Symptoms and treatment of infectious mononucleosis in children
First about infectious mononucleosis learned in 1887. The description of febrile pathology in children was compiled by the Russian scientist N. F. Filatov. And up to the present day, interest in Filatov's illness does not fade.
What it is?
For a long time, especially in Russian medical practice, infectious mononucleosis was called Filatov disease. This zemstvo doctor drew attention to the fact that many babies have similar clinical signs: an increase in peripheral lymph nodes, frequent headaches or dizziness, pain in the joints and muscles when walking. Filatov called this condition glandular fever.
Currently, science has stepped far forward. With the help of various diagnostic tests and high-precision devices, scientists obtained up-to-date information about what causes the disease. In the medical world, it was decided to change the name of the disease. Now it is simply called infectious mononucleosis.
There is a credible hypothesis that the disease has a viral cause. To the development of this pathology lead viruses. This leads to the fact that a person with infectious mononucleosis is potentially dangerous and infectious to others. During the entire acute period of the disease, it can infect other people with the infection.
Most often, this infectious pathology occurs in people of young age, as well as in children. Scientists note that sporadic cases can occur. Large and massive outbreaks of infectious mononucleosis are extremely rare. Basically, all the epidemics associated with this disease occur in the cold season. The peak of the incidence is autumn.
Usually, viruses that get on the mucous membranes settle in the body and trigger the inflammatory process. Their favorite primary localization is epithelial cells lining the outer surface of the nasal passages and oral cavity. Over time, the pathogenic microbes penetrate the lymph and rapidly spread throughout the body along with the bloodstream.
In a child, all the processes in the body proceed swiftly. This feature is due to the characteristics of the physiological structure of the child's body.
Fast processes need a baby for active growth and development. The blood flow in babies is quite rapid. Pathogenic viruses, getting into the body, usually within a few hours or days spread and activate the inflammatory infectious process.
Infectious mononucleosis can be dangerous. The disease is characterized by the development of remote complications or adverse effects. Some babies, especially those who are frequently ill or suffer from immunodeficiency diseases, have a risk of a more severe course. Predict how the disease will develop in a particular child will not work. To prevent potential long-term effects of the disease, the baby should be closely monitored throughout the acute period of the disease and during recovery.
Causes
Herpes virus causes the development of the disease.He has his own name - Epstein - Barr. Favorite localization for exerting its destructive effect for these viruses is lymphoid reticular tissue. They actively affect the lymph nodes and spleen. Penetrating into the body, viruses can also cause damage to internal organs.
Infection with pathogenic microbes can be in different ways:
- Contact-household. Most often, babies become infected when their personal hygiene rules are violated. Other people's dishes, especially those that are not well processed and pre-cleaned, can be a source of infection. The smallest components of the saliva of a sick person can remain on the plate or circle for quite a long time. Violating the rules of hygiene and eating food from the same dish with an infected person can easily become infected.
- Airborne. Quite a frequent variant of transmission of viruses from a sick child to a healthy one. Viruses are the smallest microorganisms in size. They easily enter the body from the carrier by air. Usually, infection occurs during a conversation, as well as when sneezing.
- Parenteral. In pediatric practice, this infection is extremely rare. It is more characteristic for adults. Infection in this case is possible during various surgical operations or during blood transfusion. Violation of the safety of medical procedures leads to infection.
- Transplacentally. In this case, the source of infection for the baby is the mother. The child becomes infected from her even in utero. During pregnancy, an infected mother can transmit viruses that can cross the placenta to her baby. If a pregnant woman has various abnormalities and pathologies associated with placental insufficiency, then the risk of infecting the baby with infectious mononucleosis increases several times.
The development of this disease contributes to a strong decrease in immunity. Usually this happens after frequent colds or as a result of the impact of pronounced psycho-emotional stress.
Severe hypothermia also markedly reduces the performance of the immune system. The body of the baby becomes very sensitive to the penetration of any pathogenic microorganisms, including herpes Epstein - Barr viruses.
Usually the clinical signs of the disease appear in children older than one year. In infants, this infectious pathology is extremely rare. This feature is due to the presence of specific passive immunoglobulins. They protect the children's body from various infections, including the dangerous herpes viruses. Babies get these protective immunoglobulins from mom with mother's milk during breastfeeding.
