Screening during pregnancy at 12 weeks: how do they do it and what does it show?
If the pregnancy is uneventful, the mother feels good, then for the first time she will be able to look at her baby during the first screening at about 12 weeks of pregnancy. That is a screening study at this time, we will tell in this article.
What it is?
There are three screenings for pregnancy. It is recommended to hold the first Ministry of Health for a period of 11-13 weeks, the 12th week is considered optimal. Then the screening study takes place in the second and third trimesters (at 16-24 weeks and at 30-36 weeks).
The survey that is carried out at the very beginning of the process of carrying a baby includes Ultrasound, and biochemical analysis of blood for the content of the hormone hCG and protein PAPP-A. For a number of characteristic markers that are found in the ultrasound diagnosis room, as well as on the concentration of hormones and proteins in the analysis of a pregnant woman, a preliminary calculation is made of the risks of a baby with incurable and fatal genetic pathologies.
This stage of prenatal diagnosis reveals women who are most likely to have a toddler with Down syndrome, Turner and Cornelia de Lange syndromes, Patau syndrome, Edwards syndrome, gross neural tube defects, and other developmental abnormalities that do not leave any chance for a cure. and normal life.
Previously, screening was performed only for pregnant women who are at risk — women who are already 35 years old and older who become pregnant by blood relation, those who have previously had children with genetic problems or women who have relatives with hereditary diseases. for my part or my husband's side. If the expectant mother took drugs that are prohibited during the child's early term, she was also prescribed a screening study.
Now this diagnosis is prescribed to all the fair sex in an “interesting position”. Of course, a woman may, for personal reasons, and refuse screening, but this is not entirely reasonable, because the examination itself does not oblige anyone to anything.
It should be noted that According to the results of screening during pregnancy at 12 weeks, no one will make any diagnosis. This is not part of the task of screening research. A woman will only be counted on individual risks to give birth to a sick baby, and whether they are healthy, it can be established by other methods that will be recommended by an obstetrician and a geneticist in the event that the risks are high.
The first screening is considered the most important and informative. They carry it out free of charge in consultations at the place of residence, the directions for a blood test and a ticket to the ultrasound examination room are issued by the doctor, to whom the woman has registered for pregnancy.
Procedure and preparation
During the first trimester perinatal examination, it is very important to follow a strict procedure.Ultrasound diagnosis and delivery of blood from a vein is planned for one day so that the time interval between these two actions is minimal.
Usually, they are first examined in an ultrasound examination room, and then with a filled out form, they are taken to the treatment room to donate blood. However, in some consultations the order is reversed. In any case, both surveys are undergoing strictly in one day.
So that the test results are not affected by negative factors, which include biochemical changes in the blood, the accumulation of gases in the intestines, the woman is recommended carefully prepare for the diagnosis. Two days should go on a short diet - do not eat fatty and very sweet food, fried and smoked, six hours before the blood test should not eat at all. A blood test is taken on an empty stomach.
Before the ultrasound for a couple of hours should take "Smektu" or "Espumizan"To get rid of intestinal gases, which are faithful companions of pregnancy, because they can put pressure on the pelvic organs and the ultrasound results may be inaccurate.
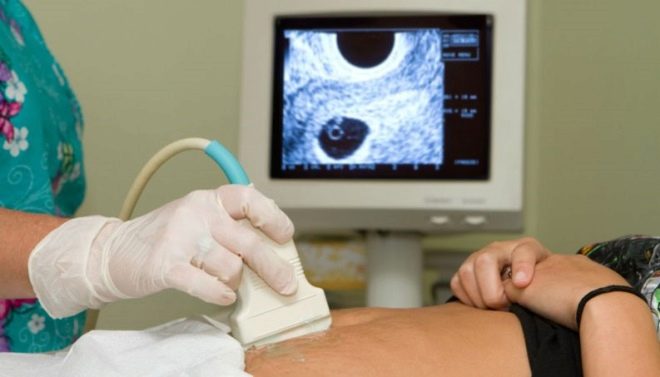
Ultrasound at 12 weeks is performed with a transvaginal probe.; the second way is on the stomach, until it gives a clear picture and understanding of what is happening inside the uterus.
On the appointed day, a woman comes to the office of her obstetrician-gynecologist, is weighed, her height is measured and a detailed questionnaire is filled out. The more data it contains, the more accurately the risks will be calculated. Data on previous pregnancies, miscarriages, abortions, age and weight of a woman, data on her bad habits (smoking, alcohol), information about her husband and health of close relatives are entered into the questionnaire.
Then there will be an ultrasound, and then blood donation. The overall results will make a single form, a special program "compare" the genetic portrait of a pregnant woman, along with her analyzes, with the "portraits" of women with great risks to give birth to a sick baby. As a result, will be given an individual calculation.
