Rickets in children
The diagnosis of "rickets" at the hearing of all. Parents of newborns and babies take it especially anxiously, since they remember from their own childhood how they were frightened with rickets if they refused to have a good lunch or drink an evening glass of milk. Is it so dangerous rickets, as it seems, and what to do if the child is diagnosed with this, we will tell in this article.
What it is?
Rickets is not related to the amount of food. About this, many have learned only by becoming adults. This ailment is indeed characteristic precisely for children, but it occurs due to other reasons, primarily due to a deficiency of vitamin D in the body. This vitamin is extremely important for the baby during the period of active growth. When the deficiency is disturbed bone mineralization, there are problems with the bone skeleton.
Rickets is usually observed in infants, in many cases it passes on its own, without consequences for the child’s body. However, there are more adverse outcomes when the child develops systemic osteomalacia - chronic mineral deficiency of the bones, which leads to their deformation, dysfunction of the skeleton, diseases of the joints and other serious problems. The most susceptible to rickets are children with dark skin color (Negroid race), as well as babies who were born in winter and autumn due to the small number of sunny days.
Vitamin D is produced when the skin is exposed to direct sunlight, if there is no such effect or it is not enough, then a deficit state develops.
Rickets was first described by doctors in the 17th century, and at the beginning of the 20th century, a series of experiments was conducted on dogs, which showed that cod fish oil can be used against rickets. At first, scientists believed that vitamin A was the matter, but then, through trial and error, they discovered that vitamin D, without which the structure of the bones is broken. Then, in Soviet schools and kindergartens, children without exception began to give nasty and sharply smelling fish oil with spoons. Such a measure at the state level was fully justified - the incidence of rickets in the middle of the last century was quite high and required mass prophylaxis.
Today in Russia, rickets, according to statistics, occurs much less frequently - only in 2–3% of infants. This is about true rickets. The diagnosis of "rickets" is made much more often, and this is the problem of diagnosis, which we describe below. Thus, in our country, according to the Ministry of Health, these or other signs of rickets are detected by doctors in six out of ten children.
If a child is diagnosed with this, this does not mean that there is a real rickets. Most often we are talking about overdiagnosis, banal "reinsurance" of doctors, and sometimes - about rickets-like diseases, which are also associated with vitamin D deficiency, but which are not amenable to treatment with this vitamin. These diseases include phosphate diabetes, de Tony-Debre-Fanconi syndrome, nephrocalcinosis and a number of other pathologies.
In any case, the baby’s parents should calm down and understand one thing - rickets is not as dangerous as most Russians imagine; with proper care and therapy, the prognosis is always favorable, the disease is actually not as common as the district pediatricians say in their reports.
However, there are really serious cases that you need to know in more detail, so as not to overlook the pathology of your child.
The reasons
As already mentioned, rickets develops with a lack of vitamin D, in violation of its metabolism, as well as metabolic disorders associated with this substance calcium, phosphorus, vitamins A, E, C, and B vitamins. Vitamin D deficiency can develop for the following reasons:
- The child walks a little, rarely gets sunbathing. This is especially true for children who live in the northern regions, where the sun does not exist for half a year. It is the lack of sunlight that explains the fact that children who become ill with rickets in late autumn, in winter or at the very beginning of spring, are sick longer, harder and more often face the negative consequences of the disease. In the southern regions, a child with rickets is more likely a rarity than normal pediatric practice, and in Yakutia, for example, 80% of infants of the first year of life make this diagnosis.
- The child does not get the right substance from food. If it is fed cow or goat milk in the absence of breastfeeding, the balance of phosphorus and calcium is disturbed, which invariably leads to vitamin D deficiency. baby food manufacturers in such mixtures. Peanut, which is breastfed, should get vitamin D from breast milk. There will be no problems with this if the woman herself happens to be in the sun or, if such walks are impossible, she takes medications with the necessary vitamin.
- The baby was born prematurely. If the crumb hastened to be born, all his systems and organs did not have time to ripen, otherwise the metabolic processes take place. In premature tots, especially those born with a small weight, the risks of developing true rickets are higher than in healthy and well-born children.
