Why do we need screening in the first trimester, when it is conducted and what it shows?
The first weeks of pregnancy are a very important time for both the future mom and her baby. During this period, the child is laying all the vital organs and systems. In order that doctors could not miss a single pathology, the first screening is carried out.
The essence of the study
Prenatal examinations are very important procedures that have appeared in Russia relatively recently. It was developed by specialists from the Ministry of Health, who were concerned about the high maternal and infant mortality. Quite often, various indicators lead to an increase in these indicators. "Silent" pathologywhich develop during pregnancy or at mother, or at her kid.
Doctors call screening specific “screening”. In this case, all women with any pathology of pregnancy are identified. However, pathological conditions do not always manifest themselves in the earliest weeks. It often happens that such pathologies appear only during the 2nd trimester of pregnancy.
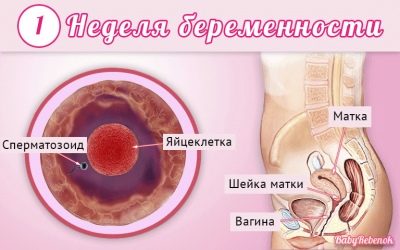
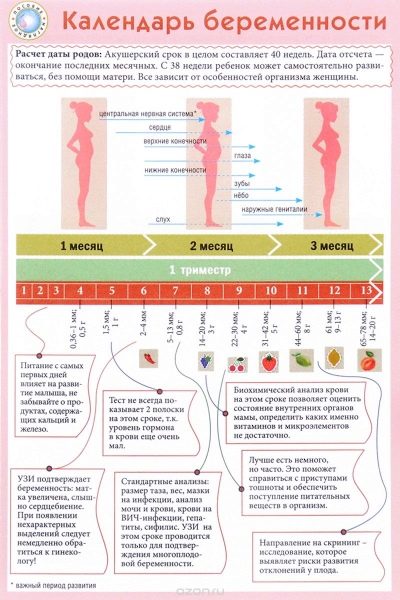
Doctors use obstetric weeks, not months, to determine a term. They divide the entire term of carrying a baby into several equal periods, which are called trimesters. Each of them consists of 12 obstetric weeks. The first screening is carried out in the first trimester of pregnancy.
It is important to note that the obstetric term does not correspond to the term of pregnancy, which future moms calculate.
Usually they consider the first date of pregnancy from the first calendar week from the day of conception. In this case, 12 obstetric week corresponds to the 14th calendar week.
For the entire period of pregnancy you need to spend 3 such sets of studies. They are held every trimester. The complex of studies conducted in each period of pregnancy is different. This is due to the daily changing hormones in a pregnant woman, as well as the physiology of the developing fetus.
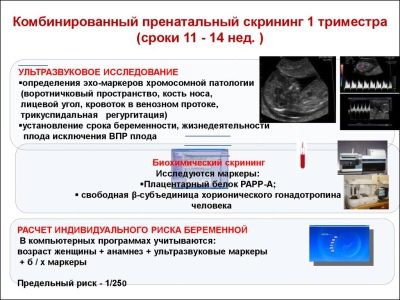
A comprehensive screening study includes the delivery of some biochemical analyzes and the mandatory ultrasound. Combined methods allow for more accurate results. The evaluation of the results obtained is carried out by an obstetrician-gynecologist. If, after the study, the doctor cannot exclude the presence of any genetic diseases in the future mom, he will refer her for a consultation to the genetics.
Dates
Usually the first screening is carried out at 11-13 obstetric weeks of pregnancy. Dates of the diagnostic complex can be shifted by 7-10 days for medical reasons.The exact timing of the first screening must be determined jointly with an obstetrician-gynecologist, who observes a pregnant woman during the entire period of pregnancy.
The duration of the first screening may be different. Such time diagnostics usually lasts several days. Between the delivery of biochemical analyzes and ultrasound may take a couple of weeks. This is a completely normal situation and is quite common. Any changes to the dates of the research must be agreed with your doctor.
