Signs and treatment of rickets in children older than one year
Diseases associated with deficient conditions occur in children quite often. Not only babies, but also older babies can become ill. Today we will talk about rachitis in children older than one year.
What it is?
Rickets is a childhood pathology associated with a pronounced impairment of calcium-phosphorus metabolism. This pathological condition is caused by various causes of lack of vitamin D or calciferol in the body. Normally, this biologically active substance is involved in the internal metabolism of calcium and phosphorus, which ensures normal concentrations of these substances.
Usually the early adverse signs of rickets appear in the child in the first months and within 1 year after birth. However, the disease is also reported in children and at an older age.
According to statistics, this disease is more susceptible to children living in northern countries.
Boys suffer from rickets as often as girls. A pronounced deficiency of vitamin D in the children's body leads to a metabolic disorder between calcium and phosphorus. Both of these substances provide bone strength. In case of disturbed calcium-phosphorus metabolism, a child has various adverse symptoms associated with a pronounced deficiency of biologically active substances.
Usually the first signs of rickets are detected by a pediatrician during regular examinations of the baby. Diagnosis of the disease does not cause significant difficulties for medical specialists.
The reasons
Various causes lead to the development of the disease in babies, which contribute to a decrease in the level of calciferol. In some cases, the effects of causes can be combined. Understanding exactly which causative factors caused the disease in a baby is very important. Only the elimination of the cause of the disease will lead to the complete recovery of the child.
The peak in the incidence of rickets occurs in infancy. Usually the first manifestation of rickets occurs within the first three months of the birth of the child. In some cases, with mild disease, clinical signs are not visible, which makes diagnosis much more difficult. In such a situation, the diagnosis is usually established only by the age of 2-3 years.
The most common causes leading to a deficiency in the child’s body of calciferol include:
- Inadequate intake of vitamin D with food. In babies under one year old, rapid breastfeeding leads to this. In older children, the cause of exogenous deficiency in the intake of calciferol is unbalanced and inadequate nutrition. The lack of animal products and vegetarian food can cause rickets in the baby.
- Living in the northern regions. The lack of solar insolation leads to the fact that an insufficient amount of endogenous (internal) vitamin D is synthesized in the children's body. The exposure of the ultraviolet spectrum rays to the skin causes a cascade of biological reactions in the baby that trigger calciferol synthesis.
The kids who live in countries with a long winter and a short day of light, according to statistics, have higher chances of getting rickets than their peers living in the south.
- Chronic diseases of the digestive system. The leading role is assigned to intestinal pathologies.Chronic enteritis, accompanied by a strong violation of the absorption of various substances from food, often leads to the formation of various deficient states in children. Without treatment of the underlying disease in this case, the adverse symptoms of rickets can not cope.
- Prematurity and congenital abnormalities. The birth of a baby earlier than planned is often a starting point for the development of rickets. This can be explained by the fact that the premature baby has not completed the formation of many internal organs. Disorders of fetal development often cause various health problems in the future.
Symptoms
The development of the disease undergoes several successive stages. The initial period of the disease is accompanied mainly by the appearance of autonomic disorders. This is manifested by violations in the behavior and mood of the baby. The child becomes nervous, easily irritated on trifles. Kids lose interest in their favorite games, try to limit active movement. Usually the initial stage lasts about a month.
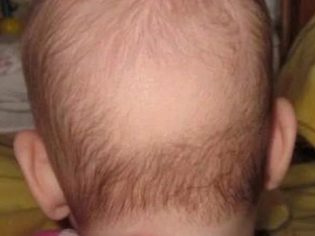
This period of the disease is also characterized by the appearance of a characteristic symptom - sweating increases in a child. Its smell also changes. Sweat becomes caustic, sour. Its abundant secretion on the skin contributes to the development of irritation and prickly heat. Toddlers often comb the affected skin. The change in the smell of sweat is due to a change in its chemical composition and electrolytes entering it due to impaired metabolism.
After the initial stage, the disease passes into a period of heat. This is a more unpleasant time, characterized by the appearance of numerous symptoms. The baby has the first deformation of bone tissue. Basically all tubular and flat bones that actively grow are involved in the process. Diagnosis of the disease at this time is not difficult and does not pose a problem for the doctor.