- The baby has problems with metabolism and mineral metabolism. In this case, the child will have enough time to spend in the sun, give him adapted mixtures or preparations with the necessary vitamin, but the signs of the disease will still begin to manifest. The root of the problem is a violation of the absorption of vitamin D, a lack of calcium, which helps it to digest, as well as pathologies of the kidneys, biliary tract and liver. Lack of zinc, magnesium and iron may also additionally affect the likelihood of the development of rachitic changes.
Classification
Modern medicine divides rachitis into three degrees:
- Rachet 1 degree (easy). With such rickets, the child has slight disturbances in the nervous system, minor muscle problems (for example, tone), and no more than two symptoms from the bone system (for example, relative softening of the cranial bones). Usually this degree accompanies the very initial stage of development of rickets.
- Rickets 2 degrees (medium). In this disease, the baby has symptoms from the bone skeleton moderately expressed, disorders of the nervous system (over-stimulation, increased activity, anxiety) are also recorded, and problems with the functioning of the internal organs can sometimes be traced.
- Rachet grade 3 (heavy). With this degree of illness, several fragments of the skeletal system are affected, and, in addition, there are pronounced nervous disorders, lesions of the internal organs, the appearance of the so-called rachitic heart - the displacement of this important organ to the right due to the expansion of the ventricles and chest deformity. Usually, this single sign alone is enough for the child to be automatically diagnosed with rickets of grade 3.
The course of rickets is estimated by three parameters:
- Acute stage. With her, the child has only impaired bone mineralization and manifestations of impairment of the nervous system. Usually this stage develops in the first six months of the child’s life.
- Subacute stage. She usually accompanies the second half of the independent life of the baby. At this stage, not only disturbances in bone mineralization (osteomalacia) become apparent, but also osteoid tissue proliferation.
- Wave-like stage (recurrent). When it in the bones, undissolved calcium salts are chipped off. You can see this only on the X-ray. Usually it is possible to talk about such a stage when, in case of acute rickets, such salt deposits are found in a child, which indicates that once in active form he has already suffered rickets, which means that a relapse of the disease occurs. Such a stage is extremely rare.
Of great importance in the formation of the forecast and determining the amount of medical care for a particular child plays and the period during which the disease develops:
- Starting period. It is believed that it starts when the child turns 1 month old and ends when the child turns 3 months old. These are the maximum values. In fact, the initial period of rickets can last two weeks, a month and a half. At this time, there is a decrease in the phosphorus content in blood tests, although the calcium level may remain quite normal. The period is characterized by signs of first degree disease.
- The period of the height of the disease. Such a period can last a maximum of six months to nine months, as a rule, at the age of 1 year in a child, the height goes to a “new level”. There is a marked decrease in calcium and phosphorus in the blood, a deficiency of vitamin D is pronounced.
- The period of reparation. This is a recovery period, it can last long enough - up to one and a half years. At this time, doctors will see residual signs of rickets on X-rays. In blood tests, an obvious calcium deficiency will be traced, but it will be more likely a favorable sign - calcium goes to the bone, goes to recovery. Phosphorus levels will be normal. During this period, due to the withdrawal of calcium in the bone tissue, convulsions may occur.
- The period of residual effects. This period is not limited to specific time frames, calcium and phosphorus in blood tests are normal. Changes that caused the active stage of rickets, can recover on their own, and can remain.
Symptoms
The earliest signs of rickets by parents can go completely unnoticed. They, as a rule, can manifest themselves already from the first month of the crumbs' life, but now they are usually becoming closer to three months. The first symptoms are always related to the functioning of the nervous system. It:
- frequent causeless crying, moodiness;
- shallow and very disturbing sleep;
- disturbed sleep frequency - the baby often falls asleep and often wakes up;
- excitement of the nervous system manifests itself in different ways, most often in fearfulness (the baby shudders strongly from loud sounds, bright light, sometimes such flinching occurs without obvious reasons and irritants, for example, during sleep);
- The baby's appetite at the initial stage of rickets is noticeably disturbed, the child sucks weakly, reluctantly, gets tired quickly and falls asleep, and after half an hour wakes up from hunger and screams, but if you give the breast or the mixture again, then he will eat very little again and get tired;
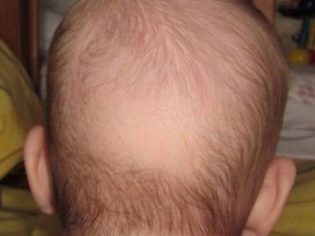
- the child is sweating heavily, especially in sleep, with the head and limbs sweating most of all, the smell of sweat is rich, sharp, and sour in color. Sweating causes itching, especially in the scalp, the baby rubs on the bed, diaper, hair is wiped, the back of his head goes bald;
- a baby with rickets has a tendency to constipation, in any case, with such a delicate problem, the parents of the infant are faced with enviable regularity, even if the child is breastfed.
