At what time do the third ultrasound during pregnancy and on what rates of indicators to focus?
In the last trimester of pregnancy, the expectant mother will have a third planned examination, which will include screening ultrasound. This procedure is important not only to ensure that doctors can make sure that the child and the woman are all right. This is also a great opportunity to look at the baby, because now he is very big and he can do a lot. That is the third ultrasound, we will discuss in this article.
Dates
Ultrasound in the third trimester is part of third screening, which in addition to this includes fetal cardiotocography (CTG) and USDG (doplerometry). Biochemical analysis of blood for most pregnant women is no longer required, but in some cases it is also performed. If in the first and in the second trimester, it was the results of the tests that were of particular importance, then at the end of the baby's term in the first place, the data obtained as a result of ultrasound diagnostics come to the fore.
The third routine ultrasound is usually tried to be assigned for the period from 30 to 36 obstetric week. The best is considered a study for a period of 32-34 weeks. For many, this ultrasound will not be the third, but the fifth or sixth, it all depends on how many similar examinations a woman has undergone in the first two trimesters. An ultrasound scan is not considered mandatory, and the Ministry of Health only recommends it, but if a woman does not want to undergo an examination, then no one has the right to force her.
Purpose and indications
The third ultrasound has several important goals:
- fetal development evaluation;
- assessment of the state of the placenta;
- assessment of maternal organism readiness for the upcoming delivery;
- choice of tactics of delivery.
Since ultrasound in the third trimester is not mandatory, and it requires the consent of the woman, doctors try to clarify for what indications should not abandon the ultrasound and doplerometrii during this period.
The first survey is necessary for:
- future moms expecting twins or triplets;
- women who have had abnormalities or deviations from the normal course of pregnancy at earlier stages;
- pregnant women with severe obstetric history (in the past there were miscarriages, a large number of abortions, missed pregnancies, premature birth);
- pregnant women who have previously had children with congenital genetic abnormalities;
- women carrying a large child, as well as women whose children previously “showed” an ultrasound “showed” some developmental lag from normal values;
- pregnant women who have previously been diagnosed with low or insufficient placentation, lack of water or high water, and pelvic or transverse presentation of the fetus;
- pregnant women over 35 years old.
The reason for refusing to undergo ultrasound is sometimes the unwillingness of the woman to cause the child anxiety and harm. The ultrasound procedure is harmless to the child, especially since it is already big and strong.
Preparation and method of examination
Ultrasound examination in the last third of the gestation period is carried out transabdominal - through the anterior abdominal wall. There is no need to fill the bladder, the baby is beautifully visualized in the grown uterus. There is also no need to take drugs to reduce gas formation.. Even if such a delicate problem torments a woman (and this is not at all uncommon in late pregnancy!), Then the swollen intestine cannot affect the quality of the ultrasound scan, it does not squeeze the pelvic organs.
The procedure lasts about 5-10 minutes, it does not cause any special inconvenience and pain. It becomes very difficult for some future moms to stay in a horizontal position on their backs as this big baby pinches the abdominal artery, puts pressure on the spine and kidneys of the mother. The third ultrasound is done only in this position, so for a few minutes the woman will have to suffer.
What will the ultrasound show?
On the third scheduled ultrasound, the doctor examines the placenta with special attention, because the condition depends on her condition on how comfortable the baby will be in the womb in the last weeks before birth. No less carefully studied the state of the cervical canal, cervix, umbilical cord, the number and transparency of amniotic fluid. If earlier the woman had surgery on the uterus, including cesarean section, the diagnostician will carefully examine the condition of the postoperative scar.
After 30 weeks on the ultrasound, you can well consider the child - his arms and legs, count the fingers on them. The doctor will measure the growth of the baby, the length of his limbs, the parameters of the head, using a special computer program built into the ultrasound scanner, or using formulas, to calculate the estimated weight of the fetus.
The position of the baby in the uterus on the third ultrasound will determine the further tactics of pregnancy and childbirth. If the ultrasound shows that the child is sitting or is in a transverse position, then a planned cesarean section can be offered to the woman, although the baby still has time to turn in the correct position.
To clarify the floor of the baby on the third scheduled ultrasound does not make much sense, because no matter how the child is located in the uterus, he is already big enough, he has to take "compact" poses, stretching his legs and arms. Such poses make it difficult to inspect the genitals, and the probability of medical error in predicting the sex of a baby increases tenfold.
