Krivosheya in newborns
Any pathology at an early age needs close attention from parents and medical workers. This is especially true of such a problem as torticollis. If you do not notice it in time and do not make a correction, the consequences can be very sad.
What it is?
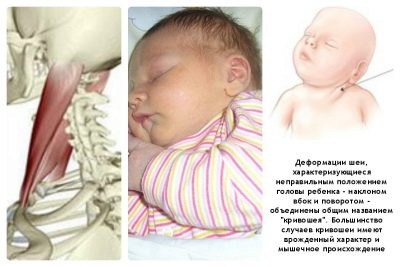
Krivosheya in newborns and infants is a forced wrong position of the head, in which it is constantly tilted to one or another opposite side.
This is due to pathological changes or abnormal development of the soft tissues, skeleton, nerves. Most often the head is turned in the opposite direction due to pathologies of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, cervical vertebrae. Often torticollis is a consequence of birth injury.
The head is inclined to the shoulder and the face turns out to be turned in the other direction; the face itself may be asymmetrical. The movement of the baby's head is severely limited. In essence, the head is fixed in the wrong position.
Muscular torticollis is a very common phenomenon. Among all lesions of the musculoskeletal system in newborns, it takes a deserved third place in terms of prevalence. Before her, only congenital dislocation of the hip and clubfoot. According to Russian medical statistics, torticollis suffers up to 2% of newborns. The World Health Organization cites other figures - up to 16%.
Also, statistics says that little girls are more prone to the pathology, their disease is more common. And in 85% of cases right-sided torticollis is recorded.
The danger of this condition lies not only in the fact that the child is motor limited in development, but also in the fact that Often, torticollis is accompanied by disorders of the organs of sight, hearing, mental retardation. In the absence of adequate treatment and care, torticollis alone does not pass and in the future may cause irreversible deformity changes of the vertebrae, the skeleton, and cause disability.
Types and causes
Sometimes torticollis becomes apparent immediately after the baby is born, and then people talk about the congenital form of pathology.
If the baby was born completely healthy, and the prerequisites for the curvature of the neck appeared later, then torticollis is called acquired. Accordingly, different species have different causes.
Congenital
Such torticollis is visible almost immediately after the appearance of the toddler into the world. It is believed that the cause of the curvature of the neck are intrauterine trouble or pathological childbirth.
It is not always possible to establish the reason, since the list of possible prerequisites is quite large:
- severe maternal late toxicosis (the relationship is not proven, but very often in women with severe preeclampsia, newborns suffer from torticollis, which is currently the subject of medical studies);
- small amount of amniotic fluid (in low water, the risk of developing torticollis in the womb is assessed as high);
- multiple pregnancy (Usually, torticollis is found in one of the twins, the one who held in the uterus is not the most comfortable position for a long time);
- long entwined baby in the womb umbilical cord;
- pelvic or transverse presentation of the fetus during pregnancy;
- pathological generic process (rapid or prolonged labor, the use of obstetric forceps or a vacuum aspirator, the need to use means to stimulate childbirth);
- caesarean section in itself and in connection with the hasty extraction of the fetus through an incision in the uterus;
- violation of the biomechanism of childbirthin which the baby turned the head not in the manner prescribed by nature, in connection with which there was a birth trauma to the neck.
Congenital torticollis can be right-handed, left-handed, or even reciprocal.
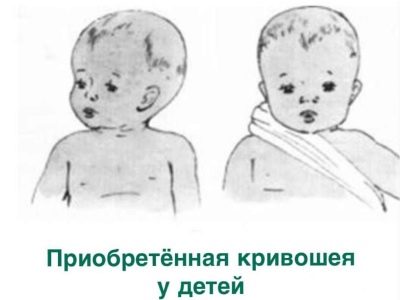
Acquired
Such a curvature of the neck in a child can happen at any age. It occurs when the mechanisms for holding the neck in the correct position are violated.
