Symptoms and treatment of meningitis in children
Every person, regardless of age, can become ill with meningitis. The most dangerous is an inflammatory disease for the child's body. With the late provision of qualified medical care, the baby may even die. Every parent should know the main clinical symptoms and manifestations of the disease. This will help protect your baby from dangerous complications and seek help on time.
Causes and provoking factors
The causes of inflammation may be several. The provoking factor causes damage to the soft membranes of the spinal cord and brain. This leads to the development of meningitis. To date, there are more than a hundred different possible causes of the disease.
The peak incidence occurs at the age of 3 years - 7 years.
The most common causes of inflammation in the meninges are:
Viruses of various types. Rubella, measles and flu infection in the event of a complication can cause disease. In a number of others, the smallpox pathogen is also noted. Viruses are quite small. This allows them to easily penetrate the blood-brain barrier, reaching the pia mater.
Pathogenic bacterial microorganisms. Most often, meningitis occurs as a result of a staphylococcal or streptococcal infection. Types A, B, and C meningococci can also cause this dangerous disease. Pseudomonas aeruginosa provokes inflammation in the pia mater in 25% of children. Meningitis caused by bacterial flora, are relatively hard and require mandatory monitoring by medical professionals.
Various fungi. The most common culprit of the disease is candida. The spread of fungal infection occurs in babies with immunodeficiency. If a child has type 2 diabetes, this can also be a cause of candidiasis in the body.
- Amebiasis or toxoplasmosis infections. In this case, the disease is caused by protozoa. Such forms of meningitis are relatively rare. The treatment requires the appointment of special drugs.
- Meningitis, developed due to other chronic diseases. In this case, when immunity is weakened, the inflammatory process spreads throughout the children's body, also damaging the meninges.
- In some babies, the disease may develop after traumatic injuries. brain or spinal cord during birth trauma or after accidents and accidents.
A large number of scientific studies prove the comparative stability of a child’s body against pathogenic bacteria and viruses that can cause inflammation in the meninges.
However, some babies are at risk for meningitis more than others.
Factors that increase the risk of disease:
Prematurity According to statistics, babies who were born prematurely or who had a relatively small weight at birth are more susceptible to this disease than their full-term peers.
Birth injuries. If a traumatic brain damage occurred during the birth of a child, this can also be the cause of the development of meningitis.
Infection with viral or bacterial infections during pregnancy from the mother. Especially dangerous is rubella virus infection. It perfectly penetrates the placental barrier and causes the fetus various disorders of the nervous system, including meningitis.
Infection in infancy with various infectious diseases (especially in babies with congenital diseases of the nervous system).
Kinds
Given the huge variety of provoking causes, all meningitis is usually divided according to certain criteria. For convenience and understanding of the essence of the process, doctors use special classifications.
Most of the most common types of infectious meningitis:
Viral. Viruses, easily penetrating into the children's body, after a few hours or days can cause a strong inflammatory process in the pia mater. Among the most common: rubella, influenza, enterovirus, poliomyelitis option. Children living in endemic areas may experience encephalitis meningitis after a tick bite.
Bacterial. The most common staph form. The culprit of the disease in this case becomes staphylococcus. Getting into the body of a child by airborne droplets, it quickly spreads through the blood and causes an inflammatory process in many organs. Impaired babies may also have tuberculous meningitis. The causative agent of infection is mycobacterium tuberculosis. Treatment of such forms of the disease requires that the baby be in a TB hospital.
- In most cases, meningitis causes meningococcal infection. In this case, the source of the disease is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. You can get sick from both an adult and a child. In some cases, a bacteriocarrier may occur with meningococcal infection. A person who has a pathogenic microbe in his body is contagious. Also, children can become infected through the household transmission path, playing with toys in kindergarten or using common dishes. Rather infrequent ways of transmission are transmissible. Infection in this case occurs when a mosquito or tick bite.
Incubation period
The inflammatory process occurs in the body not from the first seconds of the disease. All meningitis is characterized by different periods when the first symptoms begin to appear. The time from the moment the provocative agent enters the body until the first clinical symptoms appear is called the incubation period.
The incubation period for infectious meningitis is usually 5-7 days.
In viral forms, this time can be reduced to 2-3 days. Very often, babies become infected by airborne droplets. This is the most common mode of transmission. Toddlers who attend pre-school educational institutions are at greater risk of infection.
Even despite the various reasons that cause inflammation, after the incubation period, the baby develops characteristic specific signs of the disease. Recognizing meningitis at home is not an easy task. However, every mother should definitely know the main clinical manifestations of the disease.
