The first screening during pregnancy: the timing and standards
The first screening study during pregnancy is a crucial and very important stage. He is anxiously awaited by all future mothers, because this examination should answer the main question - is everything OK with the child? When and how the diagnosis is carried out, as well as what results can be considered normal, will be discussed in this article.
What it is?
Prenatal screening at times so frightens pregnant women that some even refuse to undergo such tests. This is facilitated by numerous forums for women in an “interesting position”, in which all the “horrors” of screening and experiencing moms are described in detail.
In fact, there is nothing wrong with this survey. Screening is a comprehensive study aimed at identifying potential risks to a woman produce a baby with genetic disorders.
The complex consists of ultrasound and laboratory studies of venous blood of a pregnant woman.
Translated from English, “screening” is “selection”, “screening out”, “sorting”. This term is used in economics, sociology and other fields, medicine is not an exception. Pregnant women are a special category of patients who need a special approach and more thorough medical examination. It is important to understand that the screening itself does not reveal any diseases, and no diagnoses can be made to either the mother or her unborn child.
This comprehensive examination only reveals among the total mass of future moms of women who have risks to produce a baby with gross developmental defects, genetic abnormalities higher than the rest. High risks of giving birth to a baby with pathologies are not a sentence yet, and in most cases the baby is fine, but such women should be more carefully examined.
In total, for the period of carrying a child, a woman will have three such screenings - in 1 trimester, in 2 and 3 trimesters. The first screening during pregnancy is considered the most important and informative.
Not so long ago, some two decades ago, it was quite difficult for obstetricians to even determine the sex of the unborn child, and the developmental pathologies of the baby sometimes remained a secret behind seven seals right up to the birth. Since 2000, a universal screening examination of expectant mothers has been practiced in our country, and this has reduced the number of babies born with such serious diseases as Down syndrome, Turner syndrome.
Diagnosis is completely free for the patientAll women who have registered for pregnancy receive a referral to it. The results are not a guide to immediate action. If it is later confirmed that the child is really sick, the woman will be given the direction to terminate the pregnancy according to medical indications.
Take advantage of this opportunity or save and produce a “special” baby - only the woman herself will decide; no one will force her to make any decision.
Goals
The main purpose of antenatal screening is to identify pregnant women at risk. Nature, of course, is still wiser and more sophisticated than man and all his achievements, and therefore not one, not even the most experienced doctor, not one modern diagnosis can predict all possible malformations of a baby. Therefore, the list of problems that are “calculated” during the first screening process is limited to only a few serious diseases and conditions. The first screening, in particular, reveals the likelihood of such pathologies.
Edwards syndrome
It is one of the most severe congenital malformations. The reason for its occurrence lies in trisomy 18 chromosomes. The probability of its development has a clear connection with the age of the pregnant woman - in women over 40 years old the risk of having a child with such a diagnosis is higher. In general, the disease is not considered to be common, with the “age-related” mothers, the risk is about 0.7%.
This does not mean that Edwards syndrome can only be threatened by babies of pregnant women with prerequisites because of their age, and quite young girls may have an excessive chromosome in the 18th pair, especially if they have diabetes.
In babies, there is a low birth weight, deformation of the facial and cranial bones, they have an abnormally small oral opening, strongly altered ears, and auditory passages can be completely absent. In 60% of cases there is a heart defect. Almost every kid with Edwards syndrome has a severely curved foot, convulsive seizures are observed, there are abnormalities in the development of the cerebellum. Such children are mentally retarded, pathology is classified according to the type of oligophrenia.
The vast majority of babies with this syndrome die within the first three months from the moment of birth. Until the year can live only 3-5% of children. Pathology is incurable, is not subject to correction.
Turner syndrome
The full name of the disease is Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome. Chromosomal abnormality occurs in the X chromosome. Such babies are born short, with sexual infantilism, as well as some physical mutations. Pregnancy with such a baby almost always occurs in the background. severe toxicosis and constant threat of interruptionchildbirth is most often premature.
The disease is accompanied not only by the absence or underdevelopment of the genital glands, but also by multiple bone defects - the phalanges of the fingers may be absent, elbow joints are curved, the metatarsals are shorter, there are problems with the spine. Like most chromosomal ailments, this syndrome has heart defects and large vessels. Mental retardation develops in the type of infantilism, the intelligence of most children is preserved.
