Symptoms, treatment and prevention of diphtheria in children
Children began to be vaccinated against diphtheria, but before that the death rate from this infectious disease was quite high. Now kids are more protected, but none of the vaccinated is immune from infection. You will learn about the symptoms, treatment and prevention of diphtheria in children by reading this article.
What it is?
Diphtheria is a bacterial infectious disease that causes the Löffler bacillus. These bacteria of the genus Corynebacterium in themselves do not pose any particular danger. Poisonous exotoxin, which microbes produce in the course of their vital activity and reproduction, is dangerous for humans. It blocks protein synthesis, practically depriving the body's cells of the ability to perform their nature envisaged functions.
The microbe is transmitted by airborne droplets - from person to person. The stronger the symptoms of diphtheria in a patient, the more bacteria he spreads around him. Sometimes infection occurs through food and water. In countries with hot climates, Böllilla Löffler can also be spread by contact and household routes.
A child can become infected not only from a patient, but also from a healthy person who carries a diphtheria bacillus. Most often, the causative agent of the disease affects the organs that are found first on its way: the oropharynx, larynx, less often the nose, genitals, and skin.
Today, the prevalence of the disease is not too high, since all children have to be vaccinated with DTP, ADS. The letter "D" in these abbreviations means diphtheria component of the vaccine. Due to this, the number of infections over the past 50 years has been significantly reduced, but the disease cannot be completely eradicated.
The reasons are that there are parents who refuse to vaccinate their child, and their sick children spread diphtheria to others. Even a vaccinated child may become infected, but his disease will proceed more smoothly, and the case is unlikely to reach severe intoxication.
Signs of
The incubation period, during which the wand only “looks around” in the body, without causing any changes, ranges from 2 to 10 days. In children with stronger immunity, the incubation period lasts longer; babies with weakened immune defenses can show the first signs of an infectious disease for 2-3 days.
These symptoms may remind parents of a sore throat. The baby has a fever (up to 38.0-39.0 degrees), headache, and also fever. The skin appears pale, sometimes somewhat bluish. The behavior of the child from the first day of the disease varies greatly - he becomes sluggish, apathetic, drowsy. Painful sensations appear in the throat, it becomes difficult for the baby to swallow.
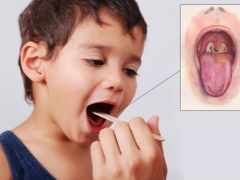
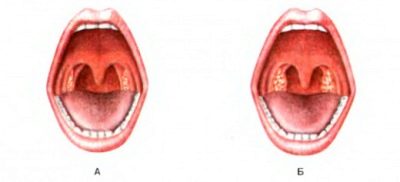
On examination of the throat, the enlarged palatine tonsils are clearly visible, the mucous membranes of the oropharynx look swollen and reddened. They are increased in size. Palatine tonsils (and sometimes the tissues bordering them) are covered with a bloom resembling a thin film. It most often has a gray or gray-white color. The film is very difficult to remove - if you try to remove it with a spatula, there are bleeding marks.
The child's voice becomes hoarse or disappears completely. However, this symptom cannot be considered a mandatory sign of diphtheria. He is more individual.
A symptom that may indicate precisely diphtheria - neck swelling. Her parents will notice without difficulty. Against the background of soft tissue swelling, you can also feel enlarged lymph nodes.
The most dangerous form of diphtheria, the toxic, is most severe. With her, all the above symptoms are more pronounced - the temperature rises to 40.0 degrees, the child may complain of severe pain not only in the throat, but also in the stomach. The raids on the tonsils and arms are very dense, serous, solid. Intoxication is strong.
Edema of the neck is pronounced, the lymph nodes are greatly enlarged and painful. It is difficult for the baby to breathe through the nose due to the hyperemia of the tonsils, sometimes the nugget is released from the nose.
The most severe manifestations of hypertoxic diphtheria. When her child is often unconscious or delirious, he manifests seizures. All symptoms (fever, fever, swelling of the larynx and tonsils) develop rapidly. If the right medical care is not provided in time, a coma occurs in two or three days. Death is possible due to cardiovascular insufficiency that has developed.
However, not all forms of diphtheria are so dangerous. Some (for example, diphtheria of the nose) proceed almost without symptoms and the child’s life is not threatened.
Danger
A rather dangerous complication of diphtheria is the development of diphtheria croup. When this occurs, stenosis of the respiratory system. Because of the swelling, the larynx narrows, the trachea and bronchi swell. At best, this leads to a change in voice, his hoarseness, difficulty breathing. At worst, it leads to suffocation.
