First ultrasound during pregnancy: the timing and standards
The first ultrasound examination during pregnancy is always an exciting and important event in the life of the future mother. This is the first "meeting" of a woman with her child, who is still very small.
This survey is expected with a special feeling - impatience mixed with anxiety. About how and when the first ultrasound scan is conducted for women in an “interesting position”, as well as what parameters are considered the norm, we will describe in this article.
Dates
The first planned ultrasound scan, which is recommended for all expectant mothers, is performed from 10 to 13 weeks inclusive. This is an important and informative first prenatal screening for doctors and women. However, for many women, this compulsory examination will no longer be the first, since up to 10 weeks, they may have already undergone such a diagnosis.
Theoretically, the first ultrasound can be informative during pregnancy already 2.5-3 weeks after the expected day of ovulation. This corresponds to approximately the fifth obstetric week.
At this time, for the first time, a technical opportunity appears on the monitor of the ultrasound scanner of the fetal egg, which will indicate the occurrence of pregnancy. But until 10-11 weeks, ultrasound diagnostics is not officially recommended without good evidence.
Why is routine ultrasound performed?
The purpose of a planned study in a designated time frame is to identify so-called markers of possible pathologies of the fetus. Up to 10-13 weeks for obstetric calculation (approximately 12-15 weeks from conception), these markers are not subject to assessment.
The dates at which the first prenatal screening is conducted are not chosen by chance, because in case anomalies are detected, a woman can get an abortion for medical reasons without waiting for the time to be great.
Complications after abortion for long periods are always greater.
The first ultrasound also does not accidentally take place in one day with the delivery of a sample of venous blood for biochemical research. The results of the ultrasound are not evaluated separately from blood counts. If markers are detected and hormonal and protein balance in the blood are broken in a certain way, the risk of having a baby with chromosomal abnormalities is higher.
Scheduled examination in the timeframe set by the Ministry of Health is aimed at finding women who are at risk of being likely to give birth to babies with severe total lesions caused by genetic "malfunction."
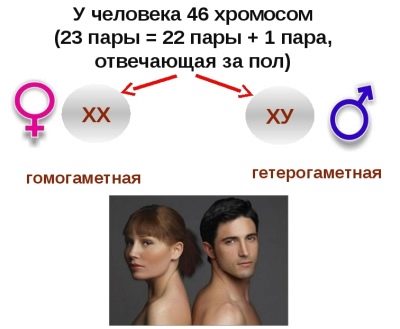
In humans, 23 pairs of chromosomes. They are all the same, with the exception of the last couple, in which the boys XY, and the girls - XX. An extra chromosome or lack of such in one of 23 pairs causes irreversible pathologies.
So, if the number of chromosomes in 21 pairs is violated, the child is diagnosed with Down syndrome, and if there is an incorrect number of chromosomes in 13 pairs, Patau syndrome develops.
It cannot be said that the first screening in general and ultrasound examination within it, in particular, can reveal all possible variants of genetic disorders, but the roughest in the majority can be found on the first planned research with the subsequent additional diagnostics. Such pathologies include: Down syndrome, Edwards, Patau, Turner, Cornelia de Lange, Smith-Lemli-Opitz, and signs of non-molar triplodia.
Coarse neural tube defects, such as a decrease or complete absence of the brain, anomalies of the development of the spinal cord, can only be detected on the second antenatal screeningwhich passes according to plan only in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Going to the first planned ultrasound, a woman should understand that no one will diagnose her baby only on the basis of what she saw on the monitor of the ultrasound scanner.
If the diagnostician suspects pathology and developmental abnormalities, he will surely indicate this in conclusion, and the woman will be sent for consultation to the genetics, who will decide on the need for more accurate than ultrasound diagnostic methods - invasive, during which doctors take particles of fetal , blood from the umbilical cord, amniotic fluid for genetic analysis. The accuracy of invasive methods is almost 99%.
The perfect counterpart is non-invasive fetal DNA analysis, which is absolutely safe for both mother and baby, as for its holding a pregnant woman you only need to donate venous blood.
