The causes, symptoms and treatment of epilepsy in children
In children's neurological practice, there are a number of diseases that have been known since antiquity. Epilepsy is considered one of these "mysterious" diseases. What should parents know about this disease in children will tell this article.
Causes
The most characteristic manifestation of this disease is the occurrence of seizures. Such manifestations can be very different. The course of the disease is usually accompanied by a repetition of such attacks for a certain time. If a child has seizures more than twice, this fact should be a reason for parents to seek additional advice from a pediatric neurologist.
Not only neurological, but also psychopathological disorders are characteristic of this condition. Doctors-neurologists in many countries consider this disease to be one of the most significant in children's medicine.
The prevalence of the disease among children is quite low. On average, it is up to 0.55 to 0.8% among all babies.
It is important to note that epilepsy is manifested for the first time at very different ages. Quite often, the first adverse symptoms begin already in children under 2 years of age. In some cases, the course of the disease can be quite unfavorable. There are certain forms of epilepsy that are difficult to correct with drug therapy. They are also quite common in babies.
Epilepsy has been known to doctors for more than one century. Previously, doctors did not have the necessary knowledge about the mechanism of the disease. In the Middle Ages, people who suffered from manifestations of the disease were considered "devil obsessed". There are also literary works of those years that describe patients with epilepsy quite well.
With the development of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic base, doctors have new information about the mechanism of disease development. This prompted the experts to the idea that it is necessary to investigate the causes that contribute to the appearance of characteristic manifestations of the disease. There is no single reason for the development of adverse symptoms of the disease. The appearance of adverse clinical signs of the disease can lead a variety of reasons.
The most unexplained form of the disease is idiopathic. The cause of the adverse symptoms of this pathological condition, scientists have not established. They suggest that hereditary predisposition leads to their appearance in this case. To date, scientific experiments are being conducted aimed at studying specific "causal" genes that trigger the onset of a disease of varying severity in a children's organism.
The development of pathological foci in the brain that produce the appearance of characteristic seizures, causes multiple factors. They are also called trigger. The impact of such factors may be even in the period of bearing a child.
Abuse of the future mother by alcohol or smoking are pretty significant triggers. In this case, the formation of the pathological area - the epileptic focus, occurs already in the period of prenatal development of the baby.The first adverse symptoms in this case may appear already in newborn babies.
Severe pregnancy It can also affect the birth of a child who has abnormal areas in the brain, causing further development of epilepsy. Gestosis and pathology of placental blood flow, especially in the first trimester and the beginning of the second, can lead to the formation of epileptogenic foci in the future baby. The number of such areas may be different. Predict their possible appearance in the baby is almost impossible at this stage.
Different types of infections Transferred by the future mom while carrying a baby are also quite frequent triggers. Bacteria and viruses, having rather small sizes, perfectly penetrate the hemato-placental barrier. Such a spread of infection quickly reaches the body of the future baby through the system of placental blood flow in common with the mother.
Viral or bacterial infections, transferred by mommy, especially at the very beginning of pregnancy, provoke the appearance of various pathological areas in the baby’s brain. In some cases, even a severe course of bacterial pediatric pneumonia can lead to the further development of adverse symptoms of epilepsy in a child.
Organic brain damage during labor - one of the most frequent causes of adverse symptoms of the disease in the future. Damage and haemorrhage in the brain cause the formation of pathological areas of altered tissue. The work of neurons in this case varies considerably.
Obstetricians-gynecologists note that There are several of the most dangerous clinical situations that arise during childbirth, which may contribute to the occurrence of adverse symptoms of epilepsy in the baby:
- cord entanglement;
- prolonged standing of the head of the fetus in the pelvis of the mother while passing through the birth canal;
- too long dry period;
- protracted labor.
The resulting oxygen starvation (hypoxia) of the brain leads to the formation of epileptogenic foci in the child. The first adverse symptoms of the disease in this case appear already in infants.
