Spotting during pregnancy. What to do?
The appearance of blood from the genital tract can scare almost every pregnant woman. Panic right away is not worth it. This article will help you to understand why there is spotting during pregnancy, as well as what to do in this situation.
Causes of
The development of blood discharge from the genital tract can contribute to various conditions. Each period of pregnancy has a number of unique physiological features. As a rule, the causes leading to the appearance of blood from the genital tract in pregnant women are different.
In the early stages
The appearance of small or moderate bleeding at a short gestational age is often associated with the peculiarities of the intrauterine development of the baby.
During implantation
In the first weeks since the conception took place, a huge number of important biological processes take place in the developing children's organism. So, the fertilized egg quickly begins to divide and turns into a small embryo. The appearance of bleeding from the genital tract at an early stage of pregnancy is often found at 6-8 days from the date of fertilization. The development of this symptom in this situation has a completely physiological feature and is due to implantation - the attachment of the ovum to the uterine wall.
In order to secure a strong fixation, the fertilized egg must firmly “join” to the wall of the uterus. During implantation, there is a slight physiological damage to the endometrium (internal uterine lining), which is manifested by the appearance of bleeding. As a rule, this symptom disappears rather quickly.
Many women often do not even notice this or do not pay any special attention to this event. It also happens that they simply do not realize that in the body implantation of the ovum occurs.
If a woman did not plan a pregnancy, then in that case she does not even suspect that she is already pregnant. The appearance of pink or reddish vaginal discharge, she can "write off" on the arrival of menstruation or the exacerbation of a chronic disease. Severe implant bleeding can also be a manifestation of abnormal attachment of the ovum.
In the presence of a number of chronic diseases of the uterus (endometritis, endometriosis) bleeding may be more pronounced and abundant in quantity. Usually, in a case like this, the pregnant woman has the following symptoms: pain in the lower abdomen, slight weakness, and sometimes dizziness.
With the development of multiple pregnancy
It also happens that during fertilization several eggs are fertilized at once. Thus occurs the conception of twins. During implantation it may happen that one fertilized egg attaches and the second does not.In this case, a pregnant woman may also have a bleeding or even some bleeding. It should be noted that the death of one of the embryos can occur after implantation.
In this case, the woman may also have blood discharge from the genital tract. Usually they appear suddenly. To determine the death of one of the embryos in this case is possible through ultrasound.
Dishormonal disorders
During pregnancy, the hormonal background of the future mother is almost always changing. In the blood, the concentration of some hormones, then others. Such a constant hormonal rearrangement is necessary so that the embryo can fully develop.
A lack of certain hormones during pregnancy can lead to the development of dangerous pathologies. Thus, a significant shortage of progesterone in the blood can lead to the appearance of specific secretions.
Dishormonal disorders occurring with the development of adverse symptoms can significantly worsen the prognosis of the course of pregnancy.
On late terms
The appearance of red discharge from the genital tract in the second half of pregnancy is often an unfavorable sign. When spotting or bleeding occurs, it is very important to establish the cause that led to their occurrence. They can be very diverse.
Placental abruption
This condition is characterized by detachment of the placenta from the uterine wall. Normally, the placental tissue is firmly fixed to the uterine wall. This is necessary so that the baby, who “lives” in the womb during his intrauterine life, could receive all the necessary nutritional components for his development. Many blood vessels pass through the placenta, through which oxygen dissolved in the blood is carried.
Exfoliation of the placenta from the uterine walls occurs due to various reasons. The most prominent symptom of this pathology is usually bleeding. Most often it develops suddenly. However, it is not always the woman who notices exactly the bleeding. Sometimes placental abruption develops gradually. This contributes to the fact that a woman begins to appear reddish spotting vaginal discharge.
Placental abruption may be preceded by some mechanical effects. Thus, the detachment of the placental tissue may begin after intense exercise or lifting too heavy objects. In some cases, the pathology develops rapidly and may even be accompanied by the development of massive blood loss.
Placenta previa
Low location of the placenta relative to the internal uterine throat can also lead to the appearance of blood discharge during pregnancy. In most cases, such secretions appear systematically. They may disturb the future mother several times throughout the entire period of pregnancy.
The most common spotting placenta prevailing develop in the third trimester of pregnancy. At this time, the fetus is already quite large and strongly presses on the cervix. This contributes to the fact that in the area of the delicate mucous membrane may appear small lesions and defects that will bleed. At the same time, droplets of blood are mixed with the vaginal secretion, leading to its staining. This leads to the fact that a pregnant woman notices the appearance of red spotting.
