Boils baby
The appearance of boils in children is always accompanied by pain and deterioration in the general condition of the babies. An abscess on the skin is not as harmless as it may seem at first glance. Why boils form and how to treat them, we will tell in this material.
What it is?
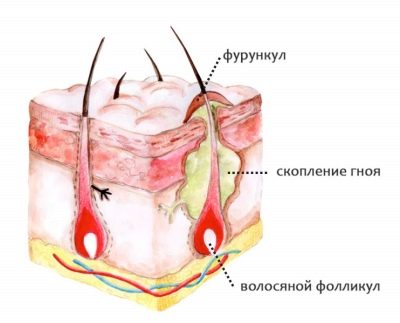
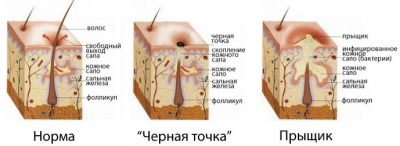
Acute purulent inflammation of the hair follicle, located near the sebaceous gland and adjacent tissues in medicine is called a furuncle, and People call this ailment "boil". In the people it is believed that such ulcers appear because of a cold or hypothermia. This is a common misconception. A boil is always closely related to the activity of pathogenic pyogenic bacteria.
Boils can appear on any part of the body. They may have different sizes. Several boils, which appeared one after another, suggest that the child has furunculosis.
It is common for many adults to underestimate the danger of boils. At the sight of such a painful phenomenon on the skin of a child, some moms and dads completely rely on their experience and recipes of traditional medicine. but it should be remembered that furunculosis is a manifestation of a staph infection that can be complicated by sepsis, toxic shock, purulent inflammation of various organs, including the brain. This can lead to disability and even death. That is why it is important not to self-medicate, not to make the child suffer, because the boil is very sore, but to immediately consult a doctor.
Causes of
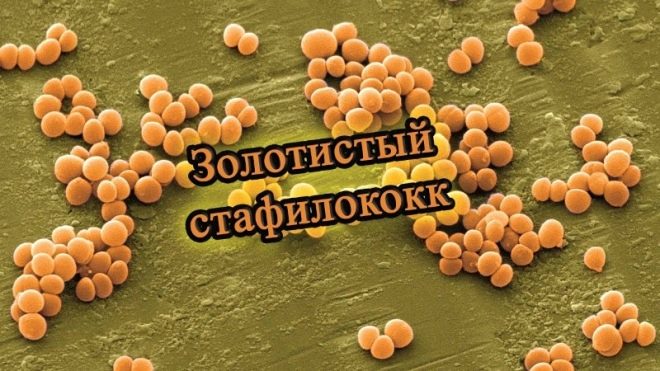
The main cause of boils are staphylococcal microbes. In 99% of cases, the causative agent is a specific representative of this kind of bacteria - Staphylococcus aureus. In 1% of cases, epidermal staphylococcus is responsible for the inflammation of the hair follicle.
Staphylococcus aureus live and live on the skin and mucous membranes of almost every person. Over 40% of adults are asymptomatic carriers of staphylococcal infection. However, not all suffer from furunculosis. The disease develops when the immune system is not able to restrain the activity of the microbe.
For the appearance of the boil, it is important that several other factors coincide with the weakness of the immunity “successfully”, which will make the microbe feel “at home”:
- skin is injured - there are abrasions, scratches, microcracks, points of injections;
- skin is badly looked after - it is polluted, on it, besides staphylococcus, several more varieties of not the most innocent pathogenic microorganisms are “found”;
- the child has acne associated with blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands;
- the child is allergic to the skin (atopic dermatitis, allergic dermatitis);
- the child has any chronic diseases and especially - diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, dysbacteriosis;
- the child has previously been diagnosed with diabetes;
- the baby has confirmed neurological diagnoses;
- there is depletion due to malnutrition, malnutrition, lack of vitamins and trace elements, blood tests show anemia;
- the child has increased physical activity (this also applies to children who are engaged in professional sports).
The common cold, which is almost always attributed to the blame for the occurrence of the next chirya, has nothing to do with furunculosis.
But there is some connection between a decrease in immunity and hypothermia. Probably, it was she who was once noticed by the people and began to be considered the main reason.With the same success, boil can appear after overheating in the sun, because any thermal effects somewhat reduce the immune defense of the child.