Cornelia de Lange syndrome
It is a hereditary disease in which gene mutations Nipbl. Because of this, the child has deformed bones of the skull and face, there are not enough fingers on the handles, there is severe mental retardation. In the syndrome, problems with visual and auditory functions are often observed, severe abnormalities affect the kidneys, the cardiovascular system, the liver, and the reproductive system.
Children have a tendency to convulsive seizures, children cannot control their own movements, and often cause injuries to themselves. By type of mental disorder are imbeciles with impairments of even the simplest mental activity.
Only in 20% of such babies the disease proceeds without gross psychomotor manifestations, but even such children are characterized by pathologies of development of bones and internal organs.
Down syndrome
This is the most common chromosomal pathology, in which there is extra chromosome in 21 pairs. In other words, the karyotype of the baby has 47 chromosomes, whereas a healthy child should have exactly 46. Such children have a peculiarly changed face - it is flatter, the neck is short, the back of the head is flattened.Four out of ten babies born with this syndrome have heart and vascular defects, and three babies have congenital strabismus.
Not without reason, genetics believes that the probability of producing a baby with Down syndrome is greater in women with increasing age. For example, a young pregnant woman at 24 years old has a base risk of 1: 1500, if the expectant mother is already 28-29 years old, the risk increases to 1: 1000. Pregnant women over 35 should remember that their risk is 1: 214. After 45, the probability the highest is 1:19.
This means that one of the 19 children born to ladies after 45 years old is born with a disappointing diagnosis.
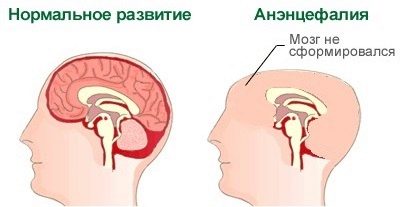
Neural tube defects (anencephaly)
Such a defect can "build up" because of the harmful or toxic effects on the maternal organism at the very beginning of the period when the baby is born. Science knows these terms for sure - this is the period between the third and fourth weeks of pregnancy.
Defects appear underdevelopment of the hemispheres of the brain or their complete absence, sometimes missing and bones of the skull. Thus, the baby simply has no head. This defect is 100% lethal. Most babies die in the womb, some manage to live to give birth, but they are not destined for a long and happy life.
Death occurs in the first hours after birth, less often a child can “hold out” for several days.
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
The state of congenital deficiency of a particular enzyme is 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase, which is responsible for the production of cholesterol. As a result lack of cholesterol all organs and systems begin to suffer at the cellular level, since the substance is extremely necessary for the living cell. The severity of the disease in a child is determined by the nature of the deficiency.
With a slight deviation, the child appears moderate mental problems, and with a serious shortage the disease is accompanied by gross defects on both the physical and mental levels.
The peculiarity of these newborns - diminished brain many suffer from autism, their bones and tendons are deformed, there are defects in the internal organs, and vision and hearing can be impaired. A deficiency in the DHCR7 gene leads to a deficiency of an important enzyme.
The disease itself is rare, but the syndrome was included in the screening for a reason - every 30th adult is a carrier of the mutated DHCR7 gene. And the only question is whether mom or dad will give this gene to his child, or not.
Non-molar triplody
A gross genetic disorder associated with a change in the number of chromosomes in any pair, occurs spontaneously, "according to the will of Mother Nature." Neither mom nor dad are to blame for the fact that instead of 23 pairs, the child lays 46 or 69. There is no way to live with such a karyotype, so most of the fetus dies even in the womb, but variations are possible - a crumb is born, but dies after a few hours, a crumb is born and dies in a few days.
Pathology can occur even when both parents are completely healthy and are not carriers of hereditary diseases.
A subsequent attempt to conceive a child in this pair can be quite successful, the probability of recurrence of non-molar triplodia is extremely low.
Patau syndrome
The development of this disease leads to an extra chromosome in pair 13, so it is also called trisomy 13 chromosomes. Doctors see a clear relationship between the occurrence of a chromosomal abnormality and the age of the mother. Risks increase with increasing age of the pregnant.
The syndrome occurs with gross developmental defects - the child has distorted facial bones, the brain has a very small size. May be underdeveloped or even underdeveloped organs of vision, hearing. Often there is the so-called cyclopia, when the child has only one eye, located in the center of the forehead. There may be multiple crevices of the facial bones.
The syndrome is accompanied by malformations of internal organs, as well as uncorrectable disorders of the central nervous system. Many children die in the first months after birth, only a few manage to live to 5-7 years old, and they are deep idiots, learning or self-care, and the interest in such a baby is completely excluded.
