Respiratory gymnastics for children: effective exercises and technique
A perfectly healthy child today is a rarity. This will confirm you any pediatrician. The state of ecology, stress, computer technology, gadgets almost from the cradle - all this can not leave its mark on the health of children. Therefore, more and more parents are interested in how to improve the health of the baby, strengthen its immunity and help cope with diseases.
One of the effective methods that helps to achieve both therapeutic and therapeutic purposes is breathing exercises for children. In this article we will tell you how and why to conduct it and whether it is possible to organize classes on your own.
What it is?
Respiratory gymnastics is a system of exercises based on spontaneous activation of the functions of the respiratory organs. From the work of the lungs, bronchi and upper respiratory tract depends largely on the oxygen saturation of all organs and systems of the child’s body. Even healers of ancient Greece drew attention to the fact that from a person's breathing depends on his well-being. For several millennia, medicine has developed a large set of breathing exercises that can help with a variety of diseases and conditions.
Children's breathing exercises are widely used for the prevention of frequent colds, because it strengthens the respiratory system, increases the volume of the lungs, strengthens the muscles. Breathing exercises allow you to avoid the state of hypoxia - the child's body gets enough oxygen. First of all, the benefit of this lies in improving the work of the cerebral cortex, heart, digestive organs and central nervous system.
The child who is engaged in respiratory gymnastics, much more confidently owns himself, and this is an indisputable fact. It is much easier for such a child in an emergency to take a deep slow breath to cope with stress. The beneficial effect of exercises on the nervous system has been noticed for a long time, and therefore complexes of the respiratory gymnastics have become indispensable for stuttering, neurasthenia, and hysteria.
Gymnastics allows you to recover faster after surgery on the adenoids, after removal of the adenoids. It acts as an adjunctive treatment and shows excellent results in bronchitis, pneumonia, bronchial asthma, as well as at the stage of recovery after an acute period of other respiratory diseases.
Speech therapy breathing exercises in a complex with a special face massage allows the child to cope with such problems as dysarthria, delayed speech development. Since the basis of any breathing exercises are nasal inhalations and exhalations, at the moment of which the receptors of the nose, nasopharynx, and pharynx are actively stimulated, the child has both local and general immunity. After a few months, it becomes noticeable that the child became less sick.
For children of preschool and school age, exercises of respiratory gymnastics are introduced into warm-ups and physical education classes to restore breathing.
Respiratory gymnastics are usually not prescribed to children of the first year of life, since for children at this age it is difficult to explain the rules of special, useful breathing, but from 2.5 -3 years, 3-4 years and older, children do an excellent job with tasks.
Kinds
There are several main types that are most common among children. The undisputed leader is considered breathing exercises Aleksandra Strelnikova. The teacher-phoniatrist initially invented a set of exercises for those involved in vocal, but the technique turned out to be useful for treatment too — Strelnikova’s own daughter, who suffers from heart disease, was able to noticeably improve her condition using the method of the mother.
Gymnastics Strelnikova valued by doctors all over the world, calling it "Russian gymnastics." It is recommended for easier breathing when coughing of any origin. Gymnastics is appreciated by sportsmen, singers, actors. For children, the technique has found the widest application.
The method is based on breaths of different depths and frequencies, on the alternation of nasal and oral inhalations and exhalations. Proper breathing in and out using the Strelnikova method are recommended for pregnant women to get rid of toxemia, to master breathing during childbirth. In childhood, such a gymnastics has its own indications and contraindications, we will tell about them below.
See the video below for an example of Alexandra Strelnikova’s class.
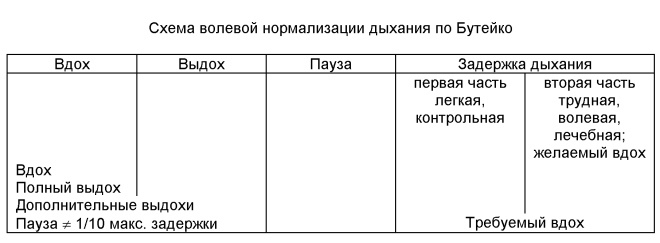
Another type of breathing exercises is gymnastics by K. Buteyko. Konstantin Buteyko is a physiologist who, in the middle of the last century, discovered his own method of treating respiratory diseases. The doctor was convinced that the cause of the illnesses is precisely deep breathing, and therefore his system is based on the suppression of deep breaths and exhalations. For children, the Buteyko shallow breathing method is not recommended from a very young age. The optimal age to start classes is 4-5 years old and older. The method allows the child not only to get rid of the respiratory diseases that torment him, but also from skin ailments - allergies, dermatitis.