Bone changes rarely begin at the initial stage, although some doctors claim that the relative softness and suppleness of the edges of the fontanel is a possible sign of the early stage of rickets. This statement is not scientifically valid.
At the height of the disease, which is also called flowering rickets, bone and muscle changes begin, as well as pathological processes in some internal organs.
At this time (usually after the child is 5-6 months old), the symptoms listed above are added to the neurological signs listed above, which the specialist should evaluate:
- appearance on the bones of the skull of large or small areas of softening, and with a heavy degree of softening are all the bones of the skull;
- processes that take place in the bone tissue of the skull, change the shape of the head - the back of the head becomes flatter, the frontal and temporal bones begin to protrude, due to which the head becomes somewhat "square";
- teething significantly slows down, sometimes the teeth are cut in the wrong order, which pathologically changes the bite;
- when rickets ribs undergo specific changes, which are called "rachitic beads". At the place of transition of the bone tissue into the cartilaginous, clearly visible fragments of thickening appear. It was they who received the name "rosary". It is easiest to find them on the fifth, sixth and seventh ribs;
- the bones of the ribs become softer, due to which the chest cell undergoes a rather rapid deformation, it looks as if squeezed sideways, in severe cases a change in breathing can be observed;
- changes may affect the spine, in the lumbar region which may appear rachitic hump;
- On the arms and legs appear the so-called rachitic bracelets - a thickening of the bone tissue in the area of the wrist and the joint between the lower leg and foot. Outwardly, such "bracelets" look like circular encircling bone mounds around the hands and / or feet, respectively;
- similarly, the bones of the phalanges of the fingers can be visually enlarged. This feature is called the "rachitic strands of pearls";
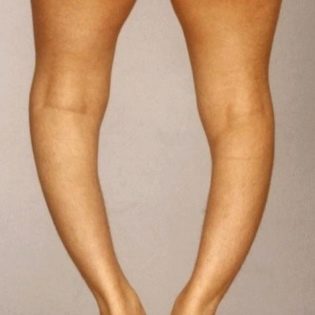
- The child’s legs are also subject to change, and perhaps the most serious - they are bent in the shape of the letter O (this is a varus deformity). Sometimes the curvature of the bones is more like the letter X (this is a valgus deformity);
- changing the shape of the abdomen. He becomes big, giving the impression of constant swelling. This phenomenon is called "frog belly". With rickets, such a visual feature is considered to be quite common;
- joints have increased flexibility and instability.
All these changes, of course, affect the work of internal organs. Children with a rachitic deformed chest often suffer from pneumonia because their lungs are squeezed. When rickets of the third degree can develop "rachitic heart", while the position of the heart changes due to its increase, usually the body is shifted to the right. The pressure is often reduced, the pulse is more frequent than it is supposed by the average children's norms, the heart sounds become deaf.
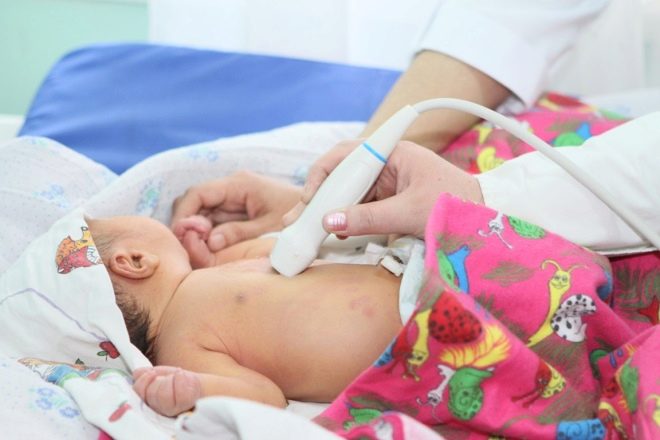
In most babies with severe rickets, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity shows an increase in the size of the liver and spleen. There may be problems with the functions of the kidneys, as well as with a weakened immune system, the consequence of the latter problems is usually the frequent incidence of viral and bacterial infections, and the episodes of the diseases themselves are more difficult, often complicated.
