The third screening during pregnancy: the timing and standards
Pregnancy comes to the end. Last stayed months, and the expectant mother is already looking forward to meeting her baby. It is at this difficult period that the last prenatal screening falls. Many people want to know in advance what lies behind this concept and what results it can give.
What it is?
The third screening completes prenatal comprehensive studies aimed at identifying possible increased risks of the birth of a baby with developmental anomalies. Screenings are carried out on the recommendation of the Ministry of Health to all pregnant women.
The first examination is scheduled for a period of 10-13 weeks and is considered the most informative, it includes fetal ultrasound and laboratory examination of the mother's blood ("double test"). The second is carried out from 16 to 20 weeks and also implies laboratory diagnosis ("triple test") and ultrasound scanning. The final third screening is the final, it combines a deep integral analysis of the results first and of the second surveys and complements the picture with your own data.
The primary task of antenatal screening research is to calculate the probability of the birth of a baby with coarse chromosomal anomalies. Markers and predisposition of a woman to such genetic pathologies as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Turner’s disease, Patau syndrome are evaluated, possible defects of the neural tube are detected. All of these anomalies are considered incurable, many of them are lethal.
Secondarily, a screening study allows us to establish how the prenatal life of a tiny person proceeds: whether there is enough nutrition and oxygen, no obstacles for his normal healthy development.
The third screening is considered special, because in addition to the possible developmental pathologies of the baby with it you can set some complications of pregnancythat may interfere with normal natural childbirth. The latter study is also necessary in order to choose the right tactics for childbirth, as well as to clarify their dates.
Dates
The third study is scheduled for the period from 30 to 36 weeks of pregnancy. Most often obstetrician-gynecologists try to send a pregnant woman for examination on the term from 32 to 34 week. This time is tacitly considered the most appropriate. Terms are due to the peculiarities of the course of pregnancy and the development of babies.
It is after the thirtieth week, when the weight of the fetus increases significantly, and there is little space in the uterus for somersaults and other movements, the risk of impairment of the uteroplacental circulation increases dramatically. The placenta itself begins to "grow old" also after 30 weeks, and the child's well-being will directly depend on the rate of its aging.
Third trimester - the right time to assess the state of the baby’s heart and blood vessels, to determine the degree of maturity of his lungs, the readiness of the brain to “take control and control”. If during the passage of previous screening studies any deviations were identified, now is the time to assess the dynamics.
If malformations of internal organs were found in the baby, it is the third screening carried out on an expert-level device, will help pediatric neonatologists decide how to help the baby immediately after birth.
What research is coming?
Unlike the first two studies that were conducted in the first and second trimesters, the third screening does not imply a mandatory list of diagnostic measures. What exactly will be included in the screening examination of this particular woman is decided by her attending obstetrician-gynecologist.
This decision is based on the history of the woman, on the risks calculated in previous periods, on her well-being and on the peculiarities of the course of pregnancy. In the course of the third screening study, only two studies are necessarily shown to all expectant mothers - Ultrasound and CTG.
The rest are recommended and appointed according to the situation.
Doplerography
Today, this type of diagnosis is strongly recommended by every pregnant woman, because a separate visit to the antenatal clinic is not required to undergo it, a Doppler examination can be carried out directly during an ultrasound scan. The principle underlying the method is identical to ultrasound scanning.
Only on the monitor during the procedure a woman will see not her baby, but several multi-colored pulsating strips: the vessels are colored in different colors, the speed of blood flow through which is different.
This method allows you to specify how well the child is provided with nutrients and maternal blood enriched with oxygen, whether there are any problems with the return of the mother of children's blood with metabolic products that are to be eliminated. Doppler examines the placenta, the umbilical cord, all three vessels of the umbilical cord (normally it has exactly 3 vessels).
If the doctor has a suspicion of fetal hypoxia or placental insufficiency, then USDG can be carried out earlier, starting from the 20th week of pregnancy., but its information content is higher in the period from 32 to 36 weeks, when the placenta works at the limit of its capabilities.
The third screening of UZDG, and perhaps even more than once, necessarily include women with signs of preeclampsia, swelling and high blood pressure, Rh-negative mothers who are carrying a Rh-positive baby, especially if blood tests show that Rh- conflict, women who in previous studies revealed anomalies of umbilical cord or placenta.
The method gives a clear idea of how the blood vessels and heart of the baby work, how its brain artery functions.
