What is ultrasound screening during pregnancy and why do it?
Screening ultrasound is very important during pregnancy. With this method, doctors receive information about how the fetus develops in the womb. This article will help expectant mothers to figure out what this research is being done for.
What it is?
At present, it is impossible to imagine the diagnosis of various pathologies of pregnancy without ultrasound examinations. The essence of the method - principle of penetration and reflection of ultrasonic waves from the internal media of the body. With the help of the pelvic ultrasound, it is possible to identify various abnormalities in the course of pregnancy during the most different periods of intrauterine development of the fetus.
The first trimester is a very important period when the embryo forms all the main internal organs. Timely diagnosis in this period allows to identify developmental anomalies and emerging anatomical defects.
It should be noted that abusing ultrasound in the first weeks of pregnancy is not worth it.
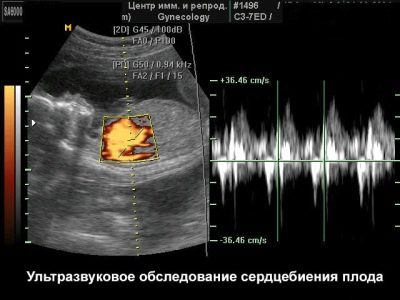
The essence of ultrasound prenatal screening, which is carried out in the 2nd trimester, is already identification of dangerous genetic and chromosomal pathologies. Also at this time it is possible to assess the functioning of all vital systems of the fetus. In this period of development of the unborn child can determine the work of the heart and heartbeat. Ultrasound can also establish a variety of orthopedic disorders.
Dates
In each period of pregnancy is carried out on 1 screening. In this case, the ultrasound can not be considered harmful. More frequent ultrasound can lead to the fact that after birth, the child will have various neurological or mental disorders.
Term 1 is a mandatory period for performing ultrasound screening. Doctors prescribe to undergo such a diagnostic course at 10-14 weeks of pregnancy. 2nd screening is carried out in the next trimester of pregnancy. In this case, the diagnostic complex is carried out at 16-20 weeks.
Screening for 3 trimesters is conducted for women with various abnormalities or abnormalities of fetal development. If the first ultrasound screening tests showed no impairment, then a third screening may not be necessary. The need for a set of studies in this period of pregnancy is determined by an obstetrician-gynecologist who is observing a pregnant woman.
Screening for 3 trimesters is usually carried out at 30-34 weeks. Its duration may be shifted by 7-10 days for medical reasons. In the third period, the identified indicators are necessary for doctors to choose the optimal tactics of obstetric aid.
Ultrasound examination carried out at this stage of pregnancy establishes the presentation of the fetus, as well as the presence or absence of signs of placental insufficiency.
The third screening allows doctors to finally figure out whether to carry out a cesarean section.
What is it for?
Doctors recommend screening for all pregnant women. It is especially important to do such research for women who have a course of pregnancy with various disorders. It is also better not to avoid the passage of ultrasound studies to future moms who conceive a child after 35 years.The presence of close genetic relatives or parents of a pregnant woman of various genetic diseases is an important reason for carrying out an ultrasound.
Possible problems
An ultrasound study conducted at 11-12 weeks, allows you to already identify a rather dangerous clinical condition - anencephaly. It is characterized by a complete or partial absence of the brain in the fetus. The presence of this symptom is an indication for abortion. This pathology is detected, as a rule, by the end of the 1st trimester.
Hydrocephalus - Another serious clinical condition of the fetus. In this case, the ultrasound specialist detects a large amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the baby. Quite often, this feature is combined with other developmental anomalies. The progression of this condition can also be a significant indication for abortion.
Encephalomeningocele - A pathological condition that is well detectable during screening. This is usually a transient pathology. In order to assess and control the course of this condition, doctors prescribe several repeated ultrasound examinations. The diagnosis is completely removed if during the next screening such violations are not established.
It is important to note that the conclusion of an ultrasound is not a diagnosis. To establish the exact pathology, it is necessary to repeat the consultation of an obstetrician-gynecologist, who supervises a pregnant woman.
During pregnancy, several screenings are performed. They allow you to track the dynamics of growth and development of the fetus.
Heart defects - A very important pathology, which can be easily installed with the help of ultrasound. To assess the level of blood flow in this case, doppler mapping is used. With the help of such a test, pathological blood flow (regurgitation) can be determined due to existing irregularities in the functioning of the heart valves. Identification of this pathology is a very important conclusion, which necessarily requires further verification.
The accumulation in the abdomen of the fetus pathological fluid (ascites) - an unfavorable sign. The appearance of this symptom requires the obligatory diagnosis of diseases of the internal organs of a child developing in the womb. In some cases, abnormal development of the cardiovascular system can lead to the development of this condition. Rhesus-conflict also contributes to the accumulation of pathological fluid in the abdominal cavity of the fetus.
