CNS lesion in newborns
The central nervous system is the very mechanism that helps a person to grow and navigate in this world. But sometimes this mechanism fails, “breaks”. It is especially scary if this happens in the first minutes and days of the child’s independent life or even before his birth. On why the child is affected by the central nervous system and how to help the baby, we will discuss in this article.
What it is
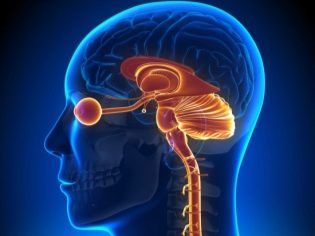
The central nervous system is a close “ligament” of the two most important links - the brain and spinal cord. The main function entrusted to the central nervous system by nature is to provide reflexes, both simple (swallowing, sucking, breathing) and complex. The central nervous system, or rather its middle and lower parts, regulate the activities of all organs and systems, provides communication between them. The highest section - the cerebral cortex. She is responsible for self-awareness and self-awareness, for the connection of a person with the world, with the reality surrounding the child.
Violations, and consequently, damage to the central nervous system, may begin as early as the development of the fetus in the womb, and may occur under the influence of certain factors immediately or some time after birth.
On which department of the central nervous system is affected, it will depend on which body functions will be impaired, and the degree of damage will determine the extent of the consequences.
The reasons
In children with disorders of the central nervous system about half of all cases occur in intrauterine lesions, doctors call it perinatal pathologies of the central nervous system. Moreover, more than 70% of them are premature babies, which appeared earlier than obstetric terms. In this case, the main root cause lies in the immaturity of all organs and systems, including the nervous one, it is not ready for autonomous work.
Approximately 9-10% of tots born with lesions of the central nervous system were born in time with a normal weight. Experts believe that the state of the nervous system is affected by negative intrauterine factors, such as prolonged hypoxia, which the baby experienced in the womb during gestation, birth trauma, and acute oxygen starvation during difficult delivery, metabolic disorders of the child, which Infectious diseases and pregnancy complications began even before birth; All the lesions, which resulted from the above factors during pregnancy or immediately after childbirth, are also called residual organic:
- Hypoxia of the fetus. Most often, the lack of oxygen in the blood during pregnancy is affected by babies whose mothers abuse alcohol, drugs, smoke, or work in hazardous production. The number of abortions that preceded these genera is also of great importance, since the changes that occur in the tissues of the uterus after the termination of pregnancy, contribute to the disruption of uterine blood flow during subsequent pregnancy.
- Traumatic causes. Birth injuries can be associated with both incorrectly chosen delivery tactics and medical errors during the birth process. The injuries include actions that lead to a violation of the central nervous system of the child after birth, in the first hours after birth.
- Disorders of fetal metabolism. Such processes usually begin in the first - the beginning of the second trimester.They are directly related to the violation of the activities of organs and body systems of the baby under the influence of poisons, toxins, and some medicines.
- Infection in the mother. Particularly dangerous diseases that are caused by viruses (measles, rubella, chickenpox, cytomegalovirus infection and a number of other ailments), if the disease occurred in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Pathology of pregnancy. The state of the central nervous system of a child is affected by the most varied features of the gestation period - high water and low water, double or triple pregnancy, placental abruption, and other reasons.
- Severe genetic diseases. Typically, pathologies such as Down and Ewards syndromes, trisomy and a number of others are accompanied by significant organic changes on the part of the central nervous system.
At the present level of development of medicine, CNS pathologies become apparent to neonatologists already in the first hours after the birth of a baby. Less often - in the first weeks.
Sometimes, especially with organic lesions of mixed genesis, the true cause cannot be established, especially if it relates to the perinatal period.
Classification and symptoms
The list of possible symptoms depends on the causes, extent and extent of lesions of the brain or spinal cord, or a combined lesion. Also, the outcome is influenced by the time of negative impact - how long the child was exposed to factors that affected the activity and functionality of the central nervous system. It is important to quickly determine the period of the disease - acute, early recovery, late recovery or the period of residual effects.
All pathologies of the central nervous system have three degrees of severity:
- Easy This degree is manifested by a slight increase or decrease in the muscle tone of the baby, converging strabismus can be observed.
- Average. With such lesions, muscle tone is always reduced, reflexes are completely or partially absent. This state is replaced by hypertonus, convulsions. Characteristic oculomotor disorders appear.
- Heavy It affects not only the motor function and muscle tone, but also the internal organs. If the central nervous system is markedly depressed, convulsions of varying intensity may begin. Problems with heart and kidney activity can be severe, as well as the development of respiratory failure. The intestine may be paralyzed. Adrenal glands do not produce the right hormones in the right quantity.
