Symptoms and treatment of enterovirus infection in children
Recently, the number of outbreaks of enterovirus infection has increased significantly. Either from one seaside resort, or from another, alarming data are received on the number of cases. But even in cities far from the sea, enterovirus infections are very common, especially in children. What it is, what are the symptoms and treatment - you will learn about all this by reading this article.
What it is?
Enterovirus infections include a large group of diseases. They are united by the fact that all of them are caused by viruses of the same family - picornaviruses. Enterovirus infection is sometimes called intestinal, but not for its manifestations, but for the ability of enteroviruses to enter the body and develop in the human gastrointestinal tract.
Enterovirus infection can manifest itself in completely different ways - from respiratory symptoms (runny nose, cough) to sore throats, from vomiting with diarrhea to disorders of the central nervous system. Viruses cause very specific diseases that cause specific symptoms.
Most often, children become infected and have ARVI. Enterovirus infections are in second place after them. Children are sick more often than adults, this is due to the weakness of the immune system of babies. Of the ten people with established enterovirus infection, eight are children, and many children are in preschool age.
The fact is that the immunity of an adult is able to quickly respond to an enterovirus - thanks to antibodies developed in the course of life. In a child, the stock of such antibodies is small or completely absent. While the immune defense is still “learning” to recognize the causative agents of various ailments, the baby is vulnerable, this is the reason for the high incidence of childhood diseases.
There are a lot of carriers of enteroviruses on the planet, and they do not get sick themselves, they are only carriers. But children and people with weakened immunity may well become infected by contact with such carriers. The virus itself lives for a long time in the body of its carrier - up to several months.
Most often, the infection occurs through contact and household routes - through water, food, various items, common toys. A greater number of cases of infection is registered in regions with a significant population density, as well as where hygiene rules are not observed.
Not all diseases caused by enteroviruses are well and thoroughly studied; in some areas, scientists and doctors are looking for answers to numerous questions. But most of the ailments that can be a consequence of the penetration of an enterovirus into the child’s body are well known to doctors, as are ways to combat these diseases.
About pathogens
The family of enteroviruses includes more than a hundred viruses dangerous for humans. Enumerate all does not make sense, so you should limit yourself to the most famous and most dangerous members of the family. Enteroviruses include 24 serotypes of Coxsackie A virus, as well as 6 serotypes of Coxsacke B.
The most numerous are the serotypes of the ECHO virus (there are 34). The smallest are 4 enteroviruses that do not belong to any group.They are designated by numbers from 68 to 71.
Enteroviruses are very resistant to low temperatures, but quickly destroyed by high temperatures - when boiling enteroviruses die almost instantly. Most often, the diseases caused by active enterovirus occur at the end of summer and the beginning of autumn.
These viruses do not like sunlight, or rather, its ultraviolet spectrum, chlorine-based disinfection products, and hydrogen peroxide. Viruses of this kind survive well in water, in soil.
Viruses enter the body through the mouth, sometimes through the nasopharynx. The most favorable for the development of viruses is the lymphoid tissue that makes up the tonsils and the spleen. Suitable for replication of these viruses and epithelial cells of the oral cavity, pharynx and digestive tract.
Then the virus spreads through the body of the child with the bloodstream, affecting the nervous tissues, muscles, eye vessels. The incubation period, which lasts from the moment the virus enters the body until the first clinical symptoms appear, lasts from 2 to 14 days.
After a disease, which usually lasts about 10 days, the child forms a temporary immunity to the virus that caused his illness.
This protection is not lifelong, but the antibodies act and confidently confront a certain virus for several years.
Kinds
There are many diseases that cause enteroviruses. To make it easier to classify them, in the last century it was proposed to divide them into potentially dangerous and less severe ones. The first group includes:
- serous meningitis;
- sudden acute paralysis;
- encephalitis;
- myocarditis;
- pericarditis;
- hepatitis.
The group of less dangerous diseases caused by enterovirus infection are:
- three days fever;
- herpangina;
- vesicular pharyngitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- gastroenteritis.
In addition, all enteroviral infections are divided into typical and atypical. Typical occur with characteristic symptoms, and atypical forms can occur without symptoms at all. Atypically, almost half of cases of infection with Coxsackie, ECHO, and almost 90% of cases of infection with polio viruses, which are also part of the enterovirus family, occur.
According to the severity of symptoms, infectious diseases of enterovirus origin can be mild, moderate and severe. According to the assessment of consequences - complicated and uncomplicated.