Many parents ask questions about whether a child can get infectious mononucleosis several times in his life. Opinions of scientists and doctors are separated. Some experts believe that after the illness, the baby is formed of a strong immunity. Their opponents say that herpes viruses can not be cured. Microbes persist in the children's body and can remain there throughout life, and with a decrease in immunity, the disease can return again.
How many days does the incubation period of the disease last? It usually ranges from 4 days to one month. At this time, the child practically does not bother. Some very attentive parents will be able to notice small changes in the behavior of the baby. During the incubation period, the child may experience some slowness and confusion of attention, sometimes sleep is disturbed. However, these symptoms are so dimly manifested that they do not cause any anxiety in fathers and mothers.
Classification
There are various clinical variants of the disease. This served to create a separate classification of infectious mononucleosis.It lists all the main clinical variants of the disease, as well as a description of the pathological symptoms that developed in the child.
Doctors distinguish several forms of infectious mononucleosis:
- Manifest. Usually occurs with the development of various adverse symptoms. Quite vividly manifested. To eliminate the adverse symptoms, special treatment is required.
- Subclinical. Some scientists call this form also a carrier. In this case, the adverse symptoms of the disease do not appear. A child may be a carrier of infectious mononucleosis, but not even suspect it. It is usually possible to detect a disease in this situation only after applying special diagnostic tests.
Given the severity of symptoms, there are several types of the disease:
- Light or uncomplicated. Some experts call it also smooth. This clinical option is relatively mild. It is not characterized by the appearance of complications. Usually, a properly selected treatment is enough for the baby to recover.
- Complicated. In this case, the child may develop dangerous consequences of the disease. For their treatment requires mandatory hospitalization of the baby in the hospital. Therapy in this case is complex with the appointment of various groups of drugs.
- Protracted. It is characterized by a persistent and long course. Usually this clinical option is poorly amenable to drug therapy.
Symptomatology
The development of infectious mononucleosis is usually gradual. One clinical stage successively replaces the other. Usually such a course occurs in the majority of sick babies. Only in some cases, possible rapid acute progression of the disease with the development of numerous complications.
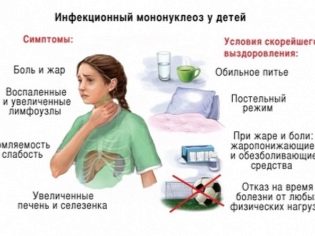
The very first period of the disease - the initial. On average, it lasts 1-1.5 months. Most clinical cases are accompanied by fever up to 39.5-40 degrees. The severity of the condition causes the appearance of a headache. It can be of varying intensity: from moderate to unbearable. Against the background of high fever and headache, the child has severe nausea and even single vomiting occurs.
In the acute period of the disease, the baby feels extremely bad. He has a strong pain in the joints and muscle weakness. He gets tired very quickly. Even the usual everyday activities for a kid lead to his quick fatigue. The child eats badly, refuses his most favorite delicacies. Aggravating loss of appetite and the presence of severe nausea.
These signs are easy to identify and self. Their appearance causes mommies a real shock. Do not panic! If adverse symptoms of the disease appear, be sure to call a doctor. Do not go with the child to the clinic. The difficult condition of the baby requires the consultation of a specialist at home.
In some cases, children have less pronounced symptoms. In this case, the body temperature does not increase so rapidly. It usually rises to subfebrile or febrile numbers in a few days. The characteristic symptoms during this period are: general malaise, severe weakness, nasal congestion and disturbed nasal breathing, eyelid edema, and also some puffiness and puffiness of the face.
In 10% of babies, the disease can begin with the appearance of three characteristic symptoms at the same time. These include: fever to febrile numbers, lymph nodes and signs of acute tonsillitis. This course is usually quite heavy.
The duration of the initial period of the disease is usually from 4 days to a week.
The next stage of the disease is peak time. Typically, the peak occurs within a week after the onset of the first adverse symptoms.The general health of the child by this time is deteriorating. He also has a fever. A very specific feature at this time is mononucleosis angina.
