What to do if a child has ears that hurt?
Parents often experience ear pain in children. There are practically no people on the planet who can boast that they have never had any illnesses in their lives. We will talk about why this happens and how to help a child in this article.
Why do ears hurt?
In childhood, the ears hurt more often than adults. This is due to the anatomical features of the structure of the hearing in children. The Eustachian tube, which connects the nose and ear, in children is shorter and quite wide, which is why through it the germs and viruses enter the ear cavity with an enviable frequency. Immunity in children is much weaker than the protective mechanisms in adults. As the baby grows, the Eustachian tube will grow, it will narrow, become longer, change the angle of inclination, become horizontal, and penetration of pathogenic microorganisms will be a rare phenomenon. Over time, immunity will produce antibodies to the most common viruses, learn to more effectively and quickly resist bacteria.
Most often, ear problems in children are caused by viral infections. This is due to the fact that the viral infections themselves are very common, they are given about 85% of all children's ailments. Less commonly, pain is “blamed” by bacteria and fungi. It is impossible not to take into account the injury of the organs of hearing, foreign objects that the kids themselves can push into the ear canal. With a long stay there they cause severe inflammatory processes. Even allergies can cause earache, as well as vascular disorders, problems with the cervical spine, jaw, lymph nodes.
Whatever the cause of the pain in the ear, the situation requires an immediate response from the parents, since the diseases that can be signaled by this pain syndrome can be not only dangerous, but also deadly.
Symptoms and diseases
The ears can get sick on their own, it will be a very specific disease, and they can accompany a pathological condition caused by another ailment, in fact, being only a symptom. If a child complains of a sharp or nagging pain in the ear with or without auricular discharge, hearing loss or its complete loss, always, in 100% of cases, urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary. Here is just an approximate list of problems that earache may say:
Otitis
The most common childhood disease associated with inflammation of one of the ear sections. There are three divisions - outer, middle and inner.
External otitis media is the easiest to recognize, and the outer ear is affected. If the auricle is swollen, reddened, then it should be carefully examined for the presence of ulcers or boils. Usually they are the cause of inflammation. The temperature can be slightly increased, and can be quite high, hearing loss in uncomplicated cases is not observed.In complicated cases, with spilled form, numerous furuncles, inflammation can also pass to the eardrum, but this fact can only be revealed by a doctor when examined with special equipment. The nature of pain is pulsating, monotonous.
Otitis media - the most common ailment among children. When it inflames the middle ear. Inflammation can be caused by viruses, bacteria, allergic reactions. The disease can be acute and chronic. And by the presence or absence of purulent discharge from the organs of hearing - catarrhal or exudative. Most often in children, otitis media can be an unpleasant “supplement” to an infectious disease (ARVI, influenza, etc.). With flu, the disease is severe, with intoxication. When scarlet fever - with abundant separation of pus.
Symptoms are well known to many parents - it is a sharp pain in the ear, fever (from subfebrile to high), with exudative otitis pus is released. In all forms of otitis media, hearing can be reduced, with improper or late treatment, hearing loss can become persistent and chronic.
Internal otitis (labyrinthitis) - This form of hearing inflammation in children is, fortunately, the most rare, but it is also the most painful and dangerous. With this ailment, the child will not complain of earache. Other symptoms will first appear — an imbalance, as the vestibular apparatus begins to suffer. Then there is a hearing loss, the child hears much worse. With a sharp course of the disease comes deafness.
These symptoms include severe dizziness, nausea and vomiting, severe pallor of the skin and increased sweating. An older child can formulate one of the main symptoms of injury or death of the auditory receptors - tinnitus. With sudden movements of the head, pain in the ear will appear.
Turbootit
This is a type of internal otitis, but we distinguish it in a separate category, since it is this form that is most common in children. When ailment occurs inflammation of the mucous membrane of the inner ear. To him leads dysfunction of the auditory tube. The ear thus loses its ability to ventilation, air does not flow into the cavity, and the multiplication of pathogenic bacteria begins.
Disturbances in the function of the auditory tube are caused by an infection that most often gets into it from the nasal cavity. In children, turbootitis is most often bilateral, that is, both ears are affected. Only qualified doctors can recognize such a disease, since the symptoms are similar to a lot of other уш ear ’signs - hearing loss, tinnitus (tinnitus), the temperature rarely rises, the pain may be mild, quite intense or not at all.
