Hip dysplasia in newborns and infants
After birth, newborns often have hip dysplasia. Diagnosis of such diseases is quite complicated. The parents will be able to suspect the first signs already in children up to one year old. This disease is dangerous development of adverse complications that can significantly impair the quality of life of the baby.
What it is?
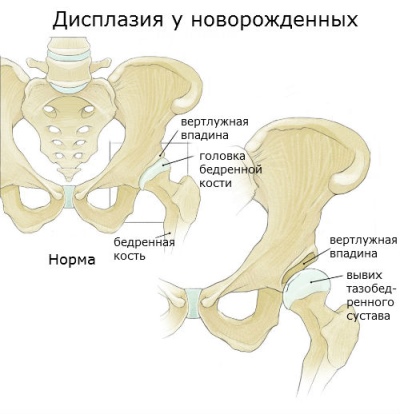
This pathology of the musculoskeletal system arises from the effects of numerous causes that lead to a violation of intrauterine organ insertion. These factors contribute to underdevelopment. hip joints, as well as all the articular elements that form the hip joints.
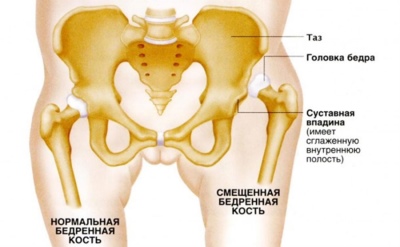
In severe pathology, the joint between the head of the femur and the acetabulum, which forms the joint, is broken. Such violations lead to the appearance of adverse symptoms of the disease and even the appearance of complications.
Congenital underdevelopment of the hip joints is quite common. Almost every third of the born hundreds of children registered this disease. It is important to note that susceptibility to this disease is higher in girls, and boys get sick less often.
In European countries, dysplasia of large joints is more common than in African countries.
Usually there is a pathology on the left side, right-sided processes are recorded much less frequently, as are cases of bilateral processes.
Causes
Provocative factors that can lead to the development of the physiological immaturity of large joints, there are several dozen. Most of the effects that lead to immaturity and disruption of the structure of large joints, occur in the first 2 months of pregnancy from the moment of conception of the baby. It is at this time passes the intrauterine structure of all elements of the musculoskeletal system of the child.
The most common causes of illness include:
- Genetics. Usually in families where there have been cases of this disease, the likelihood of a baby with pathologies of large joints increases by 40%. In this case, girls have a higher risk of getting sick.
- Exposure to toxic chemicals during pregnancy. This situation is most dangerous in the first trimester when intrauterine insertion of the organs of the musculoskeletal system occurs.
- Unfavorable environmental situation. Harmful environmental factors have a negative effect on the development of the unborn child. An insufficient amount of incoming oxygen and a high concentration of carbon dioxide can cause fetal hypoxia and lead to disruption of the structure of the joints.
- Future mother is over 35 years old.
- The weight of the child is more than 4 kilograms at birth.
- The birth of the baby ahead of time.
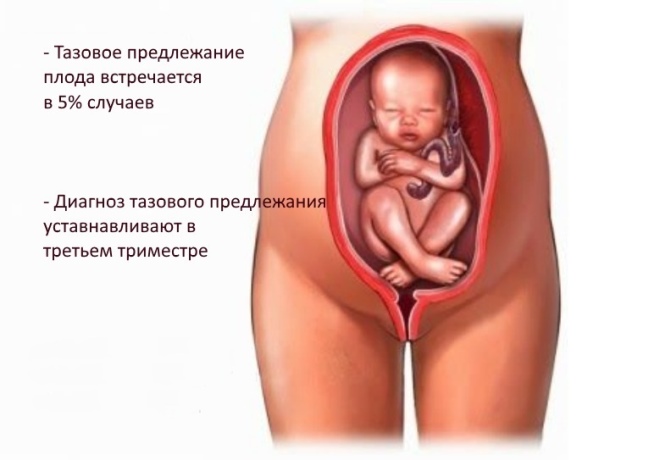
- Buttock previa.
- Bearing a large fetus with initially small size of the uterus. In this case, the kid physically lacks enough space for active movements. Such forced passivity during intrauterine development can lead to mobility impairment or congenital dislocations after birth.
- Infection with various infections of the future mother. During pregnancy, any viruses or bacteria easily pass through the placenta.Such infection in the early stages of baby development can lead to birth defects in the structure of large joints and ligaments.
- Poor nutrition, lack of essential vitaminsthat are needed for the full development of cartilage and ossification - the formation of bone tissue.
