Glomerulonephritis in children
Glomerulonephritis in children
Glomerulonephritis is considered to be one of the most common and dangerous kidney diseases in children. This ailment requires special attention from parents and doctors, because in the case of late delivery of care or improper treatment, complications can be fatal for the child. You will learn more about this disease and what the correct actions for treatment should be in this article.
Disease and its varieties
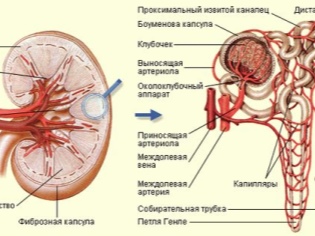
Glomerulonephritis - A disease in which specific kidney cells are affected - glomeruli, which are also called glomeruli. Small cells gave the disease and the second name - glomerular nephritis. Because of this, the kidneys cease to fully perform their functions. Many cares are entrusted to this paired organ by the nature - excretion of decomposition products, toxins, production of substances that control blood pressure and erythropoietin, which is simply necessary for the formation of red blood cells in the blood. Malfunctions of the kidneys lead to the saddest consequences.
In a child with glomerulonephritis, a huge amount of protein is found in the urine, and erythrocytes (blood in the urine) come out with it. Thus, anemia, arterial hypertension, edema develop, because of the catastrophic loss of protein by the standards of the body, immunity decreases. Due to the fact that the lesion occurs in different ways, and the reasons for which the glomeruli of the kidneys begin to die, are very heterogeneous, the disease in pediatrics is not considered to be single. This is a whole group of kidney ailments.
Glomerulonephritis most often affects children aged 3 to 10 years. Kids under 2 years old get sick much less often, only 5% of all cases fall on them. Boys are sick more often than girls.
The classification of glomerulophritis is quite complex and based on the symptoms and the clinical picture.
All glomerular nephritis are:
- primary (if the kidney pathology manifested as a separate independent disease);
- secondary (kidney problems started as a complication after a severe infection).
According to the peculiarities of the course, there are two large groups of illness:
- acute;
- chronic.
The acute form of glomerulonephritis is expressed by nephritic (sudden, abrupt) and nephrotic (developing gradually and slowly) syndromes, it is combined and isolated (when there are only changes in the urine, without other symptoms). Chronic may be nephrotic, hematuric (with the appearance of blood in the urine) and mixed.
Diffuse chronic glomerulonephritis it develops slowly and gradually, most often the changes in the body are so insignificant that it is very difficult to determine later when the pathological process leading to the death of the kidney cells began. Depending on the type of pathogen that caused the underlying disease, complicated by glomerulonephritis, there are several types of the disease, the cause of which becomes clear from the name - post-streptococcal, post-infectious, etc.
And according to the severity of symptoms and the damage that has already been delivered to the kidneys, doctors conditionally award each case 1,2 or 3 degrees with the obligatory indication of the stage of the disease (with chronic illness).
The reasons
The kidneys themselves are not affected by pathogenic microbes and other "outsiders". The destructive process is triggered by the child’s own immunity, which reacts to an allergen.Streptococci act most often as "provocateurs".
Glomerulonephritis is often a secondary complication of primary streptococcal tonsillitis, bacterial pharyngitis, scarlet fever.
Less commonly, the death of the renal glomeruli is associated with influenza viruses, ARVI, measles, hepatitis A. Sometimes the serpentine or bee venom acts as allergens that trigger the destruction of glomeruli. For reasons that are not completely clear to science, the organism, instead of simply bringing these harmful factors out, creates a whole "heavy artillery" of the immune complex against them, which hits its own filters - the kidneys. According to physicians' assumptions, at first glance, little influencing factors — stress, fatigue, climate change, place of residence, hypothermia, and even overheating in the sun — have an effect on such an inadequate response of the organism.
Possible complications
Glomerulonephritis is considered a serious disease. It is rather complex in itself and is not completely cured completely. The most predictable and expected complication of an acute ailment is its transition to a chronic diffuse form. By the way, about 50% of all cases are complicated this way.
But there are other complications that are life-threatening or may cause disability:
- acute renal failure (occurs in approximately 1-2% of patients);
- heart failure, including its acute, deadly forms (3-4% of patients);
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- acute visual impairment;
- kidney dysplasia (when the body begins to lag behind in terms of growth from the size, put on age, decreases).
Changes in the kidneys can be so significant that the child will come chronic renal failure, in which he will be shown an organ transplant.
With the transplantation of kidneys in Russia, everything is rather pitiable, the child can simply not wait for the required donor organ. An alternative (temporary) is an artificial kidney. Since the procedure should be carried out several times a week, the baby is addicted to the apparatus, because there is simply no other way to clean the body of toxins.
Symptoms and signs
Usually, 1-3 weeks after the illness (scarlet fever or sore throat), the first symptoms of glomerulonephritis may appear. The most prominent feature is discoloration of urine. It becomes red in a child, and the shade can be both bright and dirty, which is commonly called the “color of meat mud”.
Starting acute nephritic glomerulonephritis in a child can also be recognized by swelling on the face, which look like dense, poured, little changing during the day. Blood pressure rises, as a result of which vomiting and severe headaches may appear. This form of the disease has the most positive prognoses, since more than 90% of children experience full recovery with adequate treatment. The rest of the disease becomes chronic.
Acute nephrotic illness "Comes" from afar, the symptoms appear gradually, due to this, the child has no complaints for a long time. If the parents do not ignore the morning edema, which sometimes passes completely during the day, and go with the child to pass urine, then the correct signs of the disease will be found in it - proteins.
