Eczema in children
The prevalence of allergic diseases in children is now growing every day. Adverse symptoms can occur in both newborns and adolescents. In this article we will talk about eczema in children.
What it is?
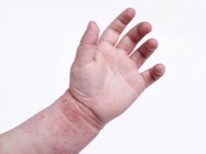
An acute inflammatory allergic reaction that occurs in the skin layers when specific allergens get into them is called eczema. The adverse symptoms of the disease can develop in a child at any age. Usually the most severe course occurs in infants.
For the development of eczema in the baby requires a special predisposition. Scientists have shown that in babies whose parents suffer from various allergic diseases, the risk of getting eczema exceeds the average incidence rates by more than 40%. If both mom and dad have an allergy at the same time, then the probability of this disease in a baby increases to 60%. This hereditary feature is due to the special functioning of the immune system in allergy sufferers.
Some specialists use a different term for this disease. They believe that it is more correct in young children to speak about the presence of not eczema, but “exudative dermatitis”. In this condition, the local sensitivity of the skin to various specific allergens is increased, the body's resistance to many infections is reduced, and there is also an increased tendency to form inflammatory exudates.
Usually doctors record cases of eczema. in the smallest patients. In older age, the incidence is somewhat reduced. The development of the disease contribute to a variety of factors. These include: the presence of diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency states, pathologies in the thyroid gland, chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, allergic diseases.
The treatment and diagnosis of this disease are engaged in children's allergists and dermatologists.
The reasons
A variety of causal factors lead to the occurrence of a child's disease. To date, a single cause of the disease does not exist. In some cases, causal factors can act simultaneously, which leads to the emergence of various clinical forms of the disease in the same child.
Doctors identify several main causes leading to the appearance of adverse symptoms on the skin in babies:
- Heredity. All genes that encode a tendency to increased allergization, to date, not installed. However, it is statistically proven that in families where close relatives have allergic diseases, eczema in children occurs twice as often.
- Pathological conditions of neurohumoral regulation. Typically, these conditions arise as a result of various pathologies and failures in the nervous system. In some cases, the symptoms of eczema occur in a baby after a strong psycho-emotional shock or stress. These include: frequent moves to a new place of residence, divorce of parents, death of a close relative (especially at an early age).
- Increased individual skin sensitivity. This condition is not a pathology. Usually, the high susceptibility of the skin to the action of various substances is present in some babies from birth. These kids, as a rule, have light and tender skin, which is prone to the appearance of redness and any irritation.
- Immunodeficiency states. Can be congenital and acquired. The impaired work of the immune system contributes to the bright course of allergic reactions with the appearance of numerous symptoms that bring pronounced discomfort to the baby. Quite often, immunodeficient pathologies occur in premature babies and children with numerous chronic diseases.
- Secondary foci of chronic infection. The presence of an infectious process in the body is always a "time bomb." With a decrease in immunity as a result of exposure to adverse environmental factors, the growth of the microbial flora is activated, which contributes to the appearance of clinical signs of eczema in a child.
- Increased propensity for any allergic reactions. In this case, the allergen that has entered the child’s body easily causes a cascade of inflammation in the child, in which exudative edema develops, and specific inflammatory elements appear on the skin.
- Improper hygiene careespecially in newborns. The use of products containing dyes and chemical fragrances, can cause the appearance on the skin of the child specific lesions.
- Artificial feeding. Rapid abandonment of breastfeeding often leads to a decrease in passive immunity in a baby. Incorrectly selected adapted mixture, which cannot compensate for the entry into the children's organism of all the nutrients necessary for its growth and development, causes the child to have an increased tendency to form allergic reactions.
Kinds
Doctors distinguish several clinical forms of this pathology. Such a difference is caused by different reasons that lead to their appearance. Each clinical form of eczema has its own distinctive features and preferential localization. There are also some differences in the treatment and diagnosis of such pathologies.
There are several clinical forms:
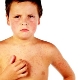
- Coin-like. It causes the child to have elongated plaques on the skin that resemble a coin in shape and medium size. Usually, skin rashes are localized on the back, buttocks, and legs. Outside, the skin plaques are covered with several layers of keratinized scales, which easily peel off from the surface at any contact with them. More often the given form meets at more advanced age.
