Mumps in boys: symptoms, treatment and effects
Not all childhood diseases are harmless. Even a simple, at first glance, infection can cause a child many long-term effects. One of these infectious pathologies in boys is considered to be parotitis.
What it is?
Epidemic mumps is an infectious disease. The names of this infection are many. Mostly they appeared many centuries ago in connection with the appearance of characteristic symptoms of the disease in a sick baby. Also, this pathology is called a "joker" or "pig." Both boys and girls can become sick with this infectious disease. However, the long-term effects of the disease are usually found in boys.
The disease has a viral nature. Salivary glands are most often involved in the inflammatory process. Much less often other anatomical structures are involved in the process. These include: the ovaries and testicles, pancreas, prostate gland and others. The disease can proceed in a mild form, as well as in a complicated version.
The prognosis of the disease is conditionally favorable, however, long-term adverse effects of infection in childhood can be observed.
The disease is anthroponotic, that is, it is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. In some cases, the carrier of the disease can be the transmitter of the infection. This is a person who has no adverse symptoms of the disease, however, he can transmit the infection to healthy people. It should be noted that this variant of infection occurs quite often.
Infection occurs mainly by airborne droplets. To infect, it is enough just to have a short communication with an infected person. Together with the smallest components of saliva viral particles quickly enter a healthy body.
Scientists say that if the carrier of the infection does not have clinical manifestations of the disease, then infection is possible only at a distance of no more than 1.5 meters from it. Often enough registered cases of infection in children playing in the sandbox or classmates.
There is also a contact-household transfer method. It is found in a much smaller number of cases. In this situation, infection occurs through pieces of furniture and household items. According to statistics, contact-household method of infection occurs in toddlers in crowded groups (kindergarten, school, sports clubs, various educational circles). It is believed that a sick person is contagious within a few hours from the moment the pathogens enter the body.
Scientists believe that The body's sensitivity to this infectious pathology is quite high. According to statistics, it is 80-90%. Little babies are most susceptible to infection. The most dangerous age is 3-5 years. Doctors say that with the help of vaccination, it was possible to significantly reduce the incidence in babies from 2 to 10 years. However, to date, cases of this disease have increased in children after a year and adolescents.
Toddlers of the first months of life are practically not subject to parotitis. This results from the fact that they have rather high protective titer of antibodies which receive from mother during breastfeeding. At an older age, the baby does not have such immune protection, which contributes to the fact that the infection occurs fairly easily. Adults with no vaccination in childhood are also quite susceptible to this infection.
After suffering mumps, the child retains a lifelong immunity. First, protective class M immunoglobulins appear in the children's body, which persist in the blood for 30-60 days. By the end of the first month from the moment of infection, the baby accumulates class G immunoglobulins, which remain in the body for quite a long time, and in some cases for the rest of their lives.
How is it developing?
The development of the disease occurs as a result of penetration into the body of paramyxoviruses, which belong to the RNA class. The peculiarity of these microorganisms is that they do not have antigenic variants. Scientists note an interesting fact that monkeys and humans are most susceptible to infection with the mumps virus. In external adverse conditions, microorganisms can persist long enough. They can be neutralized only with a 1% solution of lysol or a 2% solution of formalin.
Pathogenic microorganisms get on the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity and oropharynx through contact with a sick person. Over time, viruses spread throughout the body and enter the salivary glands. There they accumulate and multiply. Secondary viremia, the spread of the virus through the bloodstream, is also involved in the development of the disease.
Along with blood, a huge number of viral colonies can enter the pancreas, the central nervous system, and the reproductive organs.
The course of the disease may be different. This is largely due to the characteristics of viruses. In some babies, all the symptoms appear at the same time, in others - consistently, gradually increasing. Quite often it happens that only the reproductive system organs are involved in the pathological process. In boys, it is quite common testicular inflammationespecially in adolescents. The danger of this condition is that as a result of infectious inflammation, necrosis (cell death) of the glandular tissue is triggered.