After the introduction of compulsory screening, the number of children who are born with these ailments, managed to significantly reduce. So, until 2000, one of 700 babies was born with Down Syndrome, and after doctors learned to establish risks, only one in 1200 newborns suffers from such an illness, and most of the parents themselves decided so, because lately attitudes toward “sunny” children in society have changed, and some mothers consciously maintain a pregnancy, even knowing that they must have such a special baby.
Prenatal diagnosis reveals not pathologies, but only some signs of possible defects, other diagnostic methods can establish the truth, which we will discuss below.
Risk group
One of the above pathologies can occur absolutely in any woman, but there are so-called risk groups. They include future mothers, whose probability of genetic problems of the fetus is higher than that of the others.
So, among them are:
- late heterosexual (if pregnant over 35 years old);
- pregnant women who previously had miscarriages due to chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus, as well as women who gave birth to children with hereditary diseases;
- girls and women with a history of more than two miscarriages, one after the other;
- pregnant women who, due to ignorance or other reasons at the beginning of pregnancy, continued to take medication drugs that are forbidden to be taken while carrying a child;
- pregnant women from a close blood relative;
- pregnant women from donor sperm;
- women who do not have information about the state of health of the father of the child and do not have contact with him;
- women working in hazardous conditions, especially if their work is associated with radiation exposure, as well as women whose men work in such conditions and are exposed to radiation;
- women with a family history of having relatives with genetic diseases, as well as women whose spouses have such relatives.
If a girl at a young age conceived the desired child from a completely healthy man, then the risks of anomalies are lower, but they cannot be ruled out at all. That is why it is important not to refuse to pass such an examination.
Despite the fact that screening is mandatory for everyone, all procedures are carried out only with the consent of the pregnant woman, if there is none, it is forcibly to examine the future mother, even if she is at risk, no one will.
Dates
The first prenatal screening is carried out in strictly designated periods - from 11 to 13 weeks of pregnancy. It should be understood that a woman can receive a referral for tests and ultrasound both on the eleventh week (10 full obstetric weeks) and on the fourteenth week (in 13 full weeks). Later, the first trimester screening survey is not carried out, since the information content of some markers and indicators is high only in the designated period.
Obstetric weeks are not the weeks that have passed since conception, as some pregnant women mistakenly think. This time elapsed from the first day of the last menstruation. Thus, obstetric weeks is a term from conception + approximately 2 weeks. This means that at the time of the examination the fetus will be approximately 9-11 weeks from conception.
A referral is issued by a doctor who has a pregnant woman registered. If a woman got registered after 13 weeks, the first screening for it is not carried out, and the entire responsibility for the possible undetected pathology in the baby falls on her shoulders.
Training
The period in which the first screening is carried out is not so long, and therefore it is not easy for doctors to examine a tiny baby. A variety of things can affect the results of the examination - from the temperature of the mother to bad habits such as smoking or drinking alcohol. If a pregnant woman does not get enough sleep, she is very nervous, suffers from toxicosis, this can also affect the final result, especially the parameters of the blood test.
Preparation for the first study includes an assessment of overall well-being. A woman must inform her doctor about how she feels, whether her sleep is sufficient, whether there are signs of fatigue, an infectious disease, or a cold.
In order for the ultrasound results to be more accurate, and the doctor could better examine the crumb, the woman should be able to empty her bowel and bladder several hours before visiting the ultrasound room. To eliminate intestinal gas should take a dose. "Simethicone" or "Espumizana». If there is a lot of gas, the swollen intestine can squeeze the pelvic organs, which in turn makes it difficult to diagnose.
Ultrasound on this period is most often carried out in a transvaginal way, and therefore do not need to fill the bladder in advance.
Most thoroughly prepare for the blood test, because Any factor can influence biochemical research. A few days before screening, a sparing diet is recommended for a woman, which completely excludes fatty and fried foods, spices and smoked foods, too salty and pickled foods. To reduce flatulence in the intestines, it is also necessary to refrain from a large number of raw vegetables, from cabbage in any form, from legumes and fatty dairy products, from bakery and sweets.
You can not eat before the procedure. The last meal should be no later than 6 hours before testing.
Order of conduct
The first trimester screening is not only the most informative of the three prenatal screenings, but also the most stringent. It must be carried out in a specific sequence. It is important that both laboratory tests and ultrasound diagnostics are performed on the same day with a small time difference.
