Symptoms and treatment of salmonellosis in children
Intestinal infections are very common among children. This is not surprising, because the kids of the world from an early age try to know the taste.
Among intestinal ailments one of the leading places belongs to salmonellosis. About how this disease occurs in children, and how to treat a child, we will explain in this article.
What it is
An acute intestinal infection called “salmonellosis” equally affects both people and animals. Moreover, among the total mass of cases, most of them are children of preschool and school age. However, the disease can be diagnosed in newborns and infants. No one is insured against infection.
The disease is quite difficult, especially in children. Like most intestinal infections, salmonellosis occurs most often in summer when it is hotAfter all, in hot weather it is much more difficult to follow all the rules of food storage.
When salmonellosis occurs, the child must provide proper and timely assistance, and much depends on the parents on how quickly they can recognize the first signs of bacterial contamination.
The reasons
The causative agent of the disease is salmonella - a bacterium in the form of sticks. The microbe is quite common, but it cannot boast excellent health and stamina.
Salmonella fast dies when heated to 50-55 degreeshowever survives well when frozen. Dislikes wand and sunlight.
Ideal conditions for the growth of bacteria - the intestines of humans and animals. At a temperature of about 37 degrees, microbes feel great and are capable of reproduction. Salmonella behaves quite aggressively when it enters the child’s body, not only in relation to its carrier, but also to its other brethren.
If the bacterium has entrenched on the intestinal wall, it begins to produce a strong toxin, which destroys some of the other Salmonella that are competitors for it in the redistribution of the environment.
Toxin acts on the child’s body, causing symptoms of intoxication, disorders in the gastrointestinal tract. This toxin has one more unpleasant property - the body under its action begins to rapidly lose water through the intestines. For a child, this is fraught with rapid dehydration.
Science knows more than 1,600 Salmonella serotypes. Not everyone causes salmonellosis, there are germs that cause typhoid fever, including typhoid fever.
Ways of infection
A child can become infected with salmonella in different ways:
- Food path. Infection occurs when eating animal products that contain bacteria. Usually it is chicken, fish, meat, milk, eggs that have not undergone sufficient heat treatment (the microbe dies when heated).
- Contact path. In this case, the infection occurs from child to child with common toys, a pacifier. Adults who care for them can infect a child. The microbe first gets on the skin or mucous membranes and is gradually transferred by the child into the mouth.
- Vertical path. This is mother-to-child salmonella transmission during pregnancy.
- Air way. Such infection occurs infrequently, but it is not excluded. The child inhales bacteria with dust, air at the source of infection.A kindergarten, for example, can become such a focus if it already has several children who are sick, or a school class.
- Waterway. Microbe enters the body of a child with water
Quite often, the child becomes infected after contact with homeless animals. Therefore, it is worth thinking carefully before allowing the baby to stroke a stray cat or dog.
Danger and consequences
Salmonellosis is dangerous, especially for newborns and children under one year old. A specific microbial toxin causes rapid dehydration, which can be fatal, as well as cause severe complications from a variety of organs and systems, most often from the nervous system.
If the immunity is strong enough, then the disease will affect only the intestinal wall, the impact of the toxin on other parts of the body will be minimal. But children usually cannot boast of strong immunity, they only form a natural defense of the body. That is why at risk - all babies without exception.
Especially hard salmonellosis can occur in premature babies, in toddlers who often get sick, in children with existing chronic diseases, immunodeficiency.
A child who has been ill also poses a danger to other children - with a mild form of illness, the bacteria continue to be released into the environment for 2 to 4 weeks, with a severe form - up to 3 months and even longer. That is how much time the baby is contagious.
Immunity to the bacteria is not produced, and when reinfected, relapse occurs.
The danger of the disease also lies in the likelihood of its chronicity: if the treatment is not correct, chronic salmonellosis will make the child not only a carrier of the bacterium - from time to time unpleasant and dangerous relapses will occur.