Among other tasks of the first screening ultrasound is to clarify the gestational age by the size of the baby, to determine the state of female reproductive health, to assess the possible risks in the next six months of birth.
Unscheduled research - what is it for?
Today, ultrasound is more than affordable, and therefore a woman can go to him without the knowledge of the doctor and his directions. Many do, and after the home test shows two strips, they are sent to the nearest clinic to confirm the fact of pregnancy with the help of such a scan.
However, besides the desire of the woman herself to know exactly whether the conception took place, there may be medical indications for the first ultrasound before the planned time. It happens that before screening a woman has time to do several such surveys.
Medical indications for which the study may be recommended previously established The recommendations of the Ministry of Health are terms that are varied:
- Miscarriage of pregnancy. If a woman previously had two or more miscarriages at the very early stages of gestation, the first ultrasound scan is recommended when registering at a antenatal clinic to make sure that the fetus develops this time.
- Frozen history of pregnancy. If, prior to the current pregnancy, the woman had cases of non-developing pregnancy, anembryony (absence of an embryo in the fetal egg), then early ultrasound scanning is strongly recommended to find out if there is a recurrence.
- Ectopic pregnancy in history or suspected ectopic pregnancy. In this case, the task of early examination is to identify the possible ectopic fixation of the ovum as early as possible, as long as it does not pose a serious threat to the life of the woman. Suspicion arises if the level of hCG in the blood of a woman is significantly lower than the prescribed level, if there are pains, discharge, not similar to menstrual, delayed menstruation, while the uterus is not enlarged.
- Trauma and surgery on the uterus in history. If before the onset of pregnancy, the woman underwent surgical interventions affecting the main female reproductive organ, then the task of the first ultrasound at the earliest time will be to assess the place of attachment of the ovum. The farther away from the postoperative cicatrices the baby is fixed, the more favorable the prognosis for normal pregnancy and childbirth.
- Suspected multiple pregnancy. In this case, an ultrasound study of previously screened dates is necessary to confirm the fact of carrying two or more babies. A doctor can guess this by exceeding the level of hCG in the blood of a pregnant woman two or more times.
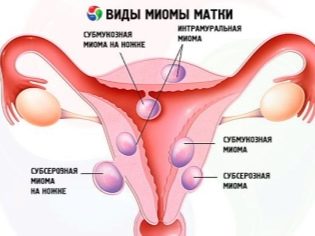
- Chronic diseases tumors, myoma. Existing pathologies of the reproductive system can affect not only the ability to conceive a child, but also the ability to bear it. Therefore, women with such illnesses are shown an early examination by ultrasound in order to assess the place of implantation and the growth rate of the ovum.
- The threat of interruption. In the earliest terms, there may also be a threat of miscarriage. Usually, it manifests as a discharge from the genitals, pulling (like during menstruation or slightly stronger) pains in the lower abdomen and in the lumbar region, deterioration of the woman’s general condition. With such symptoms, an ultrasound scan is recommended with the note “cito”, which means “urgently, urgently”.
- Doubtful test results. For a variety of reasons, there can be “disagreements” between the test strips, the blood test to determine the characteristic of pregnancy hormone hCG and the results of a “manual” gynecological examination. If the disagreements are such that the obstetrician-gynecologist cannot say with certainty whether the woman is pregnant at all, he will refer her to an ultrasound.
First diagnosis after IVF
If for some reason a couple cannot independently conceive a baby, doctors can do it for them. The whole process of in vitro fertilization, starting with preparation for it, and ending with the infusion of embryos - “three days” or “five days”, is controlled by means of ultrasound diagnostics.
After embryo transfer, the woman is assigned hormone therapyso that the babies have more chances to gain a foothold and start growing in the uterus.
The first ultrasound after IVF is recommended for 12-14 days after transplantation, if not started monthly, and the results of the blood test for human chorionic gonadotropin indicate that the pregnancy has begun.
At this stage, the task of diagnosis is to make sure that the pregnancy has taken place, and the efforts of the doctors and spouses have been crowned with success.
