Hemangioma in newborns and infants
Baby's health is always a paramount issue, so it is not surprising that any changes in the appearance or well-being of the baby cause fear and fear among parents. Every tenth mother of a newborn is confronted with a hemangioma and begins to worry about whether urgent treatment is needed, whether such education is dangerous for the crumbs and what to do.
What is it?
Hemangioma is called benign neoplasmwhose structure is represented by vascular endothelial cells.
What does it look like?
The reasons
The exact reasons for the emergence of hemangiomas in infants, doctors have not yet established. It is certain that only such tumors are not hereditary. In addition, experts have found that hemangioma occurs more often if:
- Multiple pregnancy.
- The expectant mother had eclampsia or problems with the placenta.
- The baby was born prematurely.
- When pregnancy was rhesus-conflict.
- During gestation, my mother smoked, took medicine, had acute respiratory viral infections, or consumed alcohol.
- Mom is over 35 years old.
Kinds
Given the structure of the formation and the level of location of the hemangioma, such a tumor happens:
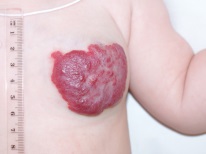
- Cavernous. This formation, usually soft to the touch, is a cavity and dilated vessels, inside which there is venous or arterial blood. Often this type of hemangiomas is located superficially in the skin, therefore, it is effectively treated by local methods of action. Such tumors are also characteristic of organs that receive a lot of blood - for the spleen, liver, brain, lungs, adrenal glands and kidneys.
- Capillary. This is a simple tumor that forms from the vessels in the dermis. It is represented by interlaced capillaries, may slightly project over the skin, often has a diameter of up to 1 cm, and rarely begins to bleed. Such hemangioma is more common than other species (approximately 95% of all entities).
- Combined. This variant of the tumor consists of two parts - the capillary part is visible from the outside, and the cavernous part is hidden under it.
- Mixed. In such a tumor, in addition to the vascular cells, there are other tissues, for example, connective, adipose, nervous, or lymphoid.
Is hemangioma dangerous?
If the hemangioma is large, thrombi can form inside such a tumor. it reduces the number of platelets in the bloodstream and causes a worsening of blood clotting.
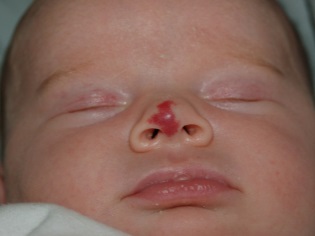
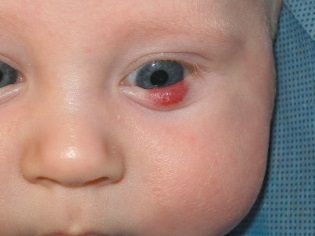
When the hemangioma is in the auricle, it can cause problems with hearing, a tumor in the eye can impair vision, and the formation of a nose or respiratory tract on the mucosa can cause breathing problems.
Cavernous hemangioma can be damaged due to blunt trauma with the formation of difficult to stop bleeding, which in the worst case is fatal. No less dangerous are such formations in the brain (if ruptured hemorrhage can lead to coma or death) and in the spleen (due to an abundance of blood vessels, profuse bleeding occurs with large blood loss).
Frequent localization
Most often (in about 80% of cases) hemangiomas are located on the head and face of a newborn, for example, on the forehead, on the back of the head or on the lip. About 1% of hemangiomas are found on the eyelids. Approximately 5% of the formations are detected on the body of a child, for example, on the back, leg, neck, arm. Up to 1% of such vascular formations are localized in the liver and other internal organs.
Liver hemangioma
Such a tumor is rare and is often represented by the cavernous type. Her presence in the body of a child causes a greater danger to life due to the high risk of damage to such a hemangioma due to blunt trauma. In 60-80% of cases of rupture of cavernous hemangioma, which is located in the liver, the patient dies.
Usually the tumor is single and its size does not exceed 3-4 cm. In many cases, neither the child nor the parents have any idea of such a pathology if it does not grow to a diameter of 5-6 cm or more. With a large size, such a hemangioma is manifested by pain in the right hypochondrium or the appearance of jaundice.
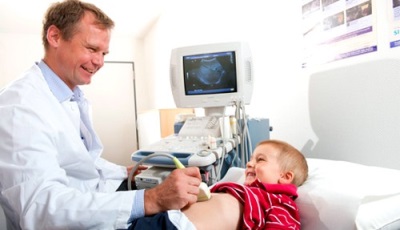
Ultrasound examination is often used to detect such a liver tumor, but tomography and angiography are no less objective. For small sizes do not touch the formation, but only observe its condition. If the size of such a hemangioma is large or the tumor grows, the child is prescribed an operation to remove it or use other methods of therapy.
