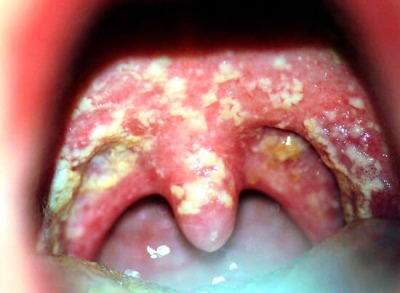
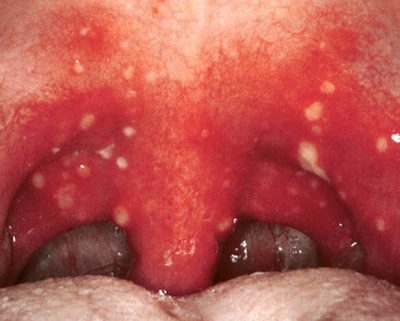
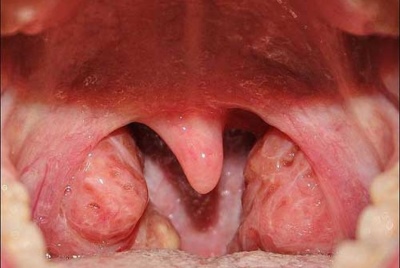
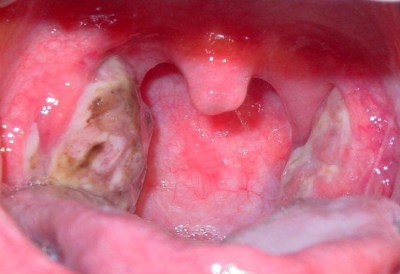
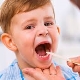
What does a sore throat look like in a child's throat?
Almost every kid can get sore throats. All parents should know what a sore throat looks like in a child. The timely detection of angina will prevent the development of dangerous complications of the disease in the future.
What causes?
Inflammation of the tonsils is called angina or acute tonsillitis. Various reasons may lead to the development of this condition. Most often, children’s acute tonsillitis is caused by viruses, bacteria and fungi. With a decrease in immunity, as well as a strong hypothermia, the child may experience adverse symptoms of the disease.
Sore throat almost never occurs in infants. This is due to the peculiarity of the anatomical structure of the tonsils in children younger than two years.
Babies get a large number of maternal antibodies that protect their body from various infections. The peak incidence occurs in age from 3 to 10 years.
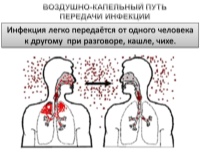
Infection most often occurs through airborne droplets. Pathogenic microbes get on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and tonsils from a sick child to a healthy one. Outbreaks of acute tonsillitis are most common among toddlers attending educational institutions. In more crowded groups, the risk of infection with angina increases many times.
What symptoms can I recognize?
To determine the disease at the initial stage is very difficult. A lot of time passes before the appearance of specific signs of the disease. For viral sore throats, the incubation period is usually 3-5 days, with bacterial - from 7 to 10 days. Fungal infections appear only after a couple of weeks from the moment of infection.
For sore throats are typical:
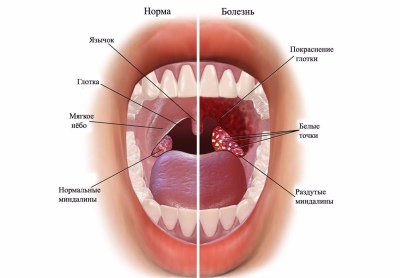
- Strong redness in the throat. It becomes brightred and sore.
- The appearance of rashes and plaque on the tonsils.
- Increase in body temperature to 38-40 degrees. It persists for 2-4 days. Lowering the temperature occurs only under the influence of antipyretics.
- Swelling and inflammation of the tonsils. They become bright red, swollen. If a spatula or spoon touches, bleeding increases, pain syndrome also appears.
- Swollen lymph nodes. The process involves the cervical, parotid and occipital. Lymph nodes become compacted, tightly welded to the skin. With severe course of their visible.
- A sharp deterioration in the well-being of the baby. The child becomes more capricious, eats badly. In some cases, kids completely refuse to eat. The first days of the disease are accompanied by increased sleepiness. The baby is in bed almost all the time. Sleep brings a short-term improvement in well-being.