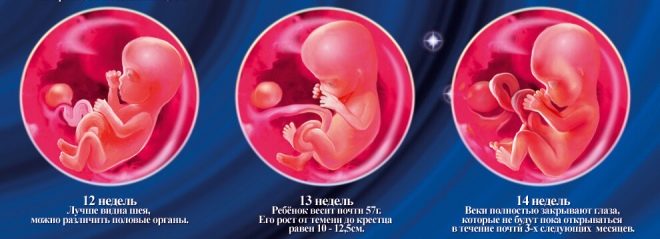
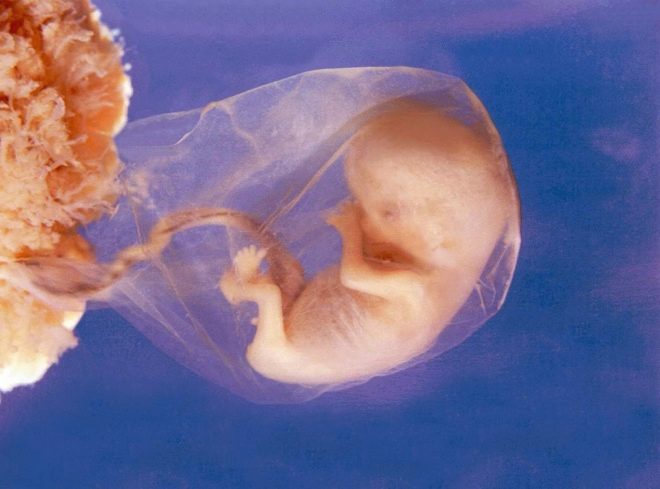
This period was chosen by chance: a new stage of pregnancy begins, which is called fetal. Previously, doctors called fetal. At the end of the twelfth week of pregnancy, doctors call the baby no longer an embryo, but a fetus.
Who should not miss the study?
Currently, doctors recommend to take such a study for all pregnant women, without exception. This preventive medical procedure allows timely identification of dangerous organogenesis pathologies in fetuses.
The first 12 obstetric weeks - a time of active growth and development of all the internal organs of the baby. The impact of any external factors can lead to the formation of pathologies. Only a comprehensive diagnosis will allow them to identify. Also at this time it is possible to identify and associated diseases of the internal genital organs of the mother.
Doctors recommend to be sure to pass screening in the first trimester for expectant mothers, in which conception occurred after their 35th birthday. It is also important to conduct such a complex of studies for all pregnant women with a burdened family history of genetic and chromosomal diseases.
There is also a high age risk for the development of these pathologies. In this case, the first screening should be women who become pregnant after 40 years. Future moms, who often had spontaneous miscarriages or abrupt pregnancies were suddenly interrupted, should also not miss such a complex diagnosis.
Doctors recommend screening in the first weeks of pregnancy also to expectant moms who have severe concomitant diseases of internal organs.
Such a diagnostic complex is also necessary for pregnant women suffering from diabetes. The most dangerous is its insulin-dependent variant.
If the future mother takes hormonal or glucocorticosteroid drugs all the time, screening is required. These agents may have an adverse effect on fetal organogenesis. If the intake of these drugs can not be canceled for the entire period of carrying a baby, it is necessary to control the course of pregnancy.
The first screening is necessarily carried out and expectant mothers who already have children suffering from genetic or severe somatic diseases. Increased genetic risk is a reason for the mandatory passage of such a complex study.
Also, the first trimester screening is necessarily carried out by pregnant women who abuse alcohol or continue to smoke. In this case, the risk of the formation of dangerous intrauterine pathologies increases several times. You should also be screened if the expectant mother and fetus different Rh factor.
How to prepare?
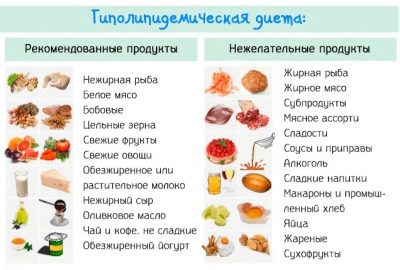
Proper preparation is necessary to obtain reliable test results. Before taking biochemical tests, doctors prescribe future moms to follow a lipid-lowering diet. It excludes the use of fatty and fried foods. Also all foods rich in cholesterol are banned. Saturated fats that enter the bloodstream along with food can cause false results.
Observe a lipid-lowering diet before the first screening should be 5-10 days before the study. Dinner on the eve of the trip to the laboratory should be made as easy as possible, but nutritious and high-calorie.Better to have a foundation power supply were protein products. You can supplement them with any cereal garnish.
To eat a lot of vegetables and fruits for 2-3 days before the screening ultrasound should not be. They can cause severe gas formation. This will make research difficult. The intestine swollen with gas often causes the phenomenon of echo negative.
If the future mom still continues to smoke while carrying the baby, then before going to the laboratory it is better not to do it. Nicotine, which is contained in cigarettes, can lead to distorted results. Also excluded any drinks that contain alcohol in its composition.
Go to the lab should on an empty stomach. Doctors recommend taking tests in the morning, immediately after waking up. Biochemical tests that are performed in the evening are often unreliable. You should not have breakfast before going to the lab. The last meal is dinner.
