Symptoms and treatment of mumps in children
Mumps refers to the category of such childhood diseases in which the child necessarily need help. And the point is not that the disease itself is dangerous. The greatest threat is its complications. How and why the mumps develops and what to do at the same time, we will tell in this material.
What it is
Mumps popularly called simply - pig. Even earlier, the disease, which has been known since time immemorial, was called earthen mouth. Both names fully reflect the clinical picture of what is happening. At the same time, the in-ear salivary glands are affected by an acute infectious disease. As a result, the oval of the face is smoothed, it becomes round, like in piglets.
The disease causes a special type of virus, inflammation is not of a purulent nature.
Sometimes it extends not only to the region of the salivary glands behind the ears, but also to the sex glands, as well as to other organs that consist of glandular tissue, for example, the pancreas. The nervous system is also affected.
Newborns with mumps almost do not get sick, as the disease does not occur in infants. Infections are susceptible to children from 3 years. The maximum age of the risk group is 15 years. This does not mean that an adult cannot get mumps from a child. Maybe, but this probability is small.
A few decades ago, and even now (by old memory), many mothers of boys are very afraid of this ailment, because parotitis, if it affects the child's gonads, can lead to infertility. Such an outcome really half a century ago was quite common. Now, due to the general vaccination, mumps cases are less common, and the course of the disease has become somewhat easier.
Boys do have mumps several times more often than girls do. Once transferred, the mumps develops a lifelong immunity in the child. However, there are cases of re-infection if, for some reason, persistent immunity has not formed for the first time. And among the "recidivists", it is also boys that predominate.
Previously, the disease was called epidemic parotiditis. Such a name in medical reference books is preserved today, but it cannot be considered absolutely reliable. This merit again vaccination. Epidemics of this disease have not happened for several decades, and therefore the adjective "epidemic" is gradually being supplanted. When a piglet is found in a child, the doctor now writes one word into the medical record - parotitis.
About the pathogen
The virus that causes this unpleasant disease belongs to the genus of rubulviruses and on this basis it is the closest “native” virus of parainfluenza 2 and 4 in humans and several varieties of parainfluenza in monkeys and pigs. It is rather difficult to call a paramyxovirus strong and stable, since, despite all its cunning, it quickly collapses in the external environment. He dies, like most of his "relatives", when heated, when exposed to sunlight and artificial ultraviolet rays, afraid of contact with formalin and solvents.
But in the cold, the mumps virus feels great.
It can even be stored in the environment at temperatures up to minus 70 degrees Celsius.
It is this particular characteristic that causes the seasonality of the disease - mumps most often get sick in winter. The virus is transmitted by airborne droplets, some medical sources indicate the possibility of infection by contact.
The incubation period from the moment of infection and until the first symptoms lasts from 9-11 to 21-23 days. Most often - two weeks. During this time, the paramyxovirus manages to “get comfortable” on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, infiltrate the blood, cause the red blood cells to “stick together” and get to the glands, because glandular tissue is the favorite and most favorable environment for its replication.
Symptomatology
At the initial stage after infection, the disease does not manifest itself, because the virus, the causative agent of the disease takes time to infiltrate and begin to act inside the child's body. One or two days before the first bright signs of mumps appear, the child may experience a slight discomfort - headache, feeling of causeless tiredness, slight muscle pain, chills, and problems with appetite.
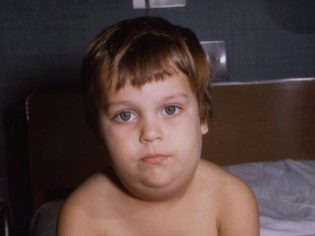
As soon as the virus enters the salivary glands, the first symptoms appear within a few hours. First, the heat rises and severe intoxication begins. Approximately in a day, the ear glands increase in size (symmetrically on one or both sides). This process is accompanied by dry mouth, pain when trying to chew or talk.
Often children, especially small ones, who do not understand exactly where it hurts, begin to complain about the “sore ear”. The pain really irradiates to the ears, so the kids are not so far from the truth. Unlike pain, tinnitus can be quite pronounced. It is associated with the external pressure of the edematous glands on the organs of hearing.
Salivary glands very rarely grow at the same time.
Usually one becomes edematous a few hours earlier than the other. The face of the child looks round, unnatural. Even more, it is rounded if the sublingual and submandibular glands are inflamed behind the ear flaps.
To the touch, the puffiness is loose, softened, friable. The skin color of the child does not change. In this somewhat “bloated” condition, the baby can stay 7-10 days. Then the disease is declining.