- Excessive and tight swaddling. Excessive pressing of the child’s legs to the body can lead to the development of multiple dysplasia variants.
Kinds
Doctors classify various forms of the disease according to several basic features. In dysplasia, such criteria are combined into two large groups: by the anatomical level of the lesion and by the severity of the disease.
By anatomical level of damage:
- Acetabular. There is a violation in the structure of the main large elements that make up the hip joint. Basically, in this variant, the limbus and marginal surface are affected. At the same time, the architecture and the structure of the articulation vary greatly. These injuries lead to impaired movements, which should be performed by the hip joint in normal conditions.
- Epiphyseal. Characterized by a violation of mobility in the joint. In this case, the norm of the angles, which are measured to assess the performance of large joints, is noticeably distorted.
- Rotary. In this variant of the disease, a violation of the anatomical structure in the joints may occur. This is manifested by the deviation of the main structures that form the hip joint from the median plane. Most often, this form manifests a violation of gait.
By severity:
- Mild degree Doctors also call this form predislocation. Strong violations that occur with this option and lead to disability, as a rule, does not occur.
- Medium heavy. May be called subluxation. In this embodiment, the femoral head usually extends beyond the articulation with active movements. This form of the disease leads to the development of adverse symptoms and even long-term negative effects of the disease, which require more active treatment.
- Heavy current. Such a congenital dislocation can lead to a leading contracture. In this form, there is a marked disturbance and deformity of the hip joint.
Symptoms
Detection of the first symptoms of anatomical defects of large joints of the joints is carried out already in the first months after the birth of the baby. You can suspect the disease already in infants. When the first signs of the disease appear, the orthopedic surgeon should show the baby. The doctor will conduct all additional examinations that will clarify the diagnosis.
The most characteristic manifestations and signs of the disease include:
- Asymmetry of the skin folds. Usually they are well defined in newborns and infants. Each mom can rate this symptom. All skin folds should be approximately at the same level. Severe asymmetry should alert the parents and suggest that the child has signs of dysplasia.
- The appearance of a characteristic sound resembling a clickwhile casting the hip joints. Also, this symptom can be identified with any movement in the joint in which the abduction or adduction occurs. This sound is caused by active movements of the femoral head on the articular surfaces.
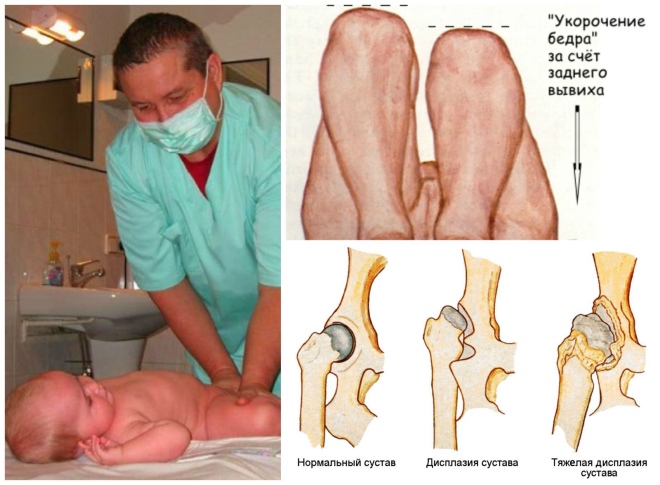
- Shortening the lower limbs. It can occur both on the one hand and on both. With a two-way process, the baby is often stunted. If pathology occurs only on one side, then the child may develop lameness and gait disturbance. However, this symptom is defined more rarely when trying to get the baby on its feet.
- Soreness in large joints. This sign is enhanced when the child tries to stand up.Increased pain occurs when performing various movements at a faster pace or with a wide amplitude.
- Secondary signs of the disease: small muscle atrophy in the lower limbs, as a compensatory reaction. When trying to determine the pulse on the femoral arteries, a slightly reduced impulsation may be observed.
Effects
Dysplasia is dangerous by the development of adverse complications that can occur with a long course of the disease, as well as with insufficiently effective and well-chosen treatment of the disease in the initial stages.
With a long course of the disease, persistent gait disturbances may develop. In this case, surgical treatment is required. After such therapy, the baby may limp a little. However, further this unfavorable symptom completely disappears.
Also, if signs of the disease have been observed for a long time, muscle atrophy may occur on the injured lower limb. Muscles on a healthy leg, on the contrary, may be overly hypertrophied.
Strong shortening also quite often leads to gait disturbance and severe limping. In severe cases, this situation can even lead to the development of scoliosis and various postural disorders. This is due to the displacement of the support function of the injured joints.