The mortality rate for salmonellosis in children is estimated at 0.2-0.5%. In most cases, it is possible to do without complications.
Incubation period
The duration of the incubation period varies greatly among different children — in some babies only 6 hours elapse between infection and the appearance of the first signs, and others take three days. But most often the incubation period is from 12 to 24 hours.
If after that the expressed intestinal infectious symptoms make themselves felt, then they speak about the acute course of the disease. In some cases, the symptoms are erased or do not appear at all. Such children become carriers of the bacteria. When carrying a disease, they themselves do not suffer, but actively infect others, without knowing it.
The incubation period in newborns is usually shorter than in older children. In most cases he is only 2-4 daysand sometimes the disease develops in 3-5 hours.
Symptoms
The first signs of the disease usually show themselves immediately after the incubation period. These are the classic symptoms of intestinal infection:
- Temperature rise. The heat can be high, up to 38.5-39.0 degrees, but more often there is a rise in temperature of 37.5-38.0 degrees.
- Weakness. The child under the influence of toxin on the nervous system becomes depressed, drowsy, moody, he has a headache.
- Digestive disorders. When salmonellosis, there is frequent liquid stool. Fecal matter watery, frothy, with a sharp unpleasant odor. Vomiting is pronounced, frequent.
- Abdominal pain. Abdominal pain may be accompanied by increased gas, a feeling of fullness, heaviness.
Depending on which serotype of the bacteria caused the disease, the course of the disease can be not only intestinal, but also generalized, when other organs and systems are drawn into the disease process.
The nervous system most often suffers, the spleen and liver can grow in size, and in case of severe illness development of a renal failure against the background of strong dehydration is not excluded.
Quite often in children, salmonellosis is manifested by unpleasant symptoms of the cardiovascular system. Blood pressure decreases, heart rate is disturbed, pulse accelerates.
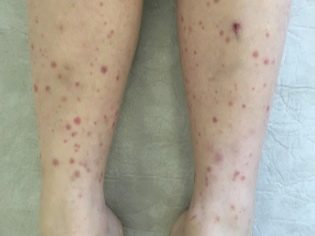
Sometimes the generalized form of the disease occurs 2-3 days after acute intestinal in the absence of assistance and appropriate treatment. Symptoms in this case may be similar to typhoid. To all of the above, a small hemorrhagic rash appears on the skin.
Symptoms of salmonellosis in children of the first year of life and newborns have their own characteristics. Such a small set of symptoms usually occurs in such small patients:
- Abundant frequent regurgitation. It will differ from the physiological one in frequency and volume, as well as in the sourish smell of the rejected masses.
- Severe anxiety and sleep disturbances. This is the action of Salmonella toxin, which causes overexcitement. Poison acts on babies more strongly than on older children.
- Bloating. The baby’s tummy looks bloated like a frog, and loose stools with mucous impurities, colic.
- Signs of dehydration. Such signs include crying without tears, cold extremities, cyanosis in under the eyes, in the area of the nasolabial triangle, dry skin.
- Tapping down the fontanel. The spring looks somewhat concave inward.
But the temperature of the baby can rise only after several days after the onset of the disease.
Diagnostics
Distinguish salmonellosis from other species. intestinal viral and bacterial infections are quite difficult, because the symptoms are very similar. Laboratory diagnosis, which is always carried out at the slightest suspicion of Salmonella infection, will help to establish the truth.
If you suspect this ailment, they try to hospitalize a child in a specialized infectious diseases hospital, and All studies are conducted on the basis of a medical institution.
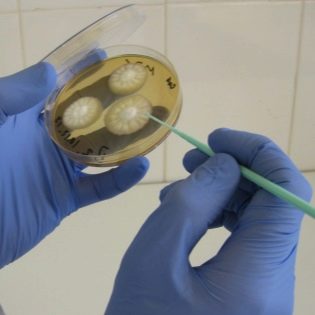
Today, the most reliable and accurate is considered bakposev. For analysis, take feces and samples of vomit.
