Symptoms and treatment of arthritis in children
Every day, doctors discover more and more cases of inflammatory diseases of the joints. Without treatment, such pathologies are very dangerous, since the serious consequences of the disease often develop. If you want to know more about the symptoms and treatment of arthritis in children, read this article.
Causes
Various causes can lead to the development of arthritis in children. Currently, there are more than a hundred. Some causes have a damaging effect mainly on the large joints: hip, shoulder and knee. Others - into smaller ones. In some childhood diseases, all groups of joints are simultaneously affected, regardless of their size.
Among the most common causes of joint damage are:
- Traumatic effects. Damage to the knee caused by this cause, develops in most cases. A blow or fall can cause a rupture of the anatomical structures that form the articulation. In this case, the formation and circulation of intraarticular fluid is impaired. The cartilage of the joint becomes more dense.
- Insufficient intake of vital substances. Diet with protein restriction, hypovitaminosis lead to metabolic disorders. This condition often contributes to insufficient cartilage nutrition. Incorrectly chosen diet leads to the development of joint pathology in children aged 2-3 years.
- Severe hypothermia. Low temperatures affecting the joint lead to a spasm of the blood vessels that feed the joints. For some time, cartilage nutrition is impaired. With prolonged exposure to cold, the outflow and the formation of intraarticular fluid are disturbed.
- Genetic predisposition. In the presence of joint diseases in parents, the likelihood of the development of the same disease in a child may exceed 50%. There are a number of genes that cause the development of the disease to a certain age. In some cases, this trait is inherited only by the mother or by the father.
- Chronic diseases of internal organs. Diseases of the intestine occupy a leading position in children on the development of arthritis. Violation of the absorption of nutrients leads to insufficient flow of them to all elements of the joints. Often this contributes to the development of reactive arthritis. Such forms of joint damage are accompanied by excessive accumulation of intraarticular fluid in them.
- Various infectious diseases. Infection with viruses or bacteria often leads to the development of infectious-allergic forms of arthritis. In this case, viral toxins have a damaging effect on the joints. Over time, the cartilages that form the joints become stiff. This condition contributes to the development of work restrictions in the joints.
- Undertake of vitamin D. Insufficient exposure to the sun on the background of malnutrition can lead to the development of rickets in the baby. In this case, bone density is disturbed. With long-term development, the disease becomes chronic and requires complex treatment.
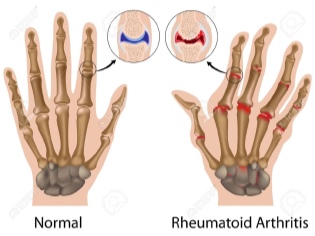
- Rheumatological diseases. As a result of the formation of autoantibodies, which are distinguished by a destructive action in relation to the body's own cells, there is a strong inflammation in the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common pathologies. To eliminate the symptoms requires the appointment of hormonal agents.
Kinds
A large variety of causes leading to the development of arthritis also determines a variety of diseases. To separate all arthritis according to the source of the disease, doctors use different classifications.
The most common in pediatric practice are the following types of arthritis:
- Juvenile idiopathic. May be in oligoarticular and polyarticular forms. The difference in them is in the number of affected groups of joints. With polyarticular arthritis, it is more than 5 groups of joints at the same time. It is characterized by an unfavorable course. To eliminate the symptoms, hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs are required, and in some cases even methotrexate is required.
- Reactive. May occur as a result of traumatic effects on the joints or as a result of secondary chronic diseases. Characterized by the formation of excessive accumulation of intraarticular fluid. Often the effects of streptococcal or viral infection. The number of arthritis detected in babies (congenital infection with chlamydia) increases annually.
- Juvenile ankylosing. It is also called Bechterew's disease. It is characterized by damage not only to the joints, but also to the spine. In the overwhelming number of cases, it is first manifested in toddlers at a very early age. The disease is characterized by a chronic course.