Symptoms of rickets subside during the period of reparation gradually, smoothly. True, because of the reduced level of calcium in the blood, convulsions can sometimes be observed.
At the final stage, during residual effects, by this time the child already, as a rule, 2-3 years or more, there are only a few consequences - the curvature of the bones, a small increase in the size of the spleen and liver.
But this is not necessary, if the rickets was easy, then the consequences will not be.
Diagnostics
With the diagnosis of rickets, everything is much more complicated than it might seem at first glance.All the above symptoms anywhere in the world, except in Russia and in the post-Soviet space, are not considered signs of rickets. In other words, it is impossible to diagnose the child “rickets” only on the basis of the fact that he eats poorly, sleeps little, cries a lot, sweats and has a bald nape. For such a verdict, radiographic data and a blood test for calcium and phosphorus are required.
However, in practice, in any Russian clinic both in large cities and in small villages, pediatricians put on rickets only by visual signs. If this happens, you should definitely check with your doctor why additional research is not scheduled. If there is a suspicion of rickets, it is important that the child take blood and send it to an X-ray of the extremities.
It should be remembered that the rachitic changes of the skeletal system on the X-ray image will appear no earlier than six months from the moment of birth. Usually the changes primarily concern the long bones. Therefore, take pictures of the feet of the child. There is no need to examine the ribs, skull and other bones with this method.
All pathological processes, if they occur, will be clearly distinguishable in the picture legs.
Donating blood and taking X-rays, if the diagnosis is confirmed, will have to repeatedly in the course of treatment so that the doctor can see the dynamics and notice possible comorbidities and complications in time. If the above studies and diagnostic methods have not confirmed the presence of rickets as such, the symptoms, which the doctor took for rickets, should be considered normal physiological. So, the head of babies is bald in 99% of cases because they begin to twist their heads from 2-3 months, being in a horizontal position. Thus, the first fragile infant hair is simply mechanically “wiped off”, and this has nothing to do with rickets.
Sweating is common to all babies due to imperfect thermoregulation. Wrong microclimate, too dry air, heat in the room where the baby lives, parental errors in the selection of clothes for the child according to the weather are more likely causes of excessive sweating than rickets.
The protruding forehead and crooked legs, in principle, can also be hereditary individual features of appearance. Just like a narrow chest. And capriciousness and heightened loudness is a common trait of the infant's character or improper care for him. Precisely because almost every symptom of rickets has a physiological and quite natural explanation, it is so important to insist on a thorough diagnosis.
And for the same reason, the similarity of the signs of the disease and the variants of the norm so often put rickets in children who have no disease.
Treatment
What will be the treatment depends on the stage, period and severity of rickets. Light rickets, detected by luck, in principle, does not need special treatment. The child often enough to walk in the sun, and if this is not possible, then take medications containing vitamin D. The main thing is not to do this at the same time, that is, not to drink "Akvadetrim»In the summer, since the likelihood of an overdose with this substance increases so much that by itself it is worse and more dangerous than rickets.
If the doctor prescribes a double dose of the drug with vitamin D for more severe degrees of the disease, then you should be wary of such a recommendation and find another specialist who will treat the child competently and responsibly. All medicines containing the necessary vitamin should be taken strictly in single age dosages, without exceeding those, regardless of the degree and severity of the disease.
Along with these vitamins, it is desirable to give the child calcium supplements (if the level of this mineral is lowered in the blood).
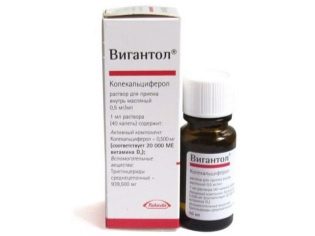
The most famous and popular products based on vitamin D:
- "Akvadetrim";
- Vigantol;
- Alpha-D3-TEVA;
- D3-Devisol Drops;
- "Colicalciferol";
- fish oil food.