Microorganisms are grown on a nutrient medium under laboratory conditions. The microbes obtained are identified by type, family, serotype, and also determine which antibiotics they are sensitive to. This gives you the opportunity to choose the right drug for treatment.
The minus of bacteriological analysis is that the process of growing sometimes takes several days, and sometimes takes a week or a half.
Naturally, a child cannot not receive treatment during this time. Therefore, materials are sent to bakposev to make sure that the versions of the doctors were correct, but they also promptly resort to other diagnostics.
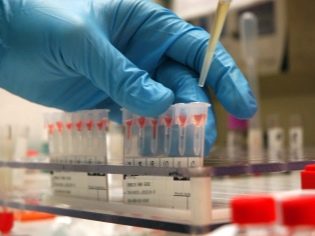
Express analysis is based on the use of special test systems that determine antibodies to Salmonella by immunofluorescence method. Such a test, conducted by an experienced laboratory technician, will allow you to answer the question of whether there is salmonella in the body, but, alas, it cannot tell you what type of bacteria caused the infection in a few minutes.
In the course of treatment, the child will take blood several times for a serological analysis, which will make it possible to judge how effective the therapy is. In the laboratory, antibodies and their number will be determined, and the dynamics of growth and decline will be assessed.
Treatment
Salmonella has long existed alongside a person for so long that they have developed sufficient protection against many types of antibiotics. So, they are almost impossible to destroy with the help of tetracyclines and aminoglycosides. But antimicrobials of the penicillin group and fluoroquinolone antibiotics can be quite effective.
With a mild course of the disease, the child is not prescribed antibiotic therapy. The main indication for the use of such agents is such a clinical feature as presence of blood impurities in feces. If there is no blood, then in mild cases, antibiotics are not required at all.
Mild disease can be treated at home. Naturally, parents will have to carefully follow all the recommendations of the doctor.
On the first day or two, it is advisable for the child with confirmed salmonellosis to have a gastric lavage, an enema. If the baby has frequent loose stools, after washing, calcium preparations are prescribed in the age dosage.
And after repeated vomiting, and after prolonged diarrhea, it is considered necessary to take oral rehydration products. "Smekty", "Rehydron"," Humana Eletkrolit " and others.
To feed the child with such solutions often and in large quantities.
If the baby refuses to drink on their own, use a syringe without a needle, infusing solutions in such a way that the fluid passes along the inside of the cheek. So the baby will be less likely to immediately spit it all back.
These solutions contribute to the recovery of mineral salts, the water balance that will prevent the development of dehydration. In addition to these solutions, should be given to drink ordinary warm water, compote of dried fruit without sugar, weak tea.
If you do not get the baby drunk in any way, then you should return to the hospital, where the child will be administered intravenous electrolytes under the supervision of doctors to prevent dehydration.
The child is shown a strict diet. While the acute stage is in full swing, it is not necessary to feed the baby at all, plenty of drink will be enough. On the second or third day, if the child himself asks for food, they begin to give light meals that will not further irritate the intestines and stomach.
Completely prohibited:
- milk and dairy products;
- products containing animal fats;
- chocolate;
- sour fruits and berries;
- seasonings and spices;
- smoked products;
- sparkling water;
- pickled food;
- fried food.
You can feed the child with foods and dishes from the following list:
- porridge mashed without milk and butter;
- vegetable broth soup;
- boiled fish;
- steam meatballs from lean meat;
- jelly.
Food should not be given hot: everything that has been prepared for a child is cooled to room temperature.
Overeating is not allowed. The amount of food is gradually increased as recovery begins, starting with a small amount of broth or porridge and leading up to the full portion of the course of treatment.
