Symptoms of Crohn's disease in children and its features
If a child complains of abdominal pain, he has a high body temperature for a long time, his chair has changed and his weight is reduced, he should immediately contact a pediatrician. Perhaps this is Crohn's disease.
What is it?
Crohn's disease is a chronic disease of the digestive system, in which the tissues of the intestines and other parts of the digestive tract become inflamed and destroyed. The name of this disease was given by one of the doctors who described it in 1932. The onset of the disease is possible at any age, but most often it is detected in people from 13 to 30 years old.
Although the pathology is quite serious and serious, many people who have Crohn's disease, receive adequate therapy, live a long time and lead an almost normal life. Most often, the course of the disease goes away with exacerbations (in most patients they occur every two years or less) and in remission.
The reasons
At the moment, the exact causes of Crohn's disease, scientists have not yet found. At the same time, the role of heredity is noted, since the frequency of occurrence of the disease is 5–20 times higher in direct relatives of patients. If the parents have Crohn's disease, the probability of the disease in a child is 5%.
Other factors contributing to the development of this pathology include infection with viruses or mycobacteria, toxins entering the intestine, certain drugs, and the effect of food.
Disease progression
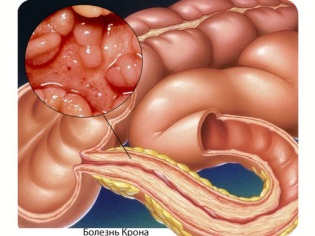
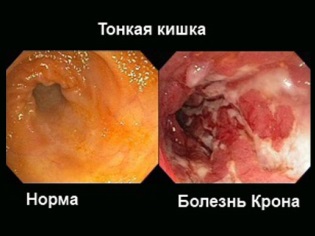
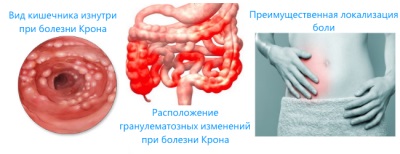
With this disease, inflammation appears in the walls of the digestive tract. Most often they occur in the ileum and caecum, as well as in the rectum.
Due to the multiplicity of foci of inflammation, the work of the intestine is disturbed, which becomes a factor in the development of anemia and hypovitaminosis.
Complications
Sometimes inflammation affects the intestinal wall so deeply that it can cause perforation, the appearance of adhesions or fistulas. Also complications in Crohn's disease include intestinal obstruction and internal bleeding. In rare cases, inflammation spreads from the digestive system to the skin (rash appears, pockets of flaking), joints (they can become inflamed and sore), eyes (vision is broken, pain is noted), kidneys and other organs.
Symptoms
During exacerbations of the disease, when the intestines become inflamed, the child is observed
- Continuously increased body temperature to 37.5-38 degrees.
- Attacks of pain in the abdomen - they are located on the lower right or near the navel and are quite strong.
- Diarrhea, which is prolonged or repeated, can sometimes be with blood. The child defecates up to 10 times a day.
- Fatigue and fatigue.
- Weight loss or insufficient gain.
- Growth retardation
With the defeat of the stomach, the disease is manifested by vomiting, heaviness in the stomach, nausea. If the inflammatory process has engulfed the rectum, pain in the anus, constipation and bleeding may occur.
Treatment
In the selection of treatment for a child with Crohn's disease take into account such moments as the activity of the inflammatory process, the condition of the child, the severity of symptoms and other factors. So the approach to the treatment of this disease will be individual. A major role is played by medical nutrition.
Medicines
If the disease has been diagnosed recently, the child is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressive drugs and hormones (prednisone). In addition, antibiotics, antidiarrheals, sorbents and enzymes may be prescribed.
If the course of the disease is severe, intravenous administration of electrolytes, amino acids, and plasma is prescribed. Sometimes, after a short course of medication, long-term remission occurs, but it is often necessary to take medication for a long time.
Surgical intervention
It cannot be avoided if the intestinal tissues collapse and the result is an abscess, a narrowing of the intestinal lumen or the formation of a fistula. Such complications can be eliminated only surgically. During surgery, the damaged part of the intestine is removed. Unfortunately, this treatment does not help to get rid of Crohn's disease completely, so they resort to surgery only when absolutely necessary.
Prevention
It is important to pay great attention to the nutrition of the child - it must be complete and rational, and also correspond to the age of the baby. You should also prevent and consistently treat any diseases of the digestive tract, including parasitic diseases and acute intestinal infections.