At the appointed time (usually this morning, because you should come on an empty stomach), the woman comes to the consultation and first goes to the office of her obstetrician-gynecologist. There she is waiting for filling in a special diagnostic form in which the data necessary for genetic projections are entered. The more facts will be indicated in the form, the more accurate the forecast will be.
Diagnostic information includes the age of the woman and her partner, the weight of the pregnant woman, height, and obstetric history. Be sure to include all pregnancies that were before the current, as well as their outcome. If there were miscarriages, then you should indicate the reason why they occurred, if it is reliably known and confirmed by biopsy results.
If a woman has previously had children with chromosomal syndromes, congenital malformations, this information is also indicated, as is the presence of relatives with hereditary diseases.
If a pregnant woman smokes or uses alcohol or drugs, this fact should also be noted, since such bad habits can not but affect the composition of the blood. All the chronic diseases that the expectant mother has in the diagnostic form are entered into the diagnostic form.
After that, the pregnant woman is sent to the ultrasound or to the treatment room. There are no clear recommendations for what should follow, most often in Russian female consultations begin with ultrasound diagnostics, and then immediately take blood from a pregnant woman for biochemical analysis. Ultrasounds can be carried out not only transvaginally, but also transabdominally, by a sensor on top of the abdomen, if the woman has a thin build and the view through the anterior abdominal wall is not difficult.
The vaginal sensor is viewed through the vaginal wall inside; this method is most preferable for the first trimester in general and for women with the threat of miscarriage in particular, since it allows, in addition to the child, examine in detail the state of the cervical canal.
Blood taken from a vein in the traditional way. All instruments and tubes are disposable, sterile. The results of the ultrasound are given to the woman immediately, the results of laboratory blood tests will have to wait several days or even weeks.
A woman receives a general conclusion about screening with calculated risks of fetal abnormalities after blood tests are completed, since an ultrasound scan is not considered separately from laboratory data.
What can be seen on ultrasound?
On ultrasound during the first screening a woman will be able to see her baby. For many - this is the first meeting with the crumbs. A child who has ceased to be an embryo and has become a fetus will be able to please his mother with his loud and rhythmic heartbeat, to show her how well he has learned to move, although she still does not feel this. On ultrasound at the end of the first trimester, you can determine the number of fruits, their viability, features of development.
Fetal sizes help you navigate the exact dates and calculate the estimated date of delivery.
A good high-resolution ultrasound scanner at this time shows the head and face profile of the fetus, its arms and legs, fingers, orbits. The doctor will be able to examine the placenta, the umbilical cord, assess the condition of the uterus and tubes, amniotic fluid. Several so-called markers of genetic pathologies will help to conclude whether the baby has the likelihood of congenital chromosomal disease.
With a favorable review and a good machine, the doctor can theoretically find out the sex of the child, but there is nothing to guarantee, because the sex differences between boys and girls during this period of pregnancy are not so strongly pronounced.
Sex determination not included in the list of questions of interest to doctors during screeningthat is why a woman will have to pay for this service at the rates for the provision of paid services to the medical organization in which she is diagnosed. The only exceptions are cases in which the genetic well-being of a baby depends on gender. For example, hemophilia occurs only in boys.
If a woman is a carrier of this disease, then the probability of transmitting it to his son is high, and therefore sexual identification has diagnostic value.
Interpretation of ultrasound results
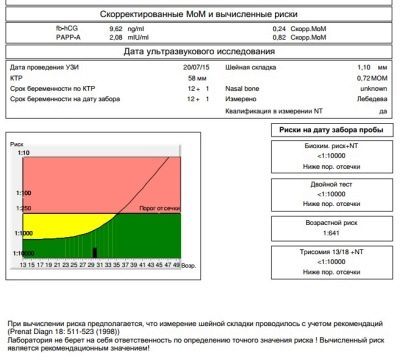
Everything that the doctor-diagnostician sees on the monitor of the ultrasound scanner is registered in the protocol of screening research. It indicates the basic information about the baby. The main dimensions that make it possible to judge the health of the baby, as well as the exact date of conception are the coccyx parietal size (visual cut from the coccyx to the crown of the head with the greatest extension), the bipariate size (distance between the temporal bones, the transverse size of the head), and the head circumference of the baby. Evaluated heart rate, as well as fetal motor activity.