But the ultrasound doctor will be able to examine the internal organs of the fetus - heart, kidneys, lungs, stomach and intestines, as well as explore the structures and contours of the brain parts of the child.
Interpretation of results and norms
With the ultrasound in the antenatal clinic, the reception is carried out on a first-come, first-served basis, and the doctor doesn’t have much time for stories and explanations for the future mother about what he sees on the monitor of the ultrasound scanner. Most likely, the woman in the first two trimesters has already managed to get acquainted with the basic terminology of the doctors, and the ultrasound protocol of the study, which she will be given on her hands, will not be a big mystery to her. But if the writing is incomprehensible, but I really want to know how the child is developing, I will have to get acquainted with the basic concepts and standards.
On the third ultrasound, as in the second, the fetometric data of the child are measured: bipariented, frontal-occipital dimensions, head circumference, chest, abdomen, and the length of paired bones (arms, legs). The first in the protocol will be indicated precisely these parameters that characterize the growth rate of the baby and may indicate its expected weight at the time of the study.
Bipariented size (BDP) in the third trimester
This size, which shows the distance between the parietal bones of the skull, is important for adjusting the date of birth, but only in combination with the other dimensions, since in the final trimester of pregnancy, BDP itself is no longer used to specify the duration of pregnancy,as it was during the second ultrasound in the middle of the term of carrying the baby. But the size from temple to temple can be an informative criterion for the development of a child.
Obstetric term | BPR - norm (mm) | BPR - valid values for the term (mm) |
30 week | 76 | 70-82 |
31 weeks | 78 | 71-85 |
32 week | 80 | 73-87 |
33 week | 82 | 75-89 |
34 week | 84 | 77-91 |
35 week | 86 | 79-93 |
36 week | 88 | 81-95 |
37 week | 90 | 83-97 |
38 week | 92 | 85-98 |
39 week | 94 | 86-100 |
40 week | 95 | 88-102 |
Separately, this head size cannot talk about anything, since it is customary to estimate it only in conjunction with other sizes. This gives an idea not only about the size of the baby, but also the proportionality of his physique.
If the value of BPR lags behind the averaged standards by no more than a week and a half, then pathology is most likely not in question. Perhaps the child inherited the shape of a small head from one of the parents. This version is confirmed by the fact that all other sizes of the baby are normal. If BPR lags behind the norm by more than two weeks, the doctor may suspect intrauterine growth retardation. At a later date, this may occur due to malnutrition, if the placenta quickly ages, during hypoxia, if present, during cord entanglement. Brain pathologies, such as microcephaly, are not excluded.
If the fetal BFR significantly exceeds the upper limit of the age norm, then doctors may suspect a large fetus, this version is confirmed by the increased size of the tummy, the sternum, and sometimes the limbs. If more than one standard head, and the remaining parameters are normal or slightly behind it, suspicion may fall on hydrocephalus - dropsy of the brain.
Frontal-head size of the fetus
This is the size measured perpendicular to the BPR. This segment connects the occipital and frontal bones. Together with the biparient size, this parameter gives a more accurate idea of what shape and size the baby has. This is important for the diagnosis of certain pathologies, including genetic ones, as well as developmental delays.
Obstetric gestational age (full weeks) | The average rate of LZR, mm | Valid values, mm |
30 | 97 | 89-105 |
31 | 101 | 93-109 |
32 | 104 | 95-113 |
33 | 107 | 98-116 |
34 | 110 | 101-119 |
35 | 112 | 103-121 |
36 | 114 | 104-124 |
37 | 116 | 106-126 |
38 | 118 | 108-128 |
39 | 119 | 109-129 |
40 | 120 | 110-130 |
If the third screening ultrasound showed a decrease in the size of the segment from the frontal bone to the back of the head of the baby for more than 2 weeks, then these figures are compared with the BPR and other parameters. Usually LZR decreases not by itself, but together with the bipariate size. If the rest of the measurements are normal, then we can talk about asymmetric developmental delay, about microcephaly. A slight deviation from the norm is characteristic of girls. (they are more miniature), as well as children whose parents themselves have small skulls.
Excessive LZR significantly higher than the permissible upper limit may indicate edema, hydrocephalus, and pathologies of the central nervous system.
