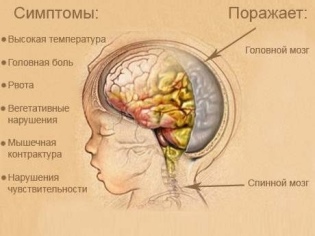
Meningitis in children under one year old
Inflammation of the meninges or meningitis in newborn babies and infants is not the most common disease. However, parents should not forget about this disease at all. Meningitis in a child up to one year can occur with numerous serious complications. Only timely delivery of treatment will help the baby recover and even save lives.
The reasons
Among the various forms of meningitis, most of them are infectious forms. Often they are caused by various viruses or bacteria. Meningococcal infection is the undisputed leader among the causative agents of the inflammatory process of the meninges. It occurs in 70-80% of cases in patients with meningitis.
Bacterial meningitis, which is quite hard and goes into purulent forms cause different types of bacteria. The most common in newborns and infants are meningococcal and streptococcal meningitis. For such diseases characterized by severe and frequent development of complications.
Serous meningitis caused by 80-85% viruses. Often pathogens become the cause of the disease. rubella, chickenpox, measles, viruses herpes and Epstein Bar. In weakened babies, meningitis can also be caused by a common flu infection. In such cases, the child, as a rule, has impaired functioning of the immune system or even immunodeficiency.
For children with diabetes or taking glucocorticosteroids since birth, infection with candidal meningitis is possible. In this case, an opportunistic fungus, Candida, spreads quickly in a weakened child’s body. When a microorganism gets into the meninges with blood flow, it quickly multiplies there and causes severe inflammation. Treatment of such forms of the disease is usually longer than bacterial forms.
The most rare forms of meningitis in babies of the first year of life include the tuberculosis variant or a disease caused by protozoa. Such forms of the disease are found only in 2-3% of all cases.
The traumatic variant occurs after birth trauma. The disease usually develops within a few days or months after the baby is born. Traumatic meningitis is difficult. Numerous complications can also occur. For the treatment of a child with a traumatic form of meningitis, a mandatory consultation with a neurosurgeon and the observation of a neurologist are required.
Risk groups
Kids of any age are not insured against the appearance of meningitis. Features of the structure and functioning of the nervous and immune systems of babies in the first months after birth make them quite vulnerable to various inflammatory diseases.
Not all babies are equally at risk for meningitis. To control and monitor the babies with a greater likelihood of illness, doctors identify risk groups for the development of meningitis. These include:
Newborn babies with very low birth weight as well as premature babies. These babies have not yet completely formed the nervous and immune systems. The blood-brain barrier of newborns does not function in the same way as in adults. Microorganisms that are small in size easily penetrate this barrier and can cause inflammation.
Children with congenital or acquired immunodeficiency. The imperfection of the cells of the immune system does not allow time to respond to an external pathogenic factor.Leukocyte immunity is not yet able to effectively eliminate any infectious agents from the body. In such children, the risk of a severe course of any, even the most harmless infection, increases many times.
Birth injuries. Have adverse effects on the nervous system. Damage to the nerve trunks and membranes of the brain during traumatic external influences also contributes to the development of meningitis in children.
Chronic congenital diseases. Weakened babies with many comorbidities are not able to fight the infection to the proper extent. The presence of congenital heart disease, diabetes, cerebral palsy affect the possible prognosis of meningitis.
What are the main signs of newborns and infants?
To determine the first manifestations of meningitis in infants is a rather difficult task for any mommy. The behavior and well-being of the child during the incubation period is practically not affected. Usually this period is from 3-5 days to two weeks. Attentive mothers can pay attention to the fact that the child becomes more sluggish, tries to rest more often.
