Ultrasound in the 21st week of pregnancy: fetal size and other features
The first half of the pregnancy was left behind. Week 21 opens the second half of this interesting and challenging period, filled with hopes and new feelings. At this time, a study can be scheduled as part of the second screening.
Purpose of the survey
The second prenatal screening, or rather, one of its components - an ultrasound examination, is conducted on any day between 18 and 21 weeks of gestation. Laboratory blood tests for hormones and proteins, the so-called triple test, are given earlier - from 16 to 20 weeks. Thus, at week 21, all pregnant women who have not had time to pass this examination in the previous three weeks will be sent for an ultrasound scan.
Purpose of the study - identify the risks of possible genetic abnormalities in the fetus. Ultrasound diagnosis in this process has a special role, its results significantly affect the overall conclusion.
In addition, the expectant mother may visit the ultrasound room at week 21 for other reasons. The appearance of pain syndrome, abnormal discharge for the period, suckling, signs of inflammation, the emergence of a threat to save pregnancy - all this is the basis for an urgent unscheduled diagnosis of the mother and fetus. The obstetrician-gynecologist may recommend an ultrasound if the height of the uterus does not correspond to the obstetric period, if the woman complains that she suddenly stopped feeling fetal movement, although they used to be.
Sometimes there is a need to clarify the timing of pregnancy and determine the date of the upcoming birth.
Preparation and features
At this time, the ultrasound procedure is transabdominal: the sensor is located on top of the abdomen, the uterus and the child are viewed through the anterior abdominal wall. The specialist can use the vaginal sensor only if visibility through the abdomen is difficult due to the excess weight of the pregnant woman, obesity, as well as in cases where it is necessary to examine the cervix and cervical canal to assess the possible threat of abortion at this time.
This ultrasound does not require specific training from a woman, there is no need to fill the bladdersince the amount of amniotic fluid is sufficient for good visualization, and intestinal gases, which had to be fought before ultrasound scanning in the first trimester, can in no way affect the result of the examination, because the uterus has grown, and it cannot be squeezed by the swollen intestines.
What can be seen on the ultrasound?
The baby grew up and “took shape”: his height was already close to 25 centimeters from the heels to the crown, and his weight exceeded 350 grams. The smallest kids in this period have a height of about 18 centimeters. A toddler with such parameters can be clearly seen on any scanner, even if this equipment does not belong to the category of modern innovative technology. 21 weeks by obstetric standards - about 19 weeks from the moment of conception. The child has learned a lot during this time and is ready to demonstrate a lot to his mother and doctor, who will watch him through the ultrasound sensor for several minutes.
Scarce perfectly mastered a variety of mimic grimaces, it will be especially good if 3D ultrasound is done. He sucks cams, plays with the umbilical cord. At this period, hair begins to grow on the baby’s head, the work of the digestive system is becoming. On the day the pussy swallows about half a liter of amniotic fluid.
At week 21, the baby learns to distinguish between tastes, since taste buds appear on his tongue at this time. The arms and legs are moving somewhat erratically so far, and on ultrasound it is easy to see, coordination of movements is the task of the near future. The child hears various sounds, during the procedure he may react to the unfamiliar voice of the doctor, to the measured buzz of the apparatus, by increasing the physical activity.
Week 21 is a great time to find out the sex of a baby. If, before this, the doctor spoke about the gender of the baby hesitantly, or did not succeed in examining the genitals, it is now the secret may become apparent. In the uterus is still quite free, and the baby is constantly changing position in space.
It is possible that it is during the ultrasound that the baby will unfold so that its external genital organs will be available for examination.
Decryption and norms
The conclusion of the doctor about the ultrasound scan always begins with determining the number of children. For each of them, the specialist sets the criteria for viability - the baby must have a heartbeat and physical activity. The specialist also sets the type of the child's position in the uterus - head, pelvic or transverse.
However bye woman should not be upset by either pelvic or transverse presentation, because before the birth still a long time, the baby moves constantly, and its position will change many times.
Fetal photometry
The obstetricians have a special relationship to the photometric data - the size of individual parts of the child’s body allows one to get an idea of how proportionately it is complex, whether it is growing and developing correctly. These data are already familiar to a woman's reduction - BPR, LZR, OG and coolant:
- The bipariental size is a visual segment drawn between the two temporal bones of the head,
- Frontal-occipital size - longitudinal section from frontal bone to occipital.