Infectious diseases leading to development meningitis or encephalitis in children also contribute to the possible development of further adverse symptoms of the disease. The most dangerous in this case are microbes that penetrate the blood-brain barrier of the brain perfectly. Getting into the cerebral blood vessels, microbes quickly lead to the development of a strong inflammatory process, leading to the development of pathological areas in the baby. This form of epilepsy is quite common in schoolchildren.
Not in all cases, doctors can determine the localization of the pathological focus. However, this does not exclude the occurrence of a new seizures in a child, seizures characteristic of this disease. This form of the disease is called cryptogenic. In the general structure of the disease, according to statistics, it accounts for almost 60% of all cases of this disease.
Currently, more and more scientific results of research are emerging, indicating that an autoimmune mechanism is present in the development of epilepsy. This confirms the fact that patients suffering from this disease have an increased amount of specific antibodies in their blood that have an adverse effect on their own brain cells.
Such manifestations also occur not only in the primary form of epilepsy, but also as a result of past infectious diseases.
During epilepsy, a whole complex of various disorders occurs in the child’s body. Their appearance is triggered by the disruption of the work of the main "computer" of the body - the brain.Interestingly, similar changes are found in the parents and immediate relatives of the sick baby. Changes in water and electrolyte metabolism, acid-base balance, and metabolic processes contribute to the change in the work of many internal organs.
Kinds
Clinical variants of the disease can be very different. This diversity is largely determined by the initial localization of the pathological focus, which is localized in the brain. In some cases, there may be several such epileptic foci. In this situation, the course of the disease, as a rule, deteriorates markedly.
Doctors distinguish several types of epilepsy, which are quite often found in children's neurological practice:
Rolandic. The first signs are found in babies, usually after 3 years. Most often characterized by the appearance of spontaneous night attacks. Involved in the pathological process is usually facial musculature. According to statistics, most babies have epilepsy attacks in their sleep from 3 to 5 times a year.
Idiopathic partial. Characterized by the development of occipital seizures. Quite often, this clinical form of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of various visual impairments and hallucinations, as well as a variety of eye symptoms. As a rule, this variant of the disease occurs in children from two years of age and up to adolescence. Quite often, the first cases of the disease are recorded in children up to 3 years.
- Benign idiopathic. The collection of genealogical history plays a crucial role in establishing the correct clinical diagnosis. Signs of epilepsy in this case are detected in the closest relatives and even in the parents of the sick baby. The disease is inherited by an autosomal dominant trait. The first signs of the disease usually appear in the first months of the baby’s life.
- Benign myoclonic epilepsy of infancy. A rather rare clinical form of this disease. This variant of the disease is characterized by the appearance of myoclonic seizures in a sick child. The kid in this case can remain in full consciousness. The first symptoms of the disease can be recognized already, as a rule, in a one-year-old child.
Children's absansnaya. It occurs in children from 1 year to 10 years. It is characterized by the appearance of various durations of absences. Motor and convulsive contractions, as a rule, are completely absent in this clinical form. The average duration of absences in this variant of the disease ranges from a couple of seconds to ½ minute.
Youth absansnaya. Debut disease - adolescence. According to clinical symptoms, it resembles a childish absans form. The first adverse symptoms appear in adolescents, however, they can also develop between the ages of 18-22 years. The duration of the epileptic period, as a rule, in this clinical form is 2-40 seconds.
Youthful myoclonus. In the development of the disease plays an important role hereditary factor. It occurs mainly in adolescents. It is characterized by the development of multiple convulsive contractions in a child. Consciousness during an attack can be maintained.
With generalized convulsive seizures. Also, this clinical form of the disease is called epilepsy with periods of awakening. Age of occurrence of the first adverse events of the disease can be very different. Symptoms of this type of epilepsy are found in both very young children and adults. An electroencephalogram examination does not reveal a clear damage center or pathological focus.
West syndrome. Appears only in children. It is characterized by the appearance of multiple convulsive contractions in a sick baby. Gypsarrhythmia is a specific change in the EEG that occurs in this clinical variant of the disease.Spasmodic attacks usually last for a few dozen seconds, but may alternately follow each other.