Stage of the disease
There are three stages of development of hemangioma in a child:
- Stage of vigorous growthduring which the hemangioma increases in size.
- Stage of stunting when the tumor does not change.
- Stage of involution during which benign education is reduced.
When does growth end most often and involution begin?
Most babies have hemangiomas formed in the first days or weeks of life. The most active tumor growth is noted up to 6 months of age.
Most often, by the year its growth is completed and after 12 months the resorption and reversal of hemangioma begins. Every second hemangioma, manifested in infancy, is completely absorbed by the age of five. About 70% of hemangiomas disappear by the age of 7 years, and by the 12th anniversary practically all of them involution.
Diagnostics
Most often, hemangioma is detected during the examination of the child. In this case, the doctor must distinguish such a benign formation from vascular malformations, nevi, squamous cell carcinoma and other pathologies.
For differential diagnosis perform dermatoscopy, ultrasound, angiography and computed tomography.
Opinion Komarovsky
The famous pediatrician calls hemangiomas the most common benign tumors. He confirms that most often these tumors appear in girls and are localized in the face or neck. Komarovsky advises parents who are concerned about the occurrence of hemangioma in a child to contact specialists who are confronted with this pathology daily (pediatric surgeons). A popular doctor does not recommend resolving the issue of treating hemangioma with a doctor who rarely sees such tumors.
According to Komarovsky, most hemangiomas disappear without a trace by the age of 5-10, so the popular pediatrician supports the tactics of active non-intervention, emphasizing that it is desirable not to touch the hemangioma, but it should be constantly monitored.
Alert hemangiomas Komarovsky calls formations on the mucous membranes near the physiological holes (oral cavity, anus or genital area, external auditory canal, eye area) and inwardly growing skin hemangiomas. Such tumors do not require observation, but treatment. Komarovsky also emphasizes the need to go to a doctor, if the hemangioma is constantly injured, its growth has not slowed down by a year or the formation has changed outwardly (it started to bleed, actively grow, ulcerate).
For more on this, see the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.
Modern methods of treatment
Surgical
During the operation, under general or local anesthesia, the tumor is partially or completely excised with a scalpel.
Such treatment is not carried out in the first month of life and is often prescribed with a rapid increase in hemangioma or located in an unfavorable place. At the same time, the operation should not disrupt the work of the organs or cause a serious cosmetic defect.
Sclerosing
This treatment helps to eliminate the cavernous hemangioma. A substance is injected inside the tumor, causing it to die off due to the "sealing" of the vessels from the inside.
The disadvantage of this treatment is pain. In addition, the hardening of large hemangiomas with a large number of vessels is a long process (it lasts 2-4 weeks).
Laser
The tumor is excised with a laser beam. The advantages of this type of coagulation are painlessness and the complete disappearance of the formation (no scars or other traces remain).
The disadvantages include a rather high cost and the need in some cases to carry out the procedure again.
Beam
This treatment option is used for large flat hemangiomas and cavernous subcutaneous formations. Also, radiation therapy is used to eliminate hemangiomas in the brain or in the eye area.
A child older than 6 months is irradiated several times, performing sessions with a pause from two weeks to six months.
Cryotherapy
Such treatment is prescribed for small superficial hemangiomas that are not located on the face.
Tissue tissue is affected by liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide. As a result, frostbite and edema are caused, after which a new skin begins to form on the site of the hemangioma, initially covered with a crust. Sometimes cryotherapy leaves a small scar.
For methods of treatment of hemangioma, see the program "Tablet".
Electrocoagulation
Hemangioma tissues are destroyed by electric current. This treatment is prescribed with a tumor diameter less than 3-5 mm. Also, electrocoagulation is resorted to in situations where the hemangioma has not been completely removed by other procedures (only small parts remain).
Medicamentous
Hormonotherapy using prednisone is used to treat large, simple hemangiomas.
Injections are injected into the tissue of education according to a specially designed scheme, complementing the intake of hormones in pills. The tumor gradually fades and subsides, after which it disappears in 80% of cases. Also for drug therapy of hemangiomas propranolol is used.
Tips
- Watch carefully for hemangioma in a child and contact your doctor immediately in case of very active growth, for example, if the child is already a year old, and education continues to increase. It is also important to consult a specialist when the hemangioma changes color and is damaged.
- People advise to remove hemangioma with celandine juice, but pediatricians oppose such treatments. They argue that no lotions and decoctions are incapable of eliminating the vascular tumor, and with the juice of celandine it is quite possible to cause a child burn, ulceration of hemangioma and the addition of a secondary infection.
For more information about the causes of hemangioma and methods of its treatment, see the program "To live healthy".