The severity of clinical symptoms may be different.
Severe disease in children older than a year is quite rare.
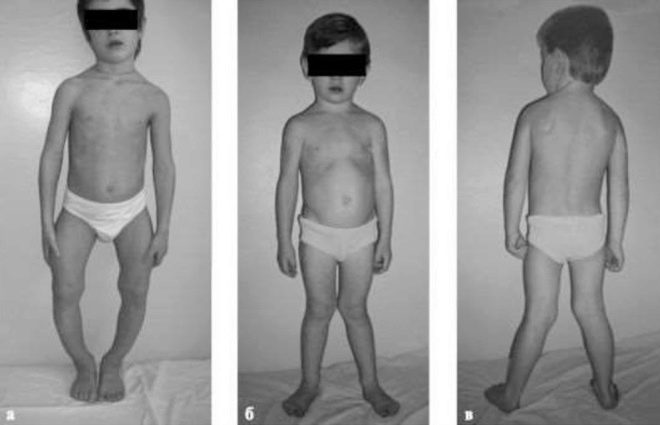
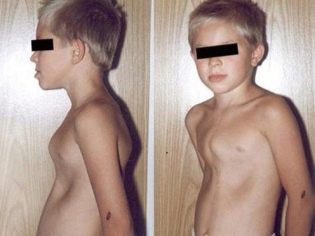
The child has a characteristic spinal curvature - scoliosis. Changes the density and thickness of the clavicle. They come forward a little. The architecture of the chest structure is also violated.
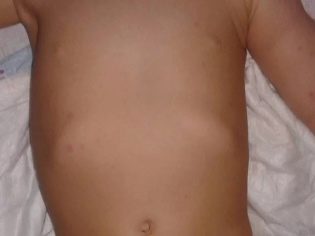
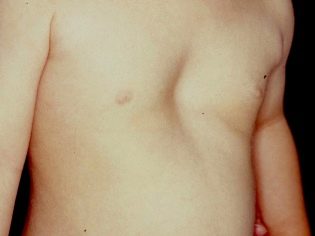
The ribs are somewhat flattened, the intercostal spaces change. Some children develop characteristic signs of rickets: depression or bulging of the lower third of the sternum. Since ancient times, the characteristic names for these states - "Shoemaker's chest" and "chicken breast". The appearance of the child varies greatly. Usually these symptoms appear in babies who are diagnosed too late.
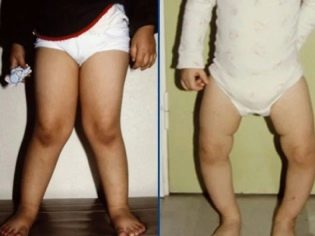
The child changes the shape of the lower limbs. They become O- or X-shaped. Usually this sign appears in babies with a pronounced course of rickets by the age of five. In order to identify this symptom, you should look at the baby from different angles. Usually the curvature of the lower limbs is clearly visible from the side.
Also during the height of the disease muscle hypotonus appears and various neuromuscular pathological states join. In a horizontal position in sick children well traced. “Frog belly”. On examination, the child’s tummy becomes flattened and slightly hangs down to the side surfaces of the body. This symptom is due to the presence of pronounced hypotonic muscles that make up the anterior abdominal wall.
Bone deformities of the skeleton also lead to abnormalities in the functioning of the internal organs. Breast pathologies contribute to a decrease in the ventilation capacity of the lungs, which leads to the development of emphysema and other pathological conditions. Respiratory failure is reflected in hemodynamics and vascular tone. Such combined conditions lead to the fact that the baby has problems in the work of the heart muscle and blood vessels.
The hypotonus of the muscles of the abdominal wall and the pronounced curvature of the spine contribute to the compression of the internal organs. In some cases, this leads to abnormalities in the liver and spleen. Bone tissue pathologies contribute to the development of many orthopedic diseases in the baby, which require the appointment of appropriate treatment. On average, the high season lasts for several months.
Timely prescribed treatment helps to normalize the condition of the child and improve his appearance.