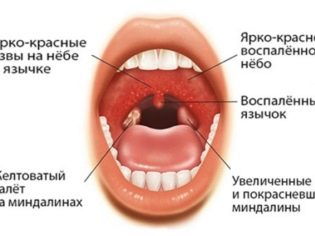
Mononuclear form of acute tonsillitis (sore throats) proceeds quite hard. It is accompanied by the appearance of numerous symptoms in the throat. Typically, angina occurs in catarrhal form. Tonsils become bright red, hyperemic. In some cases, they appear bloom. It is usually white or with a gray tint. Often the overlays on the tonsils are quite loose and are relatively well removed using a spatula or a regular spoon.
The duration of acute tonsillitis in infectious mononucleosis usually does not exceed 10-14 days. Over time, the tonsils are cleared of plaque and all the unfavorable signs of illness disappear.
During the height of the disease is often also accompanied by severe symptoms of intoxication. The child remains severe or mild headache, decreased appetite, disturbed sleep. Sick kid becomes more capricious. The child's sleep duration is disturbed. Typically, sick babies sleep longer during the daytime, and at night they experience significant problems with falling asleep.
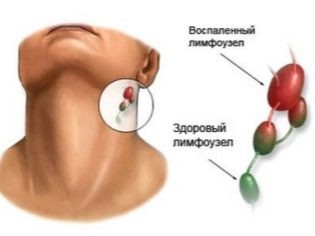
One of the characteristic signs of the height of the disease is the appearance of symptoms of lymphadenopathy. Typically, the immediate peripheral lymphatic collectors are involved in this inflammatory process. With this disease, it is the cervical lymph nodes. They increase in size several times. Sometimes inflamed lymph nodes reach the size of a walnut.
When feeling, they are quite painful and mobile. Any movements of the head and neck lead to increased pain. Overheating of the lymph nodes in the acute period of the disease is unacceptable! The imposition of warming compresses on the neck can only aggravate the course of the disease and contribute to the development of dangerous complications.
Cervical lymphadenopathy in infectious mononucleosis is usually symmetrical. It is easy to notice from the side with the naked eye. Changing the look of the baby. Severe edema of the subcutaneous fatty tissue surrounding the inflamed lymph nodes leads to the development of a “bull neck” in a child. This symptom is associated with a violation of the overall configuration of the neck and is unfavorable.
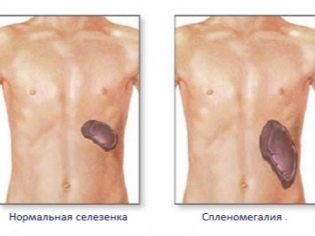
By the end of 12-14 days after the onset of the disease, the child appears clinical signs of involvement in the inflammatory process of the spleen. This is manifested by an increase in its size. Doctors call this condition splenomegaly. In an uncomplicated course of the disease, the size of the spleen is fully normal by the end of the third week since the onset of the disease.
Also, by the end of the second week, the baby has signs of liver damage. Hepatitis manifested by an increase in the size of this organ. Visually, this is manifested by the appearance of yellowing of the skin - jaundice develops. Some babies also turn yellow sclera eyes. Usually this symptom is transient and passes by the end of the peak of the disease.
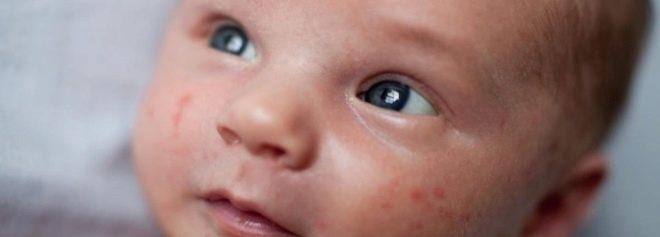
For 5-7 days after the onset of the disease, children have another characteristic sign - a rash. It occurs in about 6% of cases. Rash - maculopapular. There is no clear localization of the appearance of skin rashes. They can appear on almost the whole body. Bulk items do not itch and practically do not bring the child any anxiety.
Usually the rash goes away on its own. Skin elements disappear consistently and leave no trace of hyper- or depigmentation on the skin. After the rash disappears, the baby’s skin becomes familiar physiological color and is not changed. Residual peeling on the skin also does not remain. By the end of the period of height, the baby begins to feel much better.
By the end of the second week of the disease, his nasal congestion disappears and his breathing normalizes, his body temperature rises, and his face becomes swollen. On average, the total duration of this period of the disease is 2-3 weeks. This time may be different and depends on the initial state of the baby.
Toddlers with multiple chronic diseases of internal organs, suffer a peak period much worse. They can have it for more than a month.
