Incubation period of rotavirus infection in children, duration of illness
Suspecting the early symptoms of rotavirus infection in a timely manner is very important. This may help to further prevent the development of dangerous complications. This article will help to understand how long the incubation period of the disease lasts, as well as how long the disease lasts.
When do the first signs appear?
Scientists have found the cause of rotavirus infection. Its causative agent is rotavirus, which belongs to the family of reoviruses. Currently, 9 species of rotaviruses have been identified, but the most frequently encountered subtype of rotavirus is A.
Like most viral diseases, rotavirus infection has a rather short incubation period. On average, it is from 12-15 hours to a week. However, in most cases, the incubation period for rotavirus infection is usually only 1–2 days.
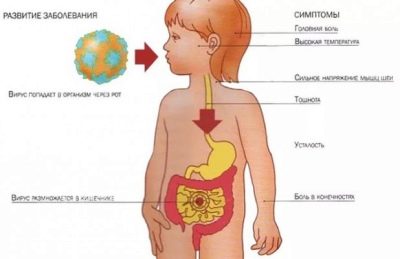
After entering the body, the virus does not immediately cause clinical symptoms. In order for a child to have adverse symptoms, an incubation period is required. The time from the moment the viruses enter the body and the development of the first symptoms is called the incubation period. At this time, trapped viruses begin to multiply actively.
For each sick child, the incubation period has a different duration, which depends on many factors. So, at the time of the first symptoms in children affect the following reasons:
- the nature of the food;
- individual susceptibility to infectious diseases;
- available chronic diseases of internal organs;
- congenital or acquired immunodeficiency.
Most often, children with the age of one to 5 years suffer from rotavirus. It is believed that babies who are breastfed are less likely to suffer from rotavirus infection. Breastfeeding provides the baby with maternal antibodies that are necessary for the baby to form passive immunity that protects the baby’s body from infection.
It often happens that the first manifestations of rotavirus infection go unnoticed. Children who attend kindergarten are rarely ill. In this case, the infection spreads quite quickly from an infected child to a healthy one.
The first signs of infection in a child are so non-specific that their parents do not immediately notice them. At the same time, they “write off” a change in the behavior of the child and tearfulness to children's whims. In such a situation it is very important that the kindergarten strictly adheres to the sanitary and epidemiological regime. A sick child should not be in contact with healthy ones. This is the only way to prevent outbreaks of diseases in children's groups.
A baby can also get infected by eating poorly washed fruits and vegetables or infected dairy products. Rotavirus tolerates cold quite well and can persist for quite a long time in adverse conditions.
How long does the temperature hold?
After the end of the incubation period, the general condition of the child begins to change. A characteristic sign of rotavirus infection, which is included in the clinical triad of the disease, is an increase in body temperature. As a rule, in the first two days it increases slightly and reaches subfebrile numbers.
After 24-48 hours, the temperature begins to increase. By the end of the second day of the acute period of the disease, the body temperature can rise to 38-39 degrees.
At this time, the child's condition is generally deteriorating. The baby begins to fever, the heat increases. The child becomes lethargic, tearful. The baby may have a dream. High body temperature in crumbs, as a rule, persists for 2-3 days. At the same time, as a rule, diarrhea appears in the baby.
Average duration of illness
The adverse symptoms of rotavirus infection may persist for several days. The duration of the disease largely depends not only on the general condition, but also on the number and activity of rotaviruses caught in the children's body.
The acute period of rotavirus infection usually lasts from three days to a week. At this time, the child and there are characteristic symptoms of the disease. The earliest signs of the disease are usually not specific. So, the baby has general weakness, headache and muscle soreness, and body temperature begins to rise. The baby usually refuses to eat, it can feel sick. In some cases, even vomiting is possible.
Rotaviruses can get into the children's body and through the respiratory tract. In this regard, the baby may appear and pain and redness in the throat. These symptoms often resemble those with ARVI. That is why rotavirus infection is often confused with other respiratory diseases.
The acute period of the disease gives way to recovery. This time is necessary for the child's body to fully recuperate the forces spent on fighting infection. Recovery time, as a rule, does not last long. On average, the recovery period (provocation) is 4-8 days.
During the recovery period, the baby normalizes the general condition. Gradually decreases, and then diarrhea disappears. At the baby the appetite begins to appear, and also the intestines work is normalized.
After the first symptoms appear, the baby is still contagious. It will be contagious about 8-10 days after the height of the disease. There are cases when a virus carrier occurs after rotavirus. In this situation, the child may be contagious for 1-2 months.
Rotavirus infection is treated with the use of various drugs. The main goal of therapy is to improve the overall well-being of the baby and the normalization of the work of his gastrointestinal tract. A sick baby must be rehydrated and detoxified, and a special diet is prescribed.
If the treatment of rotavirus infection is carried out incorrectly, the risk of complications increases. It is very important in the treatment to prevent dehydration.. To do this, the child must drink a lot from the moment the first adverse symptoms appear.
In severe cases of the disease may require the introduction of special medicinal solutions through droppers. The need for hospitalization in the hospital is determined by the pediatrician.
The initial state of immunity is a very important indicator. Good work of the immune system reduces the risk of developing this disease. From an early age should teach the child to follow simple rules of hygiene. It is very important for parents to explain to the baby that after visiting the toilet and the street, as well as before eating, he must wash his hands with soap and water.
After infection, the child gets acquired immunity. This is due to the fact that in his blood appear specific antibodies - immunoglobulins. They will protect the children's body from a future meeting with rotavirus. The development of immunity affects the general condition of the child. In some weakened babies, passive antibodies to rotaviruses are practically not formed.
How to treat rotavirus infection, see the next video.