Causes, signs and treatment of flatfoot in children
Flatfoot is an unpleasant and rather dangerous diagnosis that cannot be ignored. Such a defect causes gait disturbances, posture, and negative changes in the spinal column and many other pathologies.
Why children have flat feet, how to recognize the signs of foot abnormalities in children, and how to treat a child, we will explain in this article.
What it is
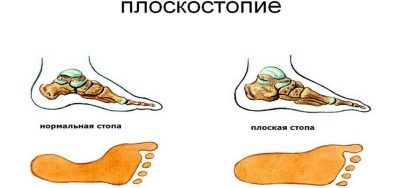
Flatfoot in children is a deformation of the skeleton of the feet. At it the form changes, the longitudinal or transverse arch is lowered and flattened. At the same time, in the diameter of the foot, it deforms in more than half of all cases, and only in 30% of cases does flatfoot have the character of a longitudinal one.
This diagnosis is the most frequently heard in the offices of pediatric orthopedic surgeons. Most patients are teenagers. More rarely, pathology is detected at the age of 7-8 years, even less often in children under 7 years of age.
Official medical literature even reports about 3% of infants who can diagnose flat feet, but this information is controversial.
The fact is that all babies, without exception, are born with flat-footedness. Their legs in the first year of life are not adapted for movement in space in an upright position, and therefore there is no natural need for the foot to immediately have high and regular arches. This flatfoot is considered quite natural, physiological.
With the growth and increase of loads on the lower limbs, the real formation of feet begins. Most often, the first prerequisites for the development of foot pathology are laid. aged 7-8 months to 1.5-2 years.
The muscles of the babies, which are just beginning to get up, are still very weak, the cartilage tissue is elastic, so any disturbance during the first load on the legs may provoke the development of flat feet.
However, there is nothing terrible in infant flatfoot. If the development of the child will proceed normally, if the physical load on the lower limbs will gradually increase, then the feet will be normalized by the age of 7-8. Unfortunately, this is not always the case.
Flat feet can not be considered a harmless disease. Nature provided foot function - support and depreciation. When flattening the arches of the foot cease to depreciate when walking in the required volume, respectively, the load on other parts of the musculoskeletal system increases significantly, and this leads to abnormally rapid wear of the knee and hip joints, spine.
Violations of the supporting system, in turn, have a significant impact on the proper functioning of many internal organs.
It’s safe to say about the presence of a flat foot in a child can only be closer to 7-8 years, when the main stage of intensive formation of the form of the support of the lower limbs is completed.
Causes
Congenital flatfoot, not physiological, but pathological, is registered quite rarely. It is associated with the processes that proceeded in utero, and with the heredity of the baby.
If the relatives of the baby suffer from flat feet, the probability of a congenital form increases.
Intrauterine causes - underdevelopment or abnormal development of muscles, ligaments, which form the longitudinal and transverse arch, tibia.
Much more often flatfoot is acquired disease. But he may also have inborn causes. Such cases, in particular, include congenital weakness of the connective tissue. In children with such a problem, flat feet are formed due to insufficient connective tissue.
This is not the only problem. The lack of connective tissue in parallel is accompanied either by an additional cardiac chord, or by myopia, or by bends and deformation of some internal organs (most often, the gall bladder).
Often flatfoot develops in children who at an early age suffered rickets, which affects the bone and muscle systems. At risk are the guys who suffered fractures of the ankle, calcaneus, as there is a risk of abnormal accretion of bones after injury.
Paralysis of the lower limbs, both full and partial, can cause abnormal development of the foot. Paralysis can be a manifestation of transferred polio, cerebral palsy, as well as frequent convulsive syndrome of the lower extremities, which can occur on the background of some neurological diseases.
Unfortunately, parents, without knowing it, often become the culprits of flatfoot development in their child. This diagnosis can lead to early verticalization of the baby.