The most dangerous complication of diphtheria is the development of myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle). Violation of heart rhythm, violation of pulmonary respiration in 2-3 days can lead to the development of respiratory as well as cardiovascular failure. This condition is also deadly for the child.
Due to the action of a strong toxin, renal failure can develop, as well as neurological disorders such as neuritis, regional paralysis. Paralysis most often are temporary and some time after recovery pass without a trace. In the overwhelming majority of cases, paralysis of cranial nerves, vocal cords, soft palate, neck muscles and upper limbs is recorded.
Some of the paralytic changes occur after the acute stage (on the 5th day), and some manifest themselves after suffering diphtheria - in 2-3 weeks after the apparent recovery.
The most common complication of diphtheria is acute pneumonia (pneumonia). As a rule, it occurs already after the acute period of diphtheria has been left behind (after 5-6 days since the onset of the illness).
The main danger lies in late diagnosis. Even experienced doctors can not always recognize diphtheria in the first day or two. Namely, this time is important in order to introduce anti-diphtheria serum to the child, which is an antitoxin, a substance that suppresses the toxic effects of exotoxin. Most often, in case of death, it turns out that the fact of late diagnosis, as a result - failure to provide proper assistance.
To prevent such situations, all doctors have clear instructions on the case of detecting doubtful symptoms, which even indirectly can indicate that a child has diphtheria.
Varieties
Very much in the choice of treatment tactics and in the prognosis for recovery depends on what kind of diphtheria and to what extent struck the baby. If the disease is localized, then it is more easily tolerated than the diffuse (widespread) form. The smaller the source of infection, the easier it is to cope with it.
The most common form that occurs in children (approximately 90% of all cases of diphtheria) is oropharyngeal diphtheria. It happens:
- localized (with minor “islands” of raid);
- spilled (with the spread of inflammation and plaque beyond the throat and oropharynx);
- subtoxic (with signs of intoxication);
- toxic (with a rapid course, swelling of the neck and severe intoxication);
- hypertoxic (with extremely severe manifestations, with loss of consciousness, critically large and extensive raids and swelling of the entire respiratory system);
- hemorrhagic (with all signs of hypertoxic diphtheria and general systemic infection with diphtheria bacillus through the bloodstream).
With the development of diphtheria croup, the child’s condition worsens, and at the same time the croup itself is divided into:
- larynx diphtheria - localized form;
- larynx and trachea diphtheria - diffuse form;
- descending diphtheria - the infection quickly moves from top to bottom - from the larynx to the bronchi, striking along the way and the trachea.
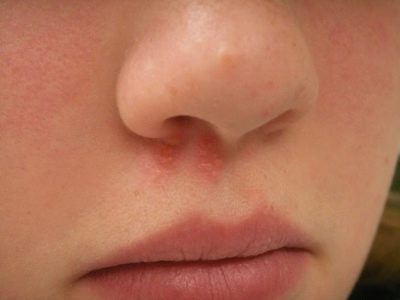
Diphtheria of the nose is considered the easiest type of ailment, since it is always localized. When it is broken nasal breathing, mucus from the nose comes off with impurities of pus, and sometimes blood. In some cases, nasal diphtheria is concomitant and accompanies pharyngeal diphtheria.
Diphtheria of the organs of vision manifests as normal. bacterial conjunctivitis, for which, by the way, quite often take damage to the mucous membrane of the eyes with the Löffler bacillus. Usually the disease is unilateral, temperature and intoxication is not accompanied. However, with toxic diphtheria of the eyes, a more rapid course is possible, in which the inflammatory process spreads to both eyes, the temperature slightly rises.
Diphtheria of the skin can develop only where the skin is damaged - there are wounds, abrasions, scratches and ulcers. It is in these places that diphtheria bacillus will start breeding. The affected area swells, becomes inflamed, and a dense gray diphtheria bloom develops on it rather quickly.
It can persist for quite a long time, while the general condition of the child will be quite satisfactory.
Diphtheria of the genitals in children is rare. In boys, foci of inflammation with typical serous raids appear on the penis near the head, in girls inflammation develops in the vagina and is manifested by bloody and serous purulent secretions.