If the ultrasound diagnosis shows the presence in the uterus of the ovum (or several fetal eggs), then the next ultrasound examination is scheduled after another two weeks to make sure that the embryos grow and develop. Then, a woman is scheduled, as for all other pregnant women, a scheduled screening examination. 10-13 weeks of pregnancy.
What can be seen on the first ultrasound?
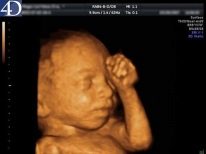
The future mother, at what time she would not go to the ultrasound room, is interested in what can be seen on one or another term. Modern types of ultrasound diagnostics significantly broaden the prospects, especially for such innovative types as 3D and 4D ultrasound, as well as 5D ultrasound, which provide an opportunity to get not a two-dimensional, but a three-dimensional and even color picture in real time.
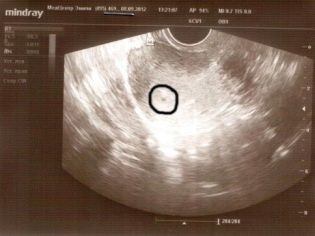
However, one should not think that the very next day after the start of the delay on any, even the most modern device, one can see at least something. The earliest period at which it is possible (again, only theoretically) to consider the fertilized egg is considered 5 obstetric week (this is three weeks after ovulation or a week after the start of the delay).
There is no need to make an expensive "volumetric" three-dimensional ultrasound on such a short period, for now you can only see the point, which is the fetal egg. Going to the first ultrasound, a woman should know what exactly she can show.
In 5-9 weeks
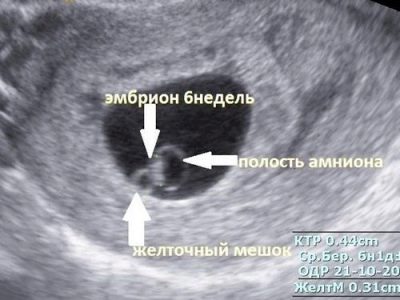
Early ultrasound, according to or without testimony, at the request of the future mother, will not be able to please the woman with impressive pictures and memorable pictures. In the earliest terms, only a rounded education in the uterine cavity with a subtle inner nucleus — the embryo — is determined.The same beautiful detailed picture of a small embryo, as they are portrayed using computer graphics, in reality will not be.
Most women can’t even consider the fertilized egg itself, especially if the diagnosis is not accompanied by detailed comments from the doctor. But there is one nice nuance - in five obstetric weeks, a tiny heart starts to knock at the tiny baby, or rather, a characteristic ripple is observed where the rib cage will soon form.
If the device on which the survey is conducted, has a fairly good resolution and a modern sensor, then the mother will be able to see how this happens. The main characteristic of the development of the baby in the initial period is the size of the ovum. It is his and the doctor will measure if a woman comes to scan at 5-9 weeks of pregnancy.
If the first ultrasound scan falls on 7 weeks for obstetric calculation of the gestational age (approximately 5 weeks from the day of ovulation), then the woman will be more likely to show her baby. The embryo on this period has a disproportionately large head and tail.
At 9 weeks, the baby will have human forms that are more understandable to the mother, although the tail and the big head will still be observed. The heart of a child at 8-9 weeks can already be heard if the ultrasound machine is equipped with acoustic speakers.
In 10-13 weeks
By the time of the first screening the baby is changing dramatically. On the first planned ultrasound scan, a woman is more likely to be shown such a baby.
He already well distinguishable pens, if you're lucky, you can even look at the fingers on them. Also distinguish the facial profile, tummy, chest. Heart crumbles baby crumble and loud, it will give to listen.
In a baby at this time, the distance from the tailbone to the crown is measured (coccyx parietal size or KTP), the distance between the temporal bones is the bipariented size of the head (BPR), they also sometimes continue to measure the size of the ovum, but this size no longer carries great diagnostic value.
The main goal is to detect, if any, the markers of chromosomal abnormalities, as discussed above. These include two sizes - the length of the nasal bones and the distance from the inner surface of the baby’s skin to the outer surface of the soft tissues of the neck.
Some pathologies tend to accumulate excess fluid in this particular area, due to which TVP (collar space thickness) increases. Many chromosomal "failures" are accompanied by various deformations of the facial bones, which is why the nasal bones also try to make out, and, if possible, measure.