This examination is considered very important for women who are carrying twins or triplets.Because in the case of multiple pregnancies, each fetus has its own bloodstream, and not all babies get the best in the same degree - nutrients, vitamins, a lot of oxygen.
Cardiotocography
This is a very simple and affordable method, and it is also prescribed to all pregnant women at least 3 times in the third trimester, and to women at risk - each time they visit an obstetrician-gynecologist. Today, in women's consultations, KTG devices are installed right in the offices where the reception is taking place, and there is no need for a woman to go somewhere for an examination. The essence of the method is in registration of fetal movements, heart rate and uterine wall contractions, which are measured by special sensors.
They are attached to the belly of a pregnant woman in the area of the alleged finding of the baby’s chest. The procedure lasts from half an hour to 2 hours.It all depends on how quickly the baby demonstrates its “abilities”. If the baby is asleep at the time of the CTG, then the information for the computer program will not be enough, and she will offer to continue the measurement.
Indicators are recorded on a computer monitor, and the program itself displays data on the status of the fetus, expressed in the number of points. CTG gives a fairly clear idea of how the baby feels in the womb.
The most necessary such examination is for women with Rh-conflict, preeclampsia, low water or high water, pregnant women suffering from hypertension, with the threat of premature birth.
This method will subsequently be applied in the maternity hospital, because the process of natural childbirth, even if they proceed without complications, is controlled CTG apparatus every 3 hours so that doctors can find out how the child feels during birth, whether he has acute hypoxia, which can lead to irreversible changes in the central nervous system.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound in the third screening is carried out abdominally through the anterior abdominal wall. The uterus is large, the amount of water makes the visualization clear. On scanning evaluate the fetometric parameters of the crumbs - the length of the bones, the size of the head, chest, abdominal circumference. The doctor carefully examines the internal organs of the child.
They are fully formed and functioning. The degree of maturity, thickness and location of the placenta, and the state of the cervix are evaluated.
For the examination of the cervical canal, if there is a threat of premature birth, an internal method can be used when the sensor is placed vaginally.
3D ultrasound in 30-36 weeks allows you to see the baby in the smallest detail. It looks almost like it will appear after its birth. Pictures taken on such an ultrasound scan can decorate a family home album. But to find out the sex of the child during the third screening is quite difficult. If earlier for some reason it was not possible to determine the sex of a baby, now it is not the best time for this. The child is too big, it is already compactly "curled up" in the uterine cavity, tucked legs at the head previa, or sitting on the bottom with the pelvic.
In any case, the genitals are covered with legs, handles, umbilical cord loops, and it is impossible to consider them. The very position of the child in the uterus during this screening is important information that is needed to select the mode of delivery. Of course, the crumbs still have a few weeks left to take the correct position. But if he does not use this opportunity, Doctors may decide to have a cesarean section for a period of 38-39 weeks.
Blood chemistry
Not everyone needs to donate blood at the third screening. Usually, referral to a treatment room at 32-34 weeks of pregnancy results in women who have high risks of genetic pathologies in the first and second trimester according to the results of screenings. Blood can be recommended to pass to women, in whom the results of previous studies were normal, but the last ultrasound revealed abnormal development of the fetus, malformations.
Biochemical analysis reveals the blood concentration of pregnant hCG, AFP, plasma protein PAPP-A. If a “quadruple test” is carried out, a determination of the concentration of placental lactogen will be added to the listed substances.
Preparation and procedure
Special preparation of the third planned screening from a woman does not require. Going to an ultrasound, it is not necessary to drink a large amount of fluid to fill the bladder, because the volume of water is already large enough to provide a clear picture on the scanner monitor. There is no longer any need to declare war on intestinal gases, which can squeeze the organs of the small pelvis, because the uterus is very large and cannot affect its position.
The only thing that should be foreseen, going to the ultrasound and Doppler research - spare napkin or small towelto wipe the abdomen from the gel after the diagnosis.
Before CTG is best to eat a small chocolate bar. Sweet, once in the amniotic fluid, will give her a pleasant taste, the child will not sleep, but will begin to show activity and even hiccup, which will allow the program to quickly plot the movements of the baby and his heartbeat in a state of activity.
With the same purpose, before entering the office where CTG is to be passed, it is worth a little bit take a walk on the street, walk along the corridor of the hospital, take a deep breath, so that the baby gets more oxygen and behaves more actively.