Kinds
Depending on the reasons that can cause the development of acute tonsillitis in babies, all of the sore throats can be divided into:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- fungal.
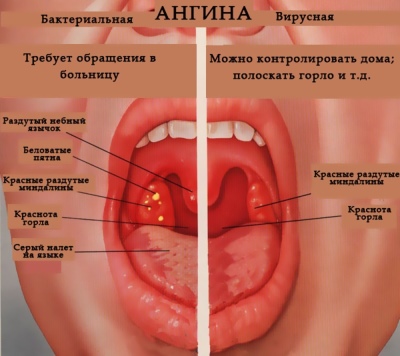
Symptoms and clinical manifestations for each angina are different. They usually depend on which pathogen caused the disease. Bacterial tonsillitis develops much harder and causes a whole complex of adverse symptoms. Viral infections cause acute tonsillitis much less frequently and are much easier. The longest - fungal options.Usually they occur in weak and frequently ill children.
According to the variant of the development of the inflammatory process and the appearance of symptoms All sore throats can be divided into several groups:
- lacunar;
- catarrhal;
- follicular;
- phlegmonous;
- fungal;
- herpes;
- ulcer-membranous;
- gangrenous.
Each type of acute tonsillitis has its own distinctive features. They manifest differences that can be detected during examination of the throat and oropharynx. Each sore throat is different. It depends on the level of local immunity, the characteristics of the pathogen causing the disease, as well as the presence of chronic diseases in a sick baby.
Catarrhal
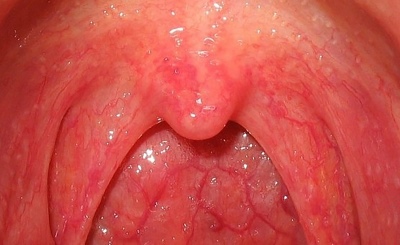
Develops in most cases. It is characterized by a fairly easy course. Good therapy. After the treatment, the child is fully restored and is recovering.
In catarrhal angina, there is a pronounced redness of the tonsils. Usually the process is two-way. Zev becomes bright red. Tonsils - swollen, inflamed. Palatine arches slightly increase in size and hang over the entrance to the mouth. Soreness increases dramatically during swallowing. Too hot and cold drinks or foods can cause increased pain.
Often this form of the disease begins with the appearance of common symptoms of intoxication. The baby has a severe headache. The child feels overwhelmed, his appetite is getting worse. During the day, the baby notes severe sleepiness. By the end of the first day, the characteristic symptoms of inflammation in the throat, as well as difficulties and pain when swallowing, join.
Catarrhal sore throat in children younger than three years is usually accompanied by a sharp temperature jump. It usually increases to 39-39,5 degrees. In older children, body temperature may remain normal, only there are characteristic changes in the mouth and tonsils.
Lacunar
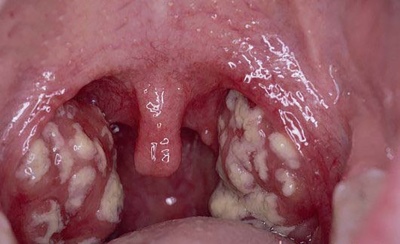
The peak incidence of this form of sore throat falls on the preschool age. Most often, babies become infected by airborne droplets. With lacunar tonsillitis, palatine tonsils increase greatly. They become swollen, swollen.
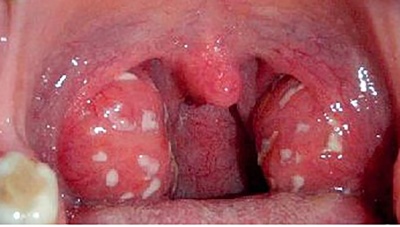
A characteristic light yellow bloom appears on the surface of the tonsils. It is well removed with a spatula. When lacunar tonsillitis body temperature rises to 39-40 degrees. Submandibular nodes greatly increase in size, become dense, painful with palpation. Already in the first day there is severe pain when swallowing.
Lacunar angina is dangerous by the development of complications. With an unfavorable course, purulent inflammation passes to the adjacent ENT organs. It contributes to the development of acute otitis, sinusitis and conjunctivitis. The kid feels very bad. At high temperature fever appears, as well as a pronounced chill.