- Tuberculosis. They are found in babies who have had tuberculosis. Often manifested damage to the hip or knee joint. When diagnosing mycobacterium tuberculosis in the blood and sputum. In order to eliminate symptoms, an intensive course of treatment is required, which lasts 8-12 months.
- Oncological. Damage to the joints in these diseases occurs as a result of the toxic effects of drugs used to eliminate and treat growing tumors. Both mono- and polyarthritis can occur. Often characterized by the formation of an excess amount of intraarticular fluid.
- Hypothyroidism. Develop as a result of a decrease in thyroid function. Characterized by the development of edema in the area of damaged joints, as well as the appearance of effusion (excessive accumulation of intra-articular fluid in the articular cavity). Most often affects the knee and ankle joints. In some cases, limiting movements in the wrist joints develop.
Symptoms and treatment
The development of the inflammatory process in the joints leads to the appearance of adverse symptoms in the baby. At the onset of the disease, they are minimal. In the absence of treatment or delayed diagnosis, symptoms begin to increase. Chronic disease is accompanied by persistent (and in some cases even disabling) consequences.
The following symptoms are characteristic of inflammatory diseases of the joints:
- Mobility restriction. The volume of possible movements in a given joint is reduced. Excessive accumulation of fluid and the density of damaged cartilage lead to the inability to perform all active and passive actions.
- Soreness It can be of different intensity and appear both among complete calm, and only after the start of movements. Usually, in case of mild disease, pain in the joint can be tolerated. The use of painkillers in such cases allows you to completely get rid of this symptom.
- Redness and swelling of the skin. Usually this symptom occurs over the area of the damaged joints. They become enlarged, somewhat swollen.If the process is one-sided, then when comparing a sore joint with a healthy one, on the other hand, asymmetry is visible. In the acute period of the disease, the skin over the affected joint becomes hot.
- The emergence of crunch and clicks. They arise during the execution of movements. Most often, such sounds are heard during arthritis of the knee or elbow joint. Flexion and extension of the limbs lead to the appearance of a crunch. A common cause of this symptom is traumatic injury.
- Changing well-being. The child becomes less mobile. He tries to limit all active games or fast walking, as this can cause him great discomfort. In case of rheumatological diseases in the period of exacerbation, the child's body temperature rises, appetite can be disturbed, as well as sleep.
- Change gait. When injuries of the joints of the lower limbs, children begin to limp. If the process is one-sided, then when walking they try to rely on a healthy leg, sparing the diseased one. With bilateral, the child completely changes his gait. He can bounce or step on only socks.
Treatment of diseases of the joints is very long. Usually it is appointed only after the advanced diagnostics.
For the treatment of various arthritis are used:
- Anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal agents. Help to eliminate pain in the joint, as well as relieve severe swelling. May be administered in the form of injections, tablets and various ointments. About these tools leave positive feedback after the application. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of tablets cannot be used for babies with ulcers in the stomach or intestines.
- Hormonal drugs. Most often prescribed for rheumatological diseases. Discharged by a rheumatologist. Usually assigned to "Prednisolone" or "Hydrocortisone". Dosage, frequency and duration of admission are chosen by the attending physician - taking into account the age of the baby, as well as the characteristics of the disease.
- Antibiotics or antivirals. Effective with reactive arthritis caused by viruses or bacteria. Discharged after a blood test, in some cases - according to the results of tests that identify pathogens. Appointed to the course reception, usually from 7-10 days.
- Drugs that have a depressant effect on the immune system. Successfully applied to the treatment of autoimmune or rheumatological diseases of the joints. The most famous drug is Sulfasalazine. This tool helps to prevent the rapid development of symptoms of the disease and somewhat delay the development of complications.
- Physiotherapy techniques. Appointed with the subsiding of the acute inflammatory period of the disease or during remission. Accelerate the regeneration (restoration) of cartilage, as well as improve blood supply in the damaged joint. Electrophoresis with drugs, magnetic therapy and ultrasound promotes rapid healing.