Doctors allow to pass laboratory tests drink some water. Drinking a lot before carrying out an ultrasound in early pregnancy should not be. This can lead to a strong filling of the bladder. Pre-consumption of fluid may be required only when carrying out transabdominal ultrasound.
Strong physical activity before the first screening should be excluded. Future moms should remember that even the usual household activities during pregnancy can lead to a distortion of the results. Doctors note that the usual cleaning of an apartment on the eve of a trip to the laboratory can lead to unreliable test results.
Strong psycho-emotional stress before the study should also be excluded. Nervous or worried future moms should not not only before the first screening, but throughout the entire period of pregnancy.
Protracted stress leads to disruption of the internal organs, which ultimately leads to a distortion of the results.
How is it going?
Screening is divided into several stages. Usually the first one is camping trip to the lab. You can take the tests both in an ordinary women's clinic and in a private one.
In the first case, you need a referral for tests, which the obstetrician-gynecologist issues for consultation. This medical form indicates the personal data of the patient, as well as the estimated duration of pregnancy.
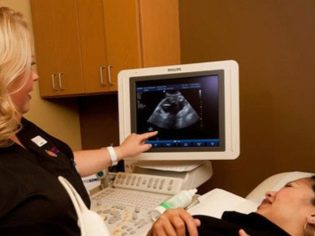
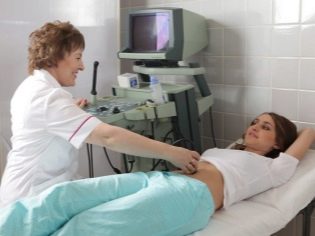
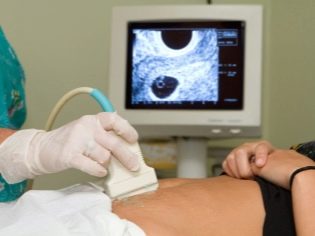
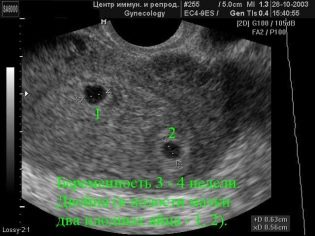
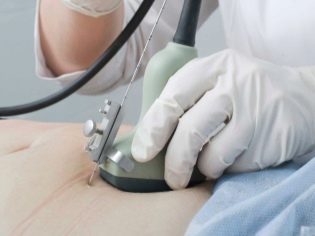
The next screening step is ultrasound. In the early term, this research can be done in different ways. If the pregnant woman does not have any medical contraindications, transvaginal examination is performed. For this purpose, a special ultrasonic sensor is used, which is inserted into the vagina.
There are a number of medical contraindications for conducting a transvaginal study:
- These include any acute diseases of the internal genital organs of the mother.
- Acute colpitis or vaginitis are reasons to choose an alternative ultrasound method.
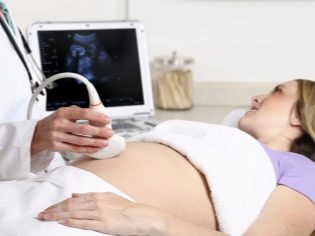
In this case, already running transabdominal examination. For his conduct, the doctor uses a special ultrasound sensor, which drives the future mom's belly. The image in this case appears on a special screen - the monitor. During the study, the future mom can see her future baby with the doctor. At such a survey may also be present and dad child.
To obtain better visualization, ultrasound specialists use a special diagnostic gel. It is applied to the skin of a “pregnant” tummy immediately before the procedure. You should not be afraid of the aggressive effects of this gel to future moms. Its composition is completely hypoallergenic.
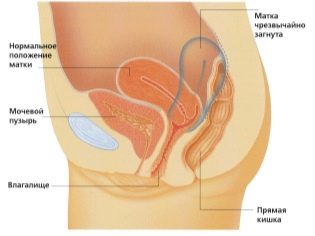
Ultrasound examination is carried out on a special couch. Future mom is laid on his back. In the early stages of pregnancy it is possible to conduct research in this position.Only in those situations when the future mom has a pathological curvature of the uterus, you may need to turn to the left or right side.
If the study is conducted in a regular clinic, then the woman should definitely bring a towel with her. It will be required in order to lay on the couch.
Also it is necessary to take along special paper handkerchiefs or napkins. They will be required in order to erase the remnants of the diagnostic gel from the abdomen.
What shows?
During the first screening, doctors examine several important biochemical markers. Any abnormality must be evaluated by an obstetrician-gynecologist.