The first swelling begins to appear on the legs, then gradually spread further - on the hands, face, lower back, and sometimes on the internal organs. Edemas are not dense, they are more friable. The baby’s skin becomes dry and the hair is brittle and lifeless. At the same time, blood pressure rarely rises, and urine has a normal color, because the protein in it does not stain the liquid. Concerning this type of disease, the forecasts are not bright: according to the doctors' estimates, only 5-6% of children recover, the rest continue to be treated, but from the chronic form.
If the child's urine changes in color (becomes more red), but there are no other symptoms and no complaints, it does not swell or hurt anything, then we can talk about isolated acute glomerulonephritis.
With timely treatment at the hospital, about half of all young patients can be cured of him. The remaining 50%, even with proper treatment, for inexplicable logical reasons, begin to suffer from a chronic disease.
If the child has all the signs of all three types of the disease described, then we can speak of a mixed form. It almost always ends with a transition to chronic disease and prognosis is unfavorable. The likelihood of recovery is influenced by the state of immunity. If it is weak or there is some defect in it, then the onset of the chronic form becomes more obvious.
In chronic glomerulonephritis, the child has periods of exacerbations with edema and urine changes and periods of remission, when it seems that the disease has been left behind. With proper treatment, only half of the patients can achieve stabilization. About a third of children develop a progressive process, and this ultimately often leads to an artificial kidney apparatus.
Hematuric chronic pyelonephritis is considered the most favorable among the chronic varieties of the disease. It does not lead to the death of a person, and is noticeable only during periods of exacerbation, when only one of all signs appears - blood in the urine.
Diagnostics
If a child has swelling, even if only in the mornings, even if only on the legs or arms, this is a reason to go to the nephrologist. If the urine has changed color, it is urgently necessary to run to the polyclinic. Parents should remember that a urine test that has been in a jar for more than an hour and a half is less reliable, so you need to be able to deliver the collected urine to the laboratory in any possible way during this time.
Diagnosis of glomerulonephritis includes a visual examination of the child and laboratory tests, the most important of which is the same urinalysis. The number of red blood cells in it will be determined, from the quality - they are fresh or leached. Not less important indicator - protein in the urine. The more it stands out, the usually worse the stage of the disease. In addition, the laboratory assistant will indicate a couple of dozen different substances, salts, and acids, which the nephrologist will be able to tell a lot about.
Usually this is enough, but with respect to young children and with very bad tests, doctors are “reinsured” by prescribing ultrasound examination of the kidneys. In doubtful situations, a kidney biopsy can also be prescribed. A chronic doctor recognizes such a disease, the symptoms of which have lasted for more than six months or if changes in urine formulas have been abnormal for more than a year.
Treatment
In acute glomerulonephritis, home treatment is strictly contraindicated.
The doctor will strongly recommend to go to the hospital and it is quite justified. After all, the child needs complete rest and the strictest bed rest. The patient is immediately prescribed diet No. 7, which does not imply salt, significantly limits the amount of fluid consumed per day, and cuts the amount of protein foods to about half the age norm.
If the disease is provoked by streptococci, then a penicillin group of antibiotics is prescribed. In a hospital, they are likely to be pricked intramuscularly. To reduce edema, diuretics are prescribed in a strict age dosage. With increased pressure will give the means that are able to reduce it.
A modern approach to the treatment of glomerulonephritis involves the use of hormones, in particular "Prednisolone"In combination with drugs - cytostatics, which can stop and slow cell growth.Such drugs are usually widely used in the treatment of cancer, but this fact should not frighten parents. With the improvement of the kidneys, they are assigned the functions of slowing the growth of immune colonies, and this will only benefit the suffering kidney cells.
If the child has concomitant chronic infectious diseases, after the acute stage of glomerulonephritis, it is strongly recommended to eliminate the nidus of infection - cure all teeth, remove adenoids, if they hurt, undergo a course of treatment for chronic tonsillitis, etc.
But you need to do this no sooner than six months after suffering acute renal disease or exacerbation of chronic. Recovery in compliance with the treatment schedule usually occurs after 3-4 weeks. Then the child was recommended to study at home for six months or a year, at least two years to be registered with a nephrologist, to attend sanatoriums that specialize in kidney diseases, to follow the strictest diet. During the year, such a child should not be given any vaccinations. And with every sneeze and the smallest signs of ARVI, parents need to urgently carry his urine samples to the clinic.
Chronic glomerulonephritis is treated in the same way as acute because it needs treatment only during periods of exacerbation.
If he also does not need to insist on home treatment, the child must be hospitalized, because in addition to therapy, there he will have a full course of examination to find out if the disease has begun to progress. For severe forms and extensive damage to the structures of the kidneys, artificial kidney procedures and donor organ transplantation are shown instead of the affected one.
With a chronic illness, the child will be in the dispensary for life. Once a month he will have to pass urine, visit a doctor, and make an ECG once a year to prevent pathological changes from the heart.
Prevention
Vaccinations from this severe disease does not exist, and therefore prevention is not specific. However, parents should know that no sore throat and pharyngitis should be treated without permission, because the disease can be streptococcal, and without antibiotics or if they are not controlled, the likelihood of such a complication as glomerulonephritis will increase significantly.
After postponed scarlet fever after 3 weeks, it is imperative that you pass a urinalysis exactly, even if the doctor forgot to prescribe it. 10 days after streptococcal sore throat or streptoderma, it is also necessary to take urine samples to the laboratory. If there is nothing alarming in them, then you need not worry. Prevention of renal diseases in general and glomerulonephritis in particular includes the correct treatment for SARS, vaccination against influenza and measles. It is important to ensure that the child does not sit on the cold floor with bare ass and does not overheat in the summer in the sun.
For more information on the diagnosis of this disease, see the following video.