The external genitalia are almost formed, and they can also theoretically be considered at 12-13 weeks, but the doctors at this time cannot talk about the sex of the little ones with confidence, because the differences still seem minimal. The diagnostician will be able to more accurately answer the mother's question about the child's field after the 18th week of pregnancy, when she comes to the second planned ultrasound scan.
Decryption and norms
Interpret the results of ultrasound should doctor. Everyone knows about this, but it is understandable curiosity and anxiety inherent in expectant mothers, make women thoroughly approach the study of complex terminology in order to understand everything on their own. This is not unusual Our task is to help pregnant women understand what is written in custody.
Svd
Under this three-digit abbreviation hides the main indicator of the development of the baby for up to 9-10 weeks. Since the embryo itself is still very small, and it is very difficult to measure embryonic parts, the state, development and duration of pregnancy at the initial stage are determined by the size of the ovum.
The shape and size of the ovum may even tell about the trouble of the baby, for example, the deformation and some “pressure” of the outlines of the fetal membrane may indicate that a woman has a miscarriage, and its simultaneous decrease in size indicates a non-developing pregnancy and embryo death.
Determination of the period of gestation on SVD in the early stages is considered to be quite reliable.
After all, for the time being, babies are not divided into large and small, thick and thin - all embryos grow at approximately the same speed in the first trimester, but they begin to show hereditary features of appearance somewhat later.
The average internal diameter of the ovum increases simultaneously with the period, and the fetal membrane grows even not by week, but by day, so it is not difficult to establish the day of conception, provided that the pregnancy develops normally.
Table of norms SVD (average)
The average internal diameter of the ovum (mm) | Compliance with gestation (week + day) |
6 | 5+3 |
7 | 5+3 |
8 | 5+4 |
9 | 5+5 |
10 | 5+6 |
11 | 6+0 |
12 | 6+1 |
13 | 6+2 |
14 | 6+3 |
15 | 6+4 |
16 | 6+5 |
17 | 6+5 |
18 | 6+6 |
19 | 7+0 |
20 | 7+1 |
21 | 7+2 |
22 | 7+3 |
23 | 7+4 |
24 | 7+5 |
25 | 7+5 |
26 | 7+6 |
27 | 8+0 |
28 | 8+1 |
29 | 8+2 |
30 | 8+3 |
31 | 8+3 |
32 | 8+4 |
33 | 8+5 |
34 | 8+6 |
35 | 9+0 |
36 | 9+1 |
37 | 9+1 |
38 | 9+2 |
39 | 9+3 |
40 | 9+4 |
41 | 9+4 |
42 | 9+5 |
43 | 9+6 |
44 | 10+0 |
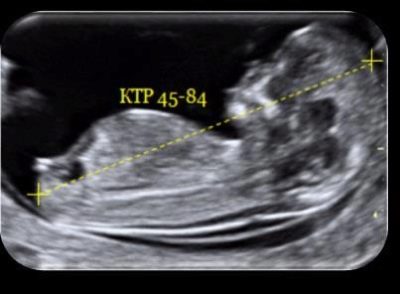
KTR
The kopchiko-parietal size allows to judge the growth rate of the child from about 7-8 weeks of pregnancy. This size is laid diagnostician. from the highest point of the head (crown) to the lowest point - coccyx with maximum embryo extension.
Growth is measured from head to toe. On ultrasound, this size is considered an indicator of importance, especially if an early study is done prior to the planned one. According to KTR, they not only determine how a baby grows, whether it is feeling well, but also the gestational age in order to clarify the expected date of birth.
At a later date, when a woman enters the second trimester, the CTE is no longer determined, since the baby becomes large enough to measure it from head to tailbone as a whole.
KTR - the size that causes serious experiences of future moms. His vibrations cause a storm of emotions.
In fact, you should not look in the tables of matches up to a millimeter. Not always insignificant deviations up or down can indicate anomalies, and not always deviations for 1-2 weeks have pathological causes.
A decrease in CTE may be due to the fact that a woman has had a late ovulation or the baby “lingers” on the way to the uterine cavity after conception, that is, the implantation occurred later than the woman thinks.
