From the ear is bleeding a child
When a child begins to bleed, it always scares the parents. But, if many people encounter the discharge of blood from the nose and it is quite simple to help the baby with nosebleeds, the blood from the ear goes much less often, so in such a situation, the mother often does not know what to do and what the reason for such bleeding.

What is it
Bleeding from the ear is often manifested as a discharge of droplets or a trickle of blood from the auricle or from the ear canal. In many cases, it occurs after some kind of external influence, for example, the child fell and hit his head or cleaned his ear, and blood began to flow. However, the mother can detect bleeding and accidentally, noticing only its effects, for example, when cleaning dried blood in the ear will be detected. In addition, blood from the ear can be released with an admixture of pus or serous fluid.
The reasons
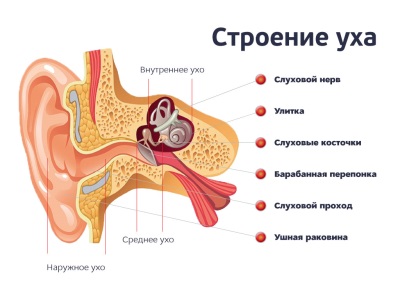
In childhood, ear problems are often limited to inflammation associated with the anatomical features of the middle ear and Eustachian tubes, as well as with frequent viral diseases and colds. If blood is emitted from a child’s ear, there are several explanations for this situation.
There is mechanical damage to the ear.
A head injury (skull fracture, labyrinth contusion) could have provoked him, but a more frequent cause is damage to the ears by other objects, for example, a child has put a cotton swab in his ear and has gone blood. As a rule, in such a situation there is a bleeding scratch of the ear canal. In addition, wanting to get rid of the discomfort in the ears, kids can shove various objects into the sink, including sharp objects (toothpicks, paper clips, matches, sticks, toys, etc.), which also often ends in bleeding.
Also, the ear can be damaged during the game, for example, when hitting the ball. Such an injury can lead to a hematoma under the shell cartilage. In addition, a strong blow can cause a rupture of the eardrum. In this case, the child will have bleeding, severe pain and hearing impairment. The membrane may rupture if your ear falls onto water or when an adult attempts to pull a foreign object out of the ear of a child.
Bleeding has an infectious cause.
Blood can be released during otitis accompanied by symptoms of middle ear inflammation, such as high body temperature, severe pain, weakness, dizziness. It is especially dangerous if a child with this inflammation from the ear to release only blood, and impurities of pus are missing. This is a sign of a deepening infection process.
Another common cause of blood from the ear is the boil. A child with such inflammation will have redness and swelling of the ear, and the temperature may increase. When the boil in the ear is opened, then after the discharge of pus and blood appears.
We recommend to watch the release of the program of Dr. Komarovsky, dedicated to this disease in children, as otitis media:
Also bleeding from the ear can be provoked. infectious inflammation of the eardrum (it's called myringitis).A child with this pathology will complain of severe pain and pronounced discomfort in the ear. In addition, myringitis often increases the temperature. When such an infection in the ear forms a bubble filled with serous fluid. When it is opened, the child's discomfort diminishes, and exudate with blood appears from the ear.
Another infectious cause of bleeding from the ears - candidiasis. Such an infection occurs when the protective forces of the child’s body are weakened. If it penetrates the ear, then it can manifest itself quite abundant bleeding.
The child has a tumor
A tumor in the ear that causes bleeding can be benign. For example, it may be a glomus tumor appearing on a vein. When it expands, the child begins to complain of dizziness and noise in the ear. A symptom of this formation is the abundant discharge of blood.
Another benign cause of ear growth that can bleed - polyps. The doctor will easily notice such formations in the ear canal of a child, and sometimes polyps expand so strongly that they go beyond the ear canal. In addition to bleeding, this pathology may manifest as dizziness, headaches and hearing loss.
Malignant tumors in the ear most often represent carcinoma, which can affect both the outer and the middle ear. Blood from the ear or ear canal is often the first symptom of such a tumor.
What to do
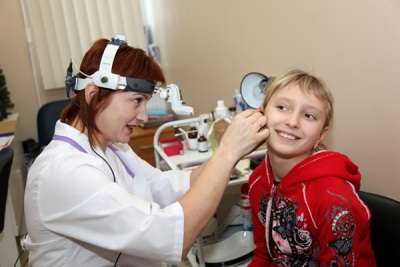
Having found bleeding from the ear in a child, in most cases, the otorhinolaryngologist should be immediately shown to the baby. If the cause of the blood has become a serious illness that needs urgent treatment, delay with a visit to the doctor can cause complications, including hearing loss. The only case where you can not rush to the ENT, and let the bleeding stop itself - this is a small mechanical injury of the skin on the ear, for example, a scratch.
How to give first aid
If the auricle is damaged
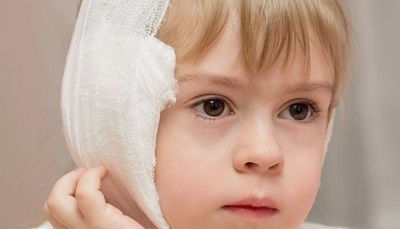
Wash the sink from contamination using warm water and a sterile bandage. Next, the wound on the sink should be smeared with iodine (alcohol solution) and closed with a bandage, and then take the child to a trauma center or other medical facility.
If blood appeared after cleansing
Moisten a cotton or gauze pad with a solution of peroxide, wipe the ear of the child, put a bandage on the auricle, and then contact your otorhinolaryngologist. Do not give the child any medication and bury his ear before being examined by a doctor.
When the eardrum ruptures
Make a cotton swab out of sterile cotton and insert it into the ear canal. Put a bandage on top and take the child to the hospital as soon as possible.
With a foreign body
Do not try to remove the object yourself, especially with sharp objects, as there is a risk of pushing the foreign body deeper. It is best to immediately refer to the ENT.
With traumatic brain injury
Lay the child on a flat surface and call an ambulance. Do not touch or rinse your ear.
Treatment
Tactics of the doctor will depend on the cause of bleeding from the ear:
- In case of purulent otitis or furuncle, an antibiotic, an anesthetic medication and other medicines will be given to the child. Also, the doctor will tell you how to wash your ear and what drops you can bury.
- For candidiasis, the child will be prescribed antifungal treatment.
- For scratches or abrasions, treatment will be to treat the ear with an antiseptic preparation.
- If the child has a broken eardrum, the doctor’s actions will be determined by the size of the perforation. Sometimes surgical assistance is required.
- For a foreign body in the ear, the doctor will remove the object and, if necessary, prescribe additional treatment.
- If a child is found, the child will be referred to an oncologist and a special therapy will be prescribed.