Follicular
Often caused by streptococcal or staphylococcal flora. This form refers to purulent tonsillitis. For this variant of the disease is characterized by the appearance of numerous yellow bubbles, which abundantly cover all the surfaces of the tonsils. Inside these rashes contains pus. When it expires, an unpleasant odor appears.
The disease is accompanied by a rise in temperature of more than 39 degrees. In the early days of the disease, it is difficult to reduce, even despite the use of antipyretic drugs. A sick child feels soreness in muscles and joints. All symptoms resemble flu.
To eliminate the adverse manifestations of follicular angina requires the appointment of high doses of antibiotics.
Phlegmonous
This form of the disease is extremely rare in childhood. It usually appears in adults. It is characterized by a very severe course and frequent development of complications. During phlegmonous sore throat, pain when swallowing is intolerable. The child has no appetite. Speech becomes slurred.
Most often, the process is one-sided.The affected amygdala significantly increases in size. Inside it is completely filled with pus. With an unfavorable course of the disease, purulent inflammation can move to other organs that are located nearby. Pus spreads through the lymphatic vessels, penetrating the mediastinum.
Phlegmonous sore throat is considered an extremely unfavorable form of the disease. In case of severe disease, even surgical treatment is required. In this case, the inflamed tonsil is removed, after which a full antiseptic treatment of the pharynx is performed.
Fungal
Most often occurs in weakened babies, as well as in children suffering from diabetes or chronic heart and vascular diseases. In some cases, is one of the manifestations of secondary immunodeficiencies resulting from viral infections.
When fungal tonsillitis on tonsils appears cheesy white bloom. When touched with a spoon or spatula, it crumbles easily and disappears. After the discharge of plaque on the surface of the tonsils bleeding wounds. For the treatment of this form of sore throat requires the appointment of antifungal and immunostimulating drugs.
Herpes
Occurs when infected with herpes viruses. It is characterized by the appearance of numerous bubbles on the tonsils. They contain muddy bloody fluid. When touched, bubbles can burst. The opening of such inflammatory elements occurs at 5-6 days of illness. After that, numerous ulcers and erosion remain on the mucous membrane of the tonsils.
The disease is accompanied by fever. It usually increases to 38-39 degrees and remains high for 3-4 days. After healing, the tonsils regain their usual pink hue. The entire acute period of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of severe pain in the throat.
For the treatment of herpes sore throat antiviral drugs are used, which have a destructive effect on herpes viruses. Medications are usually prescribed for 7-14 days.
For the prevention of recurrence of herpes sore throat, doctors recommend taking annual courses of immunostimulating treatment.
Ulcerative-membranous
It occurs in frequently ill children, as well as in children with various immunodeficiencies. With this form of tonsillitis on the tonsils, there is a strong bloom of a light yellow color, which is very poorly removed. Palatine arches swell and hang over the entrance to the mouth. The oropharynx has a bright red color. There is a strong drooling.
When you open the mouth there is a strong smell. The inflammatory process also affects the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes. They become dense, enlarged, painful when palpating. Despite the appearance, ulcerative-membranous tonsillitis is not the most dangerous form of acute tonsillitis. The disease is well treatable.
Gangrenous
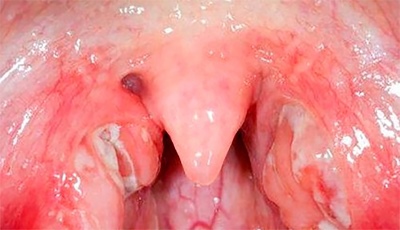
This form of angina is called Simanovsky-Vincent's disease. Often with the development of the disease, body temperature remains normal, less often rises to subfebrile values. Such a sore throat is most often caused by conditionally pathogenic flora that lives in the gum pockets.
The most common process is one-sided. A large ulcer appears on the damaged tonsil. Externally, it resembles a crater of a volcano. The ulcer has a grayish-yellow hue. Any damage causes severe bleeding. The size of the formation - from 1 to 2 cm. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of severe pain when eating, especially on the injured side.
In appearance, this form of sore throat resembles diphtheria. For the differential diagnosis requires the implementation of additional examinations and analyzes. Treatment of the disease is complex. Therapy of this form of the disease necessarily includes the appointment of immunostimulatory drugs.
Additionally, you can watch a video on the topic "Angina in children" from Dr. Komarovsky.