Among the possible adverse effects of reducing CTE - infections, including intrauterine, as well as gross genetic pathology, which do not allow the crumbs on the physical level to develop at a pace set by nature.
An increase in KTR may also indicate inaccuracies in determining the term of gestation, that is, early ovulation, as well as a tendency towards large fetus.
Table of norms of KTR (average)
Duration of gestation, (obstetric weeks) | Kopchiko-parietal size, mm |
7 | 10 |
8 | 15 |
9 | 22 |
10 | 31 |
11 | 42 |
12 | 51 |
13 | 63 |
14 | 76 |
TVP
This is the first indicator of possible chromosomal abnormalities. The thickness of the collar space is measured by the segment, which is laid from the inner surface of the skin to the border of the dark anechoic area on the back of the baby’s neck.
Some gross developmental abnormalities associated with errors of the genetic code, cause a general swelling in a child, but in this period it is possible to determine it only by one study area - collar space. After 13 weeks of pregnancy, this indicator is not measured, it is no longer considered diagnostically important.
Regarding this size, future mothers who undergo the first prenatal screening experience the most.
You should not panic, because this size, like everyone else, determined by ultrasound scanning, does not say with an accuracy of up to 100% of the presence of pathology. A small deviation from the norm does not always indicate the presence of the disease.
Statistics show that disappointing diagnoses in children with increased TST are confirmed only in 10% of cases.Among sick children, TBP above 3.0 mm was found only in units, usually true malformations correspond to an excess of 3-8 mm from the norm.
The PIT Table (averaged)
Duration of gestation (obstetric week) | Thickness of collar space, mm |
10-11 | 1.5 -1.6 (allowable up to 2.2) |
11-12 | 1.6 (allowable up to 2.4) |
12-13 | 1.6-1.7 (allowable up to 2.5) |
13-14 | 1.7-1.8 (allowable up to 2.7) |
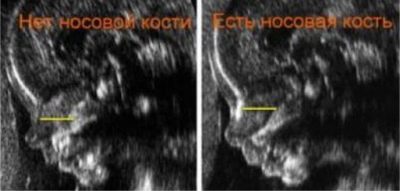
Nose bone length
As is the case with the thickness of the collar space, the bones of the nose can also speak about the likelihood of pathology of chromosomal origin. In children with Down syndrome, for example, the nasal bones may not be detected at all, and in babies with Patau syndrome, the nasal bone may be greatly shortened. But again, as with TVP, everything depends not only on the health of the baby.
Very often, doctors do not see the nasal bone due to the fact that the ultrasound unit in consultation was outdated ten years ago. Sometimes the reason for the detection of an alarm marker is the lack of experience of the diagnostician. If the result of the examination of this marker is disappointing, then the woman is assigned a control ultrasound on the apparatus of the expert class and consultation of the medical genetics.
Table of the norms of the length of the nasal bone (average)
Duration of gestation (obstetric weeks) | The length of the nasal bone, mm |
10-11 | It is not always possible to measure, but the bones should be visually determined |
12-13 | 3,1 |
14-15 | 3,8 |
Technique of
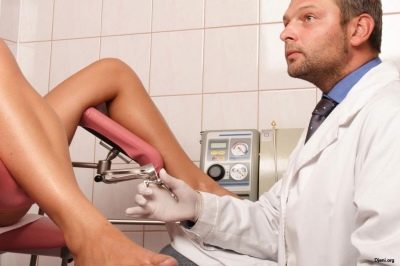
Many women are interested in how the first ultrasound is performed. Most often, doctors use a vaginal probe for examination, which is inserted into the vagina in a condom. It is possible to inspect the uterine cavity with this method through the vaginal wall. It is quite thin, and the visualization is good. therefore Intravaginal ultrasound is considered one of the most accurate.
It is theoretically possible to examine a woman during the first trimester of pregnancy and a transabdominal external sensor that is applied to the anterior abdominal wall;
The examination is carried out on a couch on which a woman is invited to stay in a supine position with her legs bent at the knees. The doctor may also examine the vaginal sensor on the gynecological chair.
