Vaccination of children against hepatitis B
Vaccination against such a dangerous virus infection as hepatitis B is included in the vaccination schedule of our country. Why is this vaccine needed and what should parents know about it?
Pros
- Early hepatitis B vaccination is important for preventing infection with this serious viral disease.
- It is worthwhile to vaccinate even babies whose mothers have a negative test for viral hepatitis B, since errors of such tests and their false results are not excluded.
- As vaccines are constantly improved, reducing the amount of extraneous additives, reactions to the Hepatitis B vaccine are extremely rare.
- A vaccinated child in the first year produces a strong immunity that can last until the end of life.
Arguments against
Although very rare, hepatitis B vaccines can cause significant side effects. If a child has such a reaction, vaccination against this infection is no longer carried out.
What is dangerous disease?
The virus infects the liver cells and as a result of the development of an infection in a child, hepatitis begins, and the risk of developing cirrhosis and cancer increases. To infect this infection, a negligible amount of human blood infected with hepatitis is sufficient. Newborns often get the virus from mothers (carriers or people with hepatitis) during childbirth.
Contraindications
Vaccination against hepatitis B is not performed if the child has:
- There is an acute illness or a chronic illness has worsened;
- There was a pronounced reaction to the first vaccine;
- Identified individual intolerance to yeast.
Vaccine safety
Research by vaccine manufacturers and health professionals confirm that hepatitis B drugs are safe, and their side effects are often mild and pass quickly. Also, studies have not confirmed the link between such vaccination and the development of autism in children.
The vaccine can be administered on the same day with any other drugs from the vaccination calendar, except for BCG. The efficacy and tolerability of vaccines does not deteriorate.
Possible complications and how to prevent them?
With the introduction of hepatitis B vaccine rarely (in 2-5% of cases) adverse reactions occur in the form of pain and swelling at the injection site, as well as an increase in body temperature. They are considered normal and pass quickly. However, in some babies, such reactions can be very pronounced - the temperature rises to 40 degrees, and there is severe swelling at the injection site. In this case, it is recommended examination by a doctor.
Preparation before vaccination
To introduce the drug can only be a healthy baby, so all babies must be examined by a pediatrician before performing the manipulation (in the maternity hospital the baby is examined by a neonatologist). If there are doubts about the condition of the baby and the risks of vaccination for it, parents are advised to go with the baby to an immunologist.

The minimum age of the child and the frequency of vaccination
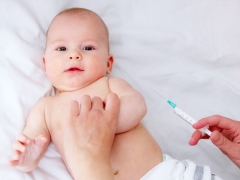
A vaccine that helps prevent hepatitis B infection is given to babies still in the maternity hospital. Usually vaccination is carried out during the first days after the appearance of the crumbs into the world. This helps prevent the virus from being infected by the mother during the birth process.
After three vaccinations (in children with an increased risk - after four), the child will develop a strong immunity until the end of life.
Vaccination scheme
Vaccination against hepatitis B is carried out according to several schemes:
- Healthy babies whose risk of contracting viral hepatitis is not increased, vaccination is carried out according to the scheme 0-1-6. The first vaccination is performed in the maternity hospital immediately after birth, the second - when the baby is one month old, the third - at the age of six months. The scheme 0-1-6 also vaccinated children older than a year and adults, if they have not been vaccinated against hepatitis B before.
- According to the second scheme, children who have an increased risk of contracting hepatitis are vaccinated. These are babies whose mothers are infected with the hepatitis virus, babies who have been transfused or have undergone any parenteral procedures and babies after surgery. For vaccination offer scheme 0-1-2-12. This means that the third vaccination of the baby is not put in half a year, but in two months, and at the age of one year the fourth vaccination is performed.
Where do the injection?
Hepatitis B vaccine is given intramuscularly. An injection is made in the thigh, since the muscles of this zone are sufficiently developed even in very young children. In children older than three years, the vaccine can be injected into the muscles of the shoulder.
Opinion Komarovsky
The well-known pediatrician advises against being vaccinated against hepatitis B, since there is always a risk of contracting the virus from both the mother during labor and blood transfusion or from relatives during household contacts, since extremely small amounts of the patient’s blood are enough to transmit the virus.
What to do with negative reactions after vaccination?
The normal reactions to vaccination, which should not be perceived negatively by parents, include a slight increase in body temperature and a local reaction to the injection. They eventually pass without a trace without any treatment. If the baby's temperature has risen more than 37.3 degrees, give the baby an antipyretic at the age dose. Usually enough of the drug in the form of candles. Do not treat the injection site with any means.