Placenta previa is a rather dangerous condition. It requires the expectant mother to comply with a number of recommendations that are made for her by doctors in order to maximize the duration of the pregnancy.
Spontaneous abortion
Unfavorable outcomes of pregnancy, unfortunately, are also found in obstetric practice. Rejection of the fetus from the uterus and its intrauterine death can occur for various reasons.One of the possible symptoms that can develop with this pathology is the appearance of bleeding. Usually it is quite strong, accompanied by severe blood loss.
In addition to the appearance of bleeding, the woman is also significantly impaired. Another characteristic symptom of this condition is the appearance of a strong pain syndrome in the abdomen. Massive blood loss is usually accompanied by clouding or even loss of consciousness. The woman is in critical condition, so she must be urgently hospitalized in the hospital.
In case of untimely medical care, the risk of danger to the life of a woman is quite high.
Bubble skid
This pathology in obstetric practice is relatively rare. This pathological condition is associated with an overgrowth of placental tissue. In the very early stages of pregnancy, a woman may feel practically no adverse signs. Dangerous symptoms manifest themselves much later.
One of the clinical signs of this condition is the appearance of specific red secretions. Usually they are quite abundant. The prognosis of this pathology is usually unfavorable.
Exacerbation of cervical erosion
The presence of an eroded area on the cervix can also cause blood-smearing discharge from the genital tract. During pregnancy, the body is constantly changing hormones. Some hormones affect the cellular layers of the cervix, which can lead to increased erosion. The color of the vaginal discharge may vary from red to brown. Generally, excretions are scant or minor.
The danger of exacerbation of cervical erosion lies elsewhere - permanent blood loss. Even small but systematic blood loss can lead to the development of an anemic condition, which is unfavorable for both the expectant mother and her baby.
Polyp injury
On the walls of the uterus can grow polypous tissue. In practice, there are often cases when pregnant women suffering from this pathology did not even know about it before the onset of pregnancy. The growth of polyps in the uterus is usually not accompanied by any discomforting symptoms. Often the first unfavorable symptoms appear in the period of pregnancy. This is largely due to the active growth of the baby.
As the fetus grows, damage can occur to a certain part of the uterus where the polyp is located. This leads to his trauma, and hence the appearance of a small bleeding.
If the polyp is quite small in size, the woman will not notice the pronounced bleeding. In this case, it may appear only a small bloody discharge from the genital tract.
At any time
Some causes of bloody discharge from the genital tract can cause adverse symptoms at any time during pregnancy. They are mainly associated with traumatic damage to the delicate mucous membranes of the female genital tract. As a rule, install them simply. Many of them are preceded by some kind of mechanical action, which contributes to damage.
After intercourse
The appearance of bloody discharge may occur after having sex. In the first weeks of pregnancy, mucous membranes lining the genital tract, a little "loosened." It is intended by nature to successfully complete the process of implantation of the ovum to the uterus. Sexual intercourse in this case can cause injury and minor damage to the vulnerable mucous membranes. It may also cause a woman to notice the appearance of blood drops or reddish discharge in her underwear.
Sexual intercourse may contribute to mucosal damage in late pregnancy.In order to avoid this, the pair should choose the most gentle poses.
After transvaginal ultrasound
Ultrasound examinations during pregnancy are performed several times. For the first time, an ultrasound scan is assigned to verify the occurrence of pregnancy, as well as to determine the location of the attachment of the ovum to the uterine wall. Also during such a diagnosis, the doctor assesses the state of the reproductive organs of the expectant mother.
Transvaginal ultrasound is performed by inserting a sensor into the vagina. With this introduction, microdamages of the mucous membrane are also possible. In this case, as a rule, the woman has a slight vaginal discharge with a reddish tint.
They usually appear without pain. Such vaginal discharge, as a rule, pass on their own.
After performing a gynecological examination
In some cases, bleeding from the genital tract may appear after an examination by a gynecologist. The appearance of this symptom leads to the introduction into the genital tract instruments for inspection. In this case, a pregnant woman may also notice the appearance of drops of blood in her underwear. This symptom, as a rule, passes on its own after a couple of days from the date of the gynecological examination.
After unsuccessfully performed douching
Violation of the technique of this procedure can contribute to damage to the mucous membranes of the genital tract. This contributes to the fact that a woman may develop bleeding or blood-like discharge. Usually they arise almost immediately after unsuccessful douching. It should be noted that it is worth resorting to carrying out syringing during pregnancy only after consultation with the doctor.