- If this is due to the weakening or excessive tension of muscle tissue, torticollis is called muscle or myogenic.
- Pathological processes in the vertebrae of the cervical region are not excluded, and then the torticollis is called bone or osteogenic.
- If the joints are affected, limiting the movement of the neck, the torticollis is called arthrogenic.
- When nerve damage is detected neurogenic torticollis.
- When the neck is forced to stay in the wrong position for a long time, a compensatory curvature develops.
Myogenic (spastic)
This form is the most common. By itself, muscle pathology may be congenital, and arising later. If a baby is born with such torticollis, then the development of a nodding or trapezoid muscle is usually impaired. Anomaly of its development may occur in the first or second trimester of pregnancy under the influence of a variety of adverse factors. It is during this period that the fetal muscle tissue is formed. By the nature of the lesion, the muscle can be underdeveloped when the vascular grid is broken, and therefore it is poorly supplied with blood.
In the acquired form, the muscular pathology is usually associated with the fact that one of the two muscles mentioned could have been injured, for example, torn, and over time its rough scarring occurred.
Often in newborns there is a combination of congenital and traumatic factors. After birth, such a form of torticollis develops most often against the background of acute myositis (muscle inflammation), in case of Grizel's disease.
Bone and articular
These forms may also have intrauterine roots. During the period of bone formation and their mineralization (the middle of the first - the beginning of the second trimester), certain factors can lead to the fact that the cervical vertebrae will not be developed correctly - they are underdeveloped, spliced together, they may have an irregular shape, for example, sphenoid, they may be smaller. what is needed, or, conversely, extra extra vertebrae are detected. In any of these cases, the functioning of the cervical spine is impaired.
In the case when such torticollis is acquired, the subluxation or dislocation of the articulation, fracture of the vertebrae, as well as their destruction and destruction due to tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, a present tumor, etc., are usually implied.
Neurogenic (neurological)
This form, if it is congenital, usually indicates that the child in the mother's womb was experiencing a state of oxygen deficiency or there was an intrauterine infection. Often accompanied by muscular dystonia.
If the cervical nerves are affected after birth, then the reasons usually lie in serious concomitant diagnoses. This form of torticollis is often found in children with cerebral palsy, in babies after polio, encephalitis, various neoplasms in the spinal cord or brain.
There is also an additional subspecies of neurogenic torticollis - reflex. It is accompanied by severe pain and most often starts if the child has parotid gland inflammation., there are pathologies of the mastoid process, the clavicle is broken, etc.
Compensatory
The compensatory form is never innate; only cases of the acquired torticollis are recorded.Most often, it develops on the background of vision problems: children with squint, astigmatism strain their necks to see better.
Installation
Sometimes the neck is bent at pathologies of the inner ear (for example, with hearing loss).
Such a diagnosis can be made to a child who hears and sees perfectly normally if he was improperly cared for: they were put in a crib all the time only on one side, they were worn regularly with their heads only on one side, rattles were bright and eye-catching and toys exclusively with the right or only on the left side.
This form is called the installation or positional.
Symptoms - how to recognize pathology?
To determine the congenital torticollis of great difficulty is not: with the naked eye can see the wrong position of the head of the baby, and the exact type of lesion is determined already in the first hours or within 1-2 days after the birth of the child.. Therefore, the new mother learns about the diagnosis back in the maternity hospital. In rare cases, a minor torticollis remains unsolved, but already in the first weeks of the baby’s life, the pediatrician manages to understand and discern the anomaly.
If the neck is crooked in the process of heavy labor, as a result of birth trauma, then it is not always possible to see this torticollis immediately, but the symptoms increase gradually, and by the 2-3 week of the baby's life they can be determined during the examination. Usually such forms are detected on the first inspection at the age of 1 month.
If the degree of curvature is light, then it can remain unsolved not only by parents, but also by a pediatrician for several months.