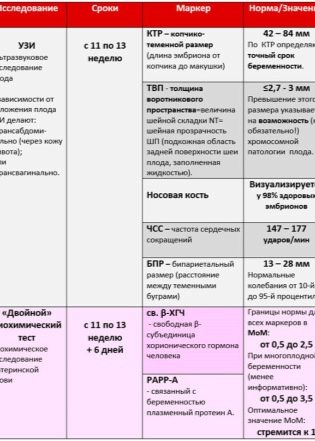
The most specific markers that can become indirect signs of gross developmental defects of the genetic sense are TVP - the thickness of the collar space and the length of the bones of the nose. Special attention is paid to these two parameters. The rates and allowable errors for the first screening are as follows.
Copical parietal size (KTP) - averaged values:
The numerical value of the CTE, mm | Corresponds to the gestation period (week + day) |
33 | 10+1 |
34-35 | 10+2 |
36 | 10+3 |
37 | 10+4 |
38 | 10+5 |
39 | 10+6 |
40-41 | 11 weeks exactly |
42 | 11+1 |
43-44 | 11+2 |
45-46 | 11+3 |
47 | 11+4 |
48 | 11+5 |
49-51 | 11+6 |
52 | 12 weeks exactly |
53-54 | 12+1 |
55-57 | 12+2 |
58-59 | 12+3 |
60-61 | 12+4 |
62-63 | 12+5 |
64-65 | 12+6 |
66-67 | 13 weeks exactly |
68-69 | 13+1 |
70-71 | 13+2 |
72-73 | 13+3 |
74-75 | 13+4 |
75-78 | 13+5 |
79-81 | 13+6 |
A decrease in the CTE may indicate that the woman’s term was delivered with an error, this could be, in particular, due to late ovulation. If indicators of this size lag behind the norm slightly, there is nothing alarming about this, just the doctors will observe the child’s development more closely.However, if the discrepancy with the standards arises for more than 10 days from the actual period and shown by measurements on ultrasound, then we can talk about fetal growth retardation, as well as possible genetic problems in which the child’s formation is slow, incorrect.
Bipariented size (BPR) - norms and options:
Duration of gestation (obstetric weeks) | BPR - the average rate, mm | BPR - allowable vibrations, mm |
10-11 week | Not determined | Not determined |
11-12 week | 17 | 13-21 |
12-13 week | 21 | 18-24 |
13-14 week | 24 | 20-28 |
The bipariented size at the first screening examination is not determined by all doctors and not in all cases. On the eleventh week, this size is quite difficult to withdraw. Strong lag of this size from the gestational age norm often indicates a slowdown in the development of the child due to adverse factors that affect the baby and mother - bad habits, chronic diseases of the woman, placental insufficiency, poor nutrition of the mother, as well as medicines, poisons and toxins - All this can lead to intrauterine growth retardation.
The excess of the transverse segment between the temporal bones sometimes says about the wrong time of pregnancy. This situation happens in women who suffer from an irregular cycle, do not remember the date of the last menstruation, as well as women with early ovulation.
Head circumference - normal:
Obstetric term | Head circumference is normal, mm | Exhaust gas - admissible normal vibrations, mm |
10 weeks | Measurements are not carried out, data not available. | Measurements are not carried out, data not available. |
11 weeks | 63 | 53-73 |
12 weeks | 71 | 58-84 |
13 weeks | 84 | 73-96 |
Heart rate - average:
Obstetric (full weeks) | HR average rate | HR - possible range of normal |
10 weeks | 170 | 161-179 |
11 weeks | 165 | 153 -177 |
12 weeks | 162 | 150-174 |
13 weeks | 159 | 147-171 |
Markers of chromosomal abnormalities - TVP and nasal bones:
Term in weeks + days | TVP-normal, mm | TVP - standard options, mm | Nose bone length - normal, mm | Nose bone length - options, mm |
10+0 -10+6 | 1,5 | 0,8 -2,2 | 1,1 | 1,6-2,7 |
11+0 – 11+6 | 1,6 | 0,8-2,4 | 2,3 | 1,8-2,9 |
12+0 – 12+6 | 1,6 | 0,8 -2,5 | 2,4 | 1,8-3,1 |
13+0 – 13+6 | 1,7 | 0,8 -2,7 | 2,7 | 1,9-3,4 |
14+0 | 1,8 | 0,8 -2,8 | 3,5 | 2,7-4,2 |
The thickness of the collar space is the size of the neck fold from skin to muscle and bone tissue. Many chromosomal abnormalities are characterized by edema, and it is in the zone of the back surface of the neck that it is easiest to examine. The indicator is considered relevant only during the first screening.