The final period of the disease - convalescence. This time is characterized by the complete termination of the disease and the disappearance of all adverse symptoms. In babies, body temperature returns to normal, plaque on the tonsils completely disappears, and normal size of the cervical lymph nodes is restored. The child feels much better at this time: appetite returns and weakness decreases. Baby begins to recover.
Usually, for the complete disappearance of all the symptoms takes time. So, the period of convalescence in babies is usually 3-4 weeks. After this comes recovery. Some children who have had infectious mononucleosis may have residual symptoms for a longer time. During this period it is very important to exercise regular medical monitoring of the baby’s well-being so that the disease does not become protracted.
Diagnostics
When the first signs of the disease appear, be sure to show the baby to the doctor. The doctor will conduct the necessary clinical examination, during which he will inspect the sore neck, feel the lymph nodes, and be able to determine the size of the liver and spleen. After such an examination, the pediatrician usually prescribes several additional laboratory tests to further clarify the diagnosis.
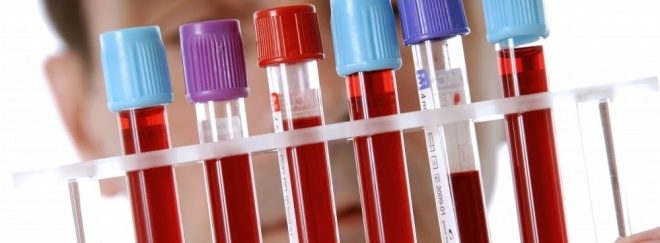
To establish the source of the disease, doctors resort to the analysis of blood for the determination of specific immunoglobulins of class M and G to the virus-Barr virus. This simple test allows you to distinguish mononucleosis tonsillitis from other viral or bacterial tonsillitis. This analysis is highly sensitive and in most cases gives a real idea of whether the virus is in the blood.
To establish the functional abnormalities that occur in the internal organs, a biochemical blood test is required. If a child has signs of mononucleosis hepatitis, then hepatic transaminases and bilirubin levels will be increased in the blood. Complete blood count will help identify all abnormalities that occur in viral diseases. The severity of these changes may be different.
In the general analysis of blood, the total number of leukocytes, monocytes, and lymphocytes increases. Accelerated ESR indicates a pronounced inflammatory process. A change in leukocyte formula indicates the presence of a viral infection in the body. At different stages of the development of the disease in the general analysis of the blood, various pathological changes appear that change with the course of the disease.
A characteristic feature is the appearance of atypical mononuclears in the analysis of specific cells. They have a large cytoplasm inside. If their number exceeds 10%, then this indicates the presence of the disease. Usually, these cells do not appear immediately after the onset of the disease, but after a few days or even weeks. In size, they resemble large monocytes with a modified structure.
Laboratory tests allow differential diagnosis to be carried out fairly accurately. Infectious mononucleosis may be disguised as diphtheria, various types of acute tonsillitis, acute leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis and other dangerous childhood diseases.In some difficult clinical cases, a whole complex of diagnostic measures is required, including the performance of various laboratory tests.
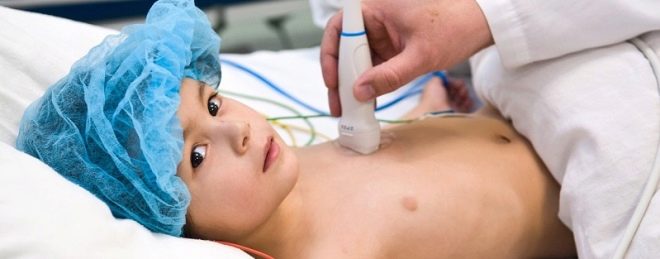
In order to accurately determine the size of the internal organs used ultrasound. Using a special sensor, a specialist studies the surface of the organs and determines their parameters. Ultrasound diagnosis helps to identify all changes that occur in the liver and spleen during the development of infectious mononucleosis. The method is quite accurate and informative.
The undoubted plus of the research is the safety and absence of any painful sensations in the child during its conduct.
Consequences and complications
The course of the disease may not always be easy. In some cases, there are health hazards. They can significantly impair the health of the child and lead to a deterioration in his condition. Failure to provide timely assistance such consequences of infectious mononucleosis have a significant impact on the quality of life of the baby in the future.