If the baby, who has not yet learned to crawl confidently, is forcedly placed in walkers and jumpers in order to enjoy the success of the baby, then the load on the spine increases significantly. The legs of the child are also not ready for a vertical position of the body, and weak muscles and ligaments eventually form incorrectly under excessive load.
Flat feet threatens and overweight, obese babies, toddlers with whom parents choose the wrong shoes, uncomfortable and unhealthy.
If a child walks too much, runs or stands for a long time, this also contributes to the incorrect formation of arches of the foot. Flatfoot is often diagnosed in children who suffer from flat-foot oralgus deformity.
Despite all the reasons listed, the strongest influence on whether a child has flat feet hereditary factor.
Proper care helps to correct possible violations, but, alas, is not able to completely prevent the occurrence of a problem if it has genetic prerequisites.
Classification and species
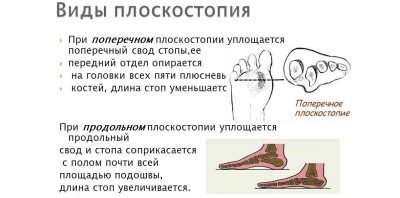
Longitudinal flat-footedness - this is such a statement of the foot, in which the child relies on almost the entire area of the foot.
Transverse - characterized by a support on the metatarsal bones. With a longitudinal foot increases in length, with a transverse - decreases.
Another type of pathology - the combined flatfoot. It combines the features of both longitudinal and transverse deformation.
Depending on which mechanism formed the basis for the development of pathology, There are several types of flattening feet:
- congenital;
- traumatic;
- paralytic;
- static.
Pathology innate properties usually they only find out, by the age of 6-7, it is difficult to distinguish it from the physiological one, and therefore no doctor takes it up.
Traumatic flatfoot occurs as a result of fractures of the heel, tibia, tarsus, ankle. Paralytic pathology is associated with paralysis of the lower extremities, especially of some muscles - the feet and legs.
Most often in about 85% of cases, static flatfoot occurs. This pathology arises in close connection between hereditary predisposition and external factors (footwear, prolonged standing, overweight, etc.)
Depending on how many degrees expressed the angle of deviation from the norm, emit four degrees of transverse disease:
- First degreeThe angle between metatarsal stones number 1 and 2 does not exceed 10-12 degrees. The thumb is inclined from the normal position no more than 15-20 degrees.
- Second degree Between the metatarsals number 1 and 2, the angle is increased to 15 degrees. The first finger has a deviation of 30 degrees.
- Third degree The angle between the above metatarsal bones is within 20 degrees. The deviation of the first finger is 40 degrees.
- Fourth degree The angle between the first and second metatarsal bones is quite large - more than 20 degrees. The first finger is rejected by more than 40%.
In longitudinal flatfoot, the severity of the disease is measured by deviations from the normal height of the arch of the foot. Values of 35 mm and above are typical for healthy children.
Flatfoot has developmental stages. At the initial stage, pathology is always easier to correct than on a running one. In addition, stable deformation is evaluated according to individual criteria.
There are fixed flat feet and flexible (mobile). Fixed flatfoot is characterized by the appearance of signs of deformation constantly, the mobile appears only at the moment of load on the child's legs. If the child is seated and removed from the legs, the arch of the foot takes on a normal look.
Symptoms and signs
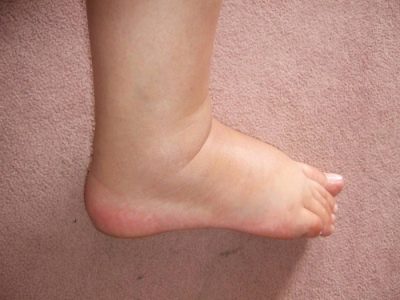
Trying to understand what the flatfoot looks like in babies up to 2-3 years old, worried parents study medical literature, but they don’t find the answer to this question. By and large, up to 6-7 years of age, all the feet of children look the same - flat.