- Viral. Various viruses provoke the appearance of adverse symptoms. Often, the causative agents of influenza, chicken pox, rubella, simple and herpes zoster and others. The rash can be located on various parts of the body: on the cheek, on the back, on the chin, on the elbows and other anatomical zones. To eliminate the adverse symptoms, it is necessary to include antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs in the treatment regimen.
- Soaking. It is characterized by the appearance of large bubbles, inside of which is a serous fluid. These skin lesions are easily traumatized with the expiration of the exudate, and therefore are called "weeping." Often unfavorable symptoms are found in the half-year-old babies. Primary localization is on the arms, buttocks, lower limbs.
- Microbial. Caused by various microorganisms. The development of adverse clinical symptoms is preceded by a pronounced decrease in immunity. Manifested by the appearance on the skin of red inflammatory skin rashes. To eliminate the clinical signs of the disease, complex treatment is required.
- Herpetic The development of this clinical form is caused by infection with various subtypes of the herpes virus. It is characterized by the formation of bubbles on the skin, filled with sero-bloody fluid. These formations can easily be injured and ulcerate.The disease can occur with a rather severe course and significantly impairs the well-being of the child.
- Bacterial. Also called microbial. It is not difficult to guess that infection with various bacteria leads to the development of this clinical form. The peak incidence occurs at the age from two to six months after the birth of the baby. To eliminate the adverse symptoms of sick children, modern antibiotics are prescribed, which have a systemic broad spectrum of action.
- Herpetiform or Kaposi eczema. Develops due to infection with the herpes virus type 8. It occurs in children, especially young age, quite hard. It is characterized by the appearance on the skin of numerous skin rashes, which easily turn into erosion. With Kaposi's eczema, peripheral lymph nodes increase and body temperature rises significantly.
- Seborrheic. The cause of this pathology is not yet established. This form is characterized by the appearance of scaly yellow plaques, which are usually located on the face, scalp and less often on other anatomical zones. Often the appearance of dandruff in babies can be due to the presence of seborrheic eczema in the child.
Skin rashes may be accompanied by slight itching.
Symptoms
The initial stage of eczema is the same for all babies - various skin rashes appear on the skin. The severity of symptoms may be different. This largely depends on the initial state of the child, the presence of concomitant chronic diseases and immunodeficiency, as well as at what age the disease develops. The appearance of rashes on the skin usually leads parents to the real horror. Panic is not worth it! When the first adverse clinical signs appear, it is very important to immediately consult a doctor.
The doctor will conduct a clinical examination, during which he will be able to establish whether the child has signs of eczema or is it another disease that occurs with similar symptoms.
The presence of a large number of clinical variants of the disease causes a variety of different forms of skin rashes. Thus, some forms of eczema occur with the appearance of bright red spots on the skin. They can reach in size from ½ to several centimeters. To the touch stains are hot. The child may feel pronounced itching.
Frequent scratching of the damaged areas of the skin leads to the fact that the secondary bacterial flora easily gets into its surface layers. This greatly aggravates the prognosis of the disease. Skin rashes can fester with the expiration of pus out. To eliminate this adverse symptom requires the mandatory appointment of antibiotics. In severe cases, they are administered by intravenous or intramuscular administration.
During the entire acute period of the disease, the sick child looks very bad. The baby appears weakness and apathy. The child plays less with his favorite toys, can avoid contact with other children and even parents. Severe itching of the skin violates the behavior of the baby. The baby is becoming more capricious.
Often, ill children sleep poorly. Eczema disrupts the duration of both day and night sleep. They can often wake up in the middle of the night due to severe itching of the inflamed skin. Some babies have impaired appetite. Infants may refuse breastfeeding.
In some cases, the course of eczema in babies can be chronic. Then it is characterized by a change of periods of exacerbation and unstable remission. Usually, adverse symptoms reappear in the cold season or after severe psycho-emotional stress. Separate cases were noted when clinical signs of eczema appeared in an allergic child after age-related vaccination.
Usually the severity of symptoms by three years gradually decreases.