Otomycosis
This is a lesion of any part of the hearing (excluding the internal) of the fungus (candida, mold, saprophytic). To recognize the disease is quite difficult, since the symptoms characteristic only for this disease, no. They are “universal” - noise in the ears or one ear, hearing loss, a feeling of congestion in the ears, sometimes - with the release of fluid from the ear. In regions with a hot climate, this disease is more common in children than in northern regions. One ear usually suffers. Only in one in ten children with otomycosis, the lesion is bilateral.
Sulfur plug can cause severe hearing loss.
At the same time there are no complaints about severe ear pain. The inflammatory process too. The essence of the disease - in the accumulation of earwax, which in children is produced more actively than in adults. It clogs the ear canal, sometimes settles in the bone part. In the second case, the symptoms associated with hearing loss are complemented by severe reflex cough, headache, nausea and dizziness.
Neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve
This disease is chronic. It is manifested by bouts of severe, sometimes unbearably severe pain in the ears.Only hearing organs rarely hurt, usually the pain spreads to the cheek, jaw, to the eye from the affected side. In the intervals between attacks of pain there. The disease is rarely seen in childhood, but it still happens.
Meningitis
Viral or bacterial damage to the lining of the brain. Often the cause of this serious disease is neglected or improperly treated purulent otitis. If the pus from the middle or inner ear did not find the way out, the membrane has not ruptured, then the pus is able to go in the opposite direction. This is what causes inflammation. Therefore, at the initial stage, after severe pain in the ears, heat, fever, the child feels some temporary relief. At the initial stage of purulent otitis, the infection is able to penetrate the sheaths of the brain in a hematogenous way - through the bloodstream.
Pain in the organs of hearing with this most dangerous disease is not considered diagnostically important, since other, more obvious symptoms come to the fore - high fever (up to 40.0 degrees), episodes of unconsciousness, delirium, severe headaches, vomiting, gray skin color. covers.
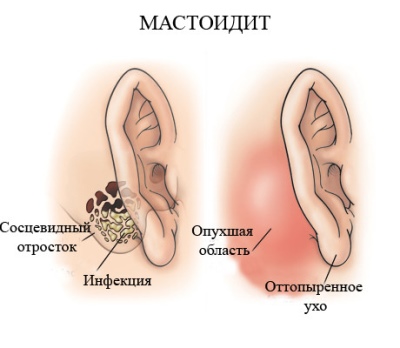
Mastoiditis
You can talk about such a disease if the mastoid process of the temporal bone is inflamed in a child. The first complaints of the child will be severe pain in the ear, then all the symptoms of purulent otitis media will appear - temperature, discharge of pus from the external auditory canal, hearing loss, headache, sleep disturbance. The noise in the ear a little later adds pain in the ear region. Behind the ear, swelling and redness may occur. The ear looks like bulging, this is due to the swelling of the skin fold behind the auricle.
Mumps (Mumps epidemic)
Ear pain with this typically childhood disease is associated with inflammation of the parotid salivary glands. The pain has the character of a dull, constant, exhausting, without strong attacks. There is no discharge from the ear. Hearing loss is rarely diagnosed, it is reversible. Complaints of ear pain will be complemented by a specific clinical picture of an infectious disease - swelling of the face, neck, high fever (39.0 - 40.0 degrees).
Chickenpox
A common childhood infectious disease, the symptoms of which are well known to all parents. However, in some cases, a watery rash, mild fever and a feeling of "weakness" can be complemented by unpleasant symptoms from the ear. This happens with moderate and severe acute infection. The pain in the ears at the same time is quite intense, the child may complain of the feeling of “squishing” or “clicks” in the ear.
Violation of cerebral circulation occurs as a result of blood flow insufficiency, aneurysm, vascular spasm and many other pathological conditions associated with the provision of blood to the brain. The pain in the ears at the same time is of a completely interesting nature - the child complains of congestion in the ear and a feeling as if water got there after bathing. But she will definitely be preceded by several episodes of severe headache. Tinnitus, nausea, convulsions may occur. Injuries and problems with the spine are also diseases that cause insufficient blood supply to the brain, especially in the cervical spine.
Ear injuries
Insects bites, heat exposure (frostbite or burns) can injure hearing organs. Acoustic injuries can be especially dangerous. They are associated with rupture of the eardrum, which arose when struck in the ear, with a strong sudden sonic effect. The pains in this case are shooting through, the child complains of a headache and a sharp decrease in hearing.