Signs of
Since the "entrance gate" for infection is the oral cavity, nasopharynx, and digestive tract, the first symptoms appear here. There is no clear list of clinical manifestations, but there is a rather impressive list of possible symptoms. Usually they are found in combination - 2-4, while the combinations are always quite unique. Here is a partial list of possible manifestations at an early stage of an enterovirus infection:
- Inflammation of the nasal cavity, his sinuses. This is manifested by a runny nose, a feeling of congestion of the paranasal sinuses, heaviness when the head is tilted down, loss of the ability to distinguish odors. Sometimes inflammation of the sinuses leads to a feeling of congestion in the ears, a temporary decrease in hearing acuity.
- Inflammation of the larynx and tonsils. The lymphoid tissue of the tonsils, in which enteroviruses actively reproduce at the initial stage, increases markedly in size, may be covered by rashes. Larynx and tonsils become swollen, reddened. There is severe pain when swallowing.
- Problems with the stomach and intestines. If the enterovirus began its replication in the membranes of the digestive tract, then the child may show increased gas formation, bloating, nausea, less often - vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain.
- Sensitivity change. The child may experience numbness in the limbs, tingling in the region of numb fingers and toes. Sometimes there is numbness of the muscles of the face with a temporary change in facial expressions.
- Headache. This symptom accompanies most diseases caused by enteroviruses.The pain itself can be quite strong, sharp and dull, aching. Much in its intensity depends on what ailment develops, as well as on the age of the child.
- Muscle and bone pain. This feature is also very common. Children from 3 to 6 years often have short spasms of the limbs, the child may complain that the "leg reduces."
- Cough. It can be of different intensity. At the initial stage, the child usually has an unproductive dry cough, later - a wet, wet. Dyspnea is possible, as well as whistling sounds when breathing.
- Temperature, fever. At the onset of the disease, the temperature always rises to fairly high values - 38.0-40.0 degrees. The temperature drops quite quickly (in 2-3 days) and subsequently persists at subfebrile values - from 37.0 to 37.9 degrees (until recovery).
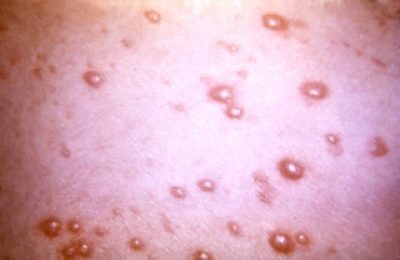
- Rash. It can appear in the mouth, on the mucous membranes of the inner surface of the cheeks, on the tongue, in the throat, on the tonsils, and can appear on the palms, feet, skin folds in young children and even in the genital area.
- Disruption of the child’s general condition. Appetite, sleep, behavior change. The baby becomes more capricious, restless or lethargic and apathetic.
- Swollen lymph nodes. Usually, the submandibular lymph nodes, as well as the occipital and cervical lymph nodes become inflamed and become larger. The nodes in the armpits, as well as in the groin, can grow.
Depending on the combinations that make up these and other symptoms, the child may have one or another complication.
Herpangina
This is a fairly common disease caused by Coxsackie A or B viruses. A child’s mouth develops white sores surrounded by a red border. At the initial stage, there is a blister inside the redness, which bursts and creates ulcerations.
Usually rashes are located on the pharyngeal wall and on enlarged reddened tonsils. The temperature rises to 38.0-39.0 degrees, the child feels pain when swallowing. Toddlers may refuse to eat at all because of this pain.
Viral conjunctivitis
Damage to the mucous membranes of the eyes of a child usually causes enterovirus 70 type. The child begins to be afraid of bright light, his eyes are watering. Eyeballs turn red, pronounced blood streaks are noticeable.
The older child will complain that “something has fallen into his eye,” the baby will simply constantly rub his eyes. Viral conjunctivitis It is often complicated by a bacterial infection that the child puts into the eyes, rubbing them. Microbial infection is characterized by the appearance of purulent discharge in the corners of the eyes. The disease lasts a long time - up to 14 days.
Viral pemphigus
This disease is always manifested by the appearance of wheals (vesicles), filled with light liquid, in the mouth, on the palms, on the feet, on the fingers and in the space between the fingers. Such a phenomenon most often causes the Coxsackie A. enterovirus.
Blisters do not hurt, do not itch. When the vesicles burst, small ulcers with a light crust remain on the skin. During the first two days, such pemphigus is accompanied by fever and symptoms of intoxication. The disease lasts about 7 days.
Myocarditis
Inflammation of the heart muscle is a fairly common complication of enterovirus infection. If only the space around the heart is inflamed, then they talk about pericarditis. In boys, this complication happens more often than in girls.