Self-medication may adversely affect the fetus. Before the introduction of any funds into the vagina, it is necessary to discuss the feasibility of their use with your obstetrician-gynecologist.
With exacerbation of chronic diseases of the genital organs
Many pregnant women even before the onset of pregnancy there are certain pathologies. This is confirmed by gynecological statistics. Doctors say that healthy women of reproductive age are few. The exacerbation of diseases of the reproductive organs contribute to various factors. One of them is the physiological reduction of immunity. Changes in the immune system during pregnancy are found in every pregnant woman and are completely normal.
The risk of exacerbation of chronic salpingitis, cervicitis, endometritis and other diseases during pregnancy is quite high. In some situations, with such pathologies, spotting may also appear. Exacerbation of chronic diseases of the intimate organs can develop at any time during pregnancy. Usually they are accompanied by the appearance of pain in the abdomen, and can also occur with an increase in body temperature.
What might they look like?
Spotting may have a different appearance. So, they can be liquid and homogeneous or clotted. Coloring also varies. It can be from pinkish to dark brown. With the development of uterine bleeding, the blood does not have time to "coagulate", which leads to the fact that the discharge from the genital tract becomes bright red and even crimson.
The amount of discharge is a very important clinical indicator.. Doctors necessarily evaluate this symptom when establishing a diagnosis and performing differential diagnostics. For example, when exacerbation of cervical erosion, the amount of discharge is usually insignificant. With placenta previa, more blood is released. Complete placental abruption is characterized by the development of massive bleeding.
What could be dangerous?
The appearance of bloody discharge from the genital tract means that blood loss occurs. Its severity is different and depends on the initial reason, which led to its development. Complications in this case depend on how often and long-term mother loses blood.
If bleeding worries a future mother several times during the entire pregnancy, then the risk of anemia is quite high. When anemic condition in the blood decreases the amount of hemoglobin and (or) red blood cells. Such a decrease in red blood cells, which are responsible for the transfer of dissolved oxygen, leads to the development of a dangerous state - hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the internal organs.
It is important to note that hypoxia in this condition develops in both the most pregnant woman and her baby.
A child who is in the womb will necessarily react to the oxygen deficiency that has arisen. This is usually manifested by the fact that the fetus significantly increases the heart rate, and also increases motor activity. These characteristic changes are also determined on the cardiotogram.
To compensate for the resulting functional impairment, doctors usually resort to prescribing iron-containing drugs. The systematic reception of these funds helps to normalize the level of red blood cells in the blood. The positive effect of such therapy is significantly higher if it is performed on the condition that the loss of blood stops. If a pregnant woman continues to lose blood due to frequent bleeding, but receives iron supplements, the effect of their use will be much lower.
Massive blood loss, for example, in case of spontaneous abortion, is dangerous even for a woman’s life. In this situation, there is a sharp decrease in circulating blood volume, and, therefore, the total fluid content in the body. In such a situation, the work of vital organs - the brain and the heart - is deteriorating. With massive blood loss, a woman carrying a baby may even lose consciousness. In this case, it is very important to provide timely medical care, including the appointment of anti-shock drugs, if necessary.
In addition to the adverse effects on the body of the future mother, the fetus may suffer.
Pathologies that are accompanied by the development of bleeding, can lead to the formation of various intrauterine developmental defects and in the fetus. This is largely due to impaired uteroplacental blood flow, which can develop in a number of pathologies.
Is it possible to keep the pregnancy in the development of bleeding?
The appearance of blood from the genital tract can be an extremely dangerous sign. However, this does not always mean a sad outcome of pregnancy. The prognosis in this situation can be very different and largely depends on the cause that influenced the development of severe bleeding, as well as on the initial state of the organisms of the expectant mother. Abundant, breakthrough bleeding can be dangerous in the development of massive blood loss. In this case, the timely provision of specialized medical care is very important.
If a pregnant woman has bleeding, then it is not worth delaying the ambulance brigade. It so happens that every minute of delay can be decisive.
How is the diagnosis?