If the other parameters of the baby are also impressive, then the doctor makes a conclusion - a large fetus, in this case, the woman can recommend giving birth by caesarean section.
Head diameter and abdominal circumference
Gestational age (full weeks) | Diameter of baby’s head, mm | Abdominal circumference, mm |
30 | 79 | 264 |
31 | 81 | 274 |
32 | 83 | 286 |
33 | 85 | 296 |
34 | 88 | 306 |
35 | 91 | 315 |
36 | 94 | 323 |
37 | 97 | 330 |
38 | 99 | 336 |
39 | 101 | 342 |
40 | 103 | 347 |
The values shown in the table are average, approximate. Individual fluctuations of these numbers may differ significantly from the average norm. Therefore, the timing of pregnancy for these indicators never compare. The tummy and chest of the little man are measured solely in order to look at the proportions of the body, to detect possible developmental lags.
Any ultrasound doctor knows that at third trimester babies grow especially uneventherefore, one baby is not at all like the other, and it’s ungrateful to compare them with each other or with tables. Therefore, no one will pay particular attention to minor deviations, no one will frighten a pregnant woman.
However, significant deviations in the diameter of the chest and abdominal circumference in the lower side can cause such an unpleasant diagnosis as IUGR - intrauterine growth retardation, entanglement by the umbilical cord.Modern medicine has enough methods to take urgent measures and support the child with medication if it is too early for him to be born.
In a twin pregnancy, the lagging of sizes from the norm in one of the fetuses is not regarded as a delay in development, this is considered to be a variant of the norm for multiple pregnancies.
Sizes of paired bones on the third ultrasound
During the third ultrasound examination, the doctor examines the most diverse bone structures of the baby - the facial bones, the bones of the skull, and the phalanges of the fingers on the small handles. But measurements under the protocol are done only in relation to the paired bones - the femur, tibia, shoulder and forearm bones.
Obstetric (full weeks) | DBK (length of the femur), mm | DKG (length of the bones of the leg), mm | WPC (humerus length), mm | DKP (length of forearm bones), mm |
30 | 59 | 79 | 50 | 46 |
31 | 61 | 81 | 52 | 48 |
32 | 63 | 83 | 54 | 49 |
33 | 65 | 85 | 55 | 50 |
34 | 66 | 88 | 57 | 52 |
35 | 67 | 91 | 58 | 53 |
36 | 69 | 94 | 60 | 54 |
37 | 71 | 97 | 61 | 55 |
38 | 73 | 99 | 63 | 56 |
39 | 75 | 101 | 64 | 57 |
40 | 77 | 103 | 65 | 58 |
If during the shortening of some bones, for example, the bones of the tibia, no markers of fetal chromosomal abnormalities were detected at the screenings, then a slight lag behind these average values should not cause any concern. Longer bones are not a cause for alarm, but rather of all, the baby will be of great height, and he inherited his long arms and legs from his father or grandfather.
The internal organs of the baby
During the third ultrasound, the doctor examines the lobes of the baby’s brain, measures the cerebellum. In addition, he conducts an examination of important internal organs. The heart should have a four-section cut, both kidneys should have the same size, even and clear contours, the degree of maturity of the lungs is determined by the period, the closer to childbirth, the higher it is. At 30 weeks - it is the first, less often - the second.
An ultrasound scanner examines the stomach, baby’s spine, gallbladder, bladder and intestines. If the doctor does not see the vices, then in the conclusion he will write - “the norm” or “without features”.
Fruit weight
In the third trimester, the baby is actively gaining weight. He increases it every day. Therefore, ultrasound using built-in scanner programs only calculates the approximate weight of the fetus. The estimated mass in practice is often quite different from the real weight (step - plus or minus 500-700 g).
Deadline (full weeks) | Estimated Weight (g) |
30 | 1500-1600 |
31 | 1600-1800 |
32 | 1800-1950 |
33 | 1950-2100 |
34 | 2100-2250 |
35 | 2250–2500 |
36 | 2500–2600 |
37 | 2600-2800 |
38 | 2800-3000 |
39 | 3000-3200 |
40 | 3200-3500 |
These data are very conditional, because the weight of some children at 38 weeks exceeds 4 kilograms, and for some it does not reach 3 kilograms. More precisely, oddly enough, the weight of the unborn child is "predicted" by experienced midwives, who measure the pregnant woman with a measuring tape at each scheduled admission in the consultation. Their assumptions are very often true.