Only cases of congenital flatfoot have distinctive visual features. In this case, usually one foot is struck, not two. The sole of such children is convex, and the upper (rear) part is unnaturally concave. Toes bulging, when placed in a vertical position, the baby rests on the heel.
The signs that should alert the parents of older children are:
- The child quickly gets tired on a walk while walking, complains of pain in the legs. Pain sensations are pulling in nature and usually increase in the evening.
- Legs after a long walk may swell. Puffiness can also be observed in the evenings.
- A baby with flat-footedness shoes shoes in a special way - the inner part of the sole and the heel are damaged from the inside.
If such signs exist, parents can use the usual millimeter ruler to understand how serious the situation is:
- The height of the arch of the foot of a seven-year-old child is 35 mm - there is no pathology.
- The height of the arch of the foot in a child of the same age is 25-35 mm - this is a longitudinal flatfoot of the first degree.
- Arch height - 17-25 mm - second degree longitudinal flatfoot.
- The height of the arch is less than 17 mm - the third degree.
The lower the height of the arch, the more pronounced the symptoms become:
- hard gait, clumsiness;
- complaints of frequent headaches;
- visual deformation of the feet;
- pain in the legs and lower back;
- the occurrence of lower extremity convulsions.
According to these clinical signs, it is possible to establish even at home the fact of the presence of flatfoot of almost any kind.
The only exception is mobile flatfoot, which usually proceeds without any symptoms at all.
In 80% of children, flexible mobile flat-footedness has the tendency to pass itself closer to adolescence, but even if it persists, it absolutely does not manifest itself and does not bother the person. With him you can serve in the army, wear any shoes, play any sport, live without restrictions.
It should be remembered that in the initial stages, all the symptoms look smoother. Therefore, deformations of the feet, which are visible to the naked eye, but which appear even at the earliest stage, are not characteristic of the initial stage. slight pain when walking and mild swelling of the ankles in the evening.
At the intermittent stage (second), short-term convulsions of the lower extremities may begin, and the feeling of fatigue during exertion, pain in the legs, “shooting through” into the knee joints, increases.
At the combined (third) stage, pain can occur even with minor loads. Visually, the foot changes - the ankle on the inside starts to show through stronger than on the outside, the heel looks somewhat flattened. The gait is changing.
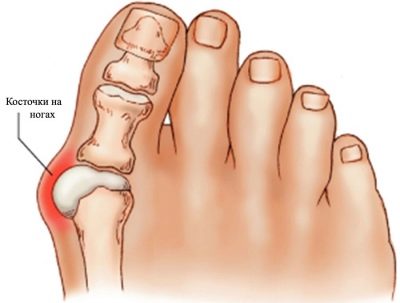
Suspected transverse flatfoot can be on a number of characteristic signs:
- The foot becomes wide. Sometimes this greatly complicates the task of buying shoes.
- "Painful bone" - the joint connecting the thumb and metatarsal bone, is deformed, enlarged, becomes painful.
- On the thumb often grows a nail.
- Gait tense, constrained.
Diagnostics
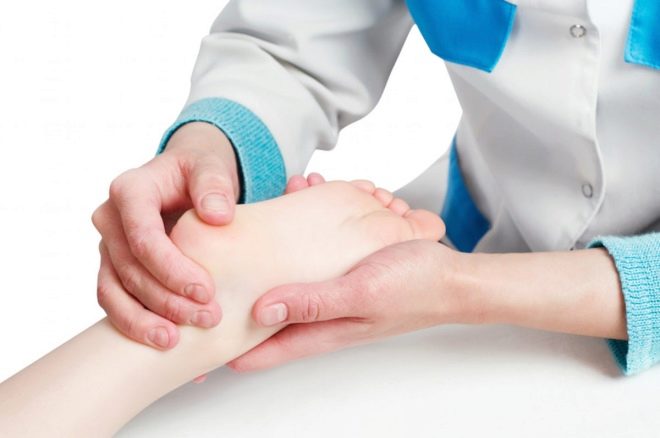
Parents may suspect flat feet in a child, and may not notice anything. To accurately determine if there is deformity of the feet, only a narrow specialist can be an orthopedic surgeon. It is to him and should go to the reception.
