Hearing impaired children: education, hearing aids and rehabilitation
According to statistics from the World Health Organization, about 6% of the world's population has hearing problems. The problem is especially acute in childhood, when a child cannot build a complete picture of the world without the ability to hear. Therefore, issues of early detection and rehabilitation of hearing loss and deafness in children are among the most important in medicine.
Parents who have learned that their the child does not hear wellit is very difficult to accept it, but gradually and they are convinced that much does not even depend on how much or how much auditory perception is lost, but on how correctly the child is rehabilitated, After all, this is important for its further development, training, life.
Why do you need a good ear?
People begin to think about the meaning of hearing mainly when they lose it. Even for an adult, being deprived of the opportunity to perceive the world at the sound becomes a real tragedy. As for the child, the ear is necessary for him to learn this world to the full. Even the restriction of the function to one ear leads to the fact that many things become inaccessible for the child, he cannot fully hear the sounds of nature, his parents turn to him, it is difficult for him to distinguish the nuances of music. If a child is deaf or hard of hearing in both ears, the acquisition of speech skills is questionable.
Speech is formed first in a passive form - the child listens to the sounds that others reproduce, and only after that he tries to repeat them himself. If he does not hear the sounds, then he simply has nothing to repeat. If the speech is underdeveloped or underdeveloped, the child does not have the necessary vocabulary for communication and learning, he suffers from logical thinking. And, naturally, the absence of good hearing cannot but affect the formation of the child’s personality as a whole.
Much depends on the time of onset of pathology. If a child has lost the ability to hear well already at the age to which he has accumulated a certain vocabulary, then without competent rehabilitation he may soon lose it.
If a baby was born deaf or hard of hearing, then without rehabilitation methods and devices he simply cannot master speech, cannot fully communicate.
Classification
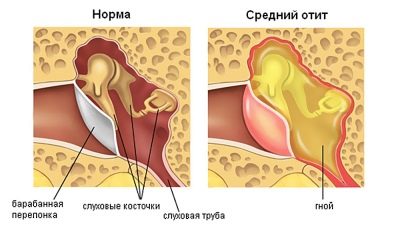
In matters of rehabilitation and prognosis, the cause of impairment or loss of hearing is very important. If a child develops otitis during influenza or ARVI and in this connection, inflammation of one of the hearing organs begins, it does not belong to the number of children with hearing impairments, since his loss is probably temporary, and hearing will recover after treatment.
Children with hearing impairments, by international definition, - these are children who have a persistent (that is, irreversible) hearing loss in both ears. At the same time, the perception of sound information may be difficult (hearing loss in a child) or not possible at all (deafness in a baby).
Deafness is considered the most severe form of auditory dysfunction, especially if it is acquired at an early age or is a congenital pathology.
Hearing loss can be of varying degrees of loss of hearing ability, and with minor forms the children are quite capable of studying in regular school.because only whisper speech is poorly perceived, and with moderate or severe hearing loss without correction and rehabilitation, learning and communication will become an impossible task, since even with residual hearing, if the child was born with hearing loss or lost an ear at an early age, speech will not develop.
All children with auditory dysfunction are divided into three groups: deaf (completely deaf), deaf and deaf late. If with the first two groups everything is more or less clear, then the third group includes children who have lost the ability to hear normally at the age when their speech was already formed.
Causes of violations
The auditory function of the human body is very finely organized; any negative factor can disrupt it, both before our birth, in the prenatal period, and after. In this regard, the causes of hearing loss or its primary absence may be very different.
The most common such factors.
- Hereditary - parents who have problems with auditory function often have offspring with a similar problem, and the child can inherit deafness or deafness from birth, not only from mom and dad, but also from grandmother and grandfather. Geneticists have proven that deafness is capable of being transmitted in both dominant and recessive ways.