Also, some parents quite successfully practice breathing exercises from hatha yoga, Chinese qigong gymnastics and many others.
According to their intended purpose breathing exercises can be divided into:
- tonic, preventive;
- medicinal;
- speech therapy;
- developing.
According to the technique of performing all breathing exercises can be dynamic and static. The first are performed strictly in motion, combined with exercise or gymnastics. Static do at rest - breathing exercises at this moment are the only load.
Contraindications
Before you begin to practice breathing exercises with your son or daughter at home, your mother must consult with a pediatrician to exclude contraindications to a preschooler or student. The circumstances that prevent self-study breathing exercises include the following diseases and conditions:
- some heart defects (for practicing Strelnikova);
- renal failure;
- myopia, glaucoma (for the Strelnikova method);
- severe vascular and blood diseases;
- mental illness;
- acute illness (with fever, fever);
- diabetes mellitus (for the Buteyko method);
- chronic tonsillitis (for Buteyko method).
Up to 5 years of study should contain only some elements of the breathing practice. Doctors recommend practicing a full respiratory gymnastics from the age of 5-6 years, and its complex forms, which are present in some types of yoga, not earlier than in 6-7 years and older.
You can not start an activity if the child has not slept, if he feels unwell, if he is in a bad mood and he is not in the mood to play and practice. Forcibly, the baby will not perform the exercise as needed, respectively, to achieve the desired result will be almost impossible.
Do not leave the child alone, carefully monitor his health at the time of the exercises.
If his face turns pale or red, there is difficulty breathing, dizziness, fainting, trembling in the hands, numbness in the extremities, the exercise must be stopped immediately and if necessary, call a doctor.
How to do?
If there are no contraindications, and the attending doctor fully approved your idea to do breathing exercises with your child, you need to choose a program that you would like to do - several types have been described above.
If you dwell on one method, you want everything at once, you can start classes on a universal complex, which includes the best and most interesting exercises for children from various techniques. We will tell about it in more detail below.
The task of parents is to teach the child to breathe as the technique of a particular exercise implies. It is best to do this in the form of a game so that the child will be interested in doing it, otherwise he will quickly become disillusioned with the classes and will not want to take part in them.
Consider the general rules that are better to learn before starting practice.
- Plan your time so that your child will pass to the breathing exercises no earlier than an hour and a half after the next meal.
- It is possible to study up to two times a day. The duration of classes at the initial stage should not exceed 10 minutes. Gradually, the lessons increase, complicate the exercises themselves, add new techniques. The maximum gymnastics time is 30 minutes.
- Respiratory gymnastics requires mandatory compliance with the recommendations on the technique of performing techniques, but only at the initial stage. Then mom can quite well devise any other exercises that her son or daughter will like based on the learned and mastered techniques.
- If it is summer outside, go outdoors to study - there will be much more benefit.
- In winter, when gymnastics is done in a room, be sure to air the room before a session begins.
- The air temperature in the room should not exceed 21 degrees Celsius - intense inhalation of warmer air can lead to drying of the mucous membranes of the respiratory system and the development or burdening of respiratory diseases.
The best example is, of course, its own example. Follow the tricks together.
Set of exercises
Often moms are interested in whether they can start practicing on their own. When there is an opportunity to hold the first session in the presence of a teacher, doctor or instructor in breathing exercises, use it. If this is not possible, do not worry - all the exercises are quite simple, they can be quite started to practice independently.
Let's start with the complex for the youngest preschoolers.