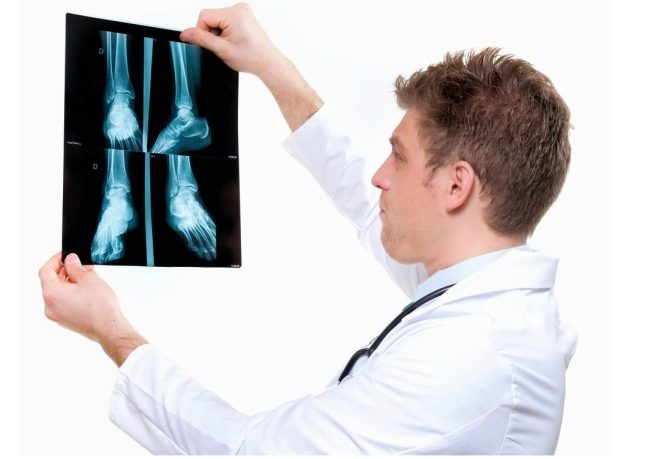
The doctor will examine the child’s legs visually and prescribe several hardware studies, which allow us to assert with great accuracy the presence or absence of pathological conditions.
Diagnose only on the basis of the examination the doctor has no right. To do this, you need to make X-rays of the feet with the load (in the standing position) in two projections.
In addition, there are several other diagnostic methods.
Plantography
This is a very common diagnostic method, it is widely used. This is a kind of foot prints. You can make them on a special device - plantographer.
The device is a frame with a stretched film. Under it - a layer of gauze with printing ink. On the film stand with two feet, and the technician marks on the received foot prints the key points by which the doctor can judge the severity of the disease. This study may be recommended for a normal or overweight teenage child.
Small children and low-weight teens are not allowed to plantography, because the lack of weight greatly distorts the results of the study, the prints are fuzzy and unreliable.
Podometry
In the course of such an investigation, individual parts of the foot are measured with the help of a stopometer and the general proportions are calculated using special formulas. The stopper is very accurate, it allows you to measure up to millimeter.
This method, in conjunction with measurements with bouncy gauges, which make it possible to evaluate the shock-absorbing properties of the foot, is often used to measure children's feet in dynamics, for example, during flatfoot correction.
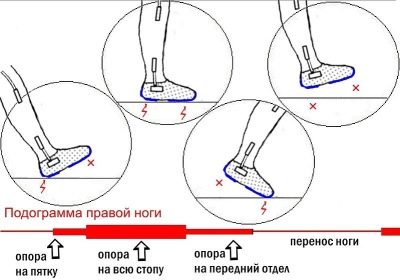
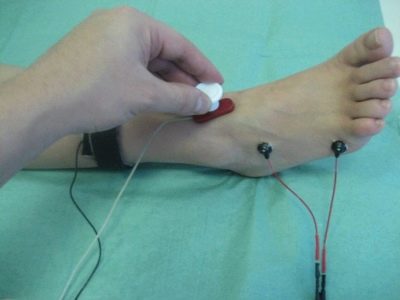
Podography
This is a method for recording gait features. It is not an independent diagnostic, but it helps the orthopedic doctor in assessing the nuances of flatfoot of a child.
The patient is shod in special shoes with metal plates - contacts. They will have to walk on a special metal track.
The obtained electromagnetic data allow us to judge the angle of foot reversal, the straightness of the gait, the step width, the uniformity of the load on the heel and toe.
Electromyography
This is a method that allows you to assess the state of the muscular system of the legs and feet. The procedure is usually indicated for paralytic flat-footedness, as well as for some traumatic varieties of foot pathology.
Electrodes can be superimposed superficially on the skin, and can be inserted as very fine needles directly into the desired muscles.