Foreign object in the ear, water in the ear after swimming, diving. This is a fairly common cause of unpleasant sensations in the organs of hearing.Children, especially small children, can easily push small parts of toys or other foreign objects into the ear canal while playing. If this object gets too far, then the baby cannot get it on his own, and the inflammation gradually begins to develop. Usually, the baby does not begin to complain about the sore ear immediately, but when the inflammatory process is already in full swing.
Quite often, parents note that complaints about the ear getting sick come after swimming in the river, at sea, after visiting the pool. Usually, water that enters the ear canal easily flows back; you just need to tilt your head to the right and left to get rid of it. But in some cases, especially in children with their characteristic structure of the organs of hearing, water can penetrate further - into the middle and even into the inner ear. There it stagnates, and bacteria start up in it, which cause severe inflammation.
The symptoms that should alert the parents are the child's complaints about the feeling of fluid transfusion inside the ears, hearing loss, distortion of the familiar and familiar sounds, small headache, slight dizziness, nausea. The temperature at the initial stage rises infrequently. But appetite and sleep disturbances are recorded in all children with water in the middle or inner ear.
Allergy
Sometimes the cause of damage to the ears of a child is a kind of inadequate allergic reaction that occurs in the body. Symptoms in this case will be similar to otitis, and the disease itself will be called allergic otitis. The exception is pain, usually with allergies. But there is a sensation of itching in the ears, hearing loss, watery discharge from the ear. Most often, this disease occurs in infants, in children up to 3 years of age against the background of a general allergic reaction, as well as after suffering respiratory diseases.
Diagnostics
The ENT doctor must understand what is really happening with the child. For this purpose, he will use special tools to inspect the nasopharynx, the ear cavity, to establish whether the eardrum is intact, if there are sulfuric plugs and obstruction of the auditory tube. Further audiological examinations may be prescribed. The state of hearing can be checked by whisper speech (the normal ear perceives it from a distance of at least 6 meters). With a clear decrease, the doctor will give a referral to an audiologist who examines hearing using the method of tonal audiometry. It will show at what frequency and how much decibels sound perception is reduced, determine the bone conduction of sound waves. All this will help to establish what exactly happened inside the organs of hearing, whether hearing is to be restored.
Most of the acute lesions of the hearing are treated with drugs. But chronic hearing loss (which occurred more than 2 months ago) may require an operation - implantation of a cochlear implant or wearing hearing aids - depending on the degree of hearing loss.
Before turning to the doctor, parents should note the following nuances of earache in a child:
- The nature of the occurrence (acute and sudden, or complaints about episodic problems with the ears have arisen for a long time).
- The intensity and nature of pain (strong or moderate, constant or paroxysmal, whether it changes from strong to weak and vice versa).
- Nuances of pain (dull, aching, sharp, shooting through, itchy).
- Duration (how many hours, days the pain continues).
- The place of dislocation of pain (outside, inside, it is difficult to determine, because the pain is spilled).
- Additional symptoms (noise in the ear, ringing or high-frequency squeaking, hearing loss, distortion of sound perception, nausea, dizziness, loss of balance, temperature).
- Discharge from the ear (whether or not, what character they are, whether they contain impurities of pus and blood).
- Changes in sensations during movement (increases or decreases pain when you change the position of the body, head tilts, turns).
If parents can, as much as possible, tell the doctor at least half of the data from this fairly comprehensive diagnostic list, this will significantly speed up the correct diagnosis and increase the likelihood of a positive outcome and successful treatment.
How to understand that a baby has an ear ache?
Breast children cannot tell what and where they have pain, so parents will have to guess about the causes of anxiety of the crumbs on the basis of subjective signs. They relate primarily to changes in baby behavior. He becomes moody, often crying, sleeping poorly and briefly, sometimes screaming during sleep. The pains are aggravated during the meal, because sucking movements cause an increase in painful lumbago in the ears. Therefore, the baby can begin to eat, and then throw the breast or bottle and start screaming. Children after 4-5 months make it easier for their mothers and fathers, as they will try to touch, scratch the diseased ear, and these movements will be able to prompt the parents for the direction of the search.
One of the objective signs by which an earache in an infant can be established is a simple action that all parents can do; it does not require special medical training. It is enough to press lightly on the ear trestle (the protruding cartilage in front of the auditory opening). At this point, the pressure on the eardrum increases, and if there is an inflammatory process, the pain increases. If a child begins to show a clear anxiety when pressure is applied to the trestle, his crying increases, then inflammation may be assumed with a high degree of probability.