After 2 weeks thereafter, a “second wave” can begin, which doctors assess as a complication of mumps. It affects the testicles in boys and the ovaries in girls in a similar way. The "blow" on the reproductive system is most often taken by boys. Cases of the defeat of the genital glands in the fair sex are the exception rather than the rule.
More rarely, the virus can reach the prostate gland in boys and the mammary gland in girls. The second coming of mumps, like the first, is accompanied by high fever and a deterioration in the general condition. The affected testicles increase in size. Ovarian lesions cannot be visually determined, but ultrasound diagnosis will come to the rescue. Also, the girl may begin to complain of pulling pain in the lower abdomen on the right or left, as well as from both sides at the same time. The condition lasts up to 7-8 days.
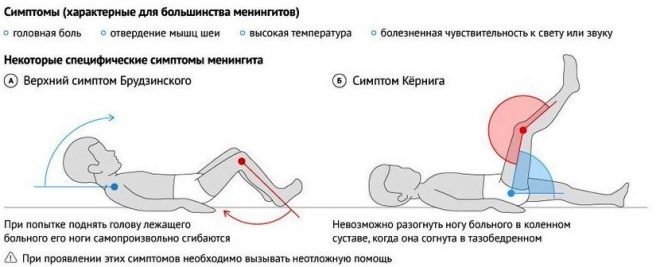
On the part of the nervous system during the "second wave" may also occur symptoms indicating complications of mumps. Most often occurs serous meningitis. Guessing that such a thing could happen to a child is possible by raising the temperature to 40.0 degrees and above, as well as by frequent painful vomiting. The child can not reach his chin to the sternum, almost can not cope with a simple task - to bend and bend the knees. If during the return of the disease, the child began to complain of pain in the abdomen, in the back against the background of heat, then it is worth investigating the state of his pancreas - Probably, the virus struck her.
The temperature at parotitis reaches its maximum usually at 2 days after the onset of the disease and lasts up to a week.
The soreness of the salivary glands is best defined by me at two points - in front of the ear lobe and behind it. These are the classic signs of mumps, however, in practice, everything can be quite diverse, because mumps has different degrees, different types and, accordingly, different symptoms.
Classification
Epidemic mumps, or, as it is called, viral mumps, in which the glands are affected by the virus, is called specific. It is most common, almost always occurs with characteristic bright symptoms. Nonspecific mumps is asymptomatic or with mild symptoms. Sometimes this makes it difficult to diagnose, especially if the first symptoms were nonspecific, the “second wave” of the virus attack in this case is perceived unexpectedly, which is fraught with complications.
Mumps is contagious, it is always caused by a virus. Non-infectious danger to others is not. The defeat of the salivary glands with banal parotid may be caused by trauma of the parotid glands, hypothermia. Such parotitis is also called non-epidemic.
Parotitis can flow in three forms:
- mild (symptoms not pronounced or mild - the temperature is 37.0-37.7 degrees without obvious intoxication);
- medium (symptoms are moderate - temperature is up to 39.8 degrees, glands are greatly enlarged);
- severe (symptoms are pronounced, the child’s condition is severe - temperatures above 40.0 degrees with prolonged presence, severe intoxication, reduction in blood pressure, anorexia).
Mumps is usually acute. But in some cases, there is also a chronic affliction, which from time to time makes itself felt as inflammation in the in-ear salivary glands. Chronic parotitis usually refers to non-infectious. Vulgar (parotitis) occurs on the background of the defeat of the salivary glands only. Complicated disease is a disease in which other glands are also affected, as well as the child’s nervous system.
Causes
When confronted with a paramyxovirus, not every child begins the disease. The main reason that affects whether a baby has mumps or not is its immune status.
If he was not immunized against parotitis, then the probability of infection increases tenfold.
After vaccination, the baby can also get sick, but in this case the mumps will be much easier for him, and the likelihood of severe complications will be minimal. In numbers, it looks like this:
- Among children whose parents refused vaccination, the incidence rate at the first contact with the paramyxovirus is 97-98%.
- Complications of mumps develop in 60-70% of unvaccinated children. Every third boy after an inflammation of the gonads remains fruitless. In 10% of unvaccinated babies, deafness develops as a result of mumps.
A lot depends on the seasonality, because at the end of winter and early spring in children, as a rule, the state of immunity worsens, at this time and accounts for the largest number of identified factor of mumps. At risk are the kids who:
- often suffer from colds and viral infections;
- recently completed a long course of antibiotic treatment;
- recently received hormone therapy;
- have chronic diseases such as diabetes, for example;
- not enough and malnourished, they are deficient in vitamins and trace elements.