First, their impulse activity is measured at rest, and then under load.
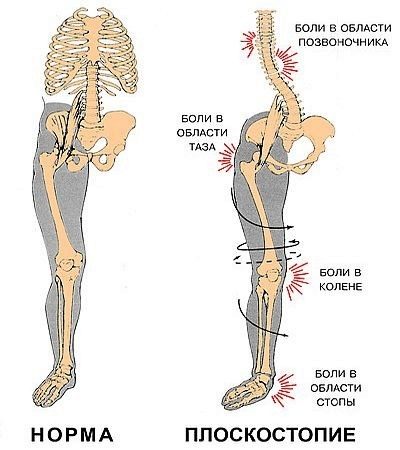
Danger and consequences
Many parents who have heard the diagnosis of flatfoot from a children's orthopedist are interested in how dangerous it is.The answer to this question is obvious - incorrect depreciation, to which flat-footedness leads, slowly but surely destructively affects other parts of the musculoskeletal system, joints, tendons.
First of all, the negative impact of heavy loads, not foreseen by nature, affects the knee and hip joints, and the spine is bent, with all the ensuing consequences until the onset of disability.
Treatment
Flatfoot is treated both conservatively and surgically, but in pediatric practice they always try to choose conservative methods that are more benign and less traumatic. We will tell about them in more detail.
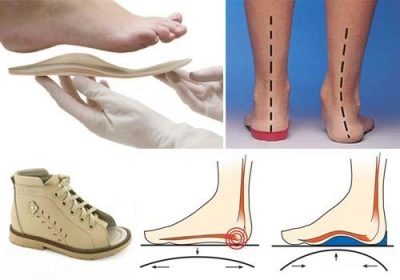
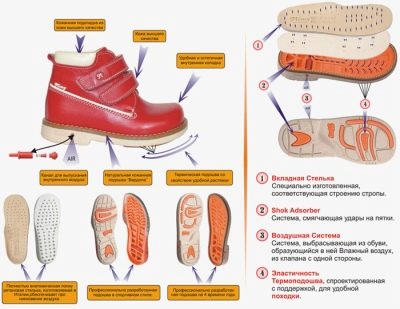
Orthopedic shoes
Wearing orthopedic shoes is an integral part of flatfoot therapy. You can buy it in a special orthopedic salon. It is better to go there with the written recommendations of an orthopedic surgeon who will indicate all the parameters of the child’s foot - height, width, points of deviation from the norm, angle of deviation, angle of turn when walking.
If there is no pair that matches the exact parameters of the baby’s feet, it will be made to order according to individual measurements.
Strict requirements are imposed on orthopedic shoes. The initial stages of the disease do not usually require wearing a heavy medical orthopedic pair; it is quite enough to confine ourselves to orthopedic insoles, but a moderate degree of flatfoot can be an indication for special corrective footwear.
She usually has a high back, fixing the ankle, soft sole, orthopedic insoles, wide rounded or square toe, instep supports, low heel. This pair gives the leg additional stability and fixation.
Many parents believe that wearing orthopedic shoes helps in the prevention of flatfoot. This is a dangerous delusion. Heavy and rather massive orthopedic shoes, designed specifically to correct foot deformities, are not suitable for prophylactic wearing.
She is forced to buy when the orthopedic surgeon insists on it. Only insoles can be used prophylactically, and even that is not all.
Massage and manual therapy
Manual techniques for influencing the feet of a child in combination with other methods give very good results, allow to correct flat feet. Such a treatment does not have a quick effect, but The benefits of systematic procedures will pleasantly surprise and parents, and orthopedic surgeon.
The essence of the impact is on kneading, improving blood circulation, elasticity of the calf muscles, the muscles of the foot, whose weakness led to the occurrence of the problem. After several courses, the muscles are tightened, the foot contour begins to take shape.
The manual therapist and professional masseuse will show parents how to properly influence the lower limbs and the spine of the child, in order to continue the massage at home.