If a woman comes to the ultrasound room before the planned screening, which happens when they are prescribed for possible complications of pregnancy, the doctor will scan only the vaginal sensor, as it allows you to study the condition of the cervix and cervix, which is very important suspected miscarriage threat, ectopic pregnancy, non-developing pregnancy.
How to prepare for the survey?
The results of an ultrasound scan at an early period can be affected by an insufficient amount of fluid, through which ultrasonic waves pass better. That is why before going to the doctor the expectant mother It is recommended to drink about half a liter of water, thereby filling your bladder.
In the later stages of pregnancy, there will be enough amniotic fluid in the uterine cavity, which will serve as an ideal medium for ultrasonic waves.
While the embryo is very tiny, any factor can distort the real picture of what is happening. So, intestines overflowing with feces, intestines, whose loops swelled from gases, can squeeze the female pelvic organs.
To better prepare for the first ultrasound scan, the expectant mother is advised not to eat foods that can cause fermentation and the formation of intestinal gases two or three days before visiting the diagnostic room.
It is better to exclude peas, white cabbage, pastry, rye bread, sweets, and carbonated drinks from the diet. On the day of the examination, the intestines should be emptied, and 2-3 hours before the ultrasound scan, take a drug that “collapses” the bubbles of intestinal gases, preventing bloating.It is possible to carry to such means allowed for pregnant women «Espumizan» or "Simethicone".
You should take an exchange card with you for the first ultrasound, if it is already in place, a passport, a policy of compulsory medical insurance, a clean diaper that can be put on a couch or gynecological chair, as well as removable shoes. Fasting, go on an ultrasound on an empty stomach is not necessary.
Probability of errors
Errors of doctors of ultrasound diagnostics are a subject of wide discussion among future mothers. Indeed, ultrasound scanning is not considered a high-precision method. Its accuracy is estimated only at 75-90%. Much of the truthfulness of the results depends on the quality of the device, the qualifications of the doctor and the timeliness of the examination.
If a woman requires the doctor to answer the question of what sex is her baby at 11-12 weeks of pregnancy, then the accuracy of this “prediction” will be no higher than 70%, however after 18 weeks, the accuracy in determining the sex will be close to 90%.
The same pattern is observed with confirmation of the pregnancy itself. If a woman came to do an ultrasound too soon, the doctor may not see anything and write in conclusion that no signs of pregnancy have been found.
If you solve issues as they arrive, within the recommended timeframe, an ultrasound scan can be considered to be a fairly accurate and informative way. And in cases where the results of ultrasound scanning cannot be interpreted unambiguously, if there are alarming markers or doubts with the doctor, he will definitely advise more accurate diagnostic methods - amniocentesis, chorionic biopsy, and a little later - cordocentesis.
If you wish, you can do non-invasive fetal DNA analysis, which is an excellent alternative to invasive tests, and absolutely safe for the baby.
In addition, in most cases, again, ultrasound helps to dispel doubts, but another class, the expert one. Such devices are available to perinatal centers, medical and genetic centers and clinics.
Does ultrasound harm the baby?
On this account there is no consensus. Modern medicine has no evidence of the harm of this diagnostic procedure for a fetus developing in the womb. However, there is no evidence of the complete safety of ultrasound. The fact is that science cannot study long-term effects. No one knows how the effect of ultrasound in the embryonic period affects a person when he turns 30, 40, 50 years old.
It is the lack of information that is fertile food for reasoning of the near-scientific sense about the effect of ultrasound waves on human DNA. The experience shows that children who were born to women who did not do an ultrasound during pregnancy at all, and children who were born to women who underwent such diagnostics more than 6 times during the gestation period, no different for health reasons from each other.
Do an ultrasound or not - the choice of a woman. The Ministry of Health only recommends three scheduled examinations for the entire duration of pregnancy, but they are not mandatory. If a woman does not want, then no one will force her.
But before rejecting screening or an unscheduled ultrasound scan, a woman should weigh all the risks well, because many pathologies in the process of gestation and childbirth can be avoided if doctors can manage to deal with disturbing symptoms in time.