The epidemic regime plays an important role in infecting a child with parotitis. If a kid attends kindergarten or attends school, then the chances of getting infected are naturally higher. The main difficulty lies in the fact that an infected child becomes contagious even a few days before the first symptoms appear. Neither he nor his parents are aware of the disease yet, and the surrounding children are already actively infected during the joint games and studies. therefore by the time of the first signs, a few dozen people may be infected.
Danger
During the course of the disease, parotitis is dangerous by complications such as febrile seizures, which can develop due to high fever and dehydration, especially in young children. In the later stages, the danger of mumps lies in the possible damage to other glands of the body.
The most dangerous lesions of the gonads and nervous system.
After orchitis (inflammation of the testicles in boys), which passes after 7-10 days, complete or partial atrophy of the testicles can occur, which leads to a deterioration in the quality of sperm and subsequent male infertility. Adolescent boys are more likely to develop prostatitis, because the virus can affect the prostate gland. In young children, prostatitis does not develop.
The consequences for girls are much less frequent, since the paramyxovirus infects the ovaries less frequently. The probability of infertility in boys after suffering mumps is estimated, according to various sources, at 10-30%. Girls who have had mumps can have children in 97% of cases. Only 3% of the fair sex who have suffered inflammation of the gonads, lose their reproductive function.
The dangerous complications of parotitis include lesions of the central nervous system - meningitis, meningoencephalitis. Meningitis is three times more common in boys than in girls. Sometimes lesions of the nervous system end with the fact that some groups of nerves lose their function, so deafness develops (in 1-5% of cases of mumps), loss of vision and blindness (1-3% of cases of mumps). With the defeat of the pancreas often develops diabetes. The pancreas suffers in approximately 65% of cases of complicated mumps. Diabetes develops in 2-5% of children.
After parotitis, the joints may become inflamed (arthritis), and this complication occurs in about 3-5% of children, and in girls - much more often than in boys. The prognosis of such arthritis is quite favorable, since the inflammation gradually disappears, 2-3 months after recovery from the mumps.
In addition, about what the mumps is dangerous, see the following video.
Diagnostics
A typical mumps does not cause difficulties in diagnosis, and the doctor already at the first look at the little patient, knows what he is dealing with. Much more complicated is the situation with parotitis atypical - when there is little or no temperature, when the in-ear salivary glands are not enlarged. In this case, the doctor will be able to identify the mumps only on the basis of laboratory tests.
Moreover, a clinical blood test can tell little about the true reason for the deterioration of the child’s well-being.
The most complete picture is given by the ELISA method, in which antibodies are determined that are produced by the child’s body against the paramyxovirus that has penetrated the body. It will be possible to find them even if the virus struck only the pancreas or only the sex glands, and there are no obvious symptoms.
In the acute stage of the disease, IgM antibodies will be found, when they recover, they are replaced by other antibodies - IgG, which remain with the child for life, are determined during each analysis and indicate that the child has suffered a mumps and is immune to the disease. It is possible to determine the presence of a virus not only in the blood, but also in washes from the pharynx, as well as in the secret of the parotid salivary gland. The virus particles are detected in the cerebrospinal fluid and in the urine.
Because the virus contains a substance that can cause allergy, a child can hold subcutaneous allergy test. If a paramyxovirus is circulating in his body, the sample will be positive after a negative one.But if in the very first days of the onset of the disease, the sample shows a positive result, then this indicates that the child has already suffered mumps, and now there is a secondary disease.
Additional diagnostics are not required, even latent forms of the disease and doubtful diagnostic cases are resolved and detected as a result of a blood test or flushing of the nasopharynx. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will definitely find out which school the child goes to, which kindergarten he attends, in order to ask the authorities that carry out sanitary control whether there have been any recent outbreaks of mumps in these institutions.
If antibodies to the virus in the active stage are found by ELISA in the child’s blood, then it will be necessary to report this to the Rospotrebnadzor and to the kindergarten or school itself.
Treatment
Parotitis can be treated at home. True, provided that the child has a mild or moderate form of the disease, only the ear glands are enlarged, and there is no high fever (above 40.0 degrees) and debilitating intoxication. A child with severe mumps, signs of disorders of the central nervous system (meningitis, meningoencephalitis), with enlarged and inflamed sex glands, severe intoxication is hospitalized.