Lennox-Gasto syndrome. The peak incidence occurs at the age of 3-6 years. This clinical form of the disease is accompanied by the development of not only neurological, but also psychopathological disorders. The sick kid lags behind its peers in the level of physical and mental development over time. Such specific deviations from the age norm occur in 90-92% of babies with this form of the disease.
With myoclonias-astatic seizures. This clinical form is also called Duse syndrome. According to statistics, the first adverse symptoms of the disease appear in children of preschool age. This form is manifested by various convulsions that occur in the arms and legs. In some cases, the child has a characteristic symptom of this clinical variant of the disease - “nodding” of the neck.
Eses syndrome. Specific signs of the disease occur during slow sleep. Accompanied by the appearance of characteristic features on the electroencephalogram (EEG). The peak incidence is from 5 to 15 years. In the scientific literature there is information about the appearance of adverse symptoms in babies of the first months of life.
Focal. It is characterized by the presence of a pathological focus in a local anatomical zone of the brain. Quite often localized in the temporal or frontal lobe. Often, doctors note that this option is secondary and occurs due to other diseases. The prognosis of this clinical form of the disease is conditionally favorable.
What are the seizures?
One of the most characteristic manifestations of the disease is the appearance of special attacks. They are accompanied by the development of seizures in the child. Their duration can be very different and depends on many different factors. The severity of the course of this disease depends largely on how often such seizures occur, as well as how long they last in a particular baby. Characteristic seizures may be partial and generalized.
Partial
This clinical view largely depends on the initial localization of the pathological focus. With this variant of the disease, the baby does not lose consciousness during an attack. He can quite well describe his feelings. The most frequent violations - motor. They are characterized by the appearance of multiple contractions of individual muscle fiber groups. Quite often, this symptom is manifested by the appearance of cramps in the legs, arms, and face.
Verbal Partial Seizures found in babies much less. They are characterized by the appearance of some sound melodies or even individual voices in a child. Sometimes the baby "hears" the conversation of several people.
Many children note that during such verbal seizures, they hear particular sounds or parts of words. Such manifestations of the disease can often be confused with various hallucinations that occur in some mental illnesses.
Individual kids feel sensory-motor changes. Such violations may occur in the arms, legs, and in some cases even affect half of the body or face.
Vegetative seizures are also recorded in toddlers. They are characterized by severe perspiration, severe pallor or redness of the skin, significant dilation of the pupils of the eyes, and other specific symptoms. It is important to note that such symptoms are quite rare and significantly complicate the differential diagnosis.
Complicated Partial Seizures accompanied by the development of a more dangerous clinical sign. During such attacks, the child may lose consciousness. A characteristic feature of this type of seizure is the preliminary appearance of an “aura”. This particular condition is described by more than 90% of babies.It is characterized by the appearance of discomfort in the stomach or strong weakness, the development of nausea and an increase in dizziness and headache.
All these symptoms appear in a child usually before losing consciousness and are very unfavorable.
Symptoms of aura can be very diverse.
Some children also note that before losing consciousness, they feel:
severe general weakness, which increases in a few minutes;
numbness in the area of the tip of the tongue, lips, and increasing pressure in the region of the larynx;
pain or discomfort in the chest;
the growing lack of air, the difficulty of forced (intensified) inhalation or exhalation with full chest;
severe drowsiness and unbearable desire to sleep;
the appearance of various voices "in the head" that speak in a language that the child does not understand.
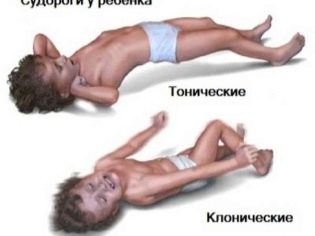
The combination of pathological symptoms that occurs during an attack can be very different. Such seizures are already called secondary-generalized. According to their mechanism of development of pathological symptoms, they can be tonic, clonic or tonic-clonic. The onset of the appearance of characteristic specific signs is a simple or complex epileptic seizure. The duration of the aura in this case is from several seconds to a couple of minutes.