With multiple pregnancies of twins or triplets, biochemical indicators at this stage of pregnancy may be somewhat different.
About PAPP-A
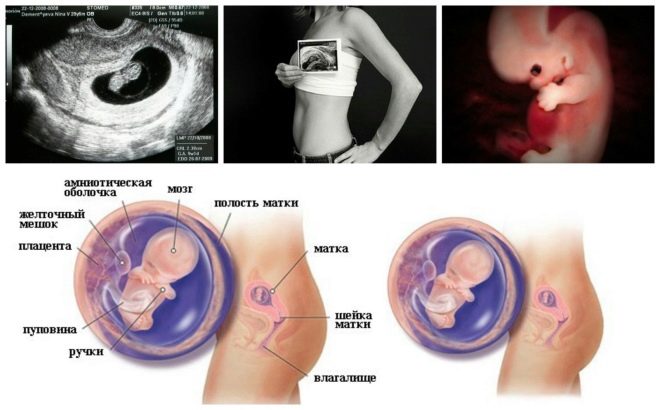
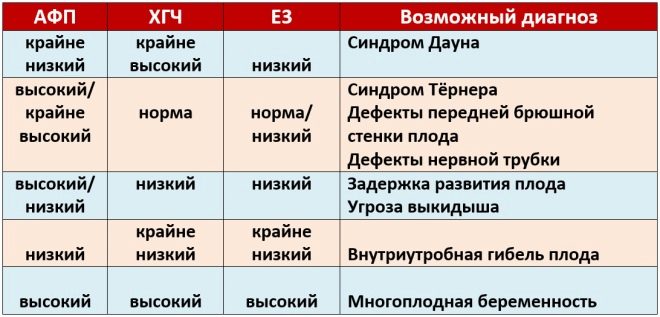
This specific biochemical marker is used to assess the risk of genetic and chromosomal abnormalities. Pregnancy associated plasma protein A or PAPP-A also allows these diseases to be identified at fairly early stages of their formation. This substance during the development of the fetus is produced by the placenta.
The delivery of this analysis is obligatory for future moms who have conceived a baby after 35 years. Also, such a study should be carried out in women who have been diagnosed with HIV - infection or parenteral hepatitis B and C.
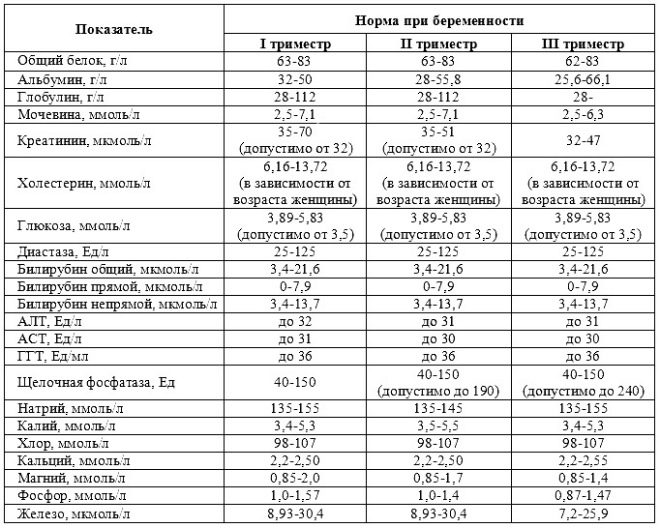
Normal values of this indicator significantly depend on the duration of pregnancy. On the term of 12 obstetric weeks, this criterion is 0.7-4.76 IU / ml. Next week the norm of this indicator is 1.03-6 IU / ml.
If in this period of pregnancy the values are significantly below the norm, then this may indicate the presence of a genetic pathology.
In this situation, the doctor will necessarily send the future mom to undergo additional diagnostics.
About chorionic gonadotropin
During the study, a particular b-fraction of this substance is determined. This hormone is also called hCG. During the entire period of pregnancy, the concentration of the substance varies. In the first weeks it is maximum. The content of gonadotropin is significantly reduced immediately before childbirth.
The gonadotropin after the conception, when the egg cell merges with the sperm cell, is quite strongly increased. In this case, the chorion begins to produce the first portions of HCG almost in the first hours after pregnancy.
The concentration in the blood of this substance increases significantly in multiple pregnancies, as well as in certain pathological situations.
In the second trimester, this indicator stabilizes and practically does not increase. This situation persists until delivery. The decrease in the concentration of hCG in the last trimester of pregnancy is physiological. It is necessary for natural childbirth.