Symptomatology
The first clinical signs of the disease do not appear immediately. The incubation period for mumps is usually 2-3 weeks. Usually at this time the child does not bother. Body temperature remains within the normal range, symptoms of intoxication are completely absent. Suspecting the disease during this period is almost impossible.
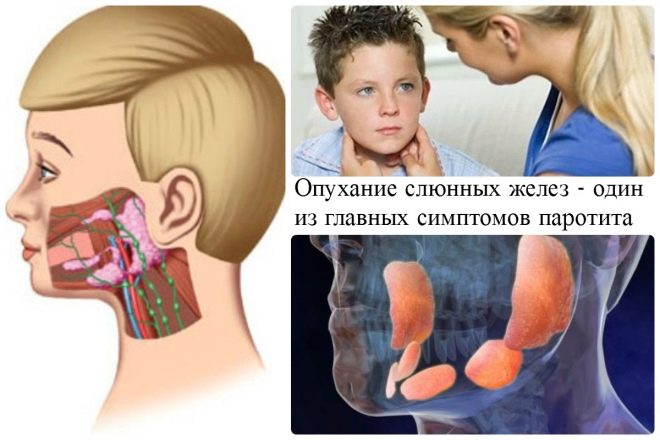
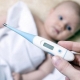
Doctors note cases when the duration of the incubation period was 8-10 days. The most common symptom of this disease is inflammation of the parotid glands. Usually it is accompanied by a sharp rise in body temperature. Its values in most cases reach 38-39 degrees. In some babies, the body temperature may rise gradually, but it also reaches quite high numbers.
Simultaneously with febrile, the child has an intoxication syndrome. It is manifested by increased weakness, fatigue, decreased appetite and various sleep disorders. In school-age children, performance is markedly reduced, because it is much more difficult for a child to concentrate on an object. Babies-babies refuse to attach to the chest, eat poorly.
As the child progresses, a variety of muscle and joint pains appear. This is also a consequence of the pronounced infectious intoxication of the child’s body. Sick kids do not sleep well in the middle of the night: they often wake up at night, and during the day they may experience pathological drowsiness.
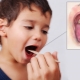
Usually, the inflammation of the salivary gland in the first days of the disease is unilateral. The second side is involved in the inflammatory process for 2-3 days after the height of the disease. An external examination shows swelling in the lower corner of the jaw. In some cases, this swelling extends to the ear.
Such a specific appearance of the child and served as the reason for the philistine name of the disease "mumps".
Inflamed salivary glands disrupt the chewing process. While chewing solid food in a child, the pain syndrome increases markedly. Also, the baby is experiencing significant difficulty with swallowing. Looking around a child Doctors distinguish several of the most painful points on palpation. They are localized in the area of the ear lobes, on the tops of the mastoid processes, and also in the area of the lower jaw cutting. These marker points are named "Points Filatov."
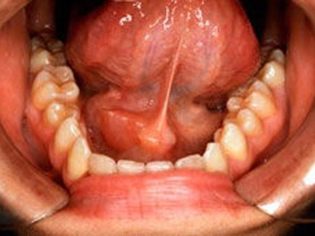
At 4-5 days, the sublingual and submaxillary glands are also involved in the inflammatory process. The defeat of these glandular organs practically does not occur at the very beginning of the disease, but occurs only after a few days. Inflammation of the sublingual salivary gland with the development of sublinguitis is quite rare. This pathological symptom can be seen when examining the oral cavity. In the sublingual region with pronounced swelling and redness.
Usually the glandular organs are inflamed during the first week of the disease. Completely inflammatory process in them is completed by the end of 21-27 days since the onset of the disease. This course of the disease is characterized by a change in periods of high and subnormal body temperature. Protracted form of the disease is unfavorable for the development of complications.