In order not to confuse the dosage, as well as to ensure that the child has enough other vitamins, which is very important in the treatment of rickets, parents can print out a table of vitamin requirements and regularly check it with it. As you can see, vitamin D infants need no more than 300-400 IU per day. Breaking these dosages is strictly prohibited.
The nutrition of a child with rickets should be reviewed radically. In the correction of the diet will help the doctor. The menu should be balanced, contain a sufficient amount of iron, calcium. If the child eats the adapted mixture, usually nothing is added to this.
During the recovery period and the period of evaluation of residual phenomena in the menu of the crumbs it is necessary to include fish, eggs, liver, greens.
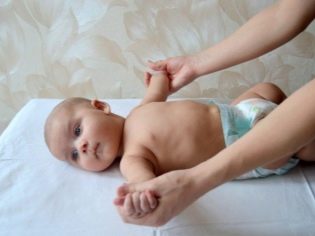
For a child with signs of rickets, it is important to spend as much time as possible in the open air, as well as take several courses of therapeutic massage and therapeutic exercises. In the initial stages, with a mild disease, a general strengthening massage is usually assigned, the task of which is to relax the muscles, relieve nervous tension, improve blood supply in the tissues. With medium and severe rickets, the massage will also play an important role, but it will have to be done very carefully and carefully, since bending and unbending the child’s limbs in the joints with pronounced bone changes pose a certain danger to the toddler - the likelihood of fracture, dislocation, subluxation increases. In addition, children with rickets get tired faster and faster during physical exertion.
Massage can be done at home using classical techniques - kneading, stroking, rubbing. However, everything should be done smoothly, slowly, carefully. Gymnastics should include flattening and dilution of the legs, bends of the limbs in the joints. During a massage and gymnastics, parents or a masseuse should avoid clapping and percussion movements as much as possible, since children with rickets are rather shy and react painfully to unexpected sensations, to sounds.
The most preferred gymnastics plan is as follows:
- In 1-2 months - spread on the tummy and rocking the child in the fetal position;
- In 3-6 months - spread on the belly, encourage crawling movements, coups with support, arms and legs bend and unbend both synchronously and alternately;
- At 6-10 months, add to the already mastered exercises lift the body from a prone position, holding the baby by divorced hands, and lifting from a prone position to the knee-elbow position;
- From the year you can use massage mats for legs, practicing daily walking on them, squats on his haunches behind fallen toys.
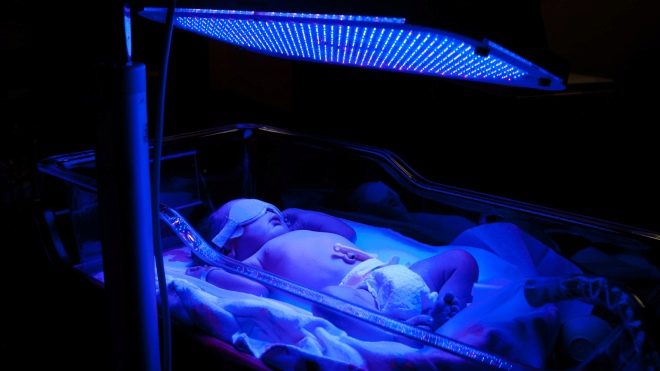
In some cases, the child is prescribed procedures for artificial irradiation with UV rays. UFO procedures are not carried out in conjunction with the intake of vitamin D preparations in order to avoid overdose with this vitamin. Some parents can afford to buy a quartz lamp home to carry out the procedure on their own, some visit the clinic clinic. Each “tanning” course under an artificial “sun” includes 10-15 sessions.
If a child's UV rays cause a pronounced redness of the skin and signs of an allergic reaction, the procedures are discarded and replaced with vitamin D supplements.
Quite often, the doctor prescribes coniferous and salt baths to the child with rickets. For their preparation using ordinary salt or sea salt, as well as dry extract of coniferous trees. Usually, a course of therapeutic baths is prescribed for 10-15 days, the duration of each procedure is from 3 to 10 minutes (depending on the age and individual characteristics of the child).