For ease of use, doctors have created a special table, which made normal indicators of hCG. Obstetrician-gynecologists use it in their daily work. Below is the table in which normal gonadotropin indices are included during the first screening:
Gestational age (in obstetric weeks) | HCG concentration |
10 | 25,8-181,6 |
11 | 17,4-130,4 |
12 | 13,4-128,5 |
13 | 14,2-114,8 |
About ultrasound
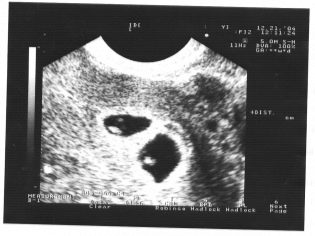
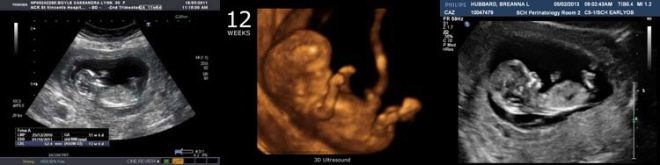
Imagine the first screening without ultrasound is impossible. Doctors have developed several criteria for assessing intrauterine development. They are different in each trimester of pregnancy.
The first weeks of pregnancy are pretty early. The frequency of technical errors and errors at this time is quite high.
During the first screening, an experienced ultrasound specialist can even determine the sex of the child. If the future boy or girl does not deviate from the ultrasonic sensor, then they can be seen quite clearly.
Determine the sex of the future baby up to 12 weeks is almost impossible. The risk of errors in this case is very high.
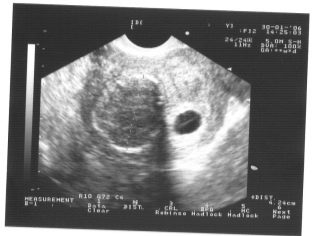
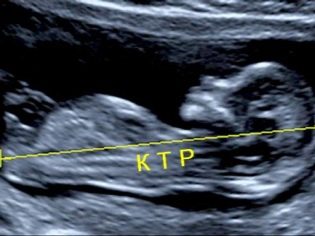
About coccyx parietal size
Copical-parietal size (CTR) is very important in assessing fetal intrauterine development. This criterion is necessarily compared with the weight of the baby and the duration of pregnancy. There is a definite pattern - the “older” the fruit, the larger the coccyx-parietal size.
During the first screening, the normal CTE values are as follows:
- at week 10 - 24-38 mm;
- at week 11 - 34-50 mm;
- at week 12 - 42-59 mm;
- at week 13 - 51-75 mm.
Future moms begin to worry much if this indicator deviates from the norm. Panic should not be. Small deviations of this indicator may not be due to the presence of any pathology. A small KTR may be a miniature baby. Especially often this feature occurs in children, whose parents are also of small stature.
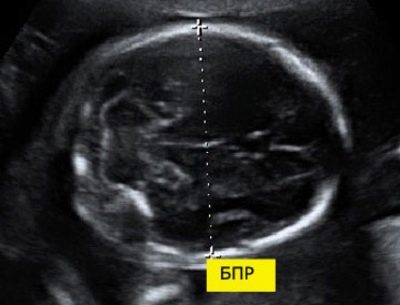
Pro biparietal size
To calculate this indicator, the linear distance between the two parietal stones is measured. Doctors also simply call this parameter - "Head size". Assessment of abnormalities of this ultrasound allows you to identify dangerous pathologies of the fetus, some of which may even lead to spontaneous abortion.
At 11 weeks of fetal development, this figure is 13-21 mm. By week 12, it changes to 18-24 mm. A week later, this figure is already 20-28 mm. Any deviations from the norm can be a manifestation of emerging pathologies.
Too big head of the fetus with a narrow pelvis of the mother may be an indication for a cesarean section. However, the need for surgical treatment is established only in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
In such a situation, doctors recommend that you definitely go through two more diagnostic systems.
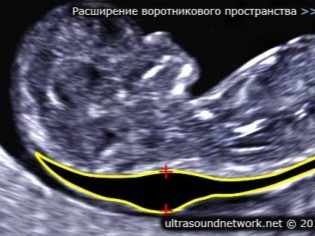
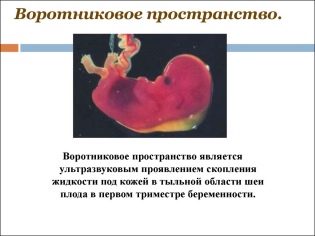
About the thickness of the collar space
Also, this indicator is what doctors call the size of the neck fold. In appearance - it is a rounded education. It is located between the neck and the upper surface of the skin fold of the fetus. It is the accumulation of fluid. This study is carried out precisely in the first trimester of pregnancy, because the neck fold is well visualized.