Another favorite localization of viruses is the reproductive organs (testicles, ovaries, mammary glands, prostate gland). Usually, the defeat of these organs is most common in adolescence. According to statistics, complications of mumps occur in 25% of cases. The most common of these is orchitis. This pathological condition is characterized by persistent disorders in the testicles ultimately leading to the development of male infertility.
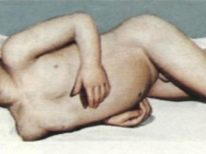
The course of orchitis is quite heavy. The child's body temperature rises. Quite often, its values reach febrile numbers. At the height of a fever, the baby feels a pronounced chill, great weakness. The testicles involved in the inflammatory process swell, increase in size, there is a strong pain syndrome in the intimate area. On examination of the skin of the scrotum, numerous blood vessels and veins are seen, which begin to protrude strongly and become visible for visualization.
Usually the process is one-sided. However, there are also bilateral clinical variants of the disease. Usually, the swelling in the scrotum lasts for about a week and then begins to pass gradually. A couple of months after the acute period of the disease, testicular atrophy appears in the child. They are significantly reduced in size, which can be determined during palpation.
There are also other, rather rare forms of the disease. One of these clinical variants of the disease is thyroiditis. It is characterized by the development of infectious inflammation of the thyroid gland. In case of dacryocystitis (inflammatory pathology of the lacrimal glands), the child has a pronounced tearing, soreness in the eyes, as well as swelling in the eyelids.
One of the rare forms of the disease is infectious meningitis and meningoencephalitis.
Usually, these conditions are recorded in babies on the 7-10 day from the onset of the disease. Mumps meningitis is quite difficult and requires intensive treatment. To establish such a diagnosis requires spinal puncture. Usually, all the adverse symptoms of parotid meningitis against the background of the treatment take place in 2-3 weeks.
Possible complications
Mild disease has a very favorable prognosis. In this case, the disease completely disappears in a few weeks, as a result of which a lasting immunity is formed.In some cases, this infectious pathology can be very dangerous. Usually this occurs in case of a complicated course of the disease, as well as when the organs of the reproductive system join the inflammatory process.
Persistent orchitis can lead to disruption of the testicles. This contributes to the fact that in the future a man who has had a complicated orchitis in childhood cannot have children.
Male infertility is usually found in 20-25% of all cases of the disease. To return fertility to a man is quite difficult, since the production of sperm is significantly impaired.
Another common complication of parotitis is pancreatitis (inflammation of pancreatic tissue). Unfavorable symptoms of the disease in this pathological condition appear, as a rule, for 5-7 days from the moment of infection. Mumps pancreatitis is characterized by the appearance of severe pain in the epigastrium and left hypochondrium, severe nausea and loss of appetite, as well as pathological muscle tension of the anterior abdominal wall. This condition has a very unfavorable prognosis, as it often turns into a chronic form.
The following pathologies are also among the complications of this disease: hearing damage, parotid arthritis, meningitis and meningoencephalitis, primary myocardial fibroelastosis, prostatitis, ooritis, myocarditis, thrombocytopenic purpura and other systemic diseases. The treatment of these conditions is long. Usually, a combination of various drugs and adjuvant treatment methods must be resorted to to draw up the tactics of therapy.
Treatment
Treat the child with parotitis should be at home. For children attending kindergarten, a compulsory measure is taken to prevent new cases of the disease - quarantine is introduced. Specific therapy for mumps has not been developed. Treatment is reduced to the appointment of complex therapy aimed at eliminating the adverse symptoms of the disease. For the prevention of complications it is very important to maintain bed rest for 10-12 days.
Doctors use various hormonal drugs to treat parotitis orchitis.. Usually they are appointed for 7-10 days. The choice of the drug and its course dosage is made by a pediatrician. The use of glucocorticosteroids is also indicated for the treatment of parotitis meningitis and meningoencephalitis. Rational combinations of drugs can achieve positive results and reduce the possible long-term effects of the disease in later life.
See the following video on what constitutes mumps.