- Congenital - prevailing during the intrauterine formation of the fetus, especially during periods when the structures of the organs of hearing and the corresponding parts of the brain are laid. The reason for the lack of hearing in a baby can be a viral infection, which the mother got sick with, especially dangerous in the first trimester, mother’s and fetus rhesus, taking pregnant antibiotics, smoking and drinking alcohol during the waiting period of the child.
- Generic - anomalies of the auditory function in this case develop as a result of birth injuries, such as, for example, compression of the head, use of obstetric forceps, abnormal labor, injuries of the cervical vertebrae, etc.
- Acquired infectious - develop in children born with normal hearing as complications of diseases. Most often deafness and hearing loss are the result of diseases such as meningitis, scarlet fever, measles, infectious parotitis (mumps). All strains of the flu virus are very dangerous for babies. Defeats of hearing in an infectious disease mainly manifest in the defeat of the auditory nerve, the cochlea. Severe, especially purulent otitis, transferred by a child, may well be complicated by the development of hearing loss, usually in a mild or moderate degree. Labyrinthitis often leads to severe hearing loss and deafness. The cause may be transferred mastoiditis, ear fistula, eustachitis.
- Acquired by others - often hearing problems develop in children suffering from adenoids. Hearing loss and deafness due to traumatic brain injury, due to the administration of ototoxic antibiotics (gentamicin, monomitsin, neomycin, streptomycin) may develop.
The hearing loss is diagnosed by different methods. First of all, on the basis of objective behavioral signs: children ask again, the baby does not hear what he is told the first time. Many tots with neurosensory hearing loss, to hear, delay the ear. Kids develop slowly, do not master the walking, syllables, words, or master, but with a big delay. After a year, the grown-up guys start frantically peering into the lips of the speaker to try to understand what they want from them.
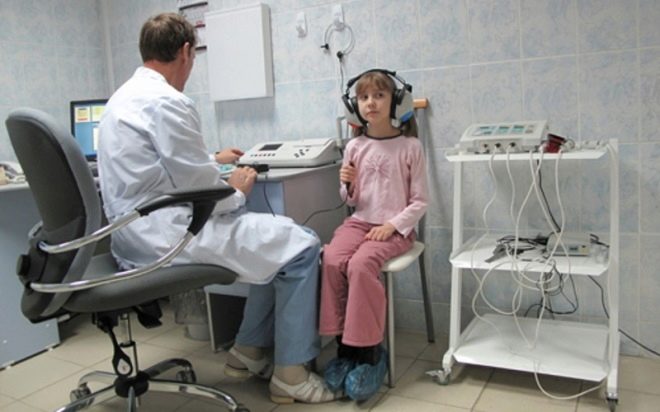
The most accurate method for determining the problem and its degree is considered to be a hardware examination - audiometry.
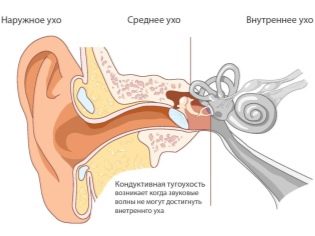
Her results show not only the type of hearing impairment (conductive or neurosensory), but also determine range of audible and indistinguishable frequencies and ranges.
Characteristics of groups
The classification of groups of children with hearing impairments has its own characteristics, which must be taken into account not only by teachers and doctors in rehabilitation and education, but also by parents in matters of family education.
Deaf
Children who do not hear at all risk becoming deaf-and-dumb even with a normally developed articulation apparatus. Without rehabilitation and a special training program, they will not be able to master conversational skills.
In more than half of the cases, children are deaf not in the womb, but after birth, at 1-2 years of age.
Children of this group have features in the development of vision, psyche, and perception of reality. Their need for communication is great, like all the other guys, but only gestures that do not meet the needs of psychological development are accessible to them.
Often deafness is accompanied by pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, as well as vision. The ability to see normally is lost due to the overstrain of the organs of vision, because in the absence of perception of sounds, the child begins to automatically straighten his eyes. A secondary defect concerns changes in timbre and sound of the voice.