Eczema may have a mild course. In this situation, only small reddenings appear on the skin, which usually do not even itch. After an acute period of the disease, such skin elements disappear completely, and the skin regains a healthy appearance. Most often, such rashes appear in a baby after washing, with teething, during active and excessively intense classes in school, after adding new unfamiliar food products to food. These clinical signs do not bring the child discomfort and after several days pass by themselves.
From a clinical point of view, microbial and seborrheic types of eczema are most common in children. In babies with a strong sensitivity of the skin to the action of various allergens, there is a tendency for mass appearance of skin rashes, as well as for their draining into large areas.
The prognosis of the disease in most cases is conditionally favorable, since there is a tendency to chronicity of the process. Only weakened children with eczema can have very unfavorable complications.
There are also quite rare types of eczema. These include: varicose and post-traumatic. When the varicose form of inflammatory skin changes appear in the veins of the lower extremities. This clinical form is associated with the presence of individual disorders of the vein trophism in the child, as well as excessive sensitivity to the effects of various bacterial flora. Varicose eczema is accompanied by the appearance on the skin of various weeping ulcers, which are poorly epithelized.
Even after healing, residual changes may remain on the skin for a long time. Usually they appear in the form of increased dryness and thinning of the skin. In some areas there is a strong peeling, which disappears after a few months.
Post-traumatic eczema appears after various injuries, burns and open damage to the skin.
Treatment
Children's allergists and dermatologists deal with the therapy of various types of eczema. If the disease has arisen due to a chronic disease, then additional consultations of other specialties - a gastroenterologist, a dentist or an otolaryngologist may be required.
Prescribing treatment tactics is carried out only after all the necessary tests are performed, which allow to clarify the severity of clinical manifestations, as well as determine the severity of the disease. Eczema therapy regimen includes the appointment of a whole complex of various therapeutic methods. Treatment of the disease is usually carried out in the acute period of the disease.
During remission, doctors recommend rehabilitation and sanatorium-resort treatment, which contributes to a longer remission.
The following methods are used in the treatment of the disease:
- Normalization of the daily routine. In the daily routine of a sick child a day rest must be present - at least three hours. At night, the baby should sleep at least 8-9 hours, babies - more. This helps the immune and nervous system to work more productively, and the baby to recover faster.
- Observe the hypoallergenic diet. All highly allergenic products are excluded from the diet of an allergic child. These include: sweets, chocolate bars, citrus fruits, seafood, tropical fruits and berries. If a child has an individual immunity of milk protein or gluten intolerance, then any food containing these components is also excluded from his menu. Observe a hypoallergenic diet baby should be throughout life.
- Local treatment. For elimination of inflammations on the skin, lotions with 2% are suitable. boric acid, 0.25% solution of amidopirin, 0.25% solution of silver nitrate and others. It is necessary to apply them according to the recommendation of the doctor.In case of severe and persistent course of the disease, various hormonal ointments and creams are used. These include drugs based on prednisone and dexamethasone.
- Antibiotic prescription. These drugs are used to treat microbial eczema, as well as in the secondary infection with bacterial flora of other skin rashes. Selection of antibiotics is carried out taking into account the child’s age, weight, and the presence of chronic concomitant diseases in the baby, which may be a relative contraindication for prescribing these drugs.
- Systemic drug administration. It is used in case of severe disease or in case of ineffectiveness of the previously performed treatment. Antihistamines have a good anti-inflammatory effect. These include: Suprastin, Claritin, Loratadine other. Dosages, frequency of use and duration of the course are chosen by the attending physician based on the individual initial well-being of the child.
- The use of gentle means household chemicals and special children's cosmetics. For the hygienic daily procedures for babies suffering from various forms of allergies, you should use gentle means. They should not contain strong fragrances and coloring additives, which can cause the appearance on the skin of a child of new allergic rashes.
- The appointment of immunomodulatory therapy. It is carried out according to strict indications to all babies with signs of immunodeficiency. Both tablets and injection forms of medicines are used as treatment. The duration of treatment is usually 10-14 days. During the year, usually 2-3 courses of such therapy.
In the next issue of Dr. Komarovsky’s program, you will learn a lot of useful information about the treatment of eczema, as well as other children's skin diseases.