If the manual impact is hard enough to reproduce at home, then any mother can master the massage. The session includes several stages:
- effects on the foot (stroking, kneading);
- massage of the lower leg (movement from the bottom up, and not vice versa, rather deep kneading with an emphasis on the inner side of the lower leg);
- impact on the hips and buttocks (a shallow, painless vibration technique is best for removing stress from the knee and hip joint).
Massage can be completed by taking warm foot baths, followed by intensive rubbing of the feet with a hard towel.
Physiotherapy
There are several dozen exercises that will help to cure flat feet in children and adolescents, making the treatment process interesting and even enjoyable. But specific exercises can only be recommended by an exercise therapy doctor, who will take into account the type and stage of developmental anomalies of the feet.
Children with flat feet are recommended at the initial stage. visit a group of exercise therapy in the clinic at the place of residence. There, the specialist will teach the child and his parents the basic techniques of therapeutic gymnastics.
It is desirable to conduct classes in a playful way, especially for children of preschool and primary school age, since classes should be fun.
The following exercises are considered to be most useful for foot deformities:
- walking on the socks;
- walking on the heels;
- walking on the outside of the foot;
- rolls with socks on the heels.
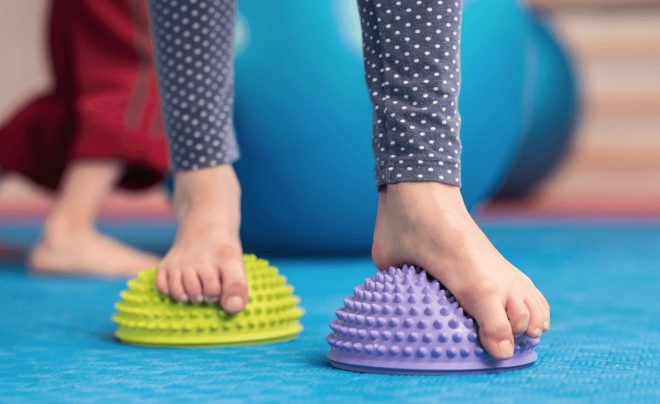
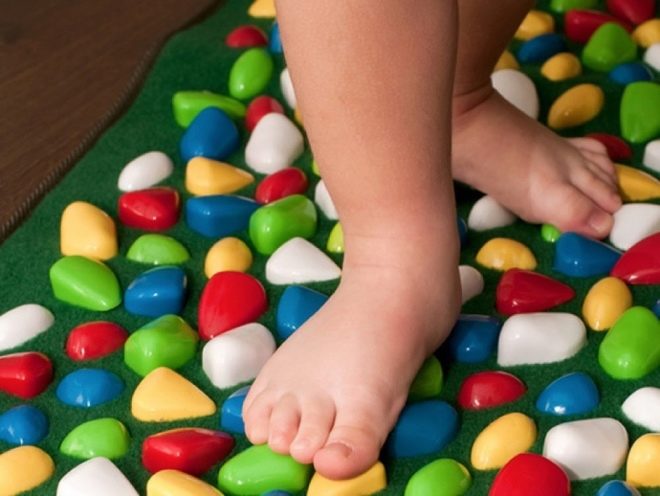
You can do all these exercises not only on a flat floor, but also on a special pad-applicator.
Orthopedic mats with a more rigid texture are usually recommended for treatment, whereas for prophylaxis mats may be used softer.
A certain relief pattern, the degree of rigidity of the product will be prompted by an orthopedist who observes the child.
Doing the exercises is best barefoot. If, when practicing on the rug, pain arises in the legs, you should pause, relax, and try again. Forcing a child to overcome pain is not the best tactic.