Dysplasia of large joints can lead to various adverse effects in adulthood. Quite often in such people cases of osteochondrosis, flat-footedness or dysplastic coxarthrosis are recorded.
Diagnostics
As a rule, this pathology begins quite erased. Only a specialist can determine the first symptoms; it is rather difficult for parents to do it on their own at home.
The first step in establishing a diagnosis is to consult an orthopedic surgeon. Already in the first year of a child’s life, the doctor determines the presence of predisposing factors, as well as the primary symptoms of the disease. It is usually possible to recognize the first orthopedic signs of the disease during the first half of the child’s life. For accurate verification of the diagnosis, various types of additional examinations are prescribed.
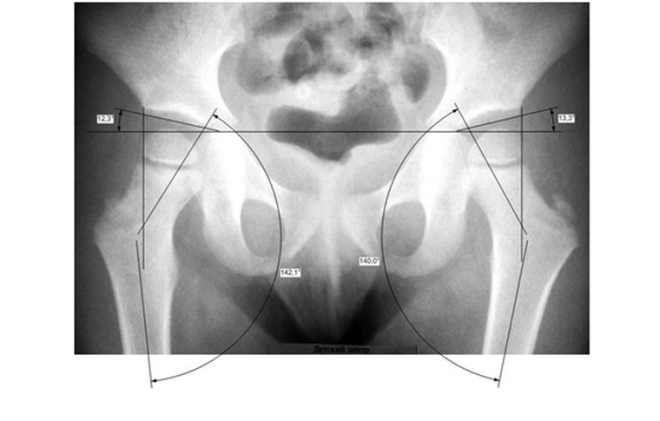
The safest and most informative method that can be used in infants is ultrasound. Decoding ultrasound allows you to install various characteristic of the disease signs. Also, this method helps to establish the transient form of the disease and to describe the specific changes characteristic of this variant occurring in the joint. Using ultrasound, you can accurately establish the timing of ossification of the nuclei of the hip joints.
Ultrasound diagnosis is also a highly informative method that clearly describes all the anatomical defects observed in various types of dysplasia. This study is absolutely safe, and is performed from the very first months after the birth of the baby. Severe radiation load on the joints during this examination does not occur.
Radiodiagnosis is used only in the most difficult cases of the disease. X-rays can not be carried out for kids younger than one year. The study allows you to accurately describe the various anatomical defects that occurred after birth. Such diagnostics is also used in complex clinical cases in which the exclusion of concomitant diseases is required.
All surgical methods for examining large joints in newborn babies are not used. In arthroscopy, doctors, using instrumental tools, study all the elements that make up the hip joint. During such studies, the risk of secondary infection increases several times.
Usually, magnetic resonance and computed tomography of large joints is carried out before planning various surgical interventions.In difficult cases, orthopedic physicians may prescribe these examinations to rule out various diseases that may occur with similar symptoms.
Treatment
It is necessary to treat diseases of the musculoskeletal system for a long time and with strict observance of the recommendations. Only such therapy allows to eliminate as much as possible all the adverse symptoms that occur in this pathology. The orthopedic therapy complex is prescribed by the orthopedic surgeon after the examination and examination of the baby.
Among the most effective and frequently used treatments are the following:
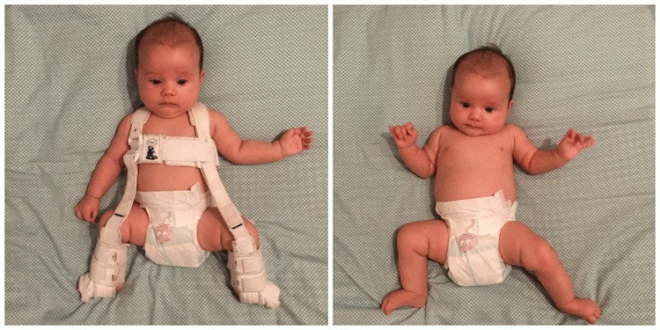
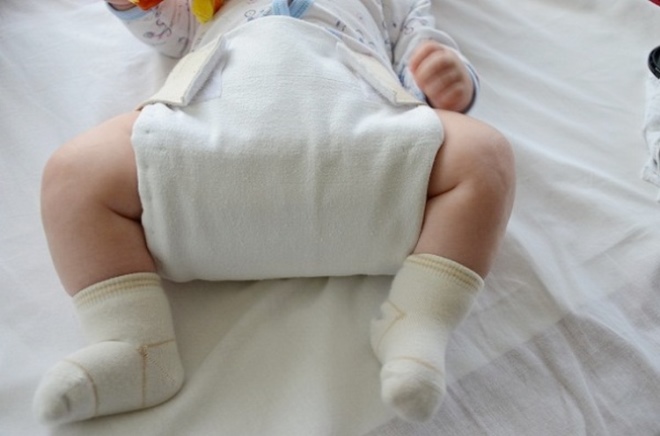
- Use wide swaddling. This option allows you to maintain the most comfortable position for the hip joints - they are in a somewhat diluted state. This kind of swaddling can be applied even in babies from the first days after birth. Becker pants are one of the wide swaddling options.