Diagnostics
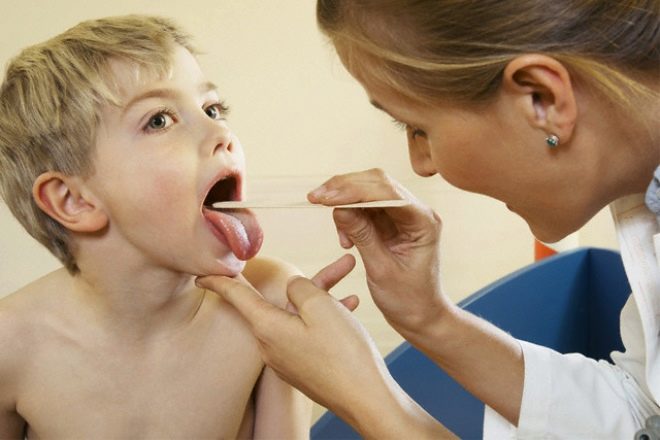
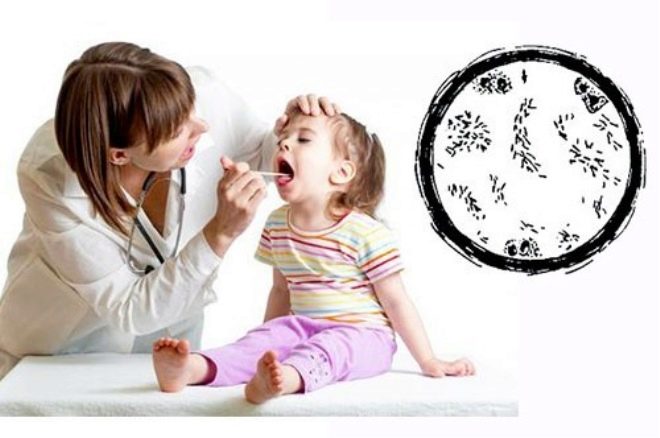
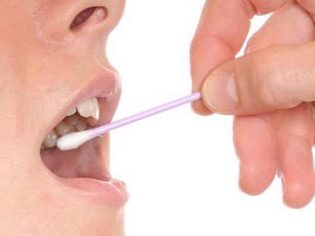
Existing laboratory tests are helpful in quickly and quickly recognizing diphtheria in a child. Have a child must take a swab from the pharynx on diphtheria stick. Moreover, it is recommended to do this in all cases when a dense grayish bloom is noticeable on the tonsils. If the doctor does not neglect the instructions, then it will be possible to establish the disease in time and introduce antitoxin to the baby.
A smear is not very pleasant, but rather painless. The doctor holds a clean trowel on a filmy bloom and sends scraping into a sterile container. Then the sample is sent to the laboratory, where experts will be able to establish which microbe caused the disease.
After establishing the fact of the presence of corynebacterium, and this usually happens 20-24 hours after the material has been received by laboratory technicians, additional tests are taken to establish how toxic the microbe is. In parallel, they begin specific treatment with anti-diphtheria serum.
As additional tests, a blood test for antibodies and a complete blood test are assigned. It should be noted that antibodies to diphtheria bacillus are found in every child who received a DTP vaccine. Based on this analysis alone, no diagnosis is made.
In diphtheria, the amount of antibodies is rapidly increasing, and at the stage of recovery it decreases. Therefore, it is important to follow the dynamics.
Complete blood count for diphtheria in the acute stage shows a significant increase in the number of leukocytes, high ESR figures (the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in acute inflammation increases significantly).
Treatment
Diphtheria should be treated exclusively in the hospital according to clinical guidelines.In a hospital, the child will be under the round-the-clock supervision of doctors who will be able to respond in time to complications if they manifest themselves. Children are hospitalized not only with a confirmed diagnosis, but also with suspected diphtheria, since the delay in this disease can have very bad consequences.
In other words - if the called doctor finds a gray dense patina and a number of other symptoms in the child's throat, he must immediately send the baby to the infectious diseases hospital, where he will be given all the necessary examinations (smear, blood tests).
Although Bacillus Löffler is a bacterium, antibiotics are practically not destroyed. No modern antibacterial drug does not act on the causative agent of diphtheria as needed, and therefore antimicrobial agents are not prescribed.
Treatment is based on the introduction of a special antitoxin - PDS (anti-diphtheria serum). It suspends the effects of the toxin on the body, and the child’s own immunity gradually cope with the wand as such.
The appearance of this serum, humanity is obliged to horses, because the drug is obtained by hypersensitization of these graceful animals with diphtheria bacillus. Antibodies from horse blood, which are contained in serum, help the human immunity to mobilize as much as possible and begin to fight the causative agent of the disease.