- The complex of therapeutic and physical education. It is an important stage of rehabilitation for children suffering from various types of arthritis. Developed special programs approved for use by children (age - almost from birth). Therapeutic exercise helps to improve the volume of movements performed in the joints and prevent the development of disability.
- Spa treatment. It is shown to all babies with diseases of the joints. Proper nutritional therapy, a set of necessary physiotherapy techniques, as well as regular monitoring by medical specialists will help the child recover from an illness faster.
Symptoms of rheumatic fever
Currently, scientists have not identified a single cause leading to the development of this disease.They explain this by the presence of a genetic predisposition to the disease and the individual characteristics of the immune system in the baby. The risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis and streptococcal infection is somewhat increased.
Typically, the peak incidence occurs in age from 6 to 14 years. Polyarthritis occurs in 45-50% of babies with rheumatoid arthritis.
The knee, elbow and hip joints are most often damaged. They become enlarged, swollen. The skin over them get a reddish tint.
When touched, you will notice that the joints become hot to the touch. In most cases, the process is two-way. When examining diseased joints, it is possible to note damage to the corresponding joints on both sides at once. The inflammatory process leads to a pronounced restriction of movements. When trying to perform any action in the joint there is a strong pain.
The course of the disease is undulating: periods of exacerbations are replaced by complete well-being. The duration of remission may be different. It depends on the stage of the process, as well as on the adequacy of the selected treatment. Treat the disease should be throughout life, as in some cases, adverse symptoms may occur again. For the treatment of disease requires the appointment of both nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and hormones.
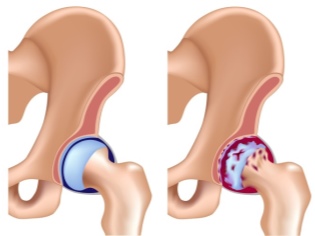
Features of coxitis of the hip joint
Coxopathies are in second place in the structure of childhood incidence of arthritis (after lesions of the knee joints). They occur in 25% of children. At an early age, the process is most often bilateral. Unilateral damage to the hip joints is characteristic of children older than three years.
When inflammation occurs in the largest joint in the body, pain occurs when making any movements. The hip joint provides a support function when walking. When a violation of the work in this joint is significantly disturbed posture and gait. In a one-sided process, the child limps and rests on a healthy foot when walking.
On examination, it is clear that the damaged joints become swollen. The skin over them turn red. In some cases, they become very hot to the touch. Painful syndrome occurs not only when attempting movements. With rheumatologic injuries of the hip joint, pain arises in the groin. It can spread down the thigh.
The behavior of the child is changing. Any attempts to walk or perform movements lead to the appearance of pain. Kids begin to cry, act up. These kids look quite passive. They try to spend more time in the crib or on the floor, without making active movements.
With a long course of coxitis, a child develops a persistent violation of posture and gait. The kid often “collapses” somewhat when walking. Usually the slope is done in a healthier way. The gait of some kids becomes springy or bouncing. They can tiptoe or lean on the heels when walking.
It is also possible to notice the damage to the hip joints when performing massage. Any attempts to spread the legs lead to the appearance of pain. Even infants show their behavior that this action leads to the appearance of pain in them. On the face of the baby there is a grimace of pain or displeasure. Some babies start whimpering and pull back their legs.
To determine the cause that caused damage to the hip joints, an extended set of diagnostic measures is required. Be sure to show the baby to the rheumatologist and orthopedist. The first signs of the disease should also be suspected by the district or attending pediatrician, who has been monitoring the development of the child since birth.After the examination, the doctor will prescribe the full range of tests and studies that allow making the correct diagnosis and agreeing on the tactics of the future treatment.