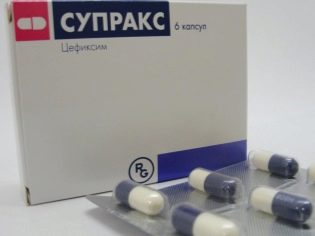
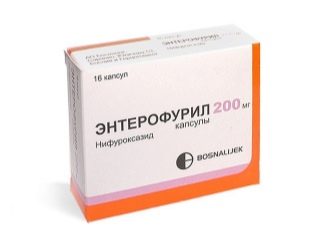
Of the antibiotics most commonly prescribed «Suprax», «Cefixime»with diarrhea «Enterofuril» in capsules, which, although it is an antimicrobial agent, is not considered an antibiotic in the full sense of the word.
In generalized infection, antibiotics of the penicillin group are prescribed for intramuscular administration.
In most cases, a mild to moderate degree of affliction is the most effective method of receiving a special Salmonella bacteriophage, a virus that is artificially grown, and which feeds on Salmonella.
A drug "Salmonella bacteriophage" exists in liquid form and in pill form.
You can even give the drug to newborns, however, in a strict age dosage. The drug can be drunk, and you can enter in the form of an enema in the intestine.
In addition, children are prescribed vitamins, potassium preparations, antipyretics, if the temperature rises above 38.0 degrees, as well as prebiotics and probiotics at the final stage of treatment.
If all medical recommendations are followed, salmonellosis is treated on average about 10 days.
Children's salmonellosis - features
In infants and newborns, a special form of salmonellosis is often diagnosed, in which infection occurs with a hospital wand, a hospital infection that is resistant to almost all types of antiseptics and antibiotics.
Usually it is introduced into the body crumbs still in the parent house or in the hospital of the children's hospital. To treat it is difficult and long. Do not self-medicate.
Quite often, after suffering a Salmonella infection at a very early age, a child prone to allergies begins to suffer from persistent allergic manifestations to certain types of food - eggs, milk.
The older the child, the less likely the development of the negative consequences of the disease for his body.
Prevention
Prevention of salmonellosis is conducted in Russia at two levels - at the national level and at the domestic level. Only a combination of both sets of measures can protect children from a dangerous and unpleasant disease.
At the state level, all sanitary and veterinary services are required to conduct research on the identification of Salmonella in poultry, cattle, as well as in finished agricultural products.
In kindergartens and schools there are special requirements for the temperature processing of food products in order to prevent dishes containing salmonella from getting on the table for children.
Carriage of bacteria annually examines all food industry workers, catering, as well as medical professionals and teachers. If an asymptomatic carrier is detected, it is isolated and treated, and the site of infection is treated repeatedly with disinfectant solutions, after which control “washes” are taken to identify bacteria.
There is no specific Salmonella vaccine, but every parent can and should take maximum measures to protect his child from infection. For this, it is important not to buy meat, milk and chicken in questionable places, in spontaneous markets, where the availability of safety certificates for products raises big questions.
All products should be thoroughly washed and given to the child only after proper heat treatment - in the baked meat there should not be a damp middle, and the steaks with blood are generally non-children's dish, like sushi with raw fish and raw chicken eggs.
Child, it is important as soon as possible to attach to basic hygiene rules - you need to wash your hands not only before eating, but also after returning from a walk, as well as after communicating with animals, including pets, because a cat or dog may have asymptomatic carriage of bacteria.
Do not allow your child to play common toys in the street, in the courtyard, and even more so do not take them in the mouth. Do not allow your child to drink from unfamiliar sources, especially natural sources - springs and keys.
Store food in the refrigerator should be in compliance with the rules of storage and commodity neighborhood. Regularly check the shelf life of products and ruthlessly get rid of everything that has already expired.
If the baby still has an infection, you should not visit shops and pharmacies with him during the treatment, walk in the yard in the company of other children. The tests will show, and the doctor will tell you when exactly the baby will cease to be infectious, and will be able to visit his garden, chat with friends on the street and walk in crowded places.
About what is dangerous salmonellosis, see the following video.