Characteristic of meningitis symptoms usually appear as:
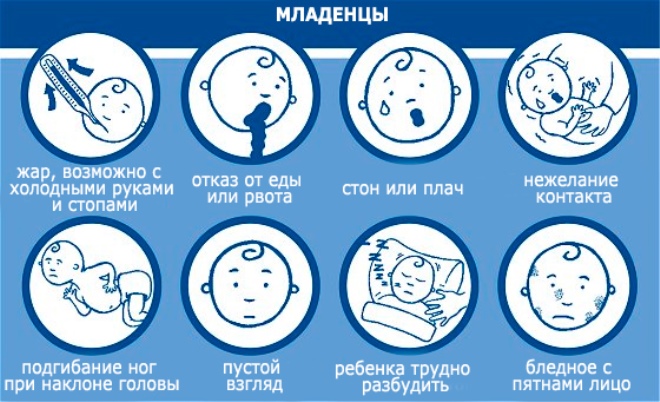
Temperature rise. Usually swift. In a few hours the temperature rises to 38-39 degrees. Babies can shiver or fever. Taking paracetamol and other antipyretic drugs does not bring relief. The temperature is kept high for 4-5 days of illness. With severe course - more than a week.
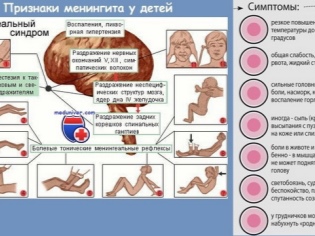
- Severe headache. Babies cannot yet say what bothers them. If the child becomes more sluggish, crying, trying to tilt his head below the level of the pillow - be sure to guard! Often this symptom is a manifestation of high intracranial pressure and requires immediate medical assistance.
- Behavior change baby. Toddlers refuse to breast, become lethargic. When touching the head and neck, the baby may start crying or avoid contact. Any attempts to tighten the legs to the stomach or take them to the side can bring severe discomfort to the baby and even lead to increased pain.
- Frequent regurgitation. Despite the usual feeding, the baby can constantly regurgitate food. This is a manifestation of severe nausea. Some babies may even experience a one-time, but severe vomiting.
- In severe cases - the appearance of seizures. Usually this symptom occurs in babies with congenital diseases of the nervous system or episindrom. The appearance of this manifestation of the disease is an unfavorable prognostic sign of the disease and requires an urgent hospitalization of the baby in the intensive care unit.
With the deterioration of the general condition and the increase in signs of the inflammatory process - clouding of consciousness or even coma. Be sure to pay attention to the look of the child. If he becomes "absent" - immediately call the attending physician! This may be one of the manifestations of meningitis.
Diagnostics
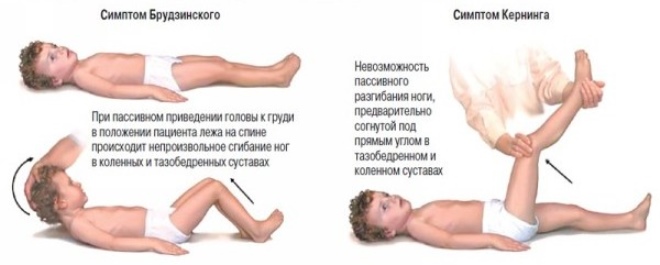
To establish the diagnosis, the doctor conducts special tests. Usually, the doctor presses the baby's legs to the stomach or torso and assesses the reaction. Strengthening pain syndrome is a positive meningeal symptom and requires additional diagnostics.
One of the most accessible tests is a complete blood count. Its result provides information to doctors about the specific cause of the disease. Most often, you can establish a viral or bacterial etiology of the disease. The leukocyte formula in the general analysis of blood shows how severe the inflammatory process is.
More accurately determine the causative agent of the disease, using bacteriological tests. They allow you to identify different types of viruses, bacteria, fungi and even the simplest.The undoubted advantage of such a test is that it is possible to carry out an additional determination of the sensitivity of the microbe to various drugs. This allows doctors to prescribe the correct and effective treatment, eliminate the cause of the disease.
In difficult cases, doctors resort to puncture. The doctor makes a puncture in the spine with a special needle and takes a little spinal fluid for examination. Using laboratory analysis, you can determine not only the pathogen, but also the nature of the inflammatory process and the form of the disease.
What consequences?
For many children who were given adequate treatment for meningitis in time, the disease ends in complete recovery. However, not all cases guarantee a similar result. If the child had aggravating factors, then the course of the disease becomes quite severe. In this case, the risk of developing an adverse last significantly increases.