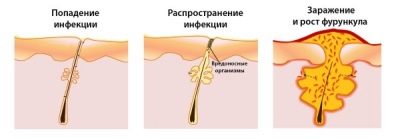
It is of this moment that staphylococcus "waits", which, taking advantage of the fact that it is not restrained by immunity, penetrates into a microcrack in the skin, into a clogged sebaceous gland, into a wound or abrasion, settles there. In the process of reproduction and vital activity, staphylococcus secretes a large amount of toxins and enzymes that cause a general deterioration of health.
Staphylococcus also affects tissues with abundant pus formation, as well as necrosis of the tissue. When all this accumulates under the skin, that boil is formed, which looks rather frightening and feels quite painful.
Symptoms
To distinguish a boil from acne or an allergic reaction is quite simple. The boil develops quickly enough, and from the second day the so-called necrotic rod is noticeable in it. Furunculosis usually begins with the appearance of a single inflammatory element.
The boil goes through three stages in its development - first there is infiltration, then suppuration, and scarring after opening:
- First stage (infiltration) is manifested by the appearance of a seal. It is in the form of a red tubercle protruding above the surface of the skin, painful to the touch. A distinctive feature of the boil is that at this stage it quickly increases in size, within a few hours adjacent tissues appear, swelling appears, the temperature may rise, the child's behavior changes, it becomes sluggish and weak.
- In the second stage intense suppuration occurs, the furuncle continues to grow, but not in breadth, but in height, as the purulent head "swells". The skin color next to it may change from reddish to lilac and even dark brown. This is due to the fact that in addition to pus, inside the head there is a layer of tissue that has undergone necrosis (death). At the time of suppuration, the temperature rises in almost all children, it can reach quite serious values - up to 38.0 degrees and higher, lymph nodes increase. The boil itself becomes incredibly painful, the child does not allow to touch it. If an unpleasant boil “popped up” on the pope, the child cannot sit, if on the leg, on the knee - walking becomes difficult, because clothes rub against the skin and cause acute pain. The boils are very painful, arising under the arm, in the nose, on the lip.
- Somewhat easier, the child will feel only after how pus will come out. It takes about 7-14 days to complete the entire life cycle of the boil. After opening, a fossa is formed, a dimple, which is gradually overgrown with tissues and smoothed out. From the deep-seated boils, traces can persist for life.
When ulcers appear alternately or simultaneously, they speak of furunculosis, and if the subcutaneous tissue and skin around the group of hair follicles are inflamed, then this inflammation is called the carbuncle.
Danger
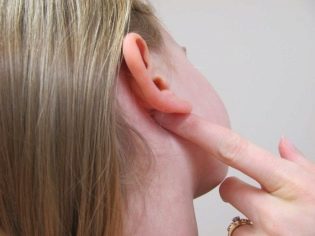
The most dangerous are the boils that appeared on the face - on the cheek, on the nose, on the eyelid, on the ear, on the scalp, on the neck, because such an arrangement creates additional risks of brain infection and the development of sepsis.
Any boil, located on the body, on the arm, leg, close to blood vessels or lymph nodes, is potentially dangerous from the point of view of sepsis, because the pus that has entered the bloodstream or lymph flow will quickly spread throughout the body.
Many do not understand how pus can penetrate there, but this gap in knowledge is restored simply - it breaks where it is thin. If the furuncle is superficial, the pus will go up, out. If the boil is deep, then a breakthrough can be internal, and this will be the main prerequisite for systemic infection.
Boil in infants and newborns - double the dangerthat is why it is customary to treat such children in the hospital. Older children can be left to be treated at home.
Treatment
Boils can be treated by conservative methods and with the help of surgical intervention. Quite often it is possible to do without an operation to open, if the boil is not deep, if we are not talking about an extensive furunculosis.
Drug treatment
The purpose of therapy in this case is to make maturation of the boil more rapid, because the very processes of infiltration and suppuration are painful for the child.
Maturation of the purulent head is accelerated:
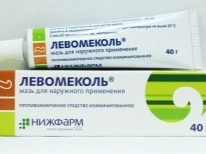
- “Asterisk” is an ointment known to many generations (the trade name is “Golden Star”);
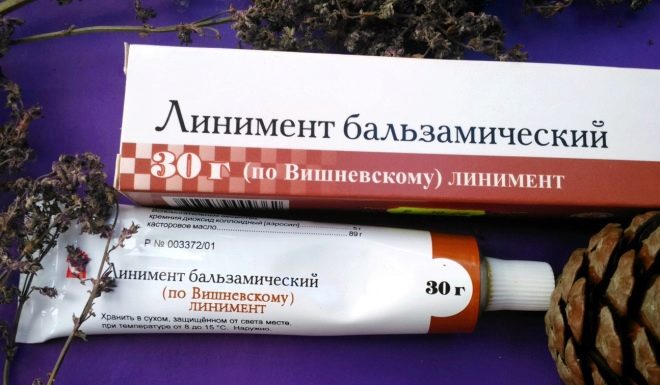
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- "Ichthyol ointment";
- Balm "Viniline».