- The use of various technical means. The most commonly used various tires and struts. They can be of different stiffness and fixation. The selection of such technical means is carried out only on the recommendation of the orthopedic surgeon.
- Exercise and exercise therapy complex should be performed regularly. Usually such exercises are recommended to be done daily. Complexes should be performed under the guidance of the medical staff of the polyclinic, and subsequently - independently.
- Massage. Appointed from the first days after the birth of the baby. It is conducted by courses several times a year. With this massage, a specialist works well on the legs and back of the baby. This method of treatment is perfectly perceived by the child and, if carried out correctly, does not cause him any pain.
- Gymnastics. A special set of exercises must be performed daily. Removing and bringing the legs in a certain sequence allows you to improve movement in the hip joints and reduce the manifestations of stiffness in the joints.
- Physiotherapy treatments. Baby can be done ozokerite and electrophoresis. Also, various types of thermal treatment and induction therapy are actively used for children. Perform physiotherapy procedures for the treatment of dysplasia can be in the clinic or specialized children's hospitals.
- Spa treatment. Helps to effectively deal with adverse symptoms arising from dysplasia. Staying in a sanatorium can significantly affect the course of the disease and even improve the baby’s well-being. For children with dysplasia of the hip joints, it is recommended to undergo a spa treatment annually.
- Full nutrition with the obligatory inclusion of all necessary vitamins and minerals. Be sure to kids with violations in the musculoskeletal system should eat a sufficient amount of fermented milk products. Calcium contained in them favorably affects the structure of bone tissue and improves the growth and physical development of the child.
- Surgical treatment of newborns, as a rule, is not carried out. Such therapy is possible only in older children. Usually, before reaching 3-5 years old, doctors try to carry out all the necessary treatment methods that do not require surgery.
- The use of painkillers nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate severe pain. Such drugs are prescribed mainly in severe variants of the disease. Prescribes an anesthetic orthopedic doctor or pediatrician after examining a child and identifying contraindications to such drugs.
- The imposition of gypsum. It is used quite rarely. In this case, the affected leg is tightly fixed with a plaster cast. After some time, the cast is usually removed. The use of this method is quite limited and has a number of contraindications.
Prevention
Even in the presence of a genetic predisposition of the disease, it is possible to significantly reduce the risk of adverse symptoms in the development of dysplasia. Regular adherence to preventive measures will help to significantly improve the well-being of the child and reduce the possible onset of dangerous complications.
In order to reduce the risk of possible development of dysplasia, use the following tips:
- Try to choose a freer or wider swaddle.If the child has several risk factors for the development of dysplasias of large joints. This method of swaddling can reduce the risk of developing disorders in the hip joints.
- Monitoring the healthy course of pregnancy. Try to limit the effects of various toxic substances on the body of the future mother. Strong stress and various infections can cause various intrauterine malformations. The future mother must take care to protect her body from contact with any ill or feverish acquaintances.
- The use of special car seats. In this case, the baby's legs are in the anatomically correct position during the entire journey in the car.
- Try to properly hold the baby in your arms.. Do not press the baby's legs tightly to the body. Anatomically more advantageous position is considered a more diluted position of the hip joints. Also remember this rule when breastfeeding.
- Preventive complex gymnastic exercises. Such gymnastics can be performed from the first months after the birth of a child. The combination of exercises with a massage significantly improves the prognosis of the disease.
- Get the diapers right. A smaller size may cause the forced condition of the legs in a child. Do not allow excessive filling of the diaper, change them often enough.
- Have regular checkups with an orthopedic surgeon. At such consultations, every baby must be present before the onset of six months. The doctor will be able to establish the first signs of the disease and prescribe the appropriate treatment complex.
With quality treatment, most of the negative manifestations of dysplasia can be almost completely eliminated. Medical surveillance of a child diagnosed with dysplasia should be for a long time. These babies are regularly examined by a neurologist and an orthopedist. Controlling the course of the disease prevents the development of dangerous and unfavorable complications.
For information on what hip dysplasia is, how it is treated and at what age it is best to start treatment, see the following video.