As soon as the woman moves to the fifteenth obstetric week (14 full), there is no longer any sense in the amount of the neck collar fold.
For future mothers, who are very worried about the TVP, interesting facts can be cited as reassurance - not every excess of the size of the TVP suggests that the child is sick. So, only 7% of children whose TVP at this time was above the norm (within 3.5-3.8 mm), subsequently were diagnosed with Down syndrome. But when exceeding the norm by 8 mm, if the TBP was 9-10 mm, more than half of the children in the course of the additional examination were sick with one or another chromosome syndrome.
The nasal bones at the very beginning of the screening (10-11 weeks) may not be measured at all, they are too small, so the doctor may simply indicate that the given bones are determined. But since 12 weeks the size is subject to a more accurate formulation.
Due to the fact that many genetic diseases and syndromes tend to flatten the face, the deformation of the facial and cranial bones, the length of the nasal seeds has an important diagnostic value.
Expectant mothers should not worry and be nervous if the nasal bones are a little less than the norm, perhaps, at the mother herself, the future father of the child also has small neat noses. Significant deviation, as well as the complete absence of nasal bones (aplasia) - again is not a reason for panic. These verdicts require additional examination, it is possible that on the next ultrasound scan, in another center, on another, more modern apparatus, the doctor will be able to see the bones of the nose, and their sizes will fully correspond to the norm.
Even if the ultrasound results do not inspire the future mother with optimism, they should not be considered separately from the blood test, because its composition is also very informative.
Decoding of biochemical analysis
It is not necessary for a woman to go into a pile of numbers that laboratory technicians indicate to indicate the amount of a substance in the blood. Everything is much simpler - there are generally accepted standards, which are calculated from the median, so the laboratory assistant always indicates the result in MoM, opposite the numbers. This equalizes the results of different laboratories that set different numerical standards for the content of something depending on the type of equipment and reagents used in the analysis.
So, in the blood of a pregnant woman during the first screening, the concentration of two substances characteristic of the gestation period is examined. This is a hormone that is produced due to the presence in the uterus of the chorion - hCG, as well as plasma protein PAPP-A, which also characterizes the "interesting position" of the woman.
Genetic defects are characterized by different laboratory pictures - with some pathologies the hormonal background decreases, with others the concentration of plasma protein decreases or increases. It is these fluctuations in the amount of pregnancy hormone hCG and protein PAPP-A that act as markers.
As in the case of ultrasound diagnostics, only the prerequisites are determined, the diagnosis is not set.
The presence of the hormone hCG and plasma protein PAPP-A is considered normal in a woman’s blood. in the amount of 0.5-2.0 MoM. If hCG is higher than normal, it is considered that the risk of developing genetic pathology, in particular Down syndrome, is elevated. A decrease in the hormone may indicate that the child is likely to develop Edwards syndrome.
At the same time, an increased level of the hormone may be in a pregnant woman who bears a completely normal child, or rather, twins or triplets - the number of children increases the hCG level in proportion.
If the PAPP-A content is below normal, it is also considered an alarming sign of a high risk of a sick baby being born, and it can also “signal” malnutrition, vitamin deficiency, hypoxia and other problems. But the increase in the PAPP-A protein does not indicate anything pathological, in any case, a high concentration of protein is not characteristic of chromosomal abnormalities.
It can occur in women who are overweight, in pregnant women who smoke, after a previous illness, and also in women who have preconditions for bearing a large fetus.
Biochemical data is interpreted in a complex - It is important to assess the balance between hCG im rarp-a. One parameter is increased or decreased - this is one degree of risk, if the norms are violated at once in two - the risks increase. Found pathologies markers for ultrasound - the risks are even higher.
How are risks determined?
I would like to immediately warn future mothers - to try to independently interpret the analyzes and the results of the ultrasound - a hopeless and nervous exercise. And the point is not that it is difficult for a woman without special education to compare the facts of the study, but that it is not a person who is involved in calculating risks, but a computer with a special screening program.
It contains all the data obtained - about the personality and illness of a woman, about her weight and age, about other important facts, ultrasound data and complex laboratory biochemical research. Based on the overall picture is created "profile".