Not so long ago it was believed that coniferous baths have a powerful anti-otitic effect. However, modern studies have not revealed any significant therapeutic benefit from such baths just with rickets.As with many other diseases, conifers and salt baths improve blood circulation and strengthen the immune system. They do not cure rickets directly, although they may well be present as part of a combination therapy - they will definitely not be worse than a child from such bathing.
Additionally, with a lack of calcium, prescribed calcium supplements, with an insufficient level of phosphorus - ATP is prescribed, the need for such drugs is determined by the results of blood tests.
Effects
Classic rickets usually has positive and favorable projections. The child fully recovers. Complications for health may occur if, for diagnostically confirmed rickets, the parents for some reason refused treatment or did not follow medical recommendations.
Only with timely and adequate response of parents and doctors to the symptoms of rickets can we expect that the disease will not cause the child trouble in the future. And complications can be very diverse. This and the curvature of the bones, especially unpleasant, if the legs are the "wheel" of the girl, it is not aesthetically pleasing. In addition, curved bones otherwise take the load of the body, they wear out faster, are more susceptible to fractures, and over time they begin to thin, which is fraught with serious injuries of the musculoskeletal system and even disability.
Children who have suffered a rather severe or moderate rickets often suffer from dental diseases - caries, periodontal disease and other ailments of the oral cavity, they have to be treated with an enviable constancy. After serious rickets, pathologies such as scoliosis and flat feet can develop. In general, children who have suffered severe rickets are more vulnerable to viruses and bacteria, due to weaker immunity, and therefore they are sick more often than their peers.
One of the most unpleasant consequences of rickets is the contraction and deformation of the pelvic bones. This consequence is extremely undesirable for girls, because such changes in the bones of the pelvis make it difficult in the long term to give birth naturally.
Quite often, rickets, transferred at an early age, is an indication for a cesarean section.
Prevention
Responsible attitude to the health of the child should begin during pregnancy. The expectant mother should eat enough calcium-containing foods, phosphorus, often in the sun, so that vitamin D deficiency does not occur. Even if the pregnancy occurs in winter, walks are important and necessary, since even the winter sun can sufficiently promote the synthesis of the necessary vitamin the skin of the future mother.
From the 32nd week of pregnancy, women who are under 30 years old are usually advised to take one of the preparations containing the required vitamin in the dosage of 400-500 IU per day.
If the future mother has a strong toxicosis or blood tests show anemia (iron deficiency), you should definitely get treatment without delaying it indefinitely.
A born child must necessarily walk on the street as soon as the pediatrician allows walking. Sunlight is the best prevention of rickets. If it is not possible to breastfeed for some reason, it should be given only milk formulas (up to half a year - fully adapted, after half a year - partially adapted). Choose the right food will help the pediatrician. Adapted blends are always marked with a “1” after the name, partially adapted with a “2”.
To feed the baby with cow's milk is unacceptable, it provokes a fairly rapid development of rickets. It is too undesirable to introduce milk as a complementary food too early. All children, without exception, pediatricians are advised to give in the cold season vitamin D at a daily dosage of not more than 400-500 IU (not more than 1 drop of the drug "Akvadetrim", for example).However, the majority of artificial children who feed on the adapted mixture should not take vitamin supplement, its amount according to the needs of the child is incorporated into the mixture. Babies who eat breast milk can be given vitamin for prophylaxis, since it is quite difficult to measure how much milk mother's milk contains, and the composition of mother's milk is not constant.
If a child with mixtures has switched to complementary foods, in prophylactic doses of vitamin D there will be a need only when the supplements make up at least two thirds of the baby’s daily ration. The dosage of vitamin D can be increased only for one category of children - for premature babies, who are much more likely to develop rickets due to more active growth rates. For them, the pediatrician determines the dosage in the range from 1000 to 1500 IU.
Vitamin D is shown to all babies until they reach the age of 3 years. Take a break in the summer months. At the age of 2-3 years, the drug is taken only from late autumn to early spring.
You should not give this vitamin to children who at birth have suffered hemolytic disease of the fetus, who have pronounced pathologies of the kidneys.
Non-specific measures for the prevention of rickets include strengthening the immunity of the infant. It is useful to practice cool baths, hardening, tonic massage. With the introduction of the first complementary foods, children are usually advised to eat calcined cottage cheese, as well as take vitamin E.
More information about rickets in children can be found in the next release of Dr. Komarovsky’s program.