temporary organ feeding the baby affects the choice of tactics of childbirth. For example, a low location or location along the anterior wall of the uterus may be a prerequisite for the appointment of a planned cesarean section.
A low placentation is established when the “baby seat” is located below 5.5 centimeters from the internal pharynx, but if this temporary organ overlaps the pharynx, in conclusion indicate that there is a placenta previa. This should by no means cause panic in a pregnant woman, because as the uterus grows, the placenta can rise higher, and often this happens closer to the end of the child's pregnancy and is confirmed by an ultrasound examination in the third trimester.
In addition to the location, the doctor identifies the thickness of the “children's place” and the degree of its maturity. A normal thickness for mid-pregnancy is 4.5 cm. If the placenta turns out to be thicker, an additional examination is prescribed, since such an increase in the temporary organ may indicate pathological processes, for example, the development of the mother’s and the fetus rhesus conflict, as well as some genetic disorders. , intrauterine infections.
The degree of maturity of the placenta in the second trimester should be zero. If the doctor assesses it as the first, it can be a question of premature aging of the “children's place”, the loss of some of its functions and potential danger to the child. This also changes the thickness - the placenta becomes thinner, usually with early aging in the middle of pregnancy, its thickness is estimated at 2 centimeters or less.
Up to 30 weeks, the placenta should ideally have a zero degree of maturity. From about week 27 she can become the first, and from 34 the second. By birth, this body "grows old" to the third degree.
Amniotic fluid (water)
Transparency, the presence or absence of suspension, as well as the amount of water surrounding the child inside the fetal bladder, has great diagnostic value. The protocol of ultrasound indicates the index of amniotic fluid, which gives an idea of whether the amount of water is normal. Polyhydramnios and water scarcity may indicate that the baby has pathologies, an infection has occurred.These conditions necessarily require medical supervision, supportive treatment and the choice of the correct tactics for the delivery.
Average rates of amniotic fluid index (IAG) in the second trimester:
Obstetric term, weeks | Norm IAG, mm | Allowable vibrations, mm |
16 | 121 | 73-201 |
17 | 127 | 77-211 |
18 | 133 | 80-220 |
19 | 137 | 83-225 |
20 | 141 | 86-230 |
21 | 143 | 88-233 |
22 | 145 | 89-235 |
23 | 146 | 90-237 |
24 | 147 | 90-238 |
25 | 147 | 89-240 |
26 | 147 | 89-242 |
27 | 156 | 85-245 |
28 | 146 | 86 -249 |
Umbilical cord
The study of the umbilical cord gives an idea of how the baby is provided with oxygen and nutrients, in addition, the pathology of the structure of the connecting "cord" may indicate possible genetic pathologies in the child.
Usually normal a healthy umbilical cord has 3 vessels, two of which are arteries and one - a vein. It is for them that an exchange takes place between a woman and a child. Mom supplies the baby with nutrition and oxygen, and the baby “sends” the waste products of metabolism that are eliminated through the mother’s body.
An insufficient number of vessels may indicate a possible development of a Down syndrome in a child, but is not a mandatory marker. Sometimes the absence of one artery in the umbilical cord is compensated by the work of another artery, and the child is born healthy, albeit with a reduced weight.
The presence of just one vessel is a sign of fetal abnormalities, and detailed genetic research and invasive diagnosis are required here.
In conclusion, an ultrasound scan, the expectant mother will thus see the number of umbilical cord vessels found by the doctor, as well as a note that the blood flow through them is normal (or there is a decrease in its speed).
Uterus
Doctors on an ultrasound scan are interested in whether a pregnant woman has a threat of interruption or premature birth. Therefore, he assesses the presence or absence of uterine wall tone. If a woman used to undergo a cesarean section or other operations on the reproductive organ, be sure to evaluate consistency postoperative scar.
If everything is in order with him, then the ultrasound protocol indicates that the scar has no features, and also indicates the thickness of the scar tissue. Features include niches, thinning of the scar, creating the risk of uterine rupture and death of the fetus and mother.
In addition, the cervix, the state of the cervical canal, is described. This indicates whether there is a threat of miscarriage or premature birth.
Final part
The final part of the protocol indicates whether the fetometry data correspond to the obstetric period. The size of the fruit allows using several formulas to calculate its estimated weight. The actual weight may differ from this value with a sufficiently large error. Weight is calculated by the program installed in the ultrasound scanner. If in your consultation the equipment of the old sample is installed, there may not be such an item in the protocol.
Fetal weight (average values) in the second trimester:
16-17 weeks - 50-75 grams.
18-19 weeks - 160-250 grams.
20-21 weeks - 215-320 gr.
22-23 week - 410-490 gr.
24-25 week - 580-690 gr.
26-27 week - 800-910 gr.
28 week 980-1000 gr.
Common Questions
After IVF
For women who become pregnant with IVF, ultrasound diagnosis is performed more often, so in the second trimester they are not waiting for the second, but the fourth or fifth ultrasound. With regard to such future mothers, they are trying to conduct research more thoroughly, in their conclusion there will be information that is not included in the standard procedure - determination of blood flow velocity in the uterine and placental vessels. It is important to understand whether the baby is feeling well "from a test tube."
In pregnancy, twins (triple)
In this case, the ultrasound of the second screening involves a detailed description of each of the fruits. Do not be afraid of the fact that the parameters of the kids will be different, because two or three little men can not develop according to one scheme, despite the fact that they are bred by one mother.
Inability to determine gender
If the doctor on the second ultrasound could not tell the parents of the future baby’s parents, this does not mean that the study was conducted poorly. This is rare, but it is possible that the baby at the time of the survey just took an uncomfortable position for review or turned his back to the sensor.
In this case, the specialist cannot guarantee an accurate result.