After this state, the child usually falls to the floor. His body is pulled out, his head is deflected to the side. Jaws tight. Respiration is usually weakened or stopped. After a few seconds, the sick baby has cramps in the limbs or the entire body. The duration of such a tonic seizure is usually from 10 to 30 seconds.
The next stage is the development of a clonic seizure. It is characterized by the appearance of strong cramps in the arms and legs. Foam appears from the mouth. Usually it is abundant with bloody streaks that appear in it due to the fact that during an attack the child bites the tip or back of the tongue.
The final stage is relaxation. During this period, the baby lies motionless, its pupils are dilated, it does not respond to external stimuli.
These specific signs are known from the most ancient times. Such a course of the disease and contributed to the emergence of a number of its names. This disease is also called "epilepsy" or "dancing". During the period of the “holy” inquisition, it was believed that at the time of the seizure, a demon infuses the child. There were even multiple rituals that were conducted to expel various demons.
Currently, the understanding of the mechanism of the disease has changed significantly. During the development of such dangerous tonic-clonic seizures, it is very important that the parents are with the baby.
It is very important for fathers and mothers of babies who have epilepsy to be aware of what should be done during the onset of a characteristic seizure attack. Help will help prevent the occurrence of adverse effects on the baby.
Generalized
Manifestations of this disease are accompanied by the development of absences, characterized by short-term loss of consciousness. In this case, the duration of clonic convulsions may be very different in time. In some cases, they may even be completely absent.
The onset of abscess epilepsy is impossible to predict. A few minutes before the consciousness is completely turned off, the small patient becomes stationary, looks at one point, or completely stops.
Memories in memory of an attack can be either present or erased. Many children during the deterioration of consciousness all also react to external stimuli. The most characteristic symptom of a generalized seizure is loss of consciousness. It should be noted that in most cases it is fully restored fairly quickly. Aura is usually not characteristic. Absans in time can be from a couple of seconds to ½ minutes.
They can be both simple and complex. The first are characterized by all the above symptoms. Complicated ones are accompanied by the development of the most diverse symptoms. The most frequent manifestation at this time is a pronounced contraction of individual muscle groups. Reviews of fathers and mothers of sick babies indicate that during such a complex absence a child may accidentally scatter or scatter objects and toys.
Many babies fall on their knees and then on the buttocks. The next stage in the development of an attack is complete loss of consciousness. Some babies have involuntary limb contractions. Usually they are finely sweeping in their amplitude. The pupils of the child expand. In a few seconds, the skeletal muscle tension increases.
Some babies have tremor of the limbs. He, as a rule, at first finely sweeping, but then goes into a separate convulsive reduction of the limbs. Usually, these adverse symptoms persist in babies for 15-25 seconds. In some babies, these manifestations can last even a few minutes.
During such an attack, it is very important that the parents or medical staff be with the child, as this will help prevent dangerous consequences and complications.
Symptoms
The severity of adverse manifestations of the disease depends largely on where the pathological epileptogenic sites are located. The age of onset or debut does not play an important role. In some cases, the disease in newborn babies is much easier than in adolescents. The presence of comorbidities in a child, as a rule, worsens the overall prognosis.
For babies with epilepsy, various types of epileptic seizures are considered the most specific manifestations of the disease. Quite often they develop Jacksonian seizures. These changes are characterized by the appearance of multiple contractions of muscle groups. They may not be the longest in time of their appearance. These specific signs are characterized by the rise of the twilight consciousness.
In a baby, certain parts of the body may become numb. Usually it is limbs, tongue or cheeks. As a rule, during an attack, contact with the child is completely broken. The kid becomes indifferent to the situation, and also practically does not respond to external stimuli.
Small seizures are also quite common in babies. They are characterized by the occurrence of frequent oculomotor movements and hypotonic face. In some clinical forms abscesses occur, which are accompanied by complete numbness of the facial muscle groups. During such attacks, the child, as a rule, rolls his eyes strongly.