- Head circumference and abdominal circumference - two additional parameters that allow to judge the development of the child.
The length of paired bones - femur, tibia, forearm and shoulder - are important signs of the successful growth of the crumbs, as well as markers of possible chromosomal abnormalities.
The table of average norms of fetometric indicators at week 20-21 is as follows:
Obstetric term | BPR, mm | LZR, mm | OG, mm | Coolant, mm |
20-21 weeks | 48-51; possible fluctuations from 45 to 56 mm | 62-66; possible fluctuations from 57 to 72 mm | 170-183 | 144-157 |
The table of norms for the length of paired bones at week 21 is as follows:
Obstetric term | Thigh length (DBK), mm | Shin Length (DKG), mm | Forearm length (DKP), mm | Shoulder length (WPC), mm |
20-21 weeks | 33-36; possible fluctuations from 29 to 40 mm | 30-33; possible fluctuations from 26 to 37 mm | 26-28; possible fluctuations from 22 to 32 mm | 30-33; possible fluctuations from 26 to 37 mm |
The inter-hemispheric size of the baby's cerebellum at this time is close to 21-23 mm. Estimated weight of the crumbs is already in the range of 350-420 grams.
Anatomical features of the fetus
All internal organs of the child are fully formed. Most of them are functioning in a streamlined mode, some are just starting to work. An ultrasound examines the cerebral hemispheres, the presence and features, if any, of the lungs, organs of the urinary system - the bladder and kidneys. The heart must have 4 cameras, beat rhythmically, smoothly. Since the gastrointestinal tract begins to work actively at week 21, The doctor carefully examines the stomach, intestines, gallbladder. Spine and bones of the face and skull are evaluated.
If no visible defects are detected, the doctor does not go into details of the description of each organ examined and indicates that they are all normal and have no features. If a defect is found, the doctor describes in detail the type of pathology, the decision on additional diagnosis and possible treatment.
In this case, all decisions will be taken by an obstetrician and a pediatrician together.
Placenta, uterus, amniotic fluid
This week is considered normal zero degree of maturity of the placenta. This means that this temporary body, which is entrusted with important responsibilities - to provide the child with everything necessary, is young enough and successfully copes with its main task. If the doctor claims that the placenta is low, you should not worry, because the uterus has yet to grow, and together with the stretching uterine walls can "migrate" and "baby seat".
However, low placentation leaves its mark on the future life of the expectant mother - she needs to treat her pregnancy more carefully and attentively, take care of yourself, do not lift weights, do not make sudden movements, take vitamins and, more often than other pregnant women, visit your doctor so that the control is constant. Amniotic fluid at week 21 should be clean, clear, not containing suspended matter. Their normal amount at this time is 143-214 mm.
The uterine walls should not be in a tonus, the cervix should not undergo changes, the cervical canal normally tightly closed.
Possible problems
There are several problems that can be identified on ultrasound at this time.
Fetometric data is different from the real term
A slight deviation of the individual size of the baby from the average norms may not speak about the pathologies of the fetus. The reason may be heredity: the small growth of the parents is likely to be passed on to the child, and therefore it is not worth expecting from him a great length of bones. If the head of the mother or father is large, then the same can be the child, and therefore the parameters of the head for ultrasound will be somewhat ahead of the regulatory data.
Anxiety is considered such a deviation at which the deadline for the tables is “shifted” by 2 or more weeks. If at 21 weeks the size of the head (BPD and LZR) is barely enough to reach 18-19 weeks, this is the basis for the appointment of additional diagnostics, since there may be many reasons for this - microcephaly, developmental defects, genetic pathologies, oxygen starvation, malnutrition of the fetus, developmental lag.
An increase in size of 2 weeks or more may also indicate possible problems in the future, but other sizes should also be assessed. If the increase is proportional, and other parameters are also ahead of the standards, then we can talk about the tendency to the birth of a large or giant child. If only certain parts of the body are enlarged, a detailed examination of the causes of this phenomenon is required.
In case of pronounced asymmetry of the child’s body parts, invasive diagnosis can be prescribed - amniocentesis or cordocentesiswhich, with a probability of 99.9%, will answer the question of whether the child has gross malformations.