The computer "compares" and compares this "portrait" with a mass of other profiles, including profiles of women at risk, and derives a mathematical fraction - this is the likelihood of the development of a particular defect in this woman.
The calculation of risks is made on a special form, checked by a specialist, a geneticist just in case, and transferred to the antenatal clinic, which sent tests and initial data to the genetic center to the genetic center.
Risks are individual, for two women of the same age different numbers will be indicated on the forms. If it is indicated that the risk of Down syndrome in a fetus is 1: 950, this means that the probability of pathology is low. The threshold is considered the probability of 1: 350. A fraction of 1: 100 means a very high risk of birth defects.
If the risks are low
If results are obtained that are regarded as low risks, then there is nothing to worry about. The doctor says that the pregnancy is developing normally, the baby is fully consistent with its gestational period. In this case, the woman will second screeningwhich takes place from 16 to 21 weeks of pregnancy.
In the interval between examinations, no special diagnostic measures occur, unless a woman can be given a direction to pass a general urine test before another visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist.
If the risks are high
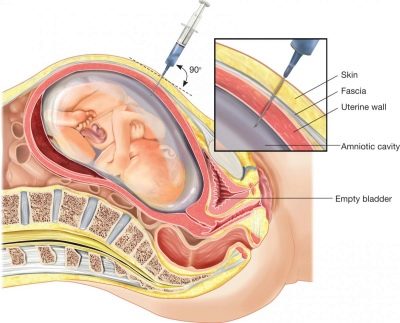
High risk of chromosomal pathology is not a diagnosis yet, so a woman is sent for a consultation to genetics. This specialist rechecks the screening data again, talks to the expectant mother, identifies additional risks and gives direction to the invasive diagnostic procedure.
At this time, a chorionic villus biopsy is done. Through a puncture with a long needle under constant observation, ultrasounds are taken to analyze particles of the chorionic villi. In the laboratory, thereafter with high accuracy - 99.9% is determined if the child has one or another genetic syndrome, neural tube defects. Also a little later, amniocentesis can be performed - the amniotic fluid is taken for analysis.
All invasive procedures pose a certain danger to the fetus, and even modern medicine, sterility conditions and an experienced doctor cannot guarantee that after taking the material for research, there will be no discharge of water, infection of the fetal membranes, death of the fetus, miscarriage.
To go on such a procedure or not, the woman decides.
There is also a non-invasive diagnosis of high accuracy - DNA test. Its essence boils down to the fact that a woman takes a blood test, in which the child's red blood cells are determined from about 8 weeks of gestation. These children's cells are isolated from the total mass and their DNA is examined, all information about the baby is encrypted in it - the available pathology, gender. The downside is that this technique is not available to all women, because its cost is estimated at tens of thousands of rubles. This new research is not included in the set of insurance medicine services.
If a non-invasive DNA test confirms pathology, then a pregnant woman will still have to undergo an invasive test with a puncture, since she can receive a referral to terminate a pregnancy for a long time only after the unfavorable diagnosis is confirmed using chorion biopsy or amniocentesis.
Research accuracy
The accuracy of 99 or 100% prenatal screening can not boast, like most non-invasive diagnostic methods. The accuracy of ultrasound is at 75-85%, the blood test is more accurate, but less informative. Errors in the interpretation of results are not excluded. - not all experts are able to flexibly and thoughtfully analyze the data received from a computer program.
Only traumatic and dangerous invasive methods can boast of high accuracy, but they should be resorted to only in the most extreme cases.
Expectant mothers should not expect from a screening study of any accurate and unambiguous answers to the questions that every pregnant woman has. Results are not a diagnosis or a final conclusion. It so happens that the screening does not show deviations, and a sick baby is born. And a woman who has earned a lot of white hair on the nerves of the soil, while the whole pregnancy went on to various geneticists and ultrasound, is born quite normal toddler.
If the first screening is good, the second can be bad. It happens and vice versa. This does not mean that in the first trimester there was a normal baby, and by the middle of the pregnancy something had happened to him.In conducting screening diagnostic studies, as nowhere else, human factor is great - Much of the results depend on the level of training and the responsible attitude of the specialist to their work, as well as the accuracy of the wording of the laboratory technicians. The facts of banal errors are not excluded.
In any case, the expectant mother should keep herself in her hands, not worry about the small discrepancies between the statistical figures and her results, and completely trust the treating physician.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, worries about screening studies are in vain, and excess tears and bad mood can harm a child.
For more information on this issue, you can find out by watching the video below.