Diagnostics
To establish the correct diagnosis for arthritis in children is quite difficult. Sometimes a variety of tests and examinations are required to identify the cause of the disease. In the most difficult cases, a collegial examination of the baby is carried out. In this situation, doctors of various specialties who deal with the problems of arthritis development in pediatric practice are invited.
Among the most common basic diagnostic methods are the following:
- General blood analysis. Allows you to establish the estimated cause of the disease. With most arthritis, there is an increase in the total number of leukocytes and an accelerated ESR. Rheumatological diseases are characterized by an increase in these indicators several times. Changes in leukocyte formula are important diagnostic signs of infection with viruses, bacteria, and also chlamydia or tuberculosis pathogens.
- Rheumatoid factor. It is a specific marker for rheumatoid arthritis. Normally, this substance is not detected in the blood. Detection and repeated increase in rheumatoid factor in the blood serves as a bell for parents - it's time to go to a rheumatologist with a child.
- A blood test for ALSO. This lab test will show the presence of antibodies to streptococcus in the children's body. The method allows to accurately determine the presence of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Ultrasound procedure. It helps reliably describe all the anatomical defects of the structures that form the joints. This study shows the total amount of intraarticular fluid. Can be used for toddlers. This method is relatively safe and does not bring any pain to the child.
- X-ray of the joints. Not used for toddlers. Appointed in difficult cases when it is necessary to determine the presence of anatomical defects. Most often used in trauma and orthopedic practices. Good for detecting traumatic joint damage.
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography. These methods are highly reliable and accurate. They describe all the defects and injuries that are present even in the smallest joints. The methods are relatively safe and do not cause pain in the baby. Less research is high cost.
Effects
The course of inflammatory diseases of the joints is usually long. To eliminate the adverse symptoms of the disease requires the use of various medicinal and non-drug methods. In most cases, properly chosen therapy leads to the child's well-being and the preservation of his usual lifestyle. With timely prescribed rehabilitation, children suffering from arthritis, almost do not lag behind their peers in terms of physical development.
In some babies, the course of the disease is severe. Even prescribed therapy does not help lead to the desired result. The long course of the disease leads to the appearance of complications.
In arthritis of the temporomandibular joint, the provision of chewing function is impaired. In the initial stage of the disease, this leads to the development of crunch and crepitations, which are heard during chewing. Then the child may break the bite.
Damage to the joints of the lower limbs leads to the development of persistent deformities. They contribute to gait disturbance. Over time, the child develops constant lameness. In some cases, this may even be the reason for establishing the disability group.
Arthritis of the small joints of the hands, which are found in rheumatological diseases, leads to the development of motility disorders. In schoolchildren this is manifested by a strong handwriting curvature.In some cases, the text is even impossible to read. Kids suffering from arthritis of small joints of the hands, it is quite difficult to fasten buttons on the shirt. Habitual actions performed in everyday life can cause them significant difficulties.
With the development of persistent complications, which significantly limit the usual way of life of the baby, doctors decide to establish a group of disability. Usually for babies with arthritis, a second or more often third group is established. Such children require constant attention and control over the course of the disease (from the side of medical workers). Children with disabilities due to arthritis are recommended regular spa treatment. Medicinal products are prescribed for them on a preferential basis.
Forecast for the future
With the right treatment and adequate rehabilitation, the child’s habitual way of life is almost completely preserved. With a mild course of the disease, babies can even attend various sports sections. The amount of physical activity must necessarily be coordinated with your doctor.
For the full development of the child should carefully plan which sports section he can attend. Children with injured knee joints should not choose football or running. These sports are suitable for children suffering from polyarthritis of small joints of the hands.
The kid who regularly undergoes spa treatment and visits the doctor is under control. In this case, his disease is easier to treat. It takes a lot of time to develop joint diseases. Regular examinations and well-chosen treatment can significantly improve the prognosis.
See the following video for advice from the Union of Pediatricians of Russia on Arthritis Prevention.