The disease can be dangerous by the development of the following negative complications:
- Rupture of the spleen. Pretty rare option. It occurs in no more than 1% of cases. A strong splenomegaly causes the outer capsule of the spleen to rupture and an organ rupture occurs. If a surgical operation is not performed on time, then a comatose state and even death may occur.
- Anemic condition. Such hemorrhagic anemia is associated with a disruption of the spleen. There are also signs of immune thrombocytopenia in the blood. This condition is caused by the impaired work of the spleen, as a blood-forming organ.
- Neurological pathologies. These include: various clinical variants of meningitis and encephalitis, acute psychotic states, sudden cerebellar syndrome, paresis of peripheral nerve trunks, Guillain-Barre syndrome (polyneuritis).
- Various disorders of the heart. They manifest altered heart rhythm. The baby has various options for arrhythmia or tachycardia. With involvement in the inflammatory process of the heart muscle and its membranes, a very dangerous condition arises - infectious pericarditis.
- Pneumonia - pneumonia. It develops as a result of the addition of a secondary bacterial infection. The most common causes of pneumonia are staphylococci or streptococci. Much less often anaerobic microorganisms lead to the development of the disease.
- Necrosis of the liver cells. This is a very unfavorable condition. The death of liver cells leads to a violation of its functions. The body disrupts many processes: hemostasis, the formation of sex hormones, the utilization of waste products of metabolism and toxic substances, the formation of bile. Hepatic failure is formed. The condition requires urgent intensive treatment.
- The development of acute renal failure. This complication is quite rare. Usually, kidney problems occur in babies with anatomical defects in the structure of the urinary organs or chronic diseases of the genitourinary system. This condition is manifested by a violation of urine excretion. Treatment of this clinical condition is carried out only in a hospital.
- Asphyxia. In this acute condition, breathing is completely impaired. The development of asphyxia often results in pronounced acute mononucleosis tonsillitis. The abundance of raids on the tonsils also contributes to respiratory failure. This condition requires emergency medical care.
Treatment
Infectious mononucleosis should be treated as soon as the first clinical signs appeared. Late therapy only contributes to the development of complications in the future.The goal of treatment: to eliminate all adverse symptoms of the disease, as well as to prevent possible secondary infection with a bacterial infection.
Hospitalization of the child in the hospital is subject to strict indications. All babies with pronounced symptoms of intoxication, fever, with the threat of various complications, must be taken to the hospital department. Home treatment for them is unacceptable. The decision about hospitalization is made by the attending physician after examining the child and conducting an examination.
In the treatment of the disease are used:
- Drug-free drugs. These include: the observance of bed rest during the acute period of the disease and medical nutrition. Day regimen for a sick child should be clearly planned. The baby must sleep at least three hours a day. Reviews of parents indicate that adherence to a diet and the correct daily regimen helps the crumbs to recover faster and significantly improve the child's well-being.
- Local treatment. For its carrying out various rinsing are used. As medicines, you can use a solution of furatsilina, baking soda, as well as various herbs (sage, calendula, chamomile). Rinse should be carried out in 30-40 minutes before or after meals. All solutions and decoctions for these procedures should be comfortable, warm temperature.
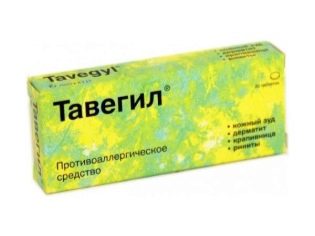
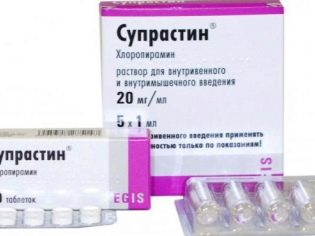
- Antihistamines. They help to eliminate the pronounced swelling of tissues, eliminate inflammation and help normalize the size of lymph nodes. As antihistamines are used: Tavegil, Suprastin, Peritol, Claritin other. Prescribed medications for the course. The dosage, frequency and duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician.
- Antipyretic. Helps to normalize fever. The duration of taking these medications is necessarily discussed with your doctor, as with prolonged use, they can cause numerous side effects. In pediatric practice, drugs are used based on paracetamol or ibuprofen.