Nursing mothers can use another diagnostic tool. If a child with an allegedly sore ear is applied to the arm while breastfeeding, then the pain is reduced, the baby calms down. Among other objective signs that indicate inflammation in the ear, it can be noted that the temperature has risen to high values, the discharge of fluid from the ear, most often a yellowish tint.
First aid
As already mentioned, any problems with the hearing organs must be evaluated and treated by a doctor. But he still needs to get to or wait until he arrives at the call. In addition, for many babies, the ear starts to hurt at night. Therefore, parents should be able to provide first-aid baby. She is, regardless of the reasons that have become the starting mechanism, will be as follows:
- Call a doctor or call the clinic.
- Provide your baby rest.
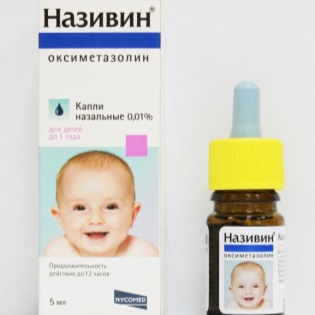
- To drip into the nose nasal drops with a vasoconstrictor effect ("Nazivin", "Nazol"). The preparations of this group narrow the distance between the vessels and eliminate swelling in the nasal cavity and in the region of the auditory tube.
- When fever, fever, heat should be given a febrifuge, it is best if it is Paracetamol.
- With poorly tolerated pain syndrome, you can give the child "Erespal"In the age dosage, avoiding the pill form.
On this list of parental actions should be limited. Everything else, including the instillation of ear drops, the use of compresses - the competence of the doctor. In the framework of first aid, a child should never bury anything in the ear, as this can lead to tragic consequences if the integrity of the eardrum is compromised. Independently assess whether it is the goal, parents can not afford, and therefore it is worth refusing to drop it altogether, including drops with antibiotics, boric acid, popular with the older generation, and other means.
Treatment
Treatment of ear problems is prescribed after the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis. Most otitis is treated symptomatically. Moreover, the use of antibacterial agents is not as necessary as parents used to think. For the treatment of uncomplicated otitis of the outer ear can be appointed ointment. With otitis media, it is often recommended to bury ear drops, such as "Otipaks», «Otinum».
Treatment of internal otitis media depends on the reasons for it and the degree of damage to the ear. For infections such as chickenpox, mumps do not treat the ears separately. Therapy is aimed at treating the underlying disease. As a means of reducing unpleasant sensations in the organs of hearing, the doctor may advise the sameOtinum". But usually there is no special need for drops, since the ear problem disappears as the child recovers from the main disease.
If a baby has a sulfuric plug, it is removed mechanically. This procedure is done quickly, in the ENT doctor's office, it is painless. Hearing after it is fully restored, an unpleasant feeling of congestion disappears.
Allergic otitis media requires treatment with antihistamines in combination with local preparations - ear drops, and otomycosis - antifungal drugs, both locally and in tablets. The foreign body in the ear is removed by the ENT doctor, and if it is too far, by an otosurgeon.
In suppurative inflammatory processes, sometimes (quite rarely) the eardrum shows high strength and does not rupture, pus does not come out. If there is a possibility of pus breakthrough in the brain area, the child is made a mechanical hole in the eardrum to release the pus. The membrane after this in a fairly short time is fully restored.
Antibiotics and antibiotic drops are usually prescribed together. Indications - a very difficult course of bacterial otitis, purulent otitis on the background of high temperature and intoxication especially if the child is under three years old. In some cases, doctors practice waiting tactics. After stating the fact of otitis, they can give two days for the disease to go away on its own. And for many young patients, this is what happens. They will not wait if the child is under 3 years old.
After the acute stage of almost any disease of the organs of hearing is passed, physiotherapy treatment is often prescribed, electrophoresis of the ear area, hearing of the auditory tube, pressure chamber, pneumomassage of the eardrum.
Emergency situations
There are some earaches that should immediately call an ambulance and not waste a minute on anything else.
You need to call an ambulance if:
- the child is not a year old (especially for newborns);
- the baby has a temperature above 39.0 degrees;
- the child vomited against the background of high temperature, and the ear began to leak;
- if an unknown insect bit into a child’s ear and edema developed;
- if, with or without acute pain, there is sudden deafness;
- if the child has lost consciousness after complaints of the ears, or he has convulsions.
How to check your hearing at home?