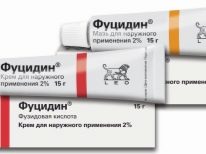
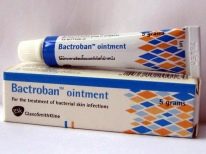
Breakthrough boils can successfully provoke ointments with antibacterial properties:
At the final stage, after the discharge of pus, the same antimicrobial ointments and lotions with hypertonic solution are used.
If chiryas appear on the face or neck, an internal antibiotic treatment is mandatory, with active local treatment. Extensive furunculosis, especially in an infant, requires the introduction of antibacterial drugs intravenously. For internal use, children are prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics - the penicillin group, and if they are ineffective, then antibiotics - cephalosporins, macrolides. Erythromycin-based drugs are very effective - “Azithromycin», «Clarithromycin».
Much depends on what kind of staphylococcus struck the baby. If the inflammation is caused by an antibiotic-resistant hospital strain of Staphylococcus aureus, the selection of an antibacterial drug will be significantly difficult, because to destroy such an infection is incredibly difficult, even with the current level of development of medicine.
As an adjuvant therapy, immunoglobulins or anti-staphylococcal plasma can be prescribed - immunomodulators. They are administered in the hospital with severe forms of infection. In home treatment, the doctor may recommend Polyoxidonium, Derinat. Always in the treatment of boils, it is useful to introduce vitamins to the child. Special importance is given to vitamins A, E, C, B1 and B 12, as well as PP.
Surgery
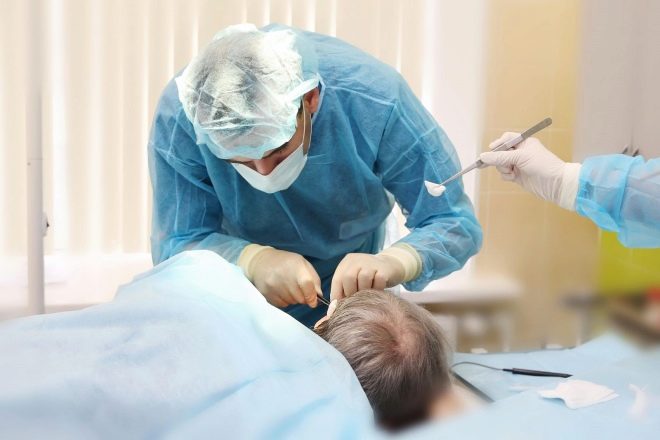
Forced opening of the boil is indicated when the doctor has every reason to believe that complications are possible, when the boil was formed at the "dangerous" place or its treatment with drugs for 5 days did not give a positive result - the pus did not move.
The operation is simple - the surgeon, under local anesthesia, makes an incision in the shape of a cross, carefully cleans the contents, including pus and necrotic fragments.
Sometimes it is impossible to do this completely, then the doctor leaves a small drainage in the cruciform wound - for the discharge of pus.
Disinfectants are applied to the site of intervention and a sterile dressing is applied. At the dressing will have to go to the clinic, if the child is allowed home treatment. It is not worth treating boils boiled in milk with onions, honey and warm compresses, as some traditional healers advise., excessive warming can benefit only at the earliest stage of the disease, when it is necessary to accelerate the suppuration.
In other periods, any warming up is extremely dangerous for the health and life of the baby.
It is even more dangerous to independently open up boils and squeeze out purulent contents from them. In the absence of sterility increases the likelihood of multiple furunculosis, as well as systemic infection of the blood. Any manipulations with boils should be carried out only in the hospital.
Prevention
- Proper hygiene. The skin of the child should be clean. But excessive washing with the use of soap dries the skin, which increases the likelihood of microtraumas. Therefore, the child should be bathed with baby soap no more than once a day, and babies should be no more than once a week.It makes sense to use a bactericidal soap only if there are purulent masses on the skin of the child.
- Timely treatment. All abrasions, scratches and wounds should be treated on time with aniline dyes, which include "green paint" and "Fukortsin».
- Strengthening immunity. To this can be safely attributed hardening, a full and balanced diet, rich in vitamins and trace elements, a sufficient number of walks in the fresh air, an active lifestyle, sports.
What is staphylococcus will tell Dr. Komarovsky in the next video.