- Antibacterial therapy. It is prescribed only in case of accession of a bacterial infection. The choice of antibiotic depends on the pathogen that caused the infection. Currently, doctors prefer modern antibacterial agents with a wide spectrum of action. Penicillin preparations in babies try not to use, since the intake of these drugs is accompanied by the development of numerous side effects.
- Hormonal drugs. Mainly used drugs based on prednisone or dexamethasone. Apply short courses, up to 3-4 days. The average dosage per course is 1-1.5 mg / kg and is calculated individually by the attending physician. Independent use of hormones is unacceptable! The funds are used only after the appointment of the attending physician.
- Multivitamin complexes. The biologically active components of these medicines help to improve the course of the disease, and also help the child to recover from the infection. Take vitamins should be a few months. Typically, a course of multivitamin therapy is 60-90 days.
- Surgery. Assigned to the risk of rupture of the spleen. Such operations are carried out solely for health reasons.
It is important to note that there is currently no specific antiviral treatment for infectious mononucleosis. Antiviral drugs can only have an indirect effect on Epstein-Barr viruses. Unfortunately, taking these medications does not lead to a complete cure for a viral infection. Basically, the treatment of the disease is symptomatic and pathogenetic.
With the development of complications, antibiotics and hormonal drugs are prescribed.Hormones allow you to eliminate pronounced hyperplasia of the inflamed lymph nodes. Severe lymphoid hyperplasia (enlargement) of the lymph nodes in the nasopharynx and larynx can lead to the development of an obstruction of the lumen of the respiratory tract, leading to asphyxiation. The appointment of hormonal drugs helps to eliminate this unfavorable and very dangerous symptom. The treatment complex is chosen by the attending physician. During the course of the development of the disease, it may change to reflect the child’s well-being.
The severity of adverse symptoms depends on the initial severity of the disease. To eliminate them requires an adequate selection of dosages of drugs and the determination of the correct duration of treatment.
Diet
Nutrition of children in the acute period of the disease should be high-calorie and balanced. Follow the recommendations to prevent many complications of the disease. Enlarged liver provokes a violation of the flow of bile and contributes to the development of digestive disorders. Compliance with the diet in this case allows to reduce the severity of all negative manifestations.
Medical nutrition includes the obligatory use of protein foods. As a protein, lean beef, chicken, turkey and white fish are excellent. All dishes should be prepared in a gentle way. Such nutrition is important especially in the period of the height of infectious mononucleosis, when inflammation develops in the oral cavity. The crushed products will not have a traumatic effect on the tonsils, and will not provoke increased pain when swallowing.
As complex carbohydrates, you can use any cereals. Try to cook cooked cereal as much as possible boiled. Supplement the diet should be a variety of vegetables and fruits. Such a varied diet contributes to the saturation of the body with all the necessary substances necessary in the fight against infection.
Rehabilitation
Recovery from infectious mononucleosis is a rather long process. It takes at least six months for the baby to return to his usual lifestyle. As rehabilitation measures, compliance with the principles of a healthy lifestyle will be required. A full balanced diet, regular exercise, optimal alternation of active leisure and recreation will help to improve immunity, weakened during the acute period of the disease.
Within a few months after the transferred infectious mononucleosis, the baby must be observed by the doctors. Clinical surveillance allows timely detection of long-term effects of the disease. For a baby who has had a serious infection, there must be medical supervision.
Parents should also be attentive. Any suspicion of a change in the baby’s well-being should be a good reason to consult a doctor.
Disease prevention
Currently, there is no universal vaccination against infectious mononucleosis. Specific prevention has not yet been developed. Non-specific prophylactic measures to prevent this disease are to avoid any contact with feverish or sick children. The child’s body of an infant who has just had infectious mononucleosis is very susceptible to infection with various infections.
Personal hygiene also helps reduce the risk of possible infection. Every kid should have their own dishes. Using someone else's - is strictly prohibited! During washing dishes it is very important to use hot water and special detergents that are approved for use in children.
During the acute period of the disease, all sickly babies should stay at home. Visiting educational institutions at this time is strictly prohibited!
Compliance with quarantine will help prevent mass outbreaks of diseases in children's groups.If the child has had contact with an infectious mononucleosis patient with a baby, then he is under mandatory medical supervision for 20 days. If you detect signs of disease, he is given the necessary treatment.
For information on what is infectious mononucleosis and how to treat it, see the next video.