Since one of the important symptoms of various diseases of the ears is hearing loss, parents should understand that it is not always the baby who will be able to formulate the fact of distortion of sound perception or sound conduction. The little ones will not demonstrate it at all, and the older children simply will not find the right words to tell them what exactly worries them. Therefore, it is important to be able to check the child’s hearing by yourself. This can be useful at the stage of treatment prescribed by a doctor, and after recovery, because hearing is not immediately restored.
In an infant, upon the occurrence of a one-sided hearing loss, the compensatory abilities of the second ear will work immediately, and outwardly practically nothing will change. To examine the ear, you need to bring a rattle with a soft tone or a plastic container with croup, first from the side of the right ear, and then from the side of the left ear. In this case, the second ear should be covered with his hand. If there is a reaction (turning the head to the sound) in both cases, there is nothing wrong with hearing, if the child turns only in one direction, then it is necessary to visit the doctor and examine the condition of the second ear using the hardware method.
For children up to one year, the methods for evaluating reactions to quite loud sounds are quite informative. If the kid shudders at a loud knock at the door, the sound of a spoon falling on the floor, blinks in response to such a sound stimulus, blinks, which means there are no reasons for worry. With children who have not yet learned to speak, use the method of whisper speech, which does not need to repeat the words. It is necessary to create silence in the room, after which a child from a distance of 5-6 meters should quietly ask a familiar question, for example, “Do you want to walk?”, “Will you have a candy?” Or simply call the crumbs by name. The reaction of the child to the question may indicate that he is quite normal to hear. Lack of response - the reason for medical research methods.
In preschool and junior high school students check is carried out in a whisper speech. It is best to pronounce words or numbers familiar to your child. The distance is at least 5-6 meters. The whisper is carried out after expiration by reserve air. It is best for schoolchildren to check in whisper speech from a distance of 5-6 meters, but for this you should use the pronunciation on the exhalation of numbers from 21 to 99. A good result is at least five consecutive correctly repeated numbers.
If there is no reaction, or it is doubtful, it is worth getting close to the child by about a meter and then whispering again. If there is no reaction, you need to approach another meter. This determines the threshold of hearing.
Treatment of folk remedies
Many parents who bring their children to the reception with hearing loss, deafness, complaints of chronic pain admit that they tried to treat the child with folk remedies. Ear diseases are not warts or acne, it is strictly prohibited to treat them with onion juice or aloe. Severe complications, up to the complete loss of the ability to hear, can result in such a "treatment" if the eardrum has deformities. In this case, onion juice and other decoctions will fall immediately into the middle and inner ear. And the practice of applying warm compresses on a diseased organ of hearing can lead to such severe complications as meningitis and encephalitis, in which inflammation passes to the meninges.
This is primarily due to the fact that when heated, ideal conditions are created for the reproduction of pathogenic bacteria. Compress can only be dry (gauze, cotton), only with the permission of the doctor, if he does not find bacterial causes of pain and only infrequently. According to experts, compresses do not affect the speed of recovery at all.
Prevention
Organ diseases in most cases can be prevented.
For this you need to know about preventive measures:
- It is necessary to observe hygiene of the ear cavity.. Clean and wash ears in time, avoid foreign objects entering into them.
- A child from an early age should be taught to blow your nose correctly., so that the mucus from the nose does not fall into the auditory tube. It is necessary to blow one's nose only with an open mouth; inhalation of mucus (that same sniffing) often leads to the defeat of the Eustachian tube and the occurrence of otitis media.
- A baby cannot be fed with a mixture or given to drink from a bottle lying down.. In this position of the body, the risk of food or water entering the auditory tube increases.
- In the pool should always give the child with a swimming cap. This significantly reduces the risk of water entering the ear cavity.
- Should protect the child from seasonal viral infections. To do this, you should be regularly vaccinated against influenza, and during the period of active distribution of acute respiratory viral infections do not take the baby to crowded places, do not go to shops, pharmacies, clinics, try not to travel in crowded public transport.
- Do not allow your child to breathe tobacco smoke, so he went in the car with a smoking adult, so he breathed too dry air. To humidify the air at home should use special devices - humidifiers. The relative humidity of air recommended by pediatricians is 50-70%.
- Do not self-medicate, do not uncontrolled antibiotics, remember that you can turn a simple ear inflammation into a severe hearing loss that cannot be treated with your own parental unreasonableness.
The doctor will tell you about the causes of otitis and how to treat it. Komarovsky in the next video.