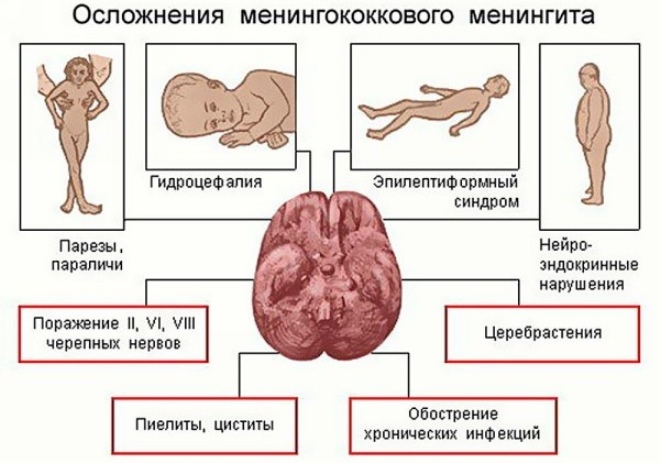
Most often, babies in the first year of life have the following complications:
Nervous system disorders. These include: a decrease in concentration and attention, some lag in mental and even physical development. After rubella meningitis - hearing loss and poor speech perception.
The appearance of episindrom. Some babies may experience cramps. This symptom is often temporary. To eliminate the adverse manifestations, a mandatory consultation with a neurologist and additional diagnostic tests are required. The babies are given EEG, neurosonography, as well as other tests to assess the level of damage to the nervous system.
Heart rhythm disorders. Transient arrhythmias are more common. Usually they appear after a few months or even years from the moment of recovery from an infection. Kids with such complications require mandatory monitoring by a cardiologist or an arrhythmologist.
How to treat?
All babies with suspected meningitis must be hospitalized without fail. Newborn babies are delivered to hospitals equipped with all necessary resuscitation equipment. The child must be watched around the clock by the medical staff.
Treatment of the disease is carried out comprehensively. The leading role in therapy is the elimination of the underlying cause that caused the disease. For infectious meningitis, large doses of antibiotics are prescribed. All antibacterial agents are administered parenterally. Intravenous administration of drugs allows you to quickly achieve the desired clinical effect and accelerate recovery.
To relieve symptoms of headache and nausea, diuretics are used. Diuretic drugs reduce high intracranial pressurecaused by inflammation and help improve the well-being of the baby.
To restore the nervous system, administration of vitamins of group B is used. Such injectable forms of drugs can reduce the toxic effect of bacterial agents on nerve trunks. Vitamins are usually prescribed for a long time, courses of 10 days.
In order to eliminate the symptoms of intoxication, various detoxification preparations are used. Often, babies are given large doses of a 5% glucose solution or an isotonic sodium chloride solution. When seizures or motor impairment appear, electrolyte solutions are added to the treatment. With such an introduction of drugs, the baby's well-being normalizes fairly quickly.
After stabilization of the condition, the babies are prescribed immunostimulatory drugs. They activate the immune system and help the immune system fight infection. Such drugs are effective enough for newborns and babies in the first year of life. They are generally well tolerated and do not cause adverse side effects.
Prevention
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene for babies of the first year is also a necessary condition for the prevention of meningitis and other inflammatory diseases. In order to prevent contamination by the contact-household method, it is imperative to monitor the cleanliness of all objects that touch the skin and mucous membranes of the child. Towels must be washed daily. To iron textiles should be a hot iron on both sides.
Babies of the first year of life should have their own dishes and cutlery. The use of adult plates and cups is prohibited. All cutlery should be without chips and cracks, as they can easily accumulate bacteria. For newborn babies, remember to sterilize feeding bottles. Processing dishes for kids carried out with the use of special tools that are approved for children.
Treatment of meningitis in infants of the first year of life should be initiated, if possible, as soon as possible. This will not only prevent possible adverse complications of a dangerous disease, but also preserve life and health.
All about meningitis in a child, see the next video of Dr. Komarovsky.