Collar space thickness gradually decreasing. Already by the 16th week of pregnancy, this formation is practically not visualized. Normal values at 12 obstetric weeks of intrauterine development are 0.8-2.2 mm. A week later, this value is already 0.7-2.5 mm.
A change in this indicator is usually a manifestation of trisomy. These dangerous pathologies are manifested by various genetic pathologies.
This is how Edwards and Patau syndrome, Down syndrome, and Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome can manifest. Trisomy is a pathology when, instead of a binary set of chromosomes, another “extra” third chromosome appears in the genetic set.
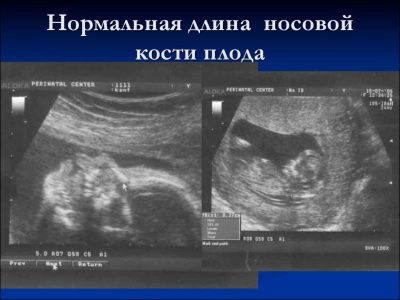
About the nasal bone
This bone formation is a very important criterion for ultrasound diagnostics of the first screening. The nasal bone is elongated, has a quadrangular elongated shape. This is a pair education. During the study, the doctor must measure the length of this bone element. At 12-13 weeks of intrauterine development, the nasal bone is 3.1–4.2 mm in size.
If this bone element in the baby is missing, then it can speak about the presence of genetic or chromosomal pathology. Reducing the length of the nasal bone is also a consequence of emerging diseases.
At weeks 10-11, an experienced ultrasound specialist can only determine the presence or absence of this bone element.
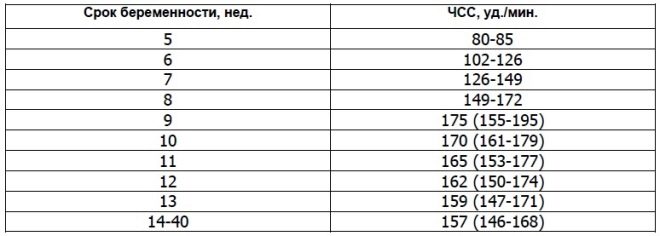
About heart rate
This important parameter is determined from the first screening and in all other weeks of pregnancy. If the heart rate deviates from the norm, then this indicates a problem in the body of the fetus. Significant deviations of this indicator can occur even with a very dangerous pathology - placental insufficiency.
Scientists have found that the fetal heart muscle begins to contract in the third week after conception. It is possible to determine this sign already from 6 obstetric weeks. For a correct assessment of this indicator, the heart rate of the fetus and its mother is correlated.
At 10 weeks of pregnancy, the rate of this indicator is 160-179 beats per minute. At week 11 - 153-178. By the 12th week of pregnancy, this figure varies to 150-174 beats per minute.
In the first 4-6 weeks of fetal development Heart rate is increased by 3 beats daily. With the help of high-precision ultrasonic equipment, this figure is well defined. For the study, ultrasound specialists use a special cardiac examination mode, which is called four-chamber. It allows you to consider the atria and ventricles.
If various irregularities were identified during the screening ultrasound, Doppler imaging may be required. It helps to detect abnormal blood flow in the heart valves.
Such regurgitation may indicate the formation of a dangerous heart disease. In order to correct the resulting irregularities in this case, surgical cardiac surgery may be required immediately after the birth of the baby.
The size of the brain is a very important parameter studied. At this stage of intrauterine development, doctors still cannot evaluate all intracerebral structures. The symmetry of their structure speaks of the normal development of the brain.
Experienced ultrasound specialists also determine the location and structural features of the chorion.
Evaluation of the structure of the cervix is a very important indication. During an ultrasound examination, doctors also evaluate the size and structural features of the internal genital organs of the future mother.
Evaluation of uterine blood flow is a very important indicator, which is examined during the first screening. Any pathologies that are detected at this stage are very important in the future prognosis of the development of pregnancy. Reduced uterine blood flow can lead to a serious complication - the development of fetal hypoxia.
Increased uterine tone - a very unfavorable condition. If doctors find this symptom during pregnancy, then they, as a rule, offer the expectant mother to be hospitalized “for preservation”. There, she will be provided with the necessary treatment that will help eliminate hypertonus and normalize the placental blood flow.
About MoM
Multiple of median or MoM is a specific indicator that is used by doctors to identify genetic pathologies in the fetus. It is calculated using a special computer program.