A rather dangerous clinical situation is epileptic seizure. This condition is accompanied by a series of several seizures, which successively replace each other. For a short time, the child may be unconscious. In this condition, muscle tone is significantly reduced, which is accompanied by hyporeflexia. During an attack, the child has cardiac abnormalities - the heart rate increases, and the pulse becomes very weak.
An epileptic seizure is usually accompanied by a change in several clinical conditions. First, the baby spontaneously falls. From a strong spasm of the glottis the child can cry out a lot. After a few seconds, the baby throws back his head. From the side, intensive movements of the chest become well visible.
The appearance of the child during an epileptic seizure usually brings parents into real horror. It is important to always remember that you can not panic! Parents should help the child and give him proper first aid. During an attack, the baby’s skin is usually pale. Lips and visible mucous membranes have a blue tint.
In some cases, babies have no tonic or clonic changes. In this situation, the child appears only visual or verbal hallucinations. Kids can see different color flashes or images that appear literally in the air. Verbal hallucinations are accompanied by the appearance in the brain of various words or sound phrases.
There are quite rare, but very interesting forms of the disease. These include epilepsy reading. In this case, adverse symptoms occur after reading the first words of any text.
Usually this form of epilepsy is recorded only at school age, and then in adults. The most frequent manifestation of this clinical option is a strong twitching of the lower jaw.
Quite often this process is one-sided. In some cases, the child appears and combined visual impairment. A child may have dyslexia - a speech disorder. Usually this symptom occurs in children with a long course of the disease. Severe course of this clinical variant of the disease can lead to pronounced disorders of mental development.
The first signs in infants
Hereditary benign idiopathic epilepsy often leads to the development of adverse symptoms in newborn babies. The first signs of the disease are detected in the first week of the child's life. This form is accompanied by the appearance of multifocal clonic seizures. They are characterized by monotonous or ocular symptoms.
Quite often, multiple convulsive contractions are accompanied by vegetative manifestations. These include: a strong salivation, increased sweating, increased heart rate and blood pressure jumps, redness of the skin of the face and upper half of the body. Characteristic changes in this case are recorded only during the attack. In the period between these seizures to identify any abnormalities on the EEG is not possible.
Benign Neonatal Spasms do not have hereditary predispositions. The first adverse symptoms in this case occur in the baby for 3-5 days of life. In this case, it is impossible to identify signs of the disease in the next of kin. This form manifests itself in a child with multiple monoclonal attacks. They can occur within 20-22 hours.
This form of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of convulsive contractions that occur in various parts of the body. First, the process may involve limbs or parts of the body, then successively include other anatomical zones.
The migration of such disorders is a characteristic feature of this clinical form of the disease in children. Some babies have whole series of epileptic conditions.
Benign myoclonic epilepsy of infancy occurs in infants of the first year of life. The process usually begins with the upper half of the body. Parents can notice these symptoms on their own. Lying in a crib during an attack, the baby can often raise the shoulders and pull the arms. Also notice this form of the disease is possible during the first steps. When getting up on the legs, the child can swing strongly, and the muscles of the lower extremities twitch very strongly.
Many parents think that if the child often falls, this may indicate the presence of epilepsy in the baby. However, this is not quite true. Typically, the duration of attacks is short and does not exceed a few seconds. They can occur at almost any time of the day. Usually, the first symptoms of the disease occur in a child in the first six months of life.
The swordsman's pose is one of the symptoms that the doctors check during the examination of the child. During this state, the baby's head is turned to the shoulder. The arm and leg are strongly extended from the same side.The other pen is turned the other way. The leg on the opposite side is bent at the knee.
Usually this condition occurs in children who have suffered strong birth injuries.
Diagnostics
The initial clinical examination is indicative only. For the correct diagnosis requires additional laboratory and instrumental examinations.