Children who have lost the ability to hear at a later age
Even if the child has lost the ability to hear normally at preschool age, his speech skills remain, but whether he will remain in the future depends on how well the child has learned to speak before the onset of hearing loss or deafness, and how he will undergo correction. Children who have already learned how to write and read retain speech.
A child who is used to hearing his own voice, but now deprived of such an opportunity, often begins to deform the pronunciation, there are speech defects that were previously unusual for him. He strangely forms sentences, makes multiple mistakes in stress, pronunciation of individual sounds.
Loss of auditory function such guys perceive much harder. Almost everyone develops mental trauma, increased anxiety. Often children become withdrawn, negatively disposed towards others. Much depends on the extent to which the child has lost hearing. Children who perceive only the low frequency range cannot distinguish speech. Children who are able to perceive medium frequencies (up to 500 Hz) can generally perceive the sound of speech if it sounds right next to the ear, and also distinguish vowels.
The most favorable is the preservation of the ability to perceive sounds in the range from 500 to 1500 Hz. Such guys can perceive the voice of a person from a distance of two meters, perceive all vowels and most of the consonants, short words and phrases.
Hearing impaired
Congenital hearing loss, usually up to a certain age, is not perceived by the child as an inconvenience. They get used to hearing the world as they can hear due to the degree of hearing loss. But in the kindergarten, the school begin to experience difficulties in communication, which form an inferiority complex in the child.
The same applies to children who have become deaf for reasons acquired. A child can no longer be able to hear normally at any age, and in each this pathology causes its inconvenience. Educational perspectives are directly dependent on the degree of hearing loss.
Features of the educational process
Children with impaired hearing have special educational needs. In any violation, the most important is the development of oral speech and the associated processes of logic, thinking.
Even total deafness (which, by the way, occurs not so often in children) is not a sentence at all. They can be taught to speak and perceive other people's speech.
Residual hearing, vision, skin sensitivity will help with this. Special educational programs and exercises have been developed for them, which the child will proceed with using amplifying equipment.
They are fairly easy to learn the art of lip reading, and for this, teachers use special articulation. In the absence of any residual hearing, the teacher develops the tactile and vibrational sensations of the baby, which perfectly complement the ability to read lips. There are special types of devices that help transform human speech into vibration.
Deaf and hearing impaired children write a lot. Handwriting and facial expression, too, is a place in learning. Be sure to take into account the peculiarities of the mental development of a particular child, attention is paid to the prevention of mental disordersthat can develop if the child begins to feel inferior.
In Russia there are special kindergartens and schools for deaf and hearing impaired children. Kids in kindergartens are accepted from 3 years, in a day nursery - from 2 years. For children of school age there are special classes of correctional schools, where training continues under specially developed programs.
Parents should remember that the possibilities for the intellectual development of children with hearing impairments are not limited. And with hearing impairments, there is an opportunity to get a brilliant education, to become an excellent specialist, to achieve high results in art, sports, and sciences.
Noticed that Children who are used to overcoming something from childhood (in this case, the problem of weak hearing) grow up to be very purposeful and successful people.
Children with mild hearing loss can be taught in regular schools for a general, non-correctional program. But even here everything is quite individual - if the child is not comfortable, they laugh at him, the defect is noticeable to others, it is better to transfer him to a specialized class, where he will have the opportunity to develop and learn without looking at others.
Often, even the fact of wearing a hearing aid confuses healthy peers. Nobody reacts to the child with glasses so sympathetically and with such attention as to the child in the hearing aid. And there is only one principle: if a child is embarrassed to wear a hearing aid in front of his peers, he needs to be transferred to the environment where wearing the device is a usual thing that will surprise no one.
Hearing correction
Medical science is not in place, and today no one is going to condemn a child for life in silence for some reason.
It is rather difficult to talk about the restoration of hearing. On the Internet, there are many references to the author’s methods of recovering even severe hearing loss, and hundreds of thousands of parents have already become victims of fraudsters, since none of them has been proven effective.