If the baby has been identified any genetic or chromosomal pathology, in this case, consultation of a geneticist is required. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe an additional series of blood tests.
Proper preparation
To obtain reliable results it is very important to properly prepare for the study. Doctors give it quite a lot of importance.
So:
- On the eve of ultrasound screening, a pregnant woman must comply lipid-lowering diet. Dinner before the study should be as light as possible. All fatty and fried foods are completely excluded. A week before the study is better to eat the most light, but high-calorie food. A pregnant woman should not limit protein. However, you should choose the lightest types of protein foods. These products include chicken, turkey, white fish and lean beef.
- 2-3 days before the ultrasound screening, the future mom should be limit the use of any vegetables and fruits. They contain quite a lot of coarse fiber, which contributes to the formation of gas. The intestines swollen from gases will not allow the ultrasound specialist to fully conduct the study. In this case, the doctor will give a conclusion about a strong echo negative effect.
- To get reliable results is very important limit intense exercise. This should be done as the firstso with the second screening.Visiting yoga for pregnant women can lead to the fact that the results of ultrasound will be unreliable.
- Pregnant women can't be nervous. Prolonged or prolonged psycho-emotional stress has a negative effect on uteroplacental blood flow. If the future mom is constantly nervous and worried, then ultimately it contributes to the formation of placental insufficiency in her.
The study can be conducted in several ways - transabdominal and transvaginal. In the early stages of pregnancy, doctors prefer to prescribe ultrasound transvaginally. Such a study is carried out only if the future mom does not have any contraindications to its conduct.
Norms
The study is usually conducted on a special couch. Future mom while lying on his back. Later gestation requires a more thorough look. To do this, the ultrasound specialist may ask the future mom to roll over to the left side.
A study with a filled bladder is also helps to get more reliable results. If such a content is required, then the future mummy must be warned about this in the women's clinic in advance. The transabdominal method is usually performed on the background of a full bladder. Transvaginal ultrasound is best done after it is emptied.
After an ultrasound exam, the results are necessarily interpreted. The obstetrician-gynecologist observes the pregnant woman. Doctors do not make ultrasound diagnostics of diagnoses. In some cases, to eliminate the existing pathology requires additional biochemical blood tests.
For better visualization, a specialist treats a pregnant belly with a special gel. This transparent substance is applied to the anterior abdominal wall, and after the study is completely removed. It should be noted that the application of this tool can not cause any allergic manifestations.
In the first trimester, a number of clinical indicators are determined:
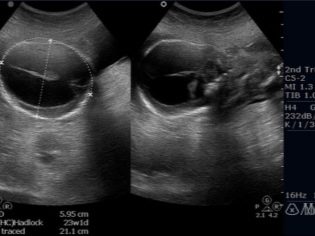
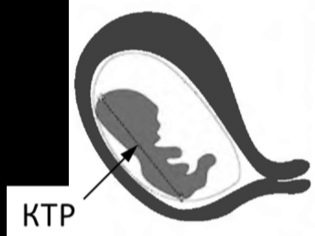
- One of them is the coccyx parietal size. (KTR). To estimate it, the estimated fetal weight is also required. With this indicator, you can set the estimated duration of pregnancy. KTR is estimated in millimeters.
- The length of the nasal bone - Another clinical indicator used to assess the initial period of fetal development of the embryo. The absence of this element in the future baby is an unfavorable symptom. If the nasal bone is absent in the fetus by the 14th week of its development, then in 75% of cases this indicates the presence of serious anomalies.
- Biparietal fetus size (BPR) allows you to evaluate a very important indicator - the development of the fetal brain. Also, this clinical sign may be an indirect manifestation of neurological disorders that form in a child. This indicator is also defined in mm. At the 10th week of pregnancy, the values of this criterion are 14 mm.
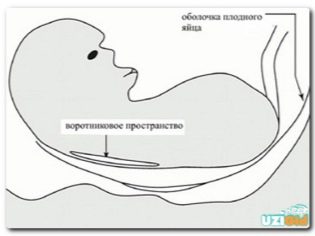
- Collar space thickness - This is an important clinical feature that allows you to identify Down syndrome in the very early stages of its formation. At 11 weeks of pregnancy, this figure is 0.8-2.4 mm. It is very important to carry out the dynamics of changes in this ultrasound criterion over several weeks. This will indirectly confirm or eliminate Down syndrome in a baby.
- For evaluation of the cardiovascular system heartbeat is computed. At 11 weeks of pregnancy, this figure is 153-177 beats per minute. A strong decrease in this criterion is an unfavorable symptom, which requires mandatory additional diagnostics.
Ultrasound screening is necessary to establish the gross pathologies of intrauterine development.This complex of research is not carried out only at the request of the future mother, and must be carried out within the strict time limits regulated for this.
You can learn about why ultrasound screening during pregnancy is done in the following video.