Ultrasound procedure
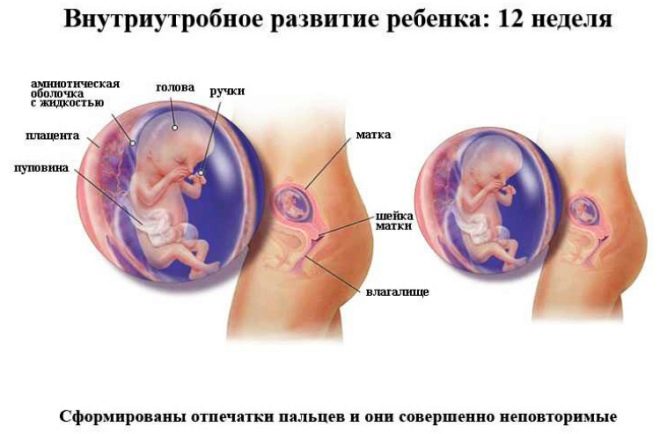
In the ultrasound room, the doctor examines the baby, determines whether everything is well with him, in which place of the uterine cavity he is entrenched, and also checks the baby for the presence of markers that show a high probability of having a child with genetic syndromes. At week 12, the future mother will be able to see her child, listen to his small heart beating, and also see the movements of the fetus, which she does not physically feel.
The doctor in the first trimester screening protocol will definitely indicate how many fetuses are visualized in the uterus, do they show signs of vital activity, They will also describe the main dimensions, which will clarify the terms of the “interesting situation” and find out how the development of the baby proceeds.
Indicators of the developmental rate at 12 weeks are:
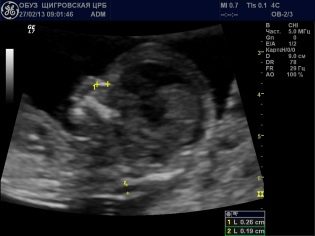
Fetal head (FH) circumference - 58-84 mm, most often - 71 mm.
The coccyx-parietal dimension (CTD) is 51-59 mm, most often 55 mm.
The bipariented head size (BPR) is 18-24 mm, most often 21 mm.
Heart rate (HR) - 140-170 beats per minute.
Motor activity is present.
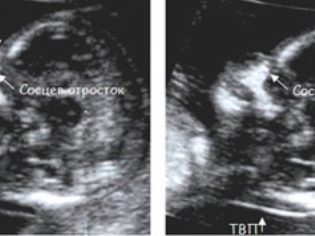
In addition, the doctor determines the two most important for the diagnosis of genetic pathologies of the marker - the thickness of the collar space and the presence of nasal seeds in the crumbs. The fact is that in children with gross developmental defects, the neck fold is enlarged due to the subcutaneous fluid (puffiness), and the nose is flattened. Consider the remaining facial bones will be able only in a half or two calendar months.
TVP (collar thickness) at 12 weeks with no pathologies does not go beyond the range of 0.7-2.5 mm. If the baby has this parameter slightly exceeded, the expectant mother may be recommended to undergo an ultrasound scan again in a week. If TVP significantly exceeds the upper limits of the norm, additional examination will be required, the risks of giving birth to a sick baby increase. It is about excess from 3,0 mm and above.
It is much more difficult to see the nasal stones, they are not always visualized at 12 weeks, the fetus can settle back to the doctor’s sensor and stubbornly don’t want to turn around and let your nose measure. If this was succeeded, the values of the length of the bones of the nose on this period are considered to be normal values that do not go beyond the range of 2.0-4.2 mm.
If the doctor has indicated that at 12 weeks these ossicles are not visualized or their sizes are less than 2 mm, the program that calculates the risks will increase the individual probabilities of the birth of a child with Down syndrome, Turner, Patau.
In fact, a baby may have just a small miniature nose, which is still difficult to capture in numerical terms, especially on the old ultrasound scanner with low image clarity.
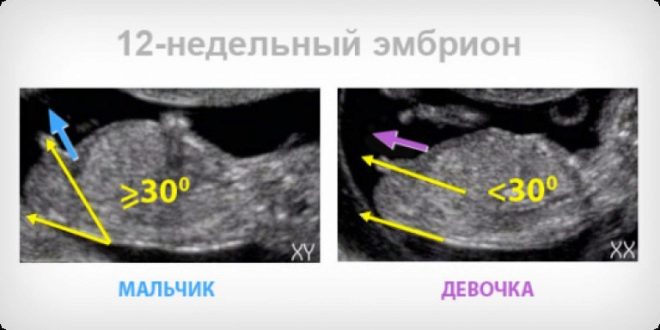
Theoretically, at 12 weeks, you can already try to determine the sex of the child, because the external genitalia are formed, and if the baby is conveniently located and open to the eye of the diagnostician, it can be easily noticed. However, one should not expect the doctor to guarantee that it is a boy or a girl who will be born. The sex at this time can only be called presumably (the probability of an accurate hit is about 75-80%). More precisely, the doctor will assess the sexual characteristics of the baby on the next ultrasound, after 16-17 weeks of pregnancy.