- "Ball". This exercise is the name for the image that the baby should keep in front of his eyes. The ball will be his own tummy at the time of a deep breath. Ask the baby to take a supine position, put a small soft toy on the belly. Slowly inhaling through the nose, the child should inflate the “ball” as much as possible, and then also slowly blow it out, exhaling through the mouth, folding the lips with a sponge.
- "Scuba Diver". This exercise can be performed in any position - standing, sitting, lying down. Ask the child to imagine that he will be immersed in water. Let him pick up as much air as possible and hold it as long as possible - mom reads out loud, praises the child if today he managed to hold the air at least a second longer than yesterday.
- "Light feather." For this exercise, you will need the most real feather from a pillow or a small balloon (by the way, it can be inflated with your child!). The goal of the game is to hold the ball or feather in the air as long as possible, making short and intense exhalations. Everything in childhood blew a feather, and therefore the technique of doing this exercise will not cause much difficulty.
Exercises for children from 5 years can also include the above techniques. In addition, add other exercises, which, in essence, are combined.
- “Closer-on”. This exercise can be performed in a sitting or standing position.Ask the child to sniff the air as if he were breathing in the scent of a wonderful flower. Exhalation needs to be done through the mouth, lip folded. In this case, the child must exhale more intensely, as if he was pushing away some light object from himself.
- "Hamster on the hunt." This exercise is usually very popular with children. Ask him to portray the hamster, inflating his cheeks as much as possible. Then the baby lets out the air sharply, slamming his palms with his palms. For a new portion of “stocks”, an imaginary rodent is sent after sniffing beforehand - the child makes a nose a series of small and frequent breaths.
- "Dragon Tosh". This exercise should be performed with children who are perfectly aware of what a dragon looks like. Tell me that the dragon is sick and can now exhale fire only through one nostril. This will be a game - alternating exhalations through one nostril (the second is covered with a finger).
- "Cams". This technique is performed simultaneously with the movement. Ask the child to stand and stretch their arms forward. Breathe in a series of four short sharp breaths, and exhale - in any convenient way. During breaths, the cams rhythmically squeeze and unclench.
There is a separate group of exercises that are designed to develop speech and improve the pronunciation of individual letters and sounds. Here are a few of them.
- "Flying geese." Mom invites the child to introduce himself as a goose that flies high. At the same time, she reads the poem "Geese, geese will fly, they will look at Seryozha (Marina, Natasha, Irina, Alyosha, etc.)." On the first line, the child takes a breath and makes movements with his hands, like a goose with wings. On the second line, you need to make an exhalation with the sound “yo y y y”, lower the arms along the torso.
- "Clock". Mom asks the child to imagine that his hands are the hour and minute hands. One hand is lifted up, the other is taken aside (position "three hours"). Then change (position "nine o'clock"). At the first position inhale, at the second - exhale. Mom reads a poem: "They will show the exact time, they will indicate the hour and day." When exhaling, the child must make a sound that is given to him with difficulty ("la la la la" or "rr-r").
- "Policeman". Mom reads a poem: “I follow the order, I can look left to the right. If anything happens, I come to the rescue! ”. The child in a standing position makes rhythmic turns of the head to the left to the left. At each turn you have to inhale, the next - exhale. The exhalation is accompanied by a draw "Zhu-Zhu-Zhuuuu."
Reviews
Many mothers regularly use breathing exercises in their daily activities and games with children of preschool age and with younger students. They note that the results are not noticeable too quickly. If every day you play with your baby and breathe correctly for at least 15 minutes, then noticeable results appear only after six months - a year. But it's worth it, say experienced mothers on thematic forums. Especially for stuttering, shy and timid children who find it difficult to maintain normal breathing in moments of excitement and stress in an unfamiliar team.
Mothers on fiction are generous. Their personal exercises, invented independently, they willingly share with others on specialized forums. Therefore, with a variety of activities for the child, there should be no problems.
Quite rarely, parents say that children do not want to do gymnastics for breathing. Usually this happens if the mother did not succeed in making the lessons interesting initially. You can rectify the situation at any stage by simply revising your own approach to breathing exercises. If the whole family is carried away by it, the child is unlikely to refuse to support the idea.