According to the etiology of the reason that caused problems with the activity of the brain or spinal cord, pathologies are divided (however, quite arbitrarily) into:
- Hypoxic (ischemic, intracranial hemorrhages, combined).
- Traumatic (birth injuries of the skull, ancestral spinal lesions, ancestral pathologies of peripheral nerves).
- Dysmetabolic (nuclear jaundice, excess of calcium, magnesium, potassium in the child’s blood and tissues).
- Infectious (consequences of mother-borne infections, hydrocephalus, intracranial hypertension).
Clinical manifestations of different types of lesions also differ significantly from each other:
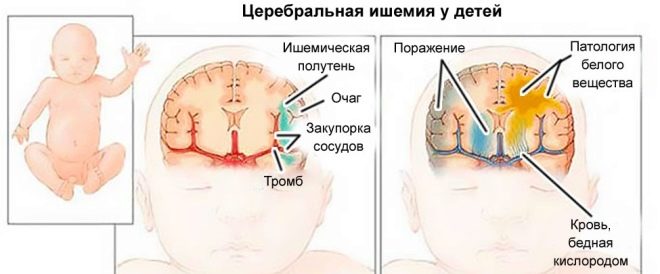
- Ischemic lesions. The most "harmless" disease is cerebral ischemia 1 degree. With her, the child demonstrates CNS disorders only in the first 7 days after birth. The reason most often lies in fetal hypoxia. The baby at this time can be observed relatively mild signs of excitation or depression of the central nervous system.
- The second degree of this disease is put in the case if violations and even seizures last more than a week after birth. It is possible to speak about the third degree if the child constantly has increased intracranial pressure, there are frequent and severe convulsions, and there are other vegetative disturbances.
Usually, this degree of cerebral ischemia tends to progress, the child’s condition worsens, and the baby may fall into a coma.
- Hypoxic cerebral hemorrhage. If, as a result of oxygen starvation, a child has had a hemorrhage inside the ventricles of the brain, then with the first degree there may be no symptoms or signs at all. And now the second and third degrees of such hemorrhage lead to severe brain damage - convulsive syndrome, the development of shock. A child may fall into a coma. If blood enters the subarachnoid cavity, then the child will be diagnosed with CNS overexcitement. The likelihood of developing dropsy of the brain in acute form.
Bleeding into the main substance of the brain is not always noticeable at all. Much depends on exactly which part of the brain is affected.
- Traumatic lesions, birth trauma. If, during the birth process, doctors had to use forceps on the baby’s head and something went wrong if there was acute hypoxia, then hemorrhage in the brain most often follows. In case of birth trauma, the child has convulsions in a more or less pronounced degree, the pupil on the one hand (the one where the hemorrhage occurred) increases in size. The main symptom of traumatic damage to the central nervous system is an increase in pressure inside the child’s skull. Acute hydrocephalus may develop. A neurologist testifies that in this case the CNS is more often excited than suppressed. Not only the brain, but also the spinal cord can be injured. This is most often manifested by sprains and tears, hemorrhage. In children, breathing is impaired, hypotension of all muscles, spinal shock is observed.
- Dysmetabolic lesions. With such pathologies, in the overwhelming majority of cases, the child has high blood pressure, convulsive seizures are observed, and consciousness is quite pronouncedly depressed. Blood tests that show either a critical calcium deficiency, or a lack of sodium, or another imbalance of other substances can determine the cause.
Periods
Projections and the course of the disease depends on the period in which the baby is. There are three main periods of the development of pathology:
- Acute. Violations have just begun and have not had time to cause serious consequences. This is usually the first month of independent life of the child, the neonatal period. At this time, the baby with CNS lesions usually sleep poorly and restlessly, often crying for no apparent reason, it is excitable, it can startle without irritation even in sleep. Muscle tone is increased or decreased. If the degree of damage is higher than the first, then reflexes can weaken, in particular, the crumb will begin to suck and swallow worse and weaker. In this period, the baby may begin to develop hydrocephalus, this will be manifested by a noticeable growth of the head and strange eye movements.
- Recovery. May be early and late. If the baby is at the age of 2-4 months, then they talk about early recovery, if he is already from 5 to 12 months old, then about late. Sometimes parents notice violations in the central nervous system in their crumbs for the first time in the early period. At 2 months, these tots almost do not express emotions, are not interested in bright hanging toys. In the late period, the child noticeably lags behind in its development, does not sit, does not walk, his cry is quiet and usually very monotonous, emotionally unpainted.
- Effects. This period begins after the child turns one year old. At this age, the doctor is able to most accurately assess the effects of a central nervous system disorder in this particular case. Symptoms may disappear, however, the disease does not disappear anywhere. Most often, doctors in such children annually render such verdicts as hyperactivity syndrome, developmental delay (speech, physical, mental).