It all starts as an acute respiratory disease, in which the child has a runny nose, cough. The disease progresses rather quickly, and the child begins to have severe shortness of breath, the heart rate is disturbed, and heart failure can develop.
Anxiety symptoms - wheezing and severe chest pain. Often the process is accompanied by fever.
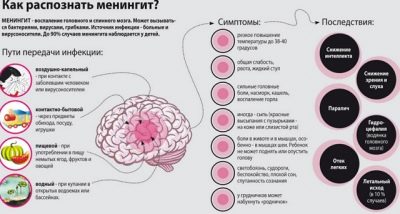
Meningoencephalitis
Such a complication can be provoked by Coxsacki enteroviruses (A and B), ECHO viruses, and enteroviruses, indicated by numbers from 68 to 71. For serous meningitis characterized by photophobia, headaches, fever. For children from 5 to 9 years old, among whom this complication is considered the most common, enteroviral meningitis is not as dangerous as it seems. However, the disease is dangerous for children in the first year of life.
The disease is diagnosed in about every third child with an enterovirus infection. Kids have noticeable swelling "fontanel", stiff neck. In children of any age with meningitis, vomiting, convulsions, clouding of consciousness and delirium can be observed. The disease lasts about 10 days and usually passes - with a very favorable prognosis. Occasionally, children as a residual phenomenon lagging speech, as well as physical development.
Enterovirus fever
It is also called a three-day fever, because the temperature lasts exactly three days. Complications are caused by Coxsackie and ECHO viruses. The disease most often occurs in the summer, for which it is also called the "summer fever."
This disease is characterized by a sharp fever, as well as redness of the throat, tonsils, the appearance of liquid discharge from the nose. The child has muscle, headache, and swollen lymph nodes. Often enough enlarged and spleen with liver. After the third day, the child begins to feel much better, and by the end of 6-7 days he usually recovers completely.
Epidemic myalgia
This disease is also called pleurodynia or “damn dance”. This name is a disease given for the chaotic movements of the arms, legs and body, which the child makes in moments of painful attacks in the muscles of the chest, abdomen, and extremities. Attacks last from 10 seconds to 20 minutes and are repeated several times a day.
This condition is caused by enteroviruses ECHO, less often - Coxsackie. It is accompanied by fever, symptoms of intoxication. The disease lasts no more than 10 days.
Paralysis
They are usually caused by poliovirus, less commonly by Coxsackie and ESNO. Spinal paralysis usually develops, which leads to a temporary inability to move limbs. Usually, this is preceded by high fever, severe intoxication, repeated vomiting, and convulsions. Paralysis is not persistent, after a few days it passes.
Gastroenteritis (intestinal flu)
This complication is most common in children up to 3-4 years. Runny nose, cough and other respiratory symptoms are mild or absent altogether. The disease occurs on the background of high temperature, diarrhea, vomiting, gas formation. Severe intestinal symptoms are usually not, but the duration of this form of enterovirus infection is quite large - the symptoms can last up to two weeks. This condition is caused by Coxsackie A and B viruses, as well as ESNO and type 68-71 viruses.
Danger
The main danger of enterovirus infection lies not in the virus itself, but in those complications that it can cause. A somatically healthy, strong child is able to cope with the infection, his immunity in a few days will produce the necessary antibodies to the penetrated virus. But children with chronic diseases, weakened immunity, HIV infection, congenital malformations, pathologies of the central nervous system, as well as infants up to one year old are not able to resist the enterovirus quickly and effectively. They are at risk for the development of severe complications. The danger of an enterovirus is in its cunning.
Many forms are “masked” as a harmless coryza or cold, but the consequences can be much more severe. Therefore, it is important to make the correct diagnosis as soon as possible and start timely treatment.
The worst complication of enterovirus infection is large lesions of the central nervous system. Possible possible swelling of the brain, which can provoke heart or respiratory failure. Among other complications that are dangerous to the life and health of the baby are the development of false croup on the background of laryngeal stenosis, as well as the addition of an infection that can cause severe pneumonia. Not very often, but it happens that enteroviral conjunctivitis causes a decrease in vision, the occurrence of cataracts and the onset of blindness.
If we evaluate medical statistics objectively, then the occurrence of dangerous consequences when enterovirus infection happens not so often. In most cases, the forecasts of doctors are very favorable. About 90% of children usually treat without any long-term health effects.
In 7% of children, certain complications occur that are reversible. Irreversible total complications are recorded only in 1-2% of cases and usually relate to children from the risk group mentioned above.