Placenta, water, umbilical cord
The “place for children” or, in the language of physicians, the placenta, may have a single degree of maturity at the time of the third ultrasound scan. Up to 30 weeks - it is zero. If the doctor indicates the first degree, there is nothing pathological in this - nature has conceived that the organ is temporary, and it gradually "grows" closer to childbirth, since with the birth of a child into the world, the placenta will no longer need.
If the degree of maturity of the placenta at 32-34 weeks is the second or the third, this may indicate that the "baby seat" is aging prematurely, and this means that the baby does not receive nutrients and vitamins from the mother's body, because the aging placenta does its job much worse .
In this case, maintenance treatment is prescribed, if severe placental insufficiency develops, a decision on premature delivery can be made.
At the third planned ultrasound, the position of the placenta is also assessed. If it is too low to the exit of the uterus - the inner throat - or covers it partially or completely, the conclusion will be indicated - "low placentation" or "placenta previa." Both of these conditions require hospitalization and hospitalization.
Doctors will monitor the “children's place”, if it does not rise to 36-37 weeks, then a cesarean section will be shown to a woman in 38-39 weeks.
The amount of water surrounding the child also has an important diagnostic value. A decrease in this amount or an increase in it may adversely affect the child’s condition. in the womb and complicate the process of childbirth, which is just around the corner. The longer the period, the lower the index of amniotic fluid, because the size of the fetus is already so large that they take up almost all the space, for water there is less space.
Obstetric (full weeks) | The amniotic fluid index (mm), mean values - fluctuations |
30 | 145 (90-234) |
31 | 144 (88-238) |
32 | 144 (86-242) |
33 | 143 (83-245) |
34 | 142 (81-248) |
35 | 140 (79-248) |
36 | 138 (77–249) |
37 | 135 (75–244) |
38 | 132 (73 -239) |
39 | 129 (72-226) |
40 | 123 (71 -214) |
In the umbilical cord, there are normally three vessels.
Doplerography
It is the third ultrasound can be carried out with an extended study, which is abbreviated as USDG, and in the people it is simply called - Doppler ultrasound. With the help of a special program on the device-scanner sensor measured the speed and volume of blood flow in the uterine vessels and the placenta. This gives an idea of how well the baby "eats", whether it is experiencing a state of lack of oxygen.
This study is mandatory for all pregnant women whose babies are lagging behind the average standard, for those who have reason to fear the development of Rh-conflict, as well as for women with multiple pregnancies. Recently, however, Doppler ultrasounds are being done to all women during the third scheduled examination.
To describe the blood flow velocity, a special indicator is used - the vascular resistance index. Normally, from 30 to 34 weeks of pregnancy, this index is in the range of 0.34-0.61. From the 35th week up to the birth, this value changes downwards and is within 0.33-0.57.
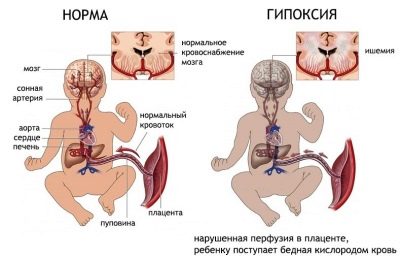
Blood flow in the umbilical cord is of particular importance for the diagnostician. By this value a conclusion is made about the possible fetal hypoxia, which may even become the basis for premature delivery of a woman to save the life of a child. Normal values of blood flow in the umbilical cord can range from 0.54 to 0.77 at 30 weeks gestation, at 31-32 weeks, the range acceptable for the normal development of the child is as follows - 0.52-0.76.
At 33-34 weeks gestation, a sensor that measures the rate at which the umbilical cord passes to the fetus, shows a number in the range from 0.49 to 0.73. At 35-36 week, this value is in the range of 0.47-0.71. At 37-38 week, the vascular resistance index is 0.44-0.69.
If the index increases, the blood flow decreases. It is very dangerous for children. Ideally, such a study should be carried out several times during pregnancy, starting at week 28, especially if there is evidence for this. With the help of Doppler sonography, pathology can be detected at their very initial stage, and in a timely manner, the pregnant woman can receive the necessary medical care.