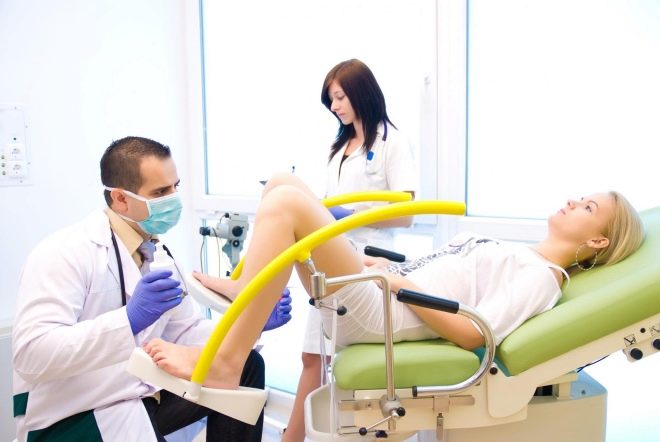
It should be immediately noted that only a doctor can determine the severity of the violations. A pregnant woman may suggest why she had bleeding from the genital tract, but only a doctor can determine the final pathology. To do this, he first needs to conduct a clinical examination. During such a simple study, the doctor determines the condition of the mucous membranes, assesses the state of health of the fetus, and also takes smears for analysis.
The examination on the gynecological chair is carried out in this case quite carefully and carefully. Inaccurate inspection may increase bleeding.
A woman who has a bloody vaginal discharge during pregnancy will be prescribed by a doctor to be tested. The simplest, but quite informative is a complete blood count. Using this routine laboratory test, you can determine the presence of inflammation, as well as assess the degree of blood loss by reducing the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
In some cases, the doctor also prescribes a biochemical study. It allows you to determine the indicators of blood clotting. This analysis helps the doctor to understand whether there are any pathologies of hemostasis and, if necessary, to prescribe the appropriate therapy.
Another method of research, which is assigned to women suffering from the appearance of bloody discharge from the genital tract, is an ultrasound. Such a survey is conducted mainly transabdominal method. In this case, a specialist examines the state of the uterus and the baby in it with a special sensor, which is carried along the anterior abdominal wall. Transvaginal ultrasound can lead to additional trauma to the mucous membranes, which only provokes repeated bleeding.
It is important to remember that before trying to cope with the discharge, you should establish the reason that led to their appearance. This can be done only through various examinations that are carried out in medical institutions.
Treatment
It often happens that a woman who is faced with the appearance of bleeding during childbirth is afraid to consult a doctor. This often leads to the fact that the diagnosis of various pathologies is carried out out of time. With such a delay, the prognosis of the course of pregnancy may change and become unfavorable.
An obstetrician-gynecologist, who is referred to by a woman suffering from the appearance of bleeding, first of all establishes the diagnosis and the cause of the developed disorders. Then he chooses the tactics of further observation of pregnancy. If necessary, the doctor sends the expectant mother to the hospital in the hospital.
The choice of medical tactics
The main task for the appearance of bleeding from the genital tract is to carry out measures aimed at stopping the bleeding that has occurred. For this, various techniques can be used. Their choice is largely determined by the underlying cause, which led to the development of adverse symptoms. If the condition of the future mother is rather difficult and there is a threat to the life of the fetus, then in such a situation it may even be necessary to have an emergency obstetric aid. Caesarean section in this situation is carried out for health reasons.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment of pathologies of pregnancy, accompanied by the development of bleeding, usually complex and multicomponent. In some cases, in order to stop bleeding, doctors may resort to the appointment of hemostatic agents. One of these drugs is Tranexam. It helps to cope with the resulting bleeding and improve the health of the pregnant woman. This remedy is prescribed by a doctor, as it has a number of contraindications.
In case of pathologies accompanied by the development of severe bleeding, it may be necessary to administer solutions through droppers. Such treatment is aimed at filling the volume of circulating fluid in the body. Together with the solution can be administered and drugs that affect blood clotting.
For disorders associated with dyshormonal disorders, drugs may be prescribed that affect the level of certain hormones in the blood. One of these tools is Duphaston.The use of this tool allows you to normalize low blood levels of one of the important pregnancy hormones - progesterone.
It is prescribed by the attending physician. It is important to remember that self-administration of hormonal drugs can be dangerous by the development of terrible complications. The duration of the intake and the course dosage are selected individually.
Surgical obstetric aid
With severe bleeding, especially with the development of severe fetal hypoxia, doctors may resort to cesarean section. In some cases, this method of delivery helps to save the life of a woman and her baby.
Before a cesarean section, a doctor must evaluate the condition of the mother and fetus. If the general condition of the pregnant woman is critical, then it is impossible to delay the caesarean section. If the condition allows for the possibility of conservative therapy, it is first carried out. If the general condition of the pregnant woman does not improve against the background of the medicinal therapy, then the doctors will have to resort to emergency obstetrics.
About what the bleeding during pregnancy means and what the pregnant woman needs to do to make and give birth to a healthy baby, look further.