It is possible to speak about recovery only in case of temporary loss (after otitis, for example). To do this, use the flushing of the auditory tubes, physiotherapy, some medications that improve blood circulation in the inner ear. But if the treatment is unsuccessful, then conduct a survey of the degree of hearing loss. And then the parents receive recommendations for the rehabilitation of the child. The sooner it starts, the more favorable it will be.
Detection of sensorineural hearing loss in a baby is a direct indication for rehabilitation, as unfortunately there are no means for effective and effective treatment of this disease.
Devices
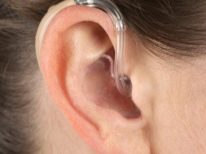
Hearing aids for children are selected individually. The hearing aid procedure is carried out if the hearing loss is about 40 dB for both ears or the same value for one ear and deafness for the other. Correctors of hearing wear infants at any age, even in the first year of life, if the pathology is detected early.
The hardest thing is hearing aid babies. If the signal gain is too large, an acoustic trauma may develop, if the signal is weak, it may not be enough for the development of speech and psyche.
Modern hearing aids are pocket (most powerful), ear and ear, which are practically invisible from the outside, especially in girls who have the ability to cover their ears with long hair. Modern devices can be configured using special computer programs in accordance with the data of a particular patient's audiometry.
Every six months, a child with a hearing aid must come to an audiologist to make an audiogram, if necessary, reconfigure the device.
The price of a hearing aid depends on its type and manufacturer, it can start from 15 thousand rubles and end with 200 thousand. When bilateral hearing loss buy two devices - in the right and left ear.
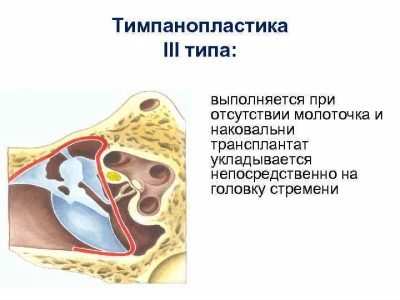
Tympanoplasty
If the examination shows dysfunctions of the middle ear, then the clinical picture is determined by otoscopy and timplanoplasty can be shown - an operation that consists of sanation, elimination of inflammation, and then plastics of the eardrum and other structures of the middle ear.
After tympanoplasty, predictions for the restoration of hearing in a natural way are quite high, but this is still not 100% even if all the recommendations and hygiene requirements are met.
Cochlear implantation
This operation is indicated for children with rather severe hearing impairments when the effect of the hearing aid is absent. An implant is a combination of two parts (one is always external, it is carried with itself, the other is implanted in the inner ear). The external consists of a microphone, a processor that converts sounds into electric pulses, and a transmitter that transmits vibrations directly to the auditory nerve.
The inner part, which is implanted, contains the receiver and the decoder of signals. There are also thin electrodes that surgeons with jeweler precision implant into the cochlea.
Implantation solves the problem of the sound-conducting apparatus of the organs of hearing that hearing aids cannot overcome. The child’s brain picks up the incoming electrical impulses and recognizes them as sounds.
The operation is indicated for deafness and severe sensorineural hearing loss in both ears, as well as for illegible speech perception in the presence of hearing aids. Rehabilitation after surgery is long, painstaking.
Implantation is not performed if the auditory nerve or the auditory center of the brain is affected. In this case, it is not effective. Do not carry out the operation due to inefficiency and in the event that the child spent a lot of time in silence, not perceiving sounds. Chances of atrophy of the branches of the auditory nerve.
The most effective are the operations that are carried out as soon as possible after the onset of deafness or severe hearing loss. The sooner the child becomes deaf, the more effective the cochlear implantation can be.
Do not think that the child will wake up from anesthesia and begin to hear everything. After surgery, he has a long period of training in a special program, which ultimately will teach him to hear. Maybe not everything, and not as good as healthy children, but it is better than living life in complete silence.