Low water or high water
A small amount of water at 21 weeks, as well as too many of them, can also be a sign of possible malformations. Some of the incurable chromosomal syndromes are indeed accompanied by lack of water or abundant water, but most often the causes are rooted in other pathologies of pregnancy - inflammation of the urogenital system, infectious diseases, Rhesus conflict, and so on.
Any deviation of the amount of water from the norm is a threat primarily to the safety of the child, therefore It is not necessary to leave the revealed violations to the mercy of fate.
Only with medical assistance can you bring the child and in some cases even give birth to a child naturally, without a cesarean section.
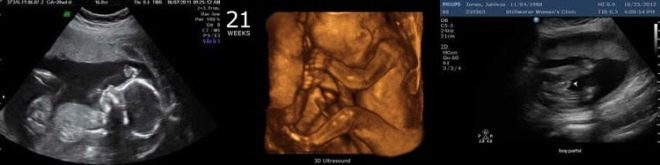
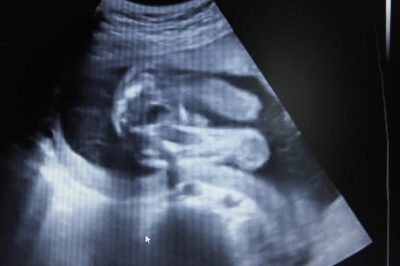
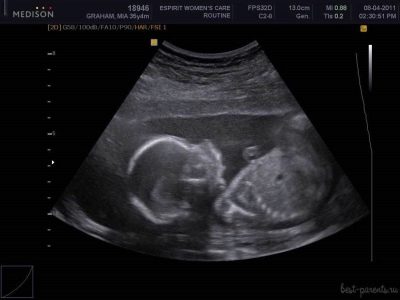
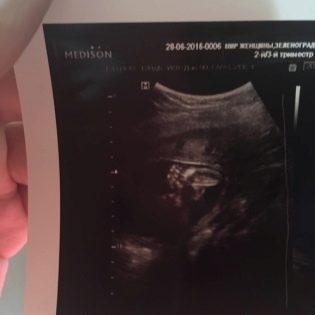
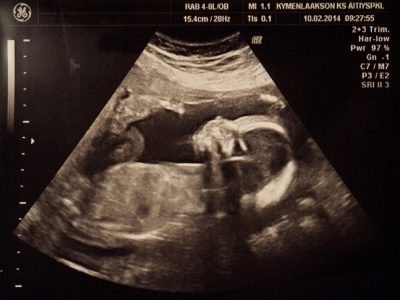
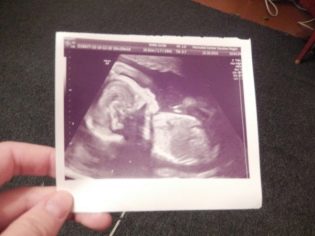
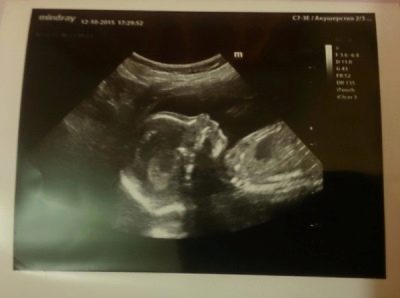
Snapshots
The ultrasound images at 21 weeks show the profile of the baby, the shape of the nose, jaw, forehead. The outlines of the spine, costal arcs, and extremities are no less noticeable. The sex of the child, if the doctor manages to choose a good angle, you can already see almost without a doubt.
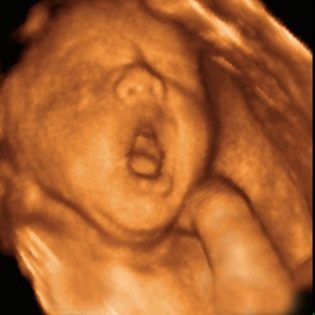
On three-dimensional photographs, the baby can be captured with an interesting grimace, on such a first “photo” the baby’s facial features are already visible, and parents can understand what their son or daughter looks like. The accuracy of sex determination and ultrasound diagnostics at this time is from 85 to 90%.
You will learn more about ultrasound in the 21st week of pregnancy, fetal size and other features from the following video.