Since such complication as orchitis (inflammation of the spermatic glands) is most dangerous for older boys, all adolescents from 12 years old are strongly advised to undergo inpatient treatment under the supervision of doctors. All the other boys definitely need strict bed rest, because its compliance reduces the probability of orchitis by 3-4 times.
General requirements
Bed rest is shown to all children, regardless of gender. To him add special food. Regardless of whether or not the pancreas is affected, the child should be given warm, grated semi-liquid food, mashed potatoes, and liquid cereals. With a strong inflammation and an increase in the breech salivary glands, it is very difficult for a child to chew, and therefore it is not necessary to give anything that requires chewing to reduce the mechanical load on the jaw.
Preference is given to steam and stewed food, fruit purees, dairy products. Prohibited all fried, smoked, salted and pickled, as well as juices and raw vegetables, fatty foods, pastries. After eating, you should gargle the throat and mouth with a weak solution of furatsilina.
A child should not be in contact with healthy children, since it is infectious throughout the entire acute period. He will be able to go for walks only after the doctor permits - usually 14 days after the onset of the disease. A prerequisite for returning to the usual daily routine and walks is the lack of temperature, intoxication, and the absence of complications.
Inflamed salivary glands can be warmed with dry heat. For this, an electric heating pad, a woolen scarf or a scarf, pre-heated salt is suitable.
It is strictly forbidden to make alcohol and ointment compresses, bandages, lotions on the swollen places. You can not inhale with parotitis.
Drug treatment
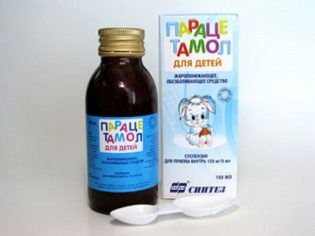
Since parotitis is a viral disease, it does not require special medical treatment. Medications are needed only for symptomatic use. In addition to diet, bed rest and dry heat, antipyretic drugs are prescribed to the affected glands of the child (when the temperature rises above 38.5 degrees). The most preferred products containing paracetamol - "Paracetamol", "Nurofen", "Panadol". Well helps nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug "Ibuprofen."
If the temperature is difficult to correct, medications do not last long and the heat rises again, you can combine Paracetamol with Ibuprofen, giving them one by one. First one medicine, and after a few hours - another. Giving the child the temperature "Asipirin" is impossible. Acetylsalicylic acid can cause life-threatening Ray's syndrome in children, which affects the liver and brain. To remove puffiness with parotitis, you can use antihistamines, of course, with the permission of your doctor. "Suprastin", "Tavegil», «Loratadine» in the age dosage will help alleviate the child’s condition, since they eliminate the sensitization caused by the virus.
During treatment, the child will definitely need to provide abundant drinking regimen. The temperature of the liquid should not be high, the best is the absorption of liquid, which is equal in temperature to the temperature of the child’s body. Antiviral drugs for the most part with parotitis have no effect and do not affect the speed of recovery in any way. The same can be said about popular homeopathic preparations with the stated antiviral effect.
Big mistake to give the child with antibiotics mumps.
Antimicrobial drugs do not affect the virus that caused the disease, but significantly undermine the immune system and thereby increase the likelihood of complications tenfold.
Antiviral drugs, mainly intravenously, in a hospital setting can only be used to treat children with severe mumps and started complications of the central nervous system - with meningoencephalitis or meningitis. These will be recombinant and leukocyte interferons. Nootropic drugs may be prescribed with them («Pantogam», «Nootropil»). They improve the blood supply to the brain, thereby minimizing the effects of the lesion.
With the defeat of the gonads in children, in addition to the antipyretic and antihistamine drugs, intravenous drip injections of glucose with ascorbic and hemodesis, as well as the administration of glucocorticosteroid hormone can be prescribed. «Prednisolone». Boys on the testicles make a special bandage that keeps the scrotum in an elevated state. For 2-3 days, cold lotions (water-based) are applied to the testicles, and then dry heat (a wool scarf, for example, or dry cotton wool) will be useful.
When inflammation of the pancreas is prescribed the drug, relieves spasms of smooth muscles, - "No-shpu", "Papaverin". To normalize the work of the body allow special enzyme-stimulating drugs - "Contric", "Aniprol". Most of these drugs are very difficult to give to the child at home, they require intravenous administration together with glucose solution, and therefore a hospitalized patient is recommended for a sick child with complications in the form of pancreatitis.
In the first days you can put a place on the pancreas cold, after two or three days you can do dry warming compresses.
You should not give your child drugs to normalize the activity of the stomach, as some parents do on their own initiative.