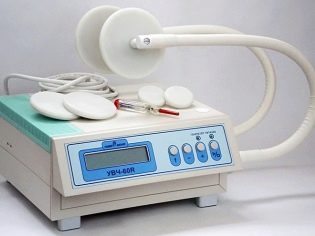
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures, such as electrophoresis, magnetic therapy sessions, UHF and so on, are designed to reduce pain in the lower extremities, improve blood flow, strengthen muscle tissue, so these procedures are an excellent addition to the main treatment - massage, gymnastics, wearing orthopedic shoes.
Correction of the pathology becomes more effective. Most children's clinics have their own physiotherapy rooms, parents are only required to comply with the schedule of attending procedures.
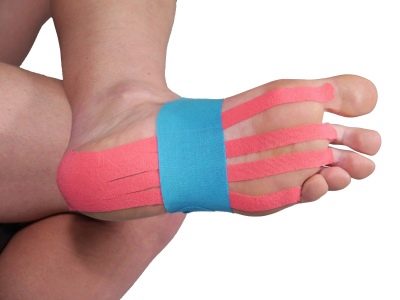
Kinesiotiping
The taping method is considered relatively new to orthopedics, whereas rehabilitation medicine has been familiar with it for a long time. The essence of the method - in the imposition of special adhesive tapes that redistribute the load on certain muscles, supporting from the outside one muscle groups, and there the most straining others.
In this case, the therapeutic action is almost always present - both during classes, and during normal walking, and during rest.
Tapes tapes are considered the most effective when children’s flat-footedness, when the leg is still growing. In adults, taping does not show such impressive results, although it is also quite often prescribed by orthopedists as maintenance therapy.
You can wear the tapes for several days, then change them. Self imposition of tapes, in any case, at first, is undesirable, since the wrong location of the tape can lead to even more significant deformations.
As an independent treatment, the tape method is not considered, but it can be used as part of complex therapy.
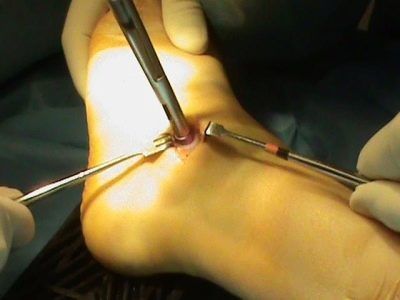
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment helps to get rid of flatfoot stages 3 and 4, when it is not possible to correct the anatomy of the foot using conservative methods.
With longitudinal flatfoot, surgical correction of the longitudinal fornix with tendon plasty is performed on the inside of the foot.
Children from 10 years old can do subtalar arto-erez, a minimally invasive operation with a small incision and a fast recovery period — within a day the child is at home.
Through a small incision, a titanium implant is implanted into the subtalane sinus of the foot. The longitudinal arches are thus modified. The implant is removed by the age of 17–18 and the correct position of the arches is maintained.
Longitudinal flatfoot as a valgus pathology can be effectively eliminated with the help of the so-called Evans operation. Surgeons extend the heel bone by implanting parts of their own bone into it. The risk of rejection is minimal.
For transverse flatfoot, two types of surgery are used - on the tendons and soft tissues and on the bone tissue of the feet.
The second method removes, in particular, the protruding "painful bone", and sometimes several metatarsal bones.After the operation, the child will wear special sandals, which will contribute to faster proper fusion.
After the operation during the month active physical exertion is not recommended, for 3 months you should not go in for sports.
Be sure to visit the physiotherapy room, where, in particular, do electrophoresis according to the method of CMT - electrophoresis using anesthetic, mineral, anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor.
Prevention
It is necessary to deal with the prevention of flatfoot with your child from the moment when he takes the first steps. Parents should pay special attention to the proper development of baby feet. To do this, they must choose the right shoes, fixing the heel with a soft sole.
High heel - compulsory for children up to 2-3 years old, after this age, the boys' gait is usually more stable, and you can buy shoe pairs with a soft back, small heel, arch support.
Preventive classes on massage mats - an excellent measure of prevention. However, before buying such a floor, it is advisable to consult with an orthopedist.