Symptoms and first signs
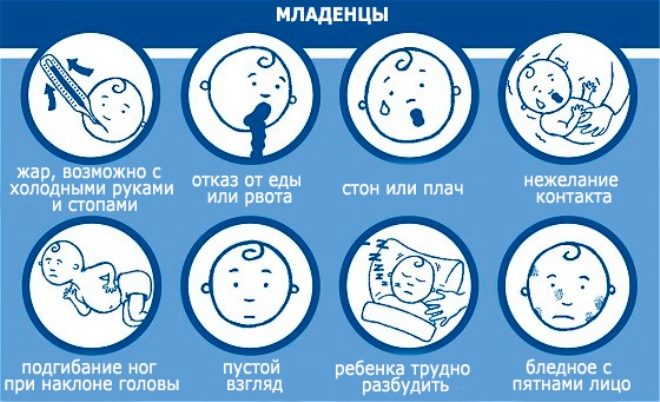
Determining the onset of meningitis is quite difficult. Often the disease begins very non-specific. The first days of the disease occur under the guise of a classic cold. The baby may simply have a fever or state of health. However, in infectious forms of the disease, development proceeds rapidly. Already in a few hours the main symptoms are increasing.
Most often, the inflammatory process in the meninges is manifested:
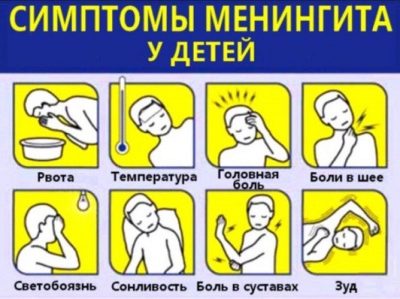
Sharp increase in body temperature. It is growing rapidly in a few hours to 38-39.5 degrees. This symptom is quite persistent. Despite attempts to bring down the temperature with antipyretic drugs, it remains high for a long time.
Severe nausea. Against the background of severe headache may even occur vomiting. These phenomena are not related to meals. Vomiting can even appear on an empty stomach. Conventional drugs for nausea do not bring a pronounced result. Toddlers feel very bad, refuse to eat, become capricious.
Severe headache. Has a bursting and spilled character. There is no characteristic epicenter of pain. The pain syndrome increases when the head turns in different directions. In a horizontal position, the headache is somewhat reduced. In some cases, when looking at closely spaced objects, double vision or blurred vision may appear.
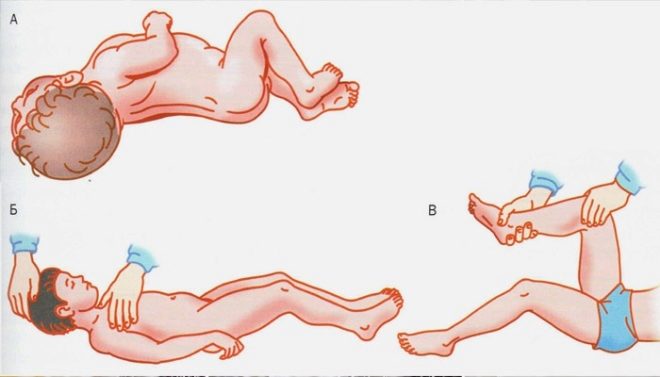
Positive meningeal signs. As a rule, these symptoms are detected by the doctor when examining a baby with suspected meningitis. The most common and reliable sign is the appearance and strengthening of the pain syndrome on the back of the neck while pulling the legs to the baby’s belly.
Characteristic forced pose. The baby is lying on the bed with its head slightly thrown back. A sick baby tries to choose such a pose so that the head is slightly below the level of the body. This is the classic specific symptom of meningitis. This condition is caused by stiff neck muscles. This symptom is already quite unfavorable and indicates an increase in intracranial pressure.
Light confusion and increased headache when exposed to loud annoying sounds. As a rule, bright light causes irritation of the retina and provokes an increase in pain. Being in a dark room brings relief to the kid. In the early days of the disease, you should speak as quietly as possible with the child, avoiding loud, annoying sounds. Acute perception of various provoking external factors can lead to a deterioration of the baby’s condition.
The appearance of seizures and episindroma in severe cases of the disease. Even in babies who do not have epilepsy, this adverse symptom may appear.
Coma or confusion. It is also found in severe disease. This condition requires immediate hospitalization and treatment in the intensive care unit.
In meningococcal infections, one of the characteristic specific signs will be the appearance of a rash on the skin. The rash quickly spreads throughout the body, including the legs and feet, as well as the buttocks. The greatest number of elements found on the side surfaces of the body. The appearance of a rash is an unfavorable symptom and requires immediate hospitalization in the hospital for intensive treatment.
Different manifestations of the disease may not appear in all babies.
To a greater extent, the individual symptoms of the child’s body and susceptibility to infections affect the development of symptoms. The most unfavorable course of the disease is for babies of early age and in premature babies. Children under 5 have a high risk of coma or even death.
Does the course of the disease differ in children of different ages?
Features of the course of the disease in children in different age categories may vary significantly. This, to a large extent, depends on the initial physiological level of development of the child. In newborn babies, the disease can be quite different from that of schoolchildren. The most dangerous age period, up to 5 years.
Features of the disease in children aged 2 years
These babies are characterized by pronounced symptoms of intoxication and fever. This is due to age-related features of thermoregulation.The body temperature in a few hours rises to 39-39.5 degrees. Toddlers become lethargic, refuse to feed. Often there is vomiting during high fever or severe headache.
Features of the disease in children aged 3 - 4 years
At this time, as a rule, the child may already tell the mother what bothers him. This allows parents to navigate much earlier and call a pediatrician. A child at the age of 3 years with meningitis will be very moody, drowsy. Habitual games and favorite activities during illness do not bring child satisfaction and joy. In children of this age often appears light and sound confusion.