If a biochemical blood test is prescribed (this happens not so often, but still it is possible), the requirements are the same as in previous screening studies. To come to the treatment room where blood is collected, you need on an empty stomach, a couple of days before the analysis you should not eat fatty, fried, smoked and pickled foods, as well as a large amount of sweet. The last meal before a visit to a medical facility should be held no later than 6 hours.
On the day of blood donation it is necessary to measure the temperature.Because a high temperature can distort the biochemical parameters of blood. If there are signs of a cold or illness, you should definitely report this to your doctor. In some cases, ill pregnant or expectant mothers who have experienced a nervous breakdown or have taken any medications on the eve of the diagnosis, do not analyze.
Interpretation - average standards
Although each of the methods has its own results, they are assessed, as in previous screening studies, only together.
Ultrasound
On ultrasound scanning, the parameters of what he saw are entered into a separate form - the screening protocol of the third trimester. The main abbreviations in this document are as follows:
- BPR - biparient head size;
- LZR - fronto-occipital head size;
- OG - head circumference;
- Coolant - abdominal circumference;
- DBK is the length of the femur;
- DKG - the length of the bones of the leg;
- Duodenum - the length of the humerus;
- DKP - the length of the bones of the forearm.
Fetometry of the baby is the third screening. Below is a table, all dimensions are in millimeters:
Term week | BPR | LZR | Og | Coolant | DBK | DKG | WPC | DKP |
30 | 75 | 97 | 285 | 264 | 56 | 53 | 53 | 46 |
31 | 77 | 101 | 294 | 274 | 58 | 55 | 55 | 48 |
32 | 79 | 104 | 304 | 286 | 60 | 56 | 56 | 49 |
33 | 81 | 107 | 311 | 296 | 62 | 58 | 58 | 50 |
34 | 83 | 110 | 317 | 306 | 64 | 60 | 59 | 52 |
35 | 86 | 112 | 322 | 315 | 66 | 61 | 61 | 53 |
36 | 88 | 114 | 326 | 323 | 68 | 62 | 62 | 54 |
If the child is fine with the internal organs, and the doctor examines the heart, lungs, stomach and intestines, kidneys and bladder, then the protocol indicates - "norm" or "examined." A “baby seat” in a normal pregnancy without complications up to 35 weeks has a maturity of -1, then it acquires a second degree. Normal placement of the placenta during this period plays a crucial role for the verdict on the possibility of carrying out an independent natural birth. The placenta and amniotic fluid are average normal values, the table below is shown:
Gestation period, full weeks | IAG-index of amniotic fluid, mm | The thickness of the placenta, mm |
30 | 145 | 30,48 |
31 | 144 | 31,33 |
32 | 144 | 32,18 |
33 | 143 | 33,04 |
34 | 142 | 33,89 |
35 | 140 | 34,74 |
36 | 138 | 35,59 |
The table of height and estimated fetal weight (average values) is as follows:
Obstetric term, weeks | Estimated weight, g | Height, cm |
30 | 1500-1650 | 40-42 |
31 | 1650 – 1800 | 41- 43 |
32 | 1800 – 1950 | 42-43,5 |
33 | 1950 -2100 | 43- 44,5 |
34 | 2100 -2300 | 44,5 — 45,5 |
35 | 2300 – 2500 | 45 — 46,5 |
36 | 2500 – 2650 | 46 – 48 |
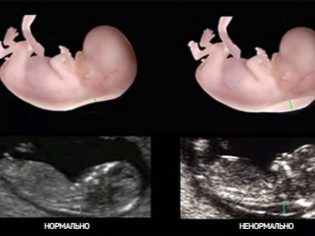
Abnormalities in ultrasound
Small differences between the average rates shown in the tables and the actual figures for a woman should not cause concern. In the third trimester, children grow up at different speeds, they already have an individual appearance, and therefore one child’s head, legs, arms, and abdomen may be larger than the other.
Dangerous from the point of view of the possible disadvantage of the baby is the lag or advance of the average statistical values more than 14 days.
The decrease in size by fetometry to the same value indirectly indicates a lag in the growth and development of the crumbs, a possible state of hypoxia, and Rh-conflict.In some cases, hospitalization or a cesarean section is needed ahead of time, if the condition is deemed to be life threatening to the peanut.