Children in 1 year such mats are not recommended, but already from one and a half years you can use one of the products of the “First steps” line. They are not as tough as medical applicators.
If parents can apply not only diligence but also fantasy to preventive activities, then daily walks along the massage path will turn into an exciting pastime and bring pleasure to the baby.
It is worth reminding that flat feet will be less likely if parents do not rush their baby in development.
Do not use walkers and jumpers earlier than 9 months of age. Better yet, abandon these verticalizing devices altogether, entrusting the development of the child to nature — she knows better when and how he is destined to rise on his legs.
Ideally, the child, before the first steps, has gone through all the stages of the development of the spine, envisaged by evolution, - sitting, crawling, and only then - raising to a vertical position.
Prevention of flatfoot in preschool age is very important, because the foot is intensively formed at this time. Make sure that the child does not wear slippers and slippers on a flat sole for a long time.
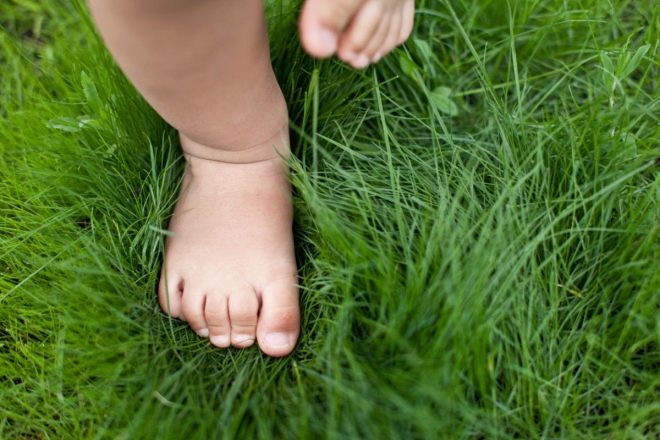
At home it is better to walk barefoot in general, and if there is an opportunity to let the child go, stomp his bare heels on the grass, sand, and earth, then she should definitely take advantage of it.
Many parents, and especially representatives of the older generation - grandparents - strongly oppose walking barefoot, citing their position that the barefooted child will certainly catch a cold and become ill.
In defense of bare feet, we note that it is almost impossible to catch a coldbecause the vessels of the feet (the only ones in the human body!) have the ability to constrict and retain internal heat. But if the child sits on the cold surface of the booty, then hypothermia is very likely, and if the little tot stomping barefoot on the floor, nothing bad will happen to him.
A child of 3-4 years can buy special Insoles Bykov. They invest in shoes for 5-6 hours. You can make it a rule to invest such insoles in a replacement shoe pair, which the kid puts on in the kindergarten.
The amount of time children spend in preschool is exactly the time recommended for wearing Bykov’s insoles. You can buy them in the orthopedic salon.
Responsible attitude of parents to the nutrition of the child will avoid such a problem (alas, common), such as obesity and overweight. Thin children are less susceptible to the development of a flat foot than chubby toads, and this should not be forgotten.
On the table in the family, where the child grows, should be regularly foods with calcium, magnesium, potassium, essential vitamins.It is useful to teach boys and girls to eat jelly or jellied meat - they contribute to the normal growth of cartilage tissue.
In the diet of a preschooler must be present lean meat, fish, dairy products, fresh vegetables, fruits, cereals.
Preventive massage of the feet and legs can be carried out to the child 1-2 times a week. In this case, special attention should be paid to the fingers, the arch of the foot, the inner and outer ribs of the foot.
Contrasting foot baths with a preventive purpose should be carried out after each swim. Cold water is gradually poured into a basin of warm water. This helps to improve the blood circulation of the lower extremities.
To prevent the development of strong flatfoot in a child, it is important at least twice a year to visit the pediatric orthopedic surgeon. This specialist will be able to consider the pathology in time at the very initial stage and prescribe conservative treatment.
More on the causes, prevention and methods of treatment of children's flatfoot will tell Dr. Komarovsky in the next video.