This can only hurt the little patient. All children are shown vitamin complexes that are age-appropriate and contain not only basic vitamins, but also minerals, because when taking antihistamines, the body can lose calcium.
Surgical intervention
Surgeons have to intervene in the treatment of mumps only in exceptional cases. This applies to inflammation of the genital glands in boys and girls, which is not amenable to medical treatment. Boys make a cut of the albugia of the testicles, girls with a strong inflammation of the ovaries can undergo laparoscopic intervention. Usually this is not necessary, and it is more a measure of despair than the existing medical practice for parotitis.
Dispensary observation
All children after parotitis should be observed in the clinic at the place of residence within a month. The guys who suffered complications from the central nervous system, for 2 years are on the dispensary with a neurologist and infectious diseases specialist.Children after the defeat of the genital glands are observed at the urologist and endocrinologist at least 2-3 years. After inflammation of the pancreas of a child, a gastroenterologist should observe for at least a year.
Graft
Mumps is not considered a deadly disease, the mortality rate is extremely low. But complications and long-term effects of mumps are quite dangerous, so children are vaccinated against mumps. Unfortunately, there are still parents who refuse vaccinations for some personal reasons. It should be noted that medically justified causes of harm such a vaccine does not exist today.
The first mumps vaccine, provided for by the National preventive vaccination calendar, is given to a child at 1 year old.
If at this moment the baby is sick, cannot be vaccinated, then the pediatrician may delay the introduction of the vaccine to one and a half years. The second vaccination is given to a child at the age of 6, provided that up to this age he has not had parotitis.
For vaccination using live vaccine, which contains weakened, but the most real particles of viruses. The vaccine is produced in Russia. Inoculate subcutaneously.
The same drug is administered to the child out of plan, if it is in contact with a person who has parotitis. It is important to introduce a vaccine. no later than 72 hours after contact. If the child was previously vaccinated, there is no need for emergency administration of a drug containing live paramyxoviruses. Most often in Russia, children are vaccinated with a three-component preparation of Belgian or American production, which simultaneously protects them from measles and rubella.
Guys with pathologically weakened immunity - with HIV infection, with tuberculosis, with some oncological ailments, receive a medical diversion from vaccination. For each of them, the decision on vaccination against parotitis is made individually; for this, choose a time when the child’s condition is more or less stable. Vaccination is contraindicated in children with diseases of the hematopoietic system.
The vaccine will be refused if the child is sick, has a fever, teeth are erupting, digestive disturbances, diarrhea or constipation. This is a temporary ban, which will be lifted immediately after the child becomes better.
A temporary taboo on parotitis vaccination is imposed and after the child has undergone a course of treatment with hormonal drugs.
With caution, the doctor will give permission for vaccination of a baby allergic to chicken protein. Most mumps vaccines are manufactured on its basis, infecting chicken embryos with the virus. Many parents mistakenly believe that such an allergy in a child is the basis for a decisive medical system. This is not true. Vaccine approved even for allergiesAfter the vaccination, the doctor will simply observe the doctor’s condition especially carefully for an hour or two so that if an allergic reaction develops, the child will be given antihistamines quickly.
Children who are not one year old are not given a vaccine even during a massive epidemic of infectious mumps.
In this case, the risk of infection is lower than the risk of getting serious complications from the introduction of the drug. Vaccination is not officially considered reactive, but in practice, doctors note that after it, malaise, fever, throat redness are possible. Some children begin to feel unwell only one week after vaccination. In this case, the child must be shown to the pediatrician.
A vaccinated child can get mumps. But this probability is much lower than if the child had not been vaccinated. The disease in the case of a disease after vaccination usually occurs in a mild form without complications, and sometimes without any characteristic symptoms. It happens that a person accidentally finds out that he has antibodies in his blood, that he had been ill with mumps.
Prevention
Epidemic parotitis is a disease that cannot be saved only by following the rules of hygiene and eating properly.The most reliable specific prevention is vaccination. Everything else is the right quarantine measures that are taken in the event of a disease of someone from the environment of the baby.
The patient is isolated for 10-12 days. During this time, quarantine for 21 days is announced in kindergarten or school. Premises, dishes, toys are treated with special care, because paramyxoviruses die when in contact with disinfectants.
All children who have not previously been vaccinated against mumps, as well as children who have not been fully vaccinated (one vaccine out of two has been made), are urgently vaccinated if not more than three days have passed since contact with the same age. From the parents for the prevention can do everything to strengthen the immunity of the child. This is the right way of life, hardening, a full and balanced diet, physical activity for the baby.