Diagnostics
Any pediatrician can diagnose an enterovirus infection by a combination of symptoms and a season. However, it is safe to say that it was the enterovirus that caused the baby’s disease, only on the basis of laboratory tests.
Not all children with suspected enterovirus infection will be sent to take tests. If the doctor has no concerns about the condition of the child, then he may not direct him to advanced laboratory diagnostics. If a doctor notices neurological symptoms, signs of meningitis, sepsis in newborns, signs of exanthema, as well as a rash in the mouth, hands and feet, symptoms of herpes sore throat, myocarditis, conjunctivitis, or myalgia, then a laboratory test will be required.
A swab from the oropharynx is sent to the laboratory, samples of the contents of the vesicles from the throat in case of herpetic sore throat, and an analysis of the feces is needed. For conjunctivitis, samples of secretions from the corner of the eye are needed. If you suspect meningitis and damage to the central nervous system, cerebrospinal fluid is necessary, which is taken by puncture.
Donate blood for enterovirus infection laid twice. Once - at the beginning of the disease, the second - 2-3 weeks after the onset of the disease.
Laboratory technicians will use several methods: virological will allow to isolate the virus; serological - to determine the presence of antibodies to it, the molecular method will allow to determine the virus serotype and its features.
In addition to laboratory tests according to individual indications, an x-ray of the chest can be prescribed. This method will allow you to explore not only the state of the lungs. It allows you to control the size of the heart, if the doctor suspects pericarditis or myocarditis. These children additionally recommend several ECG dynamics.
Electroencephalography will help investigate the state of the brain in cases of suspected meningitis or encephalitis. Examination of the organs of vision by an ophthalmologist will help to predict possible complications of enterovirus conjunctivitis.
Often, children are prescribed additional consultations by a neurologist, a gastroenterologist, an infectious disease specialist, and a cardiologist.
Treatment
The treatment of enterovirus infection in general terms resembles the treatment of any viral infection. Therapy is complex and includes not only medicines, but also the correct medical regimen, nutrition. Most children are allowed to undergo home treatment, strictly observing all prescriptions of the attending physician. They try to hospitalize only children for whom enteroviruses represent a serious danger - children with HIV infection, children under one year old, children with congenital and severe chronic diseases of internal organs and systems.
Mild forms of infection for children who are not at risk can be treated at home. Doctors try to treat moderate and severe forms of the disease in the hospital. In a hospital, there is an opportunity to respond quickly to possible complications. Children with severe forms of prescribed antiviral drugs that are administered intravenously and intramuscularly.
Such drugs on the shelves of pharmacies can not be found. They have proven efficacy - in contrast to the vast majority of drugs that are widely advertised and available in every pharmacy. Antiviral drugs with proven efficacy in Russia units. Children with a mild form of enterovirus infection do not need such drugs, but doctors often prescribe "Anaferon", "Viferon" and other drugs.
This is done so that the parents could not then blame the doctor for inattention, indifference. If the doctor honestly says that when an enterovirus infection the child does not need medicines, that there is no point in antiviral drugs, then many moms and dads simply will not understand such an honest specialist. And after the appointment of the homeopathic "Anaferon" and the doctor is calm, because the child takes a harmless (and useless) drug, and parents - they take into account the recommendations and do everything for the speedy recovery of the baby.
A big mistake with enterovirus infection is to give the child antibiotics. Some parents believe that intestinal flu (enteroviral gastroenteritis) simply cannot be cured without antibiotics. Unfortunately, doctors are still working with children, who prescribe antibiotics to a child with a viral infection with a “just in case” condition so that there are no complications.
The truth is that antibiotics have no effect on viruses. However, they influence the organism as a whole, and the probability of occurrence of complications does not decrease, but increases several times. At the same time, the joined bacterial infection will be difficult to cure, because the bacteria will form a certain “addiction” to the antibiotic.
It is up to parents to give the child antiviral drugs at home treatment or not. If the baby does not swallow pills and syrups, nothing terrible will happen. If it does, it will in no way affect the healing process and the timing.
But antibiotics should be abandoned resolutely and irrevocably.
Symptomatic treatment is usually prescribed at home:
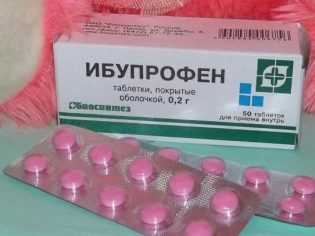
- Antipyretics. At high temperatures, the child can be given "Paracetamol" and drugs based on paracetamol, as well as the anti-inflammatory nonsteroid drug "Ibuprofen." Categorically you can not give "Aspirin" and agents based on acetylsalicylic acid, since their use can provoke a deadly disease - Ray's syndrome.