To understand if a child has torticollis, you need to watch him: babies with such an anomaly have a fixed head inclination towards the shoulder. The chin is turned in the direction opposite to the side of the damaged one.
If, for example, the right neck muscle is injured, then the inclination of the head will be toward the left shoulder.
The muscle itself, regardless of whether it is a bone, joint or other form of torticollis, will be tense. It looks somewhat enlarged. Attempts by mom or dad to gently turn the head to the correct center position or to the other side will meet violent resistance from the infant: he will cry, scream, protest in all ways and means available to him by age.
If you carefully look at the baby in the face, you can pay attention to some asymmetry: one eye, one eyebrow and one eye (on the side of the slope) are located lower than similar parts of the body from the healthy side. The eye on the side of the slope looks narrower, and the shoulder on this side is slightly raised. Respectively, it should be understood that when such signs are found on the right side, the damage or anomaly of the development of bones, muscles or nerves will be located on the left side.
If torticollis is bilateral, then in these children the head is usually tilted back or chin pressed against the sternum. The child practically can not turn his head to the right or left.
If the pathology is of a bone nature, you can look closer and see a violation of the bending of the cervical spine, the head is seated below.
In neurological disorders, the neck muscles are in hypertonia on the one hand and in the hypotonia on the other. Clamping the cam of a newborn on one side only on the affected side indicates problems with cervical nerves.. One leg is usually bent on the same side, but the child can move the head in both directions.
If the torticollis is not noticed in the first month of life, then it can be further recognized by a violation of motor functions: a baby with such an anomaly holds her head poorly at 3 and 4 monthsand this fact should alert attentive parents.If it turned out that up to 5 years the pathology was not revealed, then by this age there are changes that leave no doubt about the diagnosis: the child has a flatter cheek on one side than the other, jaws are incorrectly developed, one eye is located below another, sometimes noticeable underdevelopment of the auricle on the tilt side.
Children with undiagnosed torticollis suffer from slow, gradual deformation processes of the skeleton, skull, face. Milk teeth erupt late in their life, they much later learn to walk, sit, crawl, and creeping itself looks rather asymmetrical, they do not keep their balance in an upright position. Gradually, hearing and vision may decrease on the one hand, and squint may develop. Such children are more likely to suffer from headaches..
Surveys
To establish the appropriate diagnosis of external signs alone is not enough. If parents suspect that the newborn may have torticollis, be sure to contact your pediatrician.. The pediatrician will give referrals for consultations to an orthopedic traumatologist, to a neurologist, as well as to an ophthalmologist and an ENT to evaluate the baby’s vision and hearing.
Mom will be asked about how the pregnancy proceeded, what the birth was like, if the baby was sick with myositis, or if she had had any severe viral infections after birth. After collecting the history of the baby will be sent for examination.
Usually, ultrasound of the neck, or rather of the cervical spine, is quite informative., but other methods are sometimes recommended, such as an X-ray of the cervical vertebrae, computed tomography or MRI.
An X-ray image of the first and second cervical vertebrae is considered very informative: their position usually allows you to easily determine whether the pathology is bone or articular, whether there have been dislocations, subluxations, adhesions, whether the vertebrae are deformed.
More difficult to diagnose neurological torticollis. In order to understand whether the nerves in this part of the child's body work normally, the child is assigned electroneurography. To assess the state of muscle tissue - electromyography. Only after receiving the survey data can you determine the type, type and degree of torticollis. After this therapy is prescribed.
Treatment
The sooner torticollis is detected, the sooner treatment can begin. The younger the child, the more effective it will be, provided the parents comply with all medical prescriptions: to cure torticollis in a child under one year is always easier than in children at an older age.
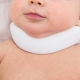
The basis of treatment is to maintain the correct position of the neck of the baby. This can be achieved with the help of orthopedic collars (a Shantz collar, for example), as well as with the help of such methods as taping, when the muscles are fixed in anatomically correct position with adhesive tapes-tapes.