For the calculation requires the introduction of the initial indicators of the future mom, as well as the results of the obtained results of the ultrasound.
Doctors believe the rate is normal from 0.5 to 2.5. For the correct interpretation of the obtained indicator, doctors also take into account a number of associated diseases in a pregnant woman, her race, as well as other necessary parameters. Abnormalities are manifestations of genetic or chromosomal pathologies.
Genetic screening
If after the screening the doctors determine any signs of genetic diseases in the baby, then the future mom is surely sent for a genetic counseling consultation.
A visit to this doctor will also not be superfluous for women whose close relatives have any chromosomal diseases. Burdened history of various congenital abnormalities - a significant reason to appeal to the family genetics for consultation.
For example, the wording “The risk of developing Down's disease in a baby is 1: 380” suggests that out of 380 healthy babies, only one child will have this congenital disease.
Obstetricians and gynecologists identify several high-risk groups.Women who fall into this category should definitely be referred to a consultation for genetics. Specialists believe that the high risk of developing pathology is a ratio of 1: 250-1: 380.
Doctors secrete several of the most common chromosomal pathologies, which often develop in the first trimester of pregnancy:
- Patau syndrome is one of these diseases. It is characterized by trisomy 13 pairs of chromosomes.
- An additional 3 chromosomes in 21 pairs leads to the development of Down's disease. In this case, 47 appears instead of 46 chromosomes in the genetic set of the baby.
- The loss of one of the chromosomes in the karyotype of a baby leads to the development of a very dangerous genetic disease - Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome. This pathology is manifested by a pronounced lag of the sick child in physical and mental development from their healthy peers.
- The presence of an additional third chromosome on pair 18 is a sign of Edwards syndrome. This pathology is extremely unfavorable. It is usually combined with the formation of many different congenital disorders and malformations. In some cases, this congenital disease may be incompatible with life.
Kids who have formed Edwards or Patau syndromes very rarely live to a year. Kids with Down's disease live much longer. However, the quality of life of these babies is significantly affected.
Such “special” children need careful care and constant attention of their parents.
Genetic screening is carried out In all countries. At the same time, only the list of biochemical analyzes included in the survey is different. Immediately it should be noted that the indications for abortion in different countries differ. This situation is largely due to better socialization of people with genetic syndromes abroad.
Genetic diseases are quite dangerous pathologies. The establishment of such a diagnosis only by the results of the screening is not done. To clarify chromosomal pathologies, a geneticist may prescribe additional research to a pregnant woman. Some of them are invasive.
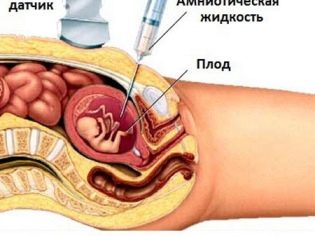
To obtain a genomic collection of the fetus often carried chorion biopsy. In some situations, puncture of the amniotic bladder is required. This study is also called amniocentesis. Also during this diagnostic procedure, experts take away the amniotic fluid for analysis.
Placental biopsy is an invasive study necessary to exclude a number of combined pathologies of the fetal membranes. To carry out this examination, doctors use special puncture needles that pierce the skin of a pregnant woman. There is a risk of a secondary infection during this procedure. It is worth carrying out this research only under strict medical indications to exclude conditions dangerous for the life of the fetus.
With the help of cordocentesis, doctors can also reveal various pathologies in a baby. For this is investigated umbilical cord blood. The timing of such a procedure may be different. Often the need for such an invasive examination is taken collectively.
Many doctors believe that the risk of developing genetic pathologies is directly related to age.
Women who decide to conceive a baby after 40 years of age should think very seriously about such a decision. Doctors quite often recommend them to contact to consult genetics still at the planning stage of pregnancy.
If during the screening the doctor has established signs of dangerous genetic diseases, then he must warn the future mom about it. Incompatible with life pathologies are absolute indications for abortion. The final decision of this question remains for the woman.
Decoding results
Interpret only one analysis or ultrasound can not.To establish the diagnosis requires a mandatory comprehensive assessment of all the obtained tests and the conclusion of ultrasound. The results are interpreted by an obstetrician-gynecologist who monitors a pregnant woman. In difficult clinical cases, it may even be necessary to have a medical consultation.
Edwards syndrome is also accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of PAPP-A in the blood. Also for this pathology is characterized by abnormal human chorionic gonadotropin. This disease occurs in babies with a frequency of 1: 8000. In the first screening, it is quite difficult to identify congenital anomalies of the internal organs. They are detected by the fetus already during the 2 and 3 screening.