Diagnostics
In order to correctly diagnose meningitis, it is not always sufficient to conduct only an examination by a doctor. Doctors, in order to prescribe an effective treatment, resort to additional laboratory tests and tests. These methods not only make it possible to clarify which microbe caused the inflammation, but also determine its sensitivity to various antibiotics.
One of the simplest and most accessible diagnostic methods is to perform a general blood test. This laboratory test allows you to establish the viral or bacterial nature of the disease. Leukocyte formula helps the doctor to orient about the stage of the inflammatory process in the body. Also, a blood test can tell about at what stage the disease is and whether the first signs of complications have already appeared.
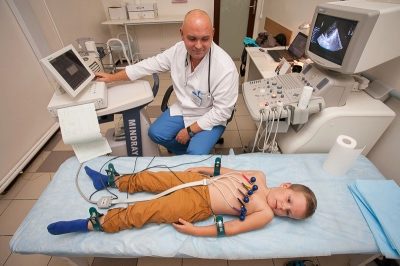
For babies with meningitis in the hospital, they also conduct additional heart examinations.
Electrocardiography is one of the important diagnostic methods for cardiac complications. Often with infectious meningitis, dangerous arrhythmias or cardiac abnormalities can occur. The electrocardiogram allows doctors to orient in time and cope with this arisen condition.
To exclude kidney complications, babies are tested for urine. In some cases, it is also possible to detect the causative agent of the disease. This simple and affordable test will allow doctors to dynamically monitor the kidney condition of the baby during infection.
Serological tests for the determination of antibodies to various infections are carried out in complex cases. The most effective way to conduct them is for the differential diagnosis of infectious diseases. With this study, you can identify toxoplasmosis or amebiasis. For this analysis, venous blood is collected. The result is ready, as a rule, after 1-2 days.
Treatment methods
Children with various forms of meningitis should definitely be hospitalized in the hospital. Delaying treatment can lead to irreparable consequences and even death. Meningitis is a really serious and dangerous disease in pediatric emergency practice.
During the stay in the hospital, a sufficiently large complex of therapeutic procedures is carried out for the sick child. So, diuretic drugs are used to reduce headaches and severe nausea. They also prevent brain swelling and impairment of consciousness.
When signs of heart rhythm disturbances appear, doctors resort to the prescription of special antiarrhythmic drugs.
Such drugs can deal with life-threatening arrhythmias. With the appearance of heart failure requires the appointment of cardiac glycosides.
For a child with meningitis, a rather large course of treatment is carried out during the entire hospital stay. All drugs are injected intravenously, many even drip. This allows you to achieve rapid absorption of substances into the blood and accelerate recovery.
If meningitis is infectious in nature, then in such cases, resorted to courses of antibiotics. The choice of the drug is carried out taking into account the characteristics of the pathogen to certain antibacterial drugs.Often used drugs of a broad spectrum of activity which are entered parenterally.
Hospital stay
According to the clinical recommendations, all babies with severe disease should undergo inpatient treatment of meningitis. Kids with an inflammatory process of the meninges require round-the-clock observation by medical personnel. The risk of life-threatening complications is too high.
Is home treatment possible?
In order to avoid complications, the treatment should be carried out in a hospital. The presence of an intensive care unit is a prerequisite for all the necessary therapy.
Consequences and possible complications
After treatment, in most cases, clinical recovery occurs. This means that life-threatening consequences are eliminated. However, not all children have meningitis easily and without complications. One of the easiest manifestations that have arisen after an illness may be a violation of remembering. Kids have deteriorating memory and attention. Some children may complain of a decrease in concentration and memory.
If complications from the kidneys occur during the illness, then after the acute period subsides, a violation of the excretory function may occur.
In severe cases, this condition can even lead to the development of chronic renal failure. This complication is quite rare and requires observation of the baby by a nephrologist.
Quite often, babies under three years old have heart rhythm disturbances. In this case, for a long time, various types of arrhythmias are recorded on children on the ECG. Such cases require mandatory consultation with a cardiologist to compile the correct tactics of monitoring the baby and the appointment of special treatment.
Prevention
In order to protect your baby, it should be remembered that the maximum risk of infection among children is possible in crowded groups. During mass outbreaks of the disease in kindergarten, quarantine must be entered. This is a necessary measure to prevent the massive infection of children. As a rule, the duration of the quarantine depends on which pathogen was found. On average, this period is 2 weeks.
All children attending preschool educational institutions should be vaccinated for their age.
Given the possible viral variants of meningitis, babies must be vaccinated against rubella, chicken pox, polio and other dangerous childhood infections. Today, a vaccine for meningococcal disease is also used worldwide. Such immunobiological preparations are approved for use by babies from 6 months of age.
Identify meningitis should be as early as possible. Only timely treatment will help minimize the possible risk of life-threatening complications of the disease. Optimal and comprehensive drug therapy will achieve a good result and help restore the children's body.
You will learn more about the symptoms and treatment of meningitis in people in the following video.