Need to understand that it takes a long time to heal, and it takes time to correct the pathology, requires patience and great diligence on the part of parents.
They are encouraged to stimulate the child's desire to turn the head in the correct position. Bright toys hanging from the “problem” side, carrying a child in their arms with their heads turned to the side of defeat help in this.
Muscular torticollis correction is a special therapeutic massage, physiotherapy, physiotherapy, electrophoresis. Massage mother can gradually learn to do at home, and this will help save nerves and family budget.
Swimming with myogenic torticollis is useful for babies. If the degree is higher than light, then the orthopedist recommends that the child wear a neck brace.. Treatment can last up to one and a half to two years. If after this time the result is not achieved and the torticollis remains, the doctors recommend an operation — a myotomy (dissection of the neck muscle, its removal) is performed, or plastic changes of the muscle state by surgery.
Bone and articular forms of torticollis require at least a long correction with a Schantz collar, special holders for the head. If a dislocation or subluxation cannot be corrected, as well as in the absence of a result from orthopedic correction, a surgical operation (spinal fusion) is performed, in which the adjacent cervical vertebrae cause immobility relative to each other.
For the neurological form of the disease, medicines are used to relax the muscles. (muscle relaxants), as well as drugs to reduce the increased excitability of the nervous system karapuz. Equally important is the massage, therapeutic exercises.
Forecasts and Prevention
No matter how terrifying the possible consequences and complications of infantile torticollis might seem, the prognoses for her are quite favorable, and this should reassure parents and make them tune in a creative way - up to 90% of babies, whose treatment of torticollis began in the first 6 months, fully recover, the deformities are a thing of the past.
If treatment is started later than a year, then it will be difficult to completely eliminate the deformity, but the child’s condition will noticeably ease. In any case, the baby who has been diagnosed with such a diagnosis, even if he is cured, will be in the dispensary of an orthopedic surgeon until he reaches the age of majority. This is the law.
To avoid an unpleasant diagnosis, prevention must be taken even during pregnancy. After the baby is born, it must be properly laid in the crib, each time changing the side at which the baby will rest, you need to hang toys in the center, as well as on the right and left side at the same time.
It is important to remember that the neck of infants is very easily injured, you need to be very careful with it.
Opinion of Dr. Komarovsky
Renowned pediatrician and TV presenter Yevgeny Komarovsky urges parents to show maximum responsibility if it is a question of diagnosed wriggle - this is a serious disease that without correction can lead to tragic consequences. Komarovsky considers therapeutic massage and orthopedic appliances to be very useful. But he urges parents not to go to extremes. In particular, he warns them to contact an osteopath.
Despite the fact that osteopathy is recognized by the Ministry of Health, unlike homeopathy, it did not become more scientific, says Komarovsky. That is why there is no intelligible proof that a child with torticollis can be cured by an osteopath. But such treatment can be harmful to him: an inept osteopath or an unknowled specialist in manual therapy can lead to additional injury to the neck, which then may require correction by surgery.
There are several cases of death of infants in the hands of osteopaths and manual therapists with dubious diplomas and reputation, but high rates for their sessions.
Much more useful, according to Komarovsky, to visit a qualified medical massage therapist and ask him to show the technique of therapeutic massage, so that later, in a homely calm environment, the mother herself could make it to the child.
You need to visit specialists of physical therapy and learn exercises for daily gymnastics, on fitball and without it, which should be directed to the proper development of the neck muscles. All this is beneficial complement the treatment program.
Reviews
According to parents, the treatment of torticollis in newborns and infants is very long and expensive. But it gives results if everything is done in strict accordance with the doctor’s prescriptions. On the Internet there are a lot of thematic forums where mothers of children with torticolls support each other, share experiences, tips, information about good massage therapists, neurologists, orthopedists.
The main thing, say experienced mommies, is not to panic. The disease is unpleasant, but not fatal and reparable.
The main thing is not to delay the therapy.