Type 1 diabetes in a child
Diabetes is a common chronic disease, while in children it is more difficult than in adulthood. When a child appears in the child, the whole family must adapt to this problem. Why does the child develop diabetes and what is the difference between type 1 and this disease?
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes
As a rule, in diabetes of the first type, the symptoms increase rather quickly. In just a few weeks, the child's condition worsens so much that he urgently enters a medical facility. So it is very important to be able to recognize the first signs of the disease, which include:
- Constant thirst. It appears due to dehydration of body tissues, as the body tries to dilute the glucose circulating in the blood by drawing water out of them. The child asks to drink water or other drinks in large quantities.
- Frequent urination. Parents notice that the child has become more likely to go to the toilet, and at night.
- Sudden weight loss. The source of energy (glucose) ceases to enter the cells of the body, therefore the consumption of fat and protein tissue increases. As a result, the child ceases to gain weight, but on the contrary, it loses weight quickly.
- Fatigue. Parents notice the child's lethargy and weakness due to lack of energy.
- Increased hunger. It is also due to the lack of glucose in the tissues, so with a large consumption of food, the child can not get enough. If the condition of the baby has deteriorated so much that he began to develop ketoacidosis, then his appetite will fall.
- Vision problems. As a result of dehydration of the lens, a child may have a fog before his eyes and visual impairment.
- Damage to fungal infection. Young children have severely treatable diaper rash, and girls may develop thrush.

If you do not pay attention to such signs of the disease, the child’s condition worsens and ketoacidosis develops. It is manifested by abdominal pain, lethargy, nausea, intermittent noisy breathing, the appearance of mouth the smell acetone. The child may lose consciousness. In addition, this complication can lead to death.
Causes
The true causes of development in children of the first type of diabetes, scientists have not yet identified. In a sick child, the immune system, which must fight off dangerous germs and viruses, suddenly begins to have a destructive effect on the pancreas (in particular, the cells responsible for insulin synthesis).
It has been established that there is a genetic predisposition to the onset of type 1 diabetes; therefore, in the presence of the disease among relatives, the risk of the occurrence of such a pathology in a child increases.
The starting factor, due to which type 1 diabetes begins, may be a viral infection (for example, influenza or rubella) or severe stress.
Risk factors for developing type 1 diabetes include:
- The presence of an insulin-dependent form of diabetes in someone from close relatives (the disease is in the parents, as well as in the sisters or brothers).
- Infections caused by viruses. Particularly often, diabetes develops after lesions with the Coxsackie virus, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus or rubella virus.
- Low vitamin D.
- Unnecessarily early feeding of cow's milk or cereal products.
- Drinking water with an increased nitrate content.

How does the disease develop?
The hormone insulin is formed in the cells of the pancreas. The main function of insulin is to help glucose pass into the cells where this carbohydrate is used as fuel.
Constant feedback is present in the exchange of glucose and insulin. In a healthy child, after ingestion of food, insulin is released into the bloodstream, as a result of which the glucose level decreases (glucose from the blood enters the cells). This leads to a decrease in insulin production so that the amount of glucose in the blood does not decrease too much. At the same time, glucose is stored in the liver so that the sugar level is maintained normal - during a strong decrease in its blood level, glucose molecules are released from the liver into the blood.
In diabetes, the number of beta cells in the pancreas is reduced, so insulin is not produced enough. The result will be both starvation of the cells, since they will not receive the fuel they need, as well as an increased content of glucose in the bloodstream, leading to the appearance of clinical symptoms of the disease.
Diagnostics
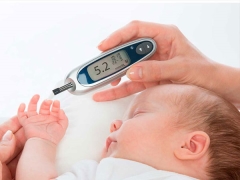
It is important to determine whether the child has diabetes, and what type of disease. If a baby is suspected of having type 1 diabetes, donate blood to determine glucose concentration. If the indicator exceeds 6.1 mmol / l, the analysis is carried out one more time to confirm the diagnosis, as well as prescribe additional tests.
To ensure that this is really type 1, an antibody test is prescribed. When this study detects antibodies to insulin or to pancreatic cells in a child’s blood, this confirms the presence of diabetes of type 1 itself.
Unlike type 2 diabetes, with the first type, the symptoms will develop more actively, the disease can begin at any age and with any body weight. Blood pressure will not be increased, and autoantibodies will be detected in the baby’s blood.
What is the treatment?
The goal of treating diabetes of the first type is to provide the child with the opportunity to develop normally, to attend the children's team, not to feel defective in comparison with healthy children. Also, treatment should be aimed at preventing serious complications of diabetes so that such severe manifestations are as remote as possible.
To continuously monitor the disease, the child needs to measure blood sugar several times a day, so parents will need to purchase an accurate blood glucose meter. In the treatment of a child with type 1 diabetes, it is also important to follow a low carbohydrate diet. You should keep a diary in which the results of glucose measurement and nutritional characteristics of the child will be noted.
Since type 1 diabetes is caused by a lack of insulin, insulin injections are the main treatment for this disease. There are many types of insulin preparations with different duration of action. For the introduction of insulin use special syringes with thin needles, as well as syringe pens. Special devices are also developed that supply the hormone in small portions - insulin pumps.
Many parents are interested in whether it is possible not to prick the child with insulin, or at least not to do it daily. This is only possible with a strict low-carb diet, if diabetes in a child has recently been identified. Meals with a minimum of carbohydrates allows you to achieve long-term remission.
Possible complications
All the complications of type 1 diabetes are divided into acute, which must be treated immediately, as well as chronic, which can be kept as far as possible with proper treatment. Complications that arise acutely include ketoacidosis, as well as hypoglycemia.
Chronic complications of the disease affect the heart, nervous system, kidneys, eyes, skin, bones and other organs and tissues. The disease leads to the appearance of retinopathy, deterioration of blood flow in the legs, osteoporosis, nephropathy, angina pectoris, neuropathy, and many other pathologies. To prevent complications of type 1 diabetes, it is important to continuously monitor glucose levels and be examined annually.

Prevention
Effective effective methods of preventing the first type of diabetes does not exist. Thanks to genetic testing, it is possible to identify a child's susceptibility to this pathology, but this will not be an exact confirmation that the baby is sick, and also can not prevent the development of the disease.