To date, the "gold standard" of diagnosis of this disease is considered electroencephalography (EEG). At the same time, it should be noted that every second baby in the absence of an attack does not have any changes on the electroencephalogram.
Identification of specific signs directly during an epileptic attack allows you to accurately enough make the correct diagnosis. In difficult clinical situations, when the diagnosis is very difficult, it requires several EEGs or daily monotoring of this indicator.
Neuroimaging is also used to establish the diagnosis. It allows you to accurately identify various organic pathologies of the brain.
Such a study not only allows to clarify the correct diagnosis, but also to determine the prognosis and further tactics of therapy. The studies that are included in neuroimaging include computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. MRI allows you to specify the local areas of pathological tissue, which trigger the appearance of adverse characteristic symptoms in the baby.
Children suffering from epilepsy are given multiple laboratory tests. These include general clinical blood and urine tests, biochemical blood tests, determination of specific autoantibodies and glucose and lactate levels, as well as serological tests.
In some cases, an examination of the abdominal organs, Doppler sonography of the neck and brain, electrocardiography and other studies are also included in the examination plan.
Treatment
Some parents believe that epilepsy can be cured. However, this is not always the case. Some forms of this disease will remain with the child for the rest of their lives. The main principle of therapy is to select the necessary scheme of symptomatic drugs that would have the proper therapeutic effect, but would not cause a complex of adverse symptoms in a sick child.
Treatment should be carried out only after the establishment of a full clinical diagnosis. In some cases, treatment of the disease is carried out with a single drug.
Complexity of treatment has several advantages:
helps to reduce the risk of seizures in about 75-85% of cases;
allows you to reduce the dosage of drugs while maintaining the maximum exerted therapeutic effect;
reduction of a possible complex of side effects as a result of the use of different drug groups.
Starting therapy of the disease - the appointment of the age dosage of the drug. Usually it is prescribed in full in accordance with age.
Selection of dosage is carried out individually. This calculation is performed by a pediatric neurologist, who treats and monitors a child suffering from epilepsy.
Currently, doctors prefer drugs that have a gradual and temporary release. Such drugs can prevent new seizures better than their predecessors. The main means are metabolites of valproic acid. These include "Depakinhrono", "Konvuleksretard." Also, carbamazepine-based medications are used to eliminate the adverse symptoms.
During the appointment of therapy it is necessary that the seizures do not appear in the child for a month or more. If this goal is not achieved, then doctors prescribe other drugs of the second and third level, and the previous drug is canceled.Cancellation is carried out quite slowly - within a couple of weeks. Such a systematic failure can reduce the possible risk of side effects.
Compliance with the therapeutic ketogenic diet plays an important role in the treatment of epilepsy. To prevent new cases of illness, the children's menu should contain the optimal amount of protein and fatty foods.
Such an intensive diet is necessary for the child to compensate for metabolic disorders. Daily caloric intake must be respected.
In some situations, barbiturates are prescribed. Currently, there are dosage forms that need to be applied only once a day. This method of treatment is mainly used for prophylactic purposes. These drugs have a lot of side effects. These include severe lethargy and general weakness, severe impairment of memory and attention, pathological difficulty with remembering, dyspeptic disorders, hepato-nephrotoxicity, damage to pancreatic tissue, various disorders of porphyrin metabolism, and the appearance of edema.
Rehabilitation
Psychosomatics plays an important role in provoking new attacks of convulsive contractions. Especially often psycho-emotional stress leads to the appearance of convulsions in adolescent girls. Prevention of excessive loads is necessary for the development of new attacks of the disease.
Observance of the optimal daily regimen is required for all babies who suffer from epilepsy.
The long course of the disease leads to the fact that the child has multiple muscle disorders. To eliminate these adverse symptoms, a course of medical baby massage is required. The sequence of massage movements allows to improve muscle tone and relieve abnormal muscle tension. Children with epilepsy are advised to conduct several courses of medical massage throughout the year.
In this video you will learn about the diagnosis of epilepsy from the "Family Doctor" clinic.