If you suspect a severe form of diphtheria, the doctors in the hospital will not wait for the test results and will inject the baby serum right away. PDS is done both intramuscularly and intravenously - the choice of the route of administration is determined by the severity of the child’s condition.
PDS serum can cause strong allergy in a child, like any foreign protein. It is for this reason that the drug is prohibited for free circulation and is used only in hospitals, where a child who develops a fast reaction to the PDS will be able to provide timely assistance.
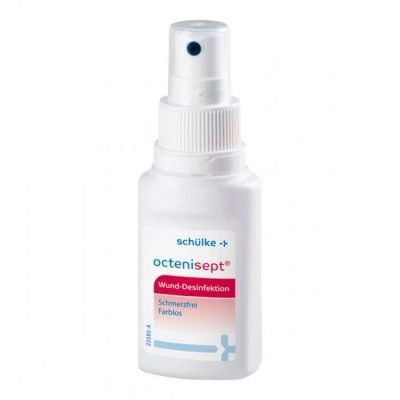
During the whole treatment, you will need to gargle with special antiseptics that have a pronounced antibacterial effect. The most commonly recommended spray or solution "Octenisept." If laboratory tests show the accession of a secondary bacterial infection, antibiotics can be prescribed in a small course - for 5-7 days. Most often prescribed drugs penicillin group - "Ampicillin" or "Amoxiclav».
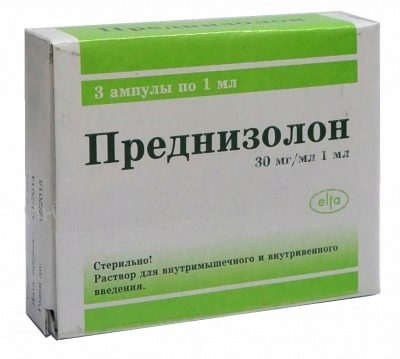
To reduce the negative impact of exotoxin on a child’s body, it is prescribed droppers with detoxifying preparations - saline, glucose, potassium preparations, vitamins, especially vitamin C. If it is very difficult for a child to swallow, prescribePrednisolone». In order to save a child's life, in severe toxic forms, plasmapheresis procedures (donor plasma transfusions) are performed.
After the acute stage, when the main danger has passed, but the likelihood of complications persists, the child is given a special diet, which is based on a gentle and soft food. Such food does not irritate the affected throat. These are porridges, soups, mashed potatoes, kissels.
Everything spicy is excluded, as well as salty, sweet, sour, spices, hot drinks, soda, chocolate and citrus.
Prevention
A person can get diphtheria several times in his life. After the first disease, acquired immunity usually lasts for 8-10 years. But then the risks of becoming infected again are high, however, repeated infections are much milder and easier.
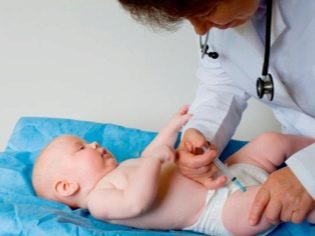
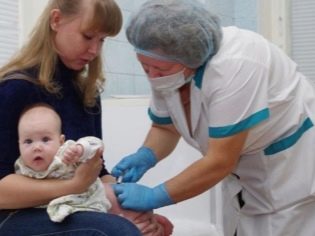
Specific prevention is vaccination. DTP and ADS vaccines contain anti-diphtheria toxoid. In accordance with the national immunization schedule, they are given 4 times: 2-3 months after birth, the next two vaccinations are performed at intervals of 1-2 months (from the previous vaccination), and the fourth vaccine is administered one year after the third vaccination. A child is revaccinated at 6 years and 14 years old, and then vaccinated every 10 years.
Early detection of the disease prevents its wide spread, which is why if you suspect tonsillitis, paratonsillar abscess or infectious mononucleosis (diseases similar to diphtheria), it is important to immediately conduct laboratory tests.
In the team, where a child with diphtheria has been identified, a seven-day quarantine is announced, and all children must take swabs from the pharynx for a diphtheria stick. If there is a child in such a team, who for some reason has not been vaccinated with DTP or DTP, they must be given anti-diphtheria serum.
Much depends on parents in the prevention of this disease. If they have taught the child hygiene, constantly strengthen his immunity, ensure that the baby grows healthy, do not refuse prophylactic vaccinations, then we can assume that they protect the child as much as possible from a dangerous disease, during which it is unpredictable. Otherwise, the consequences can be very sad.
All about the rules of vaccination against diphtheria, see the following video.