Additionally, at the end of the first trimester, ultrasound examines the likely threats of interruption of gestation - the thickened walls of the uterus may indicate the presence of hypertonia, as well as the condition of the cervix, fallopian tubes, cervical canal.
Blood chemistry
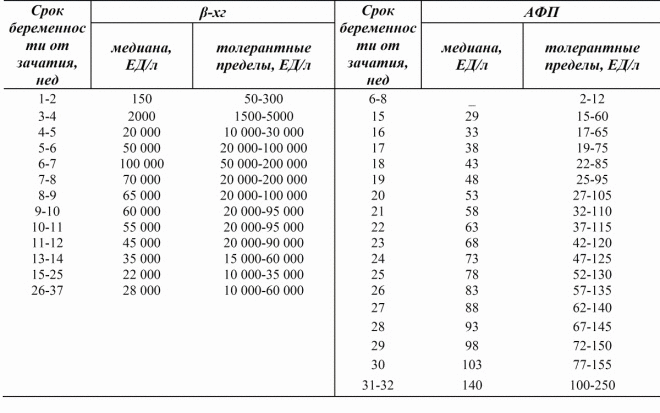
In the analysis of the venous blood of a pregnant woman, a laboratory technician detects the amount of the hormone hCG and plasma protein PAPP-A contained in it. Due to the fact that only two blood components are evaluated, the first screening test is called a “double test”. The results of this study, in contrast to the ultrasound data that a woman gives out immediately after passing, will have to wait from several days to several weeks - this depends on how long the queue lined up for research in an accredited medical genetic laboratory.
You can only guess what numbers will be as a result of analyzes, since individual laboratories use their own standards for calculations. To simplify decoding, it is customary to talk about the rate of PAPP-A and hCG in MoM - a multiple of the median. With a healthy pregnancy, when both the child and the mother are fine, both values “fit” in the range from 0.5 to 2.0 MoM.
Fluctuations from this range to a greater or lesser side give rise to a lot of experiences in pregnant women and There are many possible reasons for the reasons:
Increase hCG. A “bust” on this indicator can be a sign of Down syndrome in a baby, as well as a sign that a woman is carrying more than one child. 2 fruits together give a practical double increase in the hormone rate Elevated hCG may be a woman who suffers from obesity, edema, toxicosis, diabetes, and hypertension.
Lowering hCG. Insufficient levels of this hormone, inherent only in pregnant women, are characteristic of the development of Edwards syndrome, and can also indicate the likelihood of miscarriage or a delay in the development of the baby.
Decrease PAPP-A. The decrease in plasma protein in a sample sometimes indicates the development of such conditions as Down syndrome, Patau, Edwards, Turner. Also, an insufficient amount of this substance often indicates a child's malnutrition, that the crumb is deficient in nutrients and vitamins that it needs for normal development.
Raising PAPP-A. Enhancing protein in a sample does not have a great diagnostic value in terms of calculating the possible risk of chromosomal abnormalities. This indicator may be higher than normal with double or triple, as well as with a tendency to large fetus.
How is the risk calculation?
The results of tests and ultrasound, as well as all available information about the state of health of the pregnant woman and her age is loaded into a special program.The calculation of the individual risk is carried out, therefore, by a machine, but the person - the geneticist - checks the result.
Based on a combination of individual factors risk may look like a ratio of 1: 450 or 1: 1300 for each disease. In Russia, the risk is considered to be 1: 100. The threshold risk is 1: 101 - 1: 350. Thus, if a pregnant woman is counted on the likelihood of a baby with Down syndrome 1: 850, this means that one out of 850 children in women and identical health indicators , age and other criteria will be born sick. The remaining 849 will be born healthy. This is a low risk, no need to worry.
Women for whom screening diagnostics at 12 weeks shows a high risk for a particular genetic disease are recommended additional diagnostics because screening itself cannot be considered a basis for a final verdict, he is not so accurate. You can pass a non-invasive DNA test. Such an analysis is worth several tens of thousands of rubles and makes it exclusively in the medical-genetic centers and clinics.
If the analysis confirms the suspicion, you still have to go to the invasive test.
Amniocentesis or chorionic biopsy can be offered immediately, without wasting time and money on examining a child’s blood cells isolated from the mother’s blood, as is done with a non-invasive DNA test. However, both biopsy and amniocentesis imply penetration into the membranes to collect material for analysis. The procedure is carried out under the control of ultrasound only by experienced doctors, however, the risk that infection of the fetus will occur, the outpouring of waters, the termination of pregnancy, still remains.
Agreeing or not agreeing to undergo an invasive survey with high risks is a private matter for every woman, and no one can make her go for it. The accuracy of the analysis is 99.9%. If the disappointing assumptions are confirmed, the woman is given a direction to terminate the pregnancy for medical reasons. Whether or not to interrupt her should also be decided only by the woman herself and her family.
If it is decided to leave the child, the woman will still have enough time to prepare for the birth of the “special” crumbs.