After the third ultrasound scan, pregnant women with low placentation and presentation of this temporary subsidiary body, with premature thickening and aging of the placental structures, and pregnant women with pronounced polyhydramnios or low flow, are sent to a hospital under observation until the very birth.
CTG
Indicators are evaluated according to the following norms:
Child condition | PSP (fetal status indicator) | HR heart rate (beats per minute) |
Baby is okay | Up to 0.8 | 119-160 - alone 130-190 - while driving |
There may be some violations | From 1.05 to 2.0 | 100-119 or from 160 and higher |
The condition of the child is serious, the danger of life | From 2.01 to 3.0 | 100 or less or 180 or higher |
PSP is an indicator of the state of the fetus - the main summarizing point of the entire study. It is calculated by the program on the basis of data obtained during the passage of the diagnosis. Exceeding the normal value of the CAP (up to 0.8) is the basis for repeated CTG, possibly in a different position of the body (if the woman is sitting, you need to lie down). If the negative result is repeated, then the pregnant woman is hospitalized and already in the hospital they conduct additional research and decide on the choice of further tactics.
Doppler study (USDG)
Indicators:
| Obstetric term, weeks | Vascular Resistance Index | Pulsation index |
| 30 | 0,64 | 0,95 |
| 31 | 0,63 | 0,85 |
| 32 | 0,62 | 0,84 |
| 33 | 0,61 | 0,84 |
| 34 | 0,60 | 0,83 |
| 35 | 0,59 | 0,81 |
| 36 | 0,58 | 0,81 |
Biochemical studies (30-34 week)
The followers are as follows:
HCG content | PAPP-A content | AFP content | Lactogen content (PL) |
2700-78100 | 0.5 - 2.0 MΩ, with double - up to 3.5 MoM | 100-250 U / ml | 3 - 12 mg / l |
Any abnormalities in laboratory tests during pregnancy can tell a lot to an experienced doctor, so you should not try to decipher the results yourself. In the third screening, the quantitative indicator of hormones and proteins is not given as much importance as in the first and second screening, and therefore the range of norms presented in the table is so wide.
Only a comprehensive assessment of the results of all types of diagnostics, supplemented by a laboratory picture, can help the doctor find the true causes of a particular abnormality or pathological condition.
Possible problems
After the third screening and before this important matter, women have many questions about what problems the results of this latest diagnostic campaign can point to. The most common and serious are the following conditions and symptoms:
- Rhesus conflict - abdominal girth can be increased by fetometry, if the form of the disease is edematous, a significant excess of values is observed with the rest of the body.
- Genetic pathologies - at the final stage of pregnancy most of the syndromes and abnormalities in the development of the child are already clearly visible on ultrasound. They manifest themselves as multiple developmental defects, almost always - a heart defect, deformation of the facial bones, shortening of the bones of the thigh and lower leg.
- Fetal hypoxia - allow it to install the USDG and CTG. If the child is deficient in oxygen, it all depends on the stage of oxygen starvation. The hypoxia of the initial stage requires medical support of the toddler, since the baby is still too early to be born. Severe hypoxia - an indication for emergency surgery - a cesarean section to save a child's life.
- Low placentation. When the “baby seat” is low, the risks of premature birth increase. Almost always, with problems with the location of the placenta in the uterine cavity in the later stages, doctors tend to hospitalize a pregnant woman so that she and the baby can be under constant supervision by specialists.
- Intrauterine infection. Doctors may suspect her of the increased amount of amniotic fluid.If at the last screening the index was quite normal, and on the third ultrasound scan shows polyhydramnios, the patient is hospitalized to find out the type of intrauterine infection and to decide how to help the baby.
Research accuracy
The screening itself is not an accurate diagnostic measure, according to the results of which some indisputable diagnoses will be made to the expectant mother or her child. Screening only predicts and shows the possible risks, and even at high risks of giving birth to a sick baby, a crumb can be born completely healthy. Judge for yourself, a high risk for Turner’s disease of 1: 100 means that with such a syndrome only one out of a hundred babies with the same exact risk will be born. 99 others will be born healthy, despite alarming predictions.
The accuracy of ultrasound in the third trimester is high - about 90%. Pathologies, if any, the doctor will be able to see. Accuracy decreases only when inspecting twins or triplets - it is not always possible to examine all parts of the body of each individual baby.
In general, the third screening is given to women easier and simpler than the previous two, if you believe the reviews, then pregnant women spend less nerves during the examination, and the latest research gives much less results.