The period of recovery or recovery may range from 2 to 4 months. In some cases, it lasts up to six months. If the child has suffered rickets in severe form, then the residual symptoms of the disease he may persist for a couple of years from the moment of recovery. Usually they completely pass after the course of rehabilitation measures.
Diagnostics
Identify the signs of rickets in babies should be as early as possible. Timely diagnosis will help avoid the development of a child of remote complications and help to return the baby to an active life. The doctor can identify the very first signs of the disease and suspect rickets during regular check-ups. After conducting a clinical examination of the child, the doctor prescribes additional tests to clarify the severity of violations and confirm the diagnosis.
The following studies are used to detect the disease:
- Measurement of blood calcium and phosphorus. Normally, the level of calcium should be - 2.5-2.7 mmol / l, and phosphorus - 1.3-2.3 mmol / l. The decrease in these indicators in a child below the age norm indicates the presence of signs of impaired calcium-phosphorus metabolism.
- Alkaline Phosphatase Determination. This enzyme is actively involved in the metabolism between calcium and phosphorus. Normally, it is up to 200 U / l. The increase in this indicator indicates the presence of metabolic disorders in calcium-phosphorus metabolism.
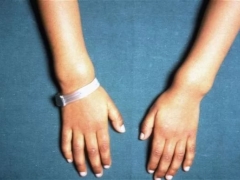
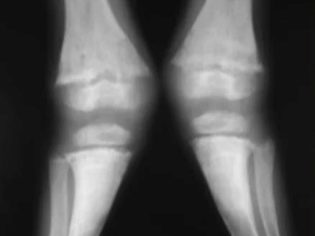
- X-ray. Allows you to clarify the presence of bone deformities and violation of the architecture of the skeleton caused by the disease. Radiography of the bones can reveal specific signs typical for rickets: “rachitic bracelets”, pathological curvature of the spinal column, “rachitic rosary”, chest pathologies, bone seals in tubular bones. This method can be used only under strict indications.
- CT scan. Conducted for the same indications as the X-ray of bone tissue. This method has a higher resolution and allows you to get the most accurate result. Using computed tomography allows doctors to assess the level of damage and the degree of functional impairment.
Effects
The prognosis of the disease in children is greatly influenced by the time spent diagnostics and treatment prescription. If rickets in a child was detected at the earliest stages, then, as a rule, there are no negative complications of the disease. With late diagnosis, the baby may have various long-term effects of the disease, which require mandatory rehabilitation measures. The common effects of rickets, suffered in childhood, include: moderate decrease in muscle tone, slight curvature of the lower limbs, bite and others.
Treatment
To eliminate the adverse symptoms of the disease, several therapeutic methods are prescribed. Monitoring the effectiveness of prescribed therapy is carried out with the obligatory determination of calcium in the blood. During the treatment, the clinical condition of the child is also evaluated. When prescribing therapy, the baby should feel better and become more active.
For the treatment of rickets in babies, the following treatment principles apply:
- Regular walks in the fresh air. Insolation by sunlight is necessary for a kid suffering from rickets.Ultraviolet rays have a pronounced therapeutic effect on the children's body, increasing the internal synthesis of calciferol. The kid should make walks in the fresh air daily. Only regularity and consistency will allow to achieve a good and stable result.
- Prescription drugs containing vitamin D in its composition. Many doctors prefer water-soluble forms. The dosage of the drug must be carried out by the attending physician individually for each baby.
Independent selection of therapeutic dose is not allowed! Such self-medication can contribute to the appearance of a very dangerous condition in a baby - an overdose of vitamin D.
- Full nutrition. Calciferol-rich foods must be present in the baby’s daily diet. These include: meat, chicken, fish, eggs, milk and dairy products, cottage cheese, cheese. The baby must eat various foods that contain vitamin D. If the child receives drugs with calciferol, the diet should be discussed with your doctor to avoid overdosing of this vitamin in the children's body.
- Conducting physiotherapy. The course of ultraviolet irradiation (ultraviolet irradiation) helps babies with rickets, improve overall health and increases bone density. It usually consists of 12-15 procedures. Their duration may be different: from 2 to 10 minutes. Physiotherapy has a number of contraindications and is appointed by the attending physician.
About what is rickets in children and how to treat it, see the next video.