The main indicators of an ultrasound scan help doctors identify various pathological conditions in the fetus at the earliest stages of their formation. Thus, an increase in biparietal size may be a sign of a developing hernia of brain tissue or a growing neoplasm. As a rule, such pathologies are considered incompatible with life and are indications for abortion.
Hydrocephalus of the brain in the fetus is also manifested by an increase in biparietal size. To assess this pathological condition, the dynamics are necessarily evaluated. To do this, doctors prescribe several repeated ultrasounds that are required in the next trimesters of pregnancy. The negative dynamics of the development of this state may lead to abortion and emergency medical treatment.
Experienced specialists during the first screening can also reveal various defects in the structure of the neural tube. Doctors call this pathological condition a meningoencephalocele. Corne de Lange syndrome is a very rare genetic pathology that is incompatible with life.
Cord hernia is another dangerous congenital malformation, which is accompanied by multiple disorders of the internal organs. In this state, they fall into the region of the anterior abdominal wall of the fetus. This pathology is extremely unfavorable.
Deviations from normal values in biochemical analyzes are very important signs of the development of genetic diseases. A decrease in PAPP-A is quite often manifested in Down syndrome. This pathology, identified on this period of intrauterine development of the fetus, can be a bright sign of a spontaneous miscarriage or spontaneous abortion.
Smith-Opitz syndrome is one of the most dangerous genetic diseases that can be suspected during the first screening. It is due to strong mutations in the genetic apparatus. This pathology is characterized by combined disorders of cholesterol synthesis, pathologies of the nervous system, as well as orthopedic disorders. This disease occurs not so often - with a probability of 1: 25 000.
.
Increased gonadotropin is also a consequence of emerging pathologies in the body of the fetus. Elevated hCG may also occur in some diseases that occur in the future mom during her pregnancy. Usually, severe forms of diabetes mellitus, as well as strong toxicosis.
Reduced hCG is often a sign of a pathological course of pregnancy. This condition can also develop with placental insufficiency. This pathology can lead to severe hypoxia. To assess the risk of the formation of various diseases, doctors use a special program called PRISCA.
After conducting such a computer diagnosis, the doctor conducting this study issues a conclusion in the hands of the future mom. It identifies all pathologies identified, as well as the risk of developing genetic diseases.
What can affect the results?
If the pregnancy occurred as a result of in vitro fertilization, the indicators of biochemical tests may be different. In this case, the interpretation of the results must be very carefully:
- Diagnosis is carried out for each of the kids. In this case, chorionic gonadotropin may exceed normal values by 20%, and PAPP-A, as a rule, decreases.
- Excessive weight in the future mother is another factor that can lead to a distortion of the results. In this condition, all the studied hormones increase. If the future mother has signs of body mass deficiency, in this case, on the contrary, the concentrations of biologically active substances are significantly reduced.
- Multiple pregnancy - reason for a more thorough interpretation of the results. In this case, hCG increases significantly. The PAPP-A level can be maintained within the normal range. An isolated assessment of biochemical markers without ultrasound during pregnancy with twins or triplets in any case should not be carried out.
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus leads to disruption of metabolic processes. Ultimately, this can lead to deviations from normal values in biochemical analyzes.
How much does research cost?
Pass the first screening can be in a normal clinic. However, not all medical institutions have a good material and technical base and equipment. Often it happens that many biochemical studies to perform in the usual female consultation simply will not work. Such a problem is especially acute in settlements where few inhabitants live.
Ultrasound examination is also mandatory component of the first screening. In some cases, it is better to conduct such a survey on the equipment of the expert level. Unfortunately, not all medical institutions are equipped with such devices. Conducting ultrasound on the equipment of the expert class is required for pregnant women with serious pathologies of pregnancy.
Future moms suffering from severe diseases of internal organs can be sent to the perinatal center. Usually pregnant women with various heart defects go there.
In this situation, the risk of developing various intrauterine defects in their future babies increases many times.
The first screening can be done at a licensed private clinic. The passage of the complex of research in this case, as a rule, is very comfortable. All consumables are already included in the cost of screening.
The cost of such a complex of diagnostics may be different. It also varies significantly in different cities. For the biochemical analyzes of the future mom will have to pay from 1200 to 3000 rubles. When expanding the complex, the cost may increase by 1.5-2 times.
The price of a screening ultrasound is usually 2000-5000 rubles. The cost of the procedure depends largely on the qualifications of the specialist who conducts the study.
The following video review will tell you what can be seen on the first screening.