- Vasoconstrictor nasal drops. With a cold, you can alleviate the child’s condition with the help of Nazivin and Nasol drops. It should be remembered that these drugs can not be used for more than 5 days, because they cause persistent addiction to drugs. To prevent nasal mucus and bacterial complications from thickening, it is often useful (every half hour) to instill ordinary saline in the nose, prepared on its own - from water and salt.
- Antihistamines. In severe edema in the larynx and nasopharynx, you can take an age dose of antiallergic drugs: "Suprastin", "Loratadine», «Tavegil". These tools are useful not only for allergies, but also when it is required to remove puffiness quickly enough.
- Enterosorbents and oral rehydration preparations. With intestinal form of enterovirus infection can not do without means that will help fill the water-salt balance, disturbed by repeated vomiting or prolonged diarrhea. These include “Regidron», «Smecta, Humana Electrolyte. When the vomiting attacks pass, it will be possible to give the child sorbents - for example, "Enterosgel».
- Probiotics. "Bifiform", "Bifistim" can be assigned to a child after the acute phase of the intestinal form of enterovirus disease (for the normalization of the intestinal flora, which significantly suffers after prolonged diarrhea or vomiting).
- Local antiseptics. In case of herpetic sore throat, with vesicular pharyngitis and other diseases of the oropharynx caused by enteroviruses, local antiseptics are prescribed - for irrigation of the throat and rinsing. This is usually furatsilina solution, "Miramistin».
In the hospital, treatment is also carried out with the use of symptomatic drugs. Cardioprotectors are prescribed for pericarditis or myocarditis. For severe intestinal forms of infection - rehydration therapy, saline infusion. Meningitis and encephalitis require the use of diuretics, which will help to quickly remove excess fluid and avoid swelling of the brain, as well as nootropic drugs that improve blood flow.
Treatment of an enterovirus infection at home and in a hospital requires adherence to bed rest - for as long as the child has a fever. It is important to ensure peace and normal psychological state of the patient. Walking in the fresh air is allowed one day after the temperature returns to normal values.
At the time of illness, the child is transferred to a special drinking regimen, this is especially important for intestinal infection. The diet should provide an adequate amount of protein foods, as well as foods containing vitamins A, E, C, B.
If it is painful for a child to swallow, food is given warm, mashed or mushy, in the form of mashed potatoes. When enteroviruses that cause vomiting and diarrhea, it is important to adhere to medical fasting (for a day). After that, the baby’s menu begins to gradually introduce broth, jelly, rice water, oil-free porridge, vegetable soups on lean broth, white bread croutons.
All drinking should be warm. Optimally, if the temperature of the liquid corresponds to the temperature of the body of the sick child, so water will be absorbed faster in the small intestine and absorbed.
It is impossible to muffle a child, put heaters near the patient's bed. It dries the air. For successful recovery without complications, it is important so that the child breathes clean air (it should not be overdried). The optimum humidity is 50-70%, the air temperature in the room should not be higher than 20 degrees Celsius.
Prevention
Prevention of enterovirus infection does not boil down to vaccination, since there is no vaccination against it. In the focus of infection, disinfection is carried out. If a kindergartener is ill, then all the children in kindergarten who have been in contact with him are heavily observed for two weeks. There is no quarantine, but every morning in the kindergarten begins with a temperature measurement. This is necessary for all babies.
It is important to teach the child to wash hands before eating and after visiting the street, and also not to take dirty hands and other people's toys and things in their mouths. It is important to monitor the quality of drinking water, as well as carefully wash the vegetables and fruits purchased in a store or on the market.
Especially often children fall ill with enterovirus infection while relaxing at sea. Prevention in this case is of particular importance. If a baby or a child of preschool age is to be taken to the resort, it is important to carefully study the epidemiological situation in this area. This can be done on the site Rospotrebnadzor. It contains all current information, including outbreaks of enterovirus infections.
Memo for vacationers who do not want to treat a child for an enterovirus during the holidays, looks simple:
- do not give your child to drink water from unfamiliar sources;
- It is important not to allow the child to swallow water from the sea or pool while bathing;
- the child should not be given untested food (especially for resort catering and national cuisine of fish and meat), and fruits and vegetables should be well washed;
- It is important to follow the rules that will reduce the impact of acclimatization on the body of a baby: not to disturb his usual routine of the day, not to take a young child to exotic countries with a climate that is very different from the usual one.
In the next video, Dr. Komarovsky will talk about what enteroviruses and how to treat them.