The most difficult diagnoses that may indicate the consequences of CNS pathologies are hydrocephalus, cerebral palsy, epilepsy.
Treatment
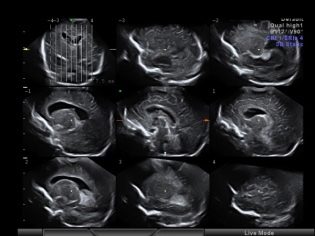
It is possible to talk about treatment when the CNS lesions are diagnosed with maximum precision.Unfortunately, in modern medical practice there is a problem of overdiagnosis, in other words, every child who has a chin trembling for a month during the examination, who eats and sleeps restlessly, can easily be diagnosed with cerebral ischemia. If the neurologist claims that your baby has CNS lesions, it is imperative to insist on a comprehensive diagnosis, which will include an ultrasound of the brain (through a spring), computed tomography, and in special cases, an x-ray of the skull or spine.
Each diagnosis, which is somehow associated with lesions of the central nervous system, must be diagnostically confirmed. If signs of a CNS disorder have been noticed in the maternity hospital, the help provided by neonatologists in a timely manner helps to minimize the severity of possible consequences. It just sounds scary - CNS damage. In fact, most of these pathologies are reversible and subject to correction if identified on time.
For treatment, commonly used drugs that improve blood flow and blood supply to the brain - a large group of nootropic drugs, vitamin therapy, anticonvulsants drugs.
An exact list of drugs can only be called by a doctor, since this list depends on the causes, extent, period and depth of the lesion. Drug treatment of newborns and infants is usually provided in a hospital. After the relief of symptoms, the main stage of therapy begins, aimed at restoring the correct functioning of the central nervous system. This stage usually takes place at home, and on the shoulders of parents falls great responsibility for complying with numerous medical recommendations.
Children with impaired functional and organic disorders of the central nervous system need:
- therapeutic massage, including hydromassage (procedures are held in water);
- electrophoresis, exposure to magnetic fields;
- Vojta-therapy (a set of exercises that allow to destroy the reflex incorrect connections, and create new ones - the right ones, thereby correcting motor disorders);
- Physiotherapy for the development and stimulation of the development of the senses (music therapy, light therapy, color therapy).
Such effects are allowed to children from 1 month and must be supervised by specialists.
A little later, parents will be able to master the techniques of therapeutic massage on their own, but for a few sessions it is better to go to a professional, although this is quite expensive.
Implications and predictions
Forecasts for the future for a child with lesions of the central nervous system can be quite favorable, provided that he is provided with prompt and timely medical assistance in the acute or early recovery period. This statement is true only for mild to moderate CNS lesions. In this case, the main predictions include the complete recovery and restoration of all functions, a slight lag in development, the subsequent development of hyperactivity or attention deficit disorder.
With severe forms, the projections are not so optimistic. The child may remain disabled, and deaths at an early age are not excluded. Most often, damage to the central nervous system of such a plan leads to the development of hydrocephalus, to cerebral palsy, to epileptic seizures. As a rule, some internal organs are also affected, the child has concurrent chronic diseases of the kidneys, respiratory and cardiovascular systems, and marble skin.
Prevention
Prevention of pathologies on the part of the CNS in a child is the task of the expectant mother. At risk - women who do not leave bad habits while carrying a baby - smoke, use alcohol or drugs.
All pregnant women must be registered with the obstetrician-gynecologist in the antenatal clinic. During pregnancy, they will be asked to undergo a so-called screening three times, which reveals the risks of giving birth to a child with genetic disorders from this particular pregnancy. Many gross pathologies of the CNS of the fetus become noticeable during pregnancy, some problems can be corrected with drugs, for example, impaired uteroplacental blood flow, fetal hypoxia, the threat of miscarriage due to a small detachment.
Pregnant women need to monitor their diet, take vitamin complexes for expectant mothers, do not self-medicate, be wary of various drugs that have to be taken during the childbearing period.
This will avoid metabolic disorders in the baby. It is necessary to pay particular attention to the choice of a maternity house (birth certificate, which all pregnant women receive, allows you to make any choice). After all, the actions of personnel during the birth of a child play a large role in the possible risks of the appearance of traumatic lesions of the central nervous system in a baby.
After the birth of a healthy baby, it is very important to regularly visit the pediatrician, protect the baby from injuries to the skull and spine, and make the vaccines that are old enough to protect the toddler from dangerous infectious diseases that can also lead to the development of central nervous system pathologies at an early age.
In the